Anatomy Week 1 - Vertebrae and Back Muscles
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
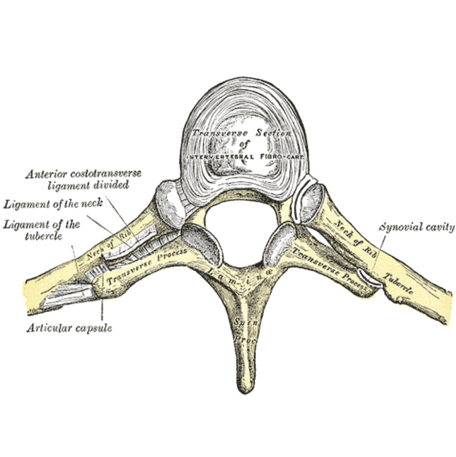
Thoracic Vertebrae
12
small(est) vertebral foramen/canal
transverse processes articulate with ribs
long spinous processes which slope downwards
Cervical Vertebrae
7
small body
prominent transverse processes which contain vertebral artery and vein + sympathetic nerves
muscle and ligament attachments at spinous process including nuchal ligament
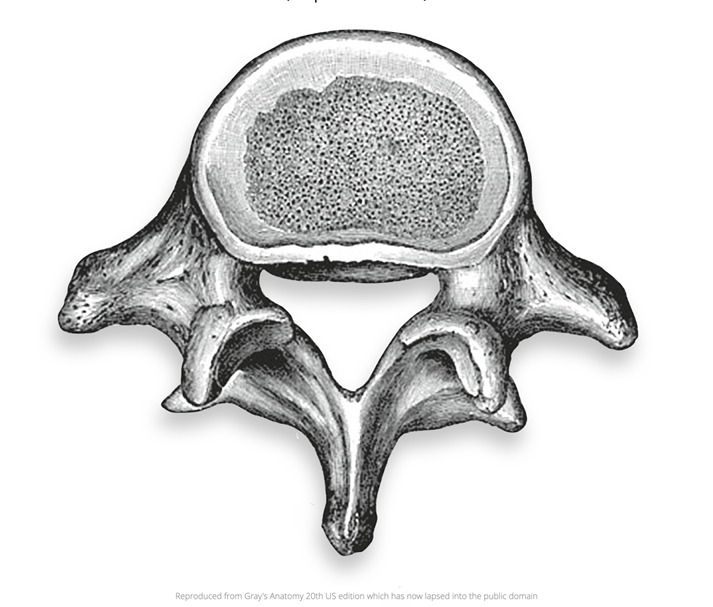
Lumbar Vertebrae
5
thick, large bodies
triangular vertebral foramen/canal. smaller than cervical but larger than thoracic
