Paper 2 - Human Geography Key Terms Quiz
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Urbanisation
The process by which an increasing proportion of a country's population come to live in towns and cities.

Urban areas
Cities and towns

Rural areas
Countryside

Mega-city
A city with a population of over 10 million people.
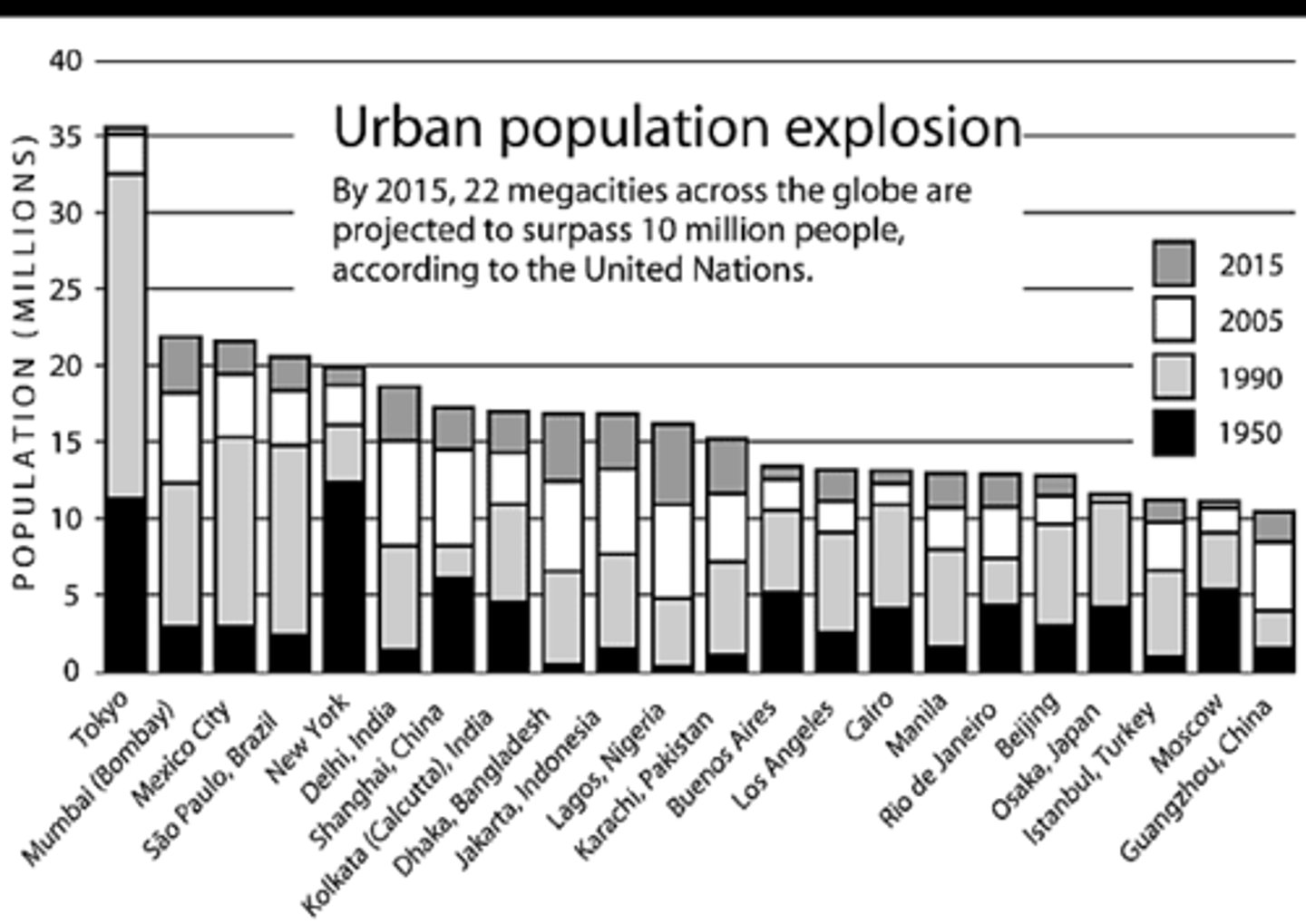
Rural to urban migration
When people move from the countryside to live in cities.
