properties of populations pt 2 (abundance->indicies of abunance)
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
abundance
number of individuals in the population + defines its size
abundance is a function of what?
1) population density
2) crude density
3) the area over which the population is distributed
population density
number of individuals per unit area OR per unit of volume
crude density
the number of individuals per unit area (determined by measuring number per area)
population density ______ from location to location
varies
what do you have to do to ensure that your population estimate is accurate?
repeat your sampling multiple times to get the most truthful estimate
what are the 3 population distribution patterns?
1) random
2) uniform
3) clumped
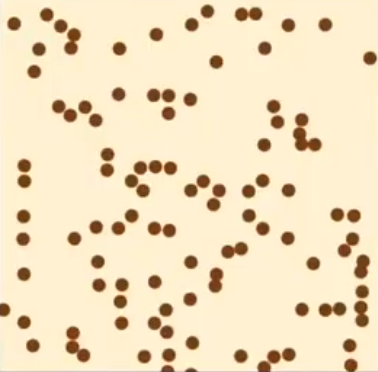
random population distribution
an individual’s position is dependent of others

uniform population distribution
results from negative interaction among individuals

clumped population distribution
results from patchy resources, social groupings, and ramet dynamics
an individual’s spatial position relative to another influences ________ ______
population density
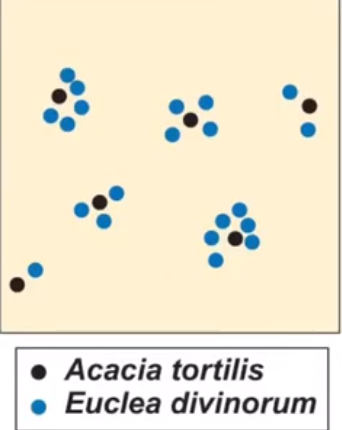
can the spatial distribution of individuals within a population be at multiple spatial levels?
yes
→ acacia trees have a uniform distribution
→ but euclea shrubs are clumped under acacia trees
ecological density
reflects the number of individuals per unit of available living space
→ this is difficult to measure
what is the difference between density and ecological density?
density is the total number of individuals in a given area
→ ecological density is the number of individuals per unit of suitable habitat
population size
density*area
how is population size estimated?
by sampling a portion of the population
what are the sampling methods for population size in plants and sessile animals?
1) counting organisms in a sub-sample (quadrants)
2) abundance estimates (may be skewed by a clumped spatial distribution)
what is the sampling method for population size in mobile animals?
capture-recapture/mark-recapture
→ also known as the lincoln or peterson index of relative population size
how does capture-recapture work?
trapping, marking, releasing a known number of marked animals (M) into the population (N)
the same population is sampled and the ratio of marked animals (R) to sampled individuals (n) in the second sample represents the ratio for the entire population
→ N/M = n/R
what sampling method should be used if capture-recapture does not work?
indicies of abundance
→ determined by counts of vocalizations, scat, tracks, or some other sign of presence