Push factors
Bad things about a place that make people want to leave.

Pull factors
Good things about a place that make people want to move there.

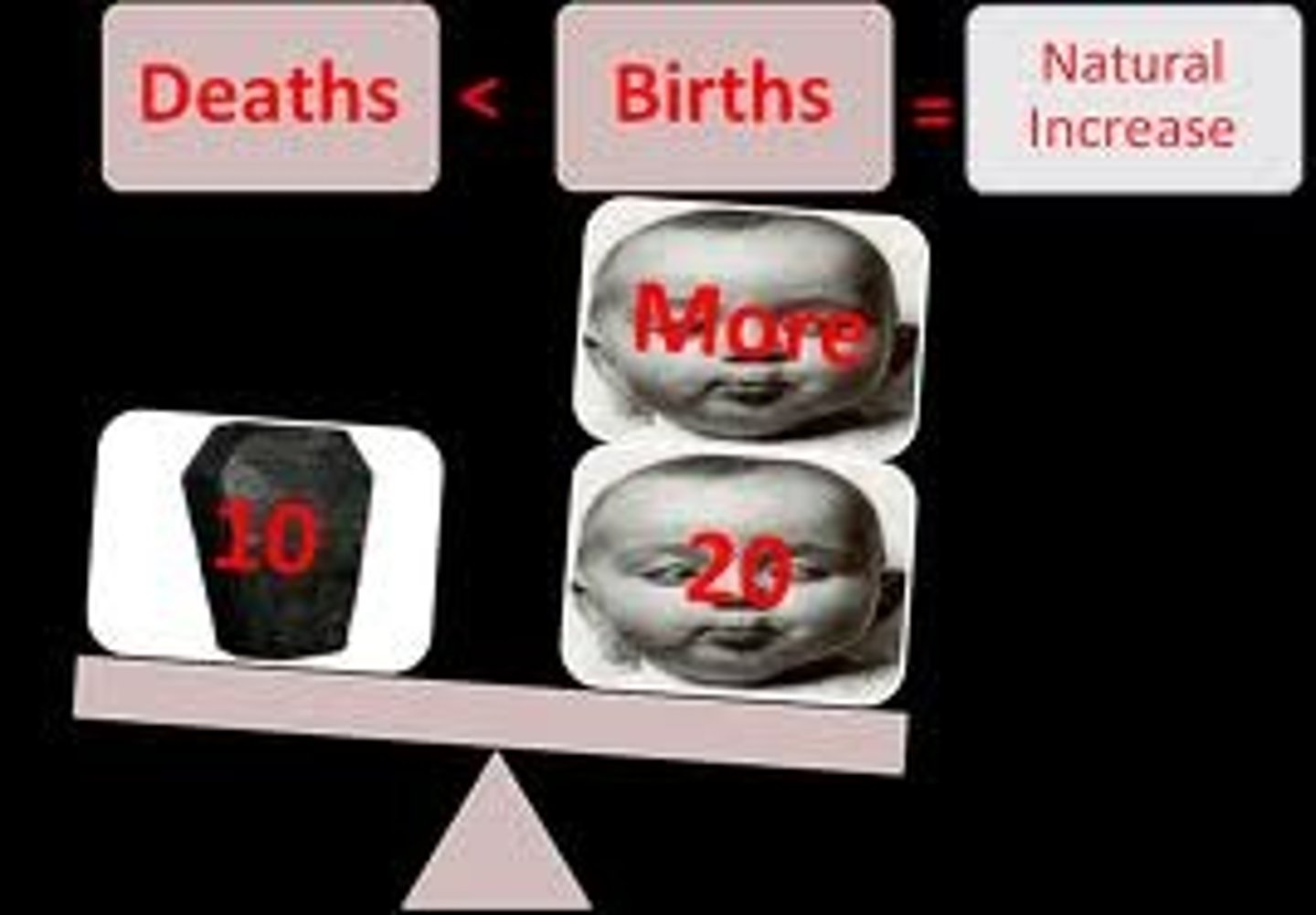
Natural increase
The birth rate minus the death rate of a population.
Brownfield site
Land that has been built on, then abandoned e.g. a derelict industrial site. Often found in urban areas in the inner city.
Greenfield site
Land that has not been built on before. Usually found in rural areas or in the greenbelt at the edge of urban areas.
Rural-urban fringe
A zone of transition between the built-up area and the countryside. There is often competition for land use e.g. from out of town shopping centres and golf courses to farmland and motorways.
Social deprivation
The degree to which a person or an area is deprived of services, decent housing, adequate income and local employment.
Dereliction
Abandoned buildings and wasteland.

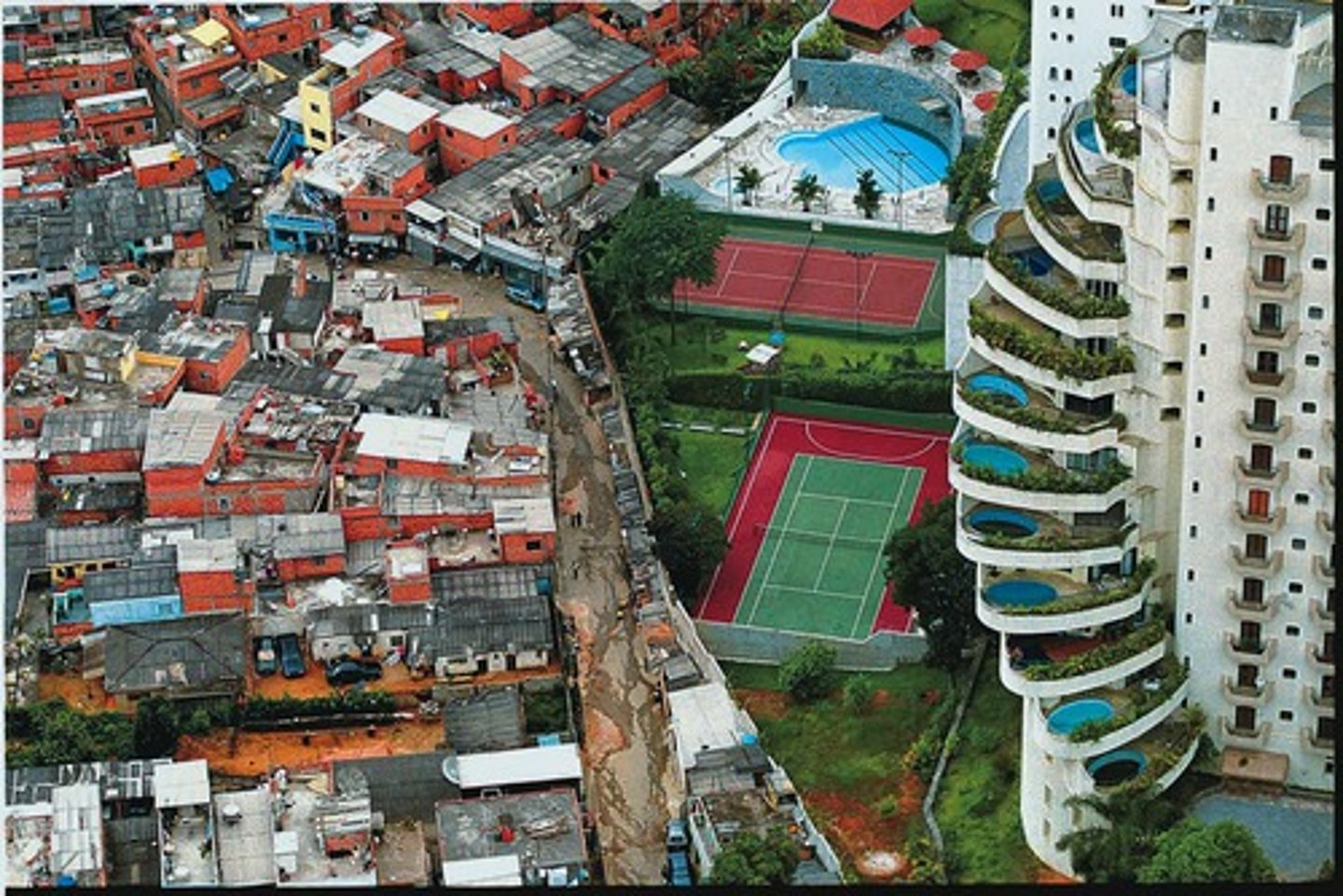
Inequalities
Differences between poverty and wealth, as well as in peoples' wellbeing and access to things like jobs, housing and education.

Urban sprawl
The unplanned growth of urban areas into the surrounding countryside.
Human Development Index (HDI)
A method of measuring development which combines economic (GDP) and social (life expectancy and adult literacy) indicators.
Primary sector
Industries that involve acquiring raw materials. For example, mining, farming, oil extraction.
Secondary sector
Industries that take the raw materials produced by the primary sector and process them into manufactured goods and products. For example, manufacturing, food processing, oil refining and energy production.
Tertiary sector
Economic activities that provide services. For example, solicitors, accountants, schools, hospitals, restaurants, cinemas, etc.
Quaternary sector
Industries providing information services, such as computing, ICT, consultancy (offering advice to businesses) and R&D (research).
Industrial Structure
The relative proportion of the workforce employed in different sectors of the economy (primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary).
Intermediate technology
Simple technology that is cheap and easy to use and maintain. Often used in LICs.
International Aid
Money, goods and services given by one country or an organisation (e.g. the World Bank) to help the quality of life and economy of another country.
Microfinance Loans
Very small loans which are given to people in LICs to help them start a small business.
Transnational Corporation (TNC)
A company that has operations (factories, offices, research and development, shops) in more than one country.
Carbon footprint
A measurement of all the greenhouse gases we individually produce, through burning fossil fuels for electricity, transport etc, expressed as tonnes (or kg) of carbon-dioxide.
Energy mix
The range of energy sources of a country, both renewable and nonrenewable.
Food miles
The distance covered supplying food to consumers.
Fossil fuel
Natural fuels such as coal, gas and oil, which formed in the geological past from the remains of living organisms.
Resource Management
The control and monitoring of resources so that they do not become depleted or exhausted.
LIC
A low income (poor) country with a GNI per person of less than $1045.
HIC
A high income (rich) country with a GNI per person of over $12746.
NEE
Countries that have begun to experience higher rates of economic development. They differ from LICs in that they no longer rely primarily on agriculture (farming). Examples include Brazil, Russia & China.
Economic opportunities
Chances for people to improve their standard of living through employment.
Social opportunities
Chances for people to improve their quality of life, for instance access to education and health care.
Integrated transport system
When different transport methods connect together, making journeys smoother and therefore public transport more appealing. This encourages people to not use their car, reducing congestion and pollution.
Migration
When people move from one area to another.
Pollution
The presence of chemicals, noise, dirt or other substances which have harmful or poisonous effects on an environment.
Sanitation
Measures designed to protect public health, including the provision of clean water and the disposal of sewage and waste.
Squatter settlement
An area of poor-quality housing, lacking in amenities such as water supply, sewerage and electricity, which often develops illegally in a city in an LIC.
Sustainable urban living
A sustainable city is one in which there is minimal damage to the environment (e.g. through using renewable energy & encouraging public transport), resources are allocated fairly and jobs are secure, and there is a strong sense of community.
Traffic congestion
Occurs when there is too great a volume of traffic for roads to cope with, so traffic jams form and traffic slows to a crawl.
Urban greening
The process of increasing and preserving open green space such as public parks and gardens in urban areas.
Urban regeneration
The revival of old parts of a built‐up area by modernising old buildings (renewal) or demolishing existing buildings and starting afresh (redevelopment).
Waste recycling
The process of extracting and reusing useful substances found in waste.
Birth rate
The number of births in a year per 1000 of the total population.
Death rate
The number of deaths in a year per 1000 of the total population.
Commonwealth
A voluntary association of 53 independent states, which were mostly territories of the former British Empire.
De-industrialisation
The decline of a country's manufacturing industry due to exhaustion of raw materials, loss of markets and competition from NEEs.
Demographic Transition Model
A model showing how populations should change over time in terms of their birth rates, death rates and total population size.
Development
The progress of a country in terms of economic growth, the use of technology and human welfare.
Development gap
The difference in standards of living and well-being between the world's richest and poorest countries (between HICs and LICs).
European Union
An international organisation of 28 European countries formed to reduce trade barriers and increase cooperation among its members.
Fairtrade
When producers in LICs are given a better price for the goods they produce.
Globalisation
The process which has created a more connected world, with increases in the movements of goods (trade) and people (migration and tourism) worldwide.
GNI
Gross national income - a measurement of economic activity. It takes into account the value of goods and services and the income earned from investments overseas.
Infant mortality
The average number of deaths of infants under 1 year of age, per 1000 live births, per year.
Information technologies
Computer, internet, mobile phone and satellite technologies - especially those that speed up communication and the flow of information.
Life expectancy
The average number of years a person might be expected to live.
Literacy rate
The percentage of people who have basic reading and writing skills
North-south divide
Economic and cultural differences between Southern England and Northern England. There are clear differences in health conditions, house prices, earnings, and political influence.
Post-industrial economy
The economy of many HICs where most employment is now in service industries.
Science and business parks
Business Parks are purpose built areas of offices and warehouses, often at the edge of a city and on a main road. Science parks are often located near
university sites, and high-tech industries are set up there. Scientific research and commercial development may be carried out in co-operation with the university.
Trade
The buying and selling of goods and services between countries.
Agribusiness
Application of business skills to agriculture.
Local food sourcing
A method of food production and distribution that is local, rather than national/international. Food is grown (or raised) and harvested close to
consumers' homes, then distributed over much shorter distances.
Organic produce
Food which is produced using environmentally friendly farming methods on organic farms. Artificial fertilisers, pesticides and dyes are banned and farmers develop fertile soil by rotating crops and using compost, manure and clover.
Biomass
Renewable organic materials, such as wood, agricultural crops or wastes, especially when used as a source of fuel or energy. Biomass can be burned directly or processed into biofuels such as ethanol and methane
Energy conservation
Reducing energy consumption through using less energy and becoming more efficient in using existing energy sources.
Energy exploitation
Developing and using energy resources to the greatest possible advantage, usually for profit.
Energy security
Uninterrupted availability of energy sources at an affordable price.
Geothermal energy
Energy generated by heat stored deep in the Earth.
Hydro-electric power
Electricity generated by turbines that are driven by moving water.
Nuclear power
The energy released by a nuclear reaction, especially by fission or fusion. Nuclear energy uses fuel made from mined and processed uranium to make steam and generate electricity.
Renewable energy
A resource which is not diminished when it is used; it recurs and cannot be exhausted (for example wind and tidal energy).
Solar energy
The Sun's energy exploited by solar panels, collectors or cells to heat water or air or to generate electricity.
Sustainable development
Development that meets the needs of the present without limiting the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Sustainable energy supply
Energy that can potentially be used well into the future without harming future generations. Sustainable energy is the combination of energy savings, energy efficiency measures and technologies, as well as the use of renewable energy sources.
Wind energy
Electrical energy obtained from harnessing the wind with windmills or wind turbines.
Commuter settlement
A settlement located in the rural-urban fringe, where most of the inhabitants commute to work in nearby towns or cities.