muscle and ligament attachments at transverse and spinous processes
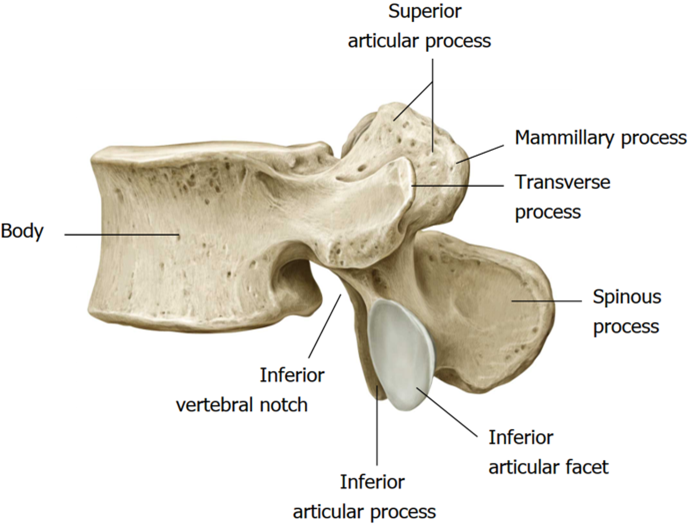
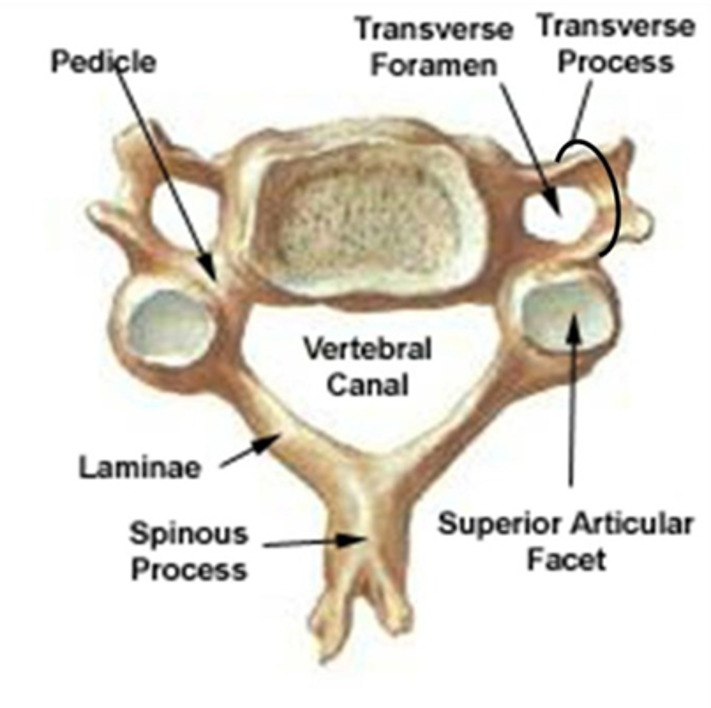
Typical Vertebrae
body
seven processes: 1 spinous, 2 transverse, 4 articular
transverse for muscle/ligament attachments
articular connect with superior and inferior vertebrae. they articulate :D
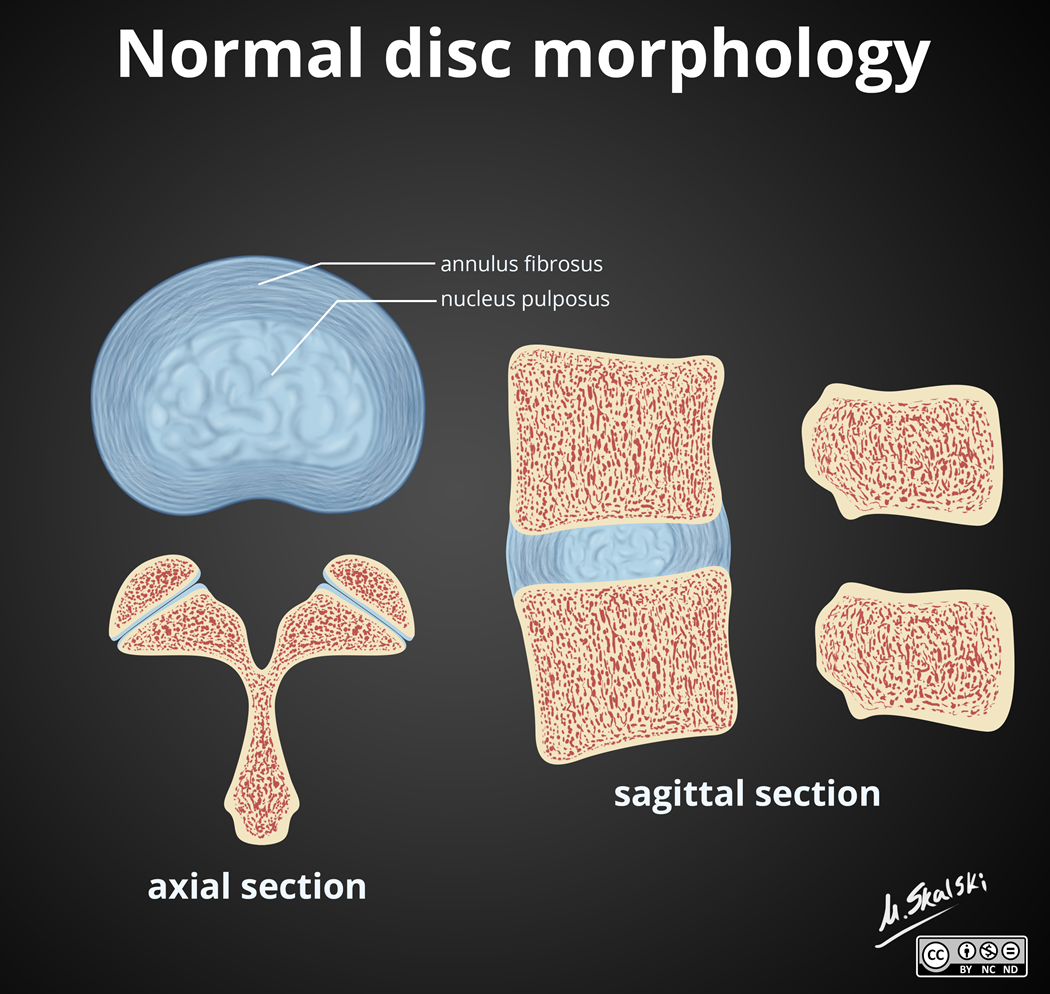
(Inter)Verterbral Discs
Fibrocartilage cushion that functions as the joint between two vertebrae
Components:
inner, spongy nucleus pulposus - essential for providing flexibility, shock absorption
surrounding annulus fibrosus - tough, fibrous structure, keeps NP in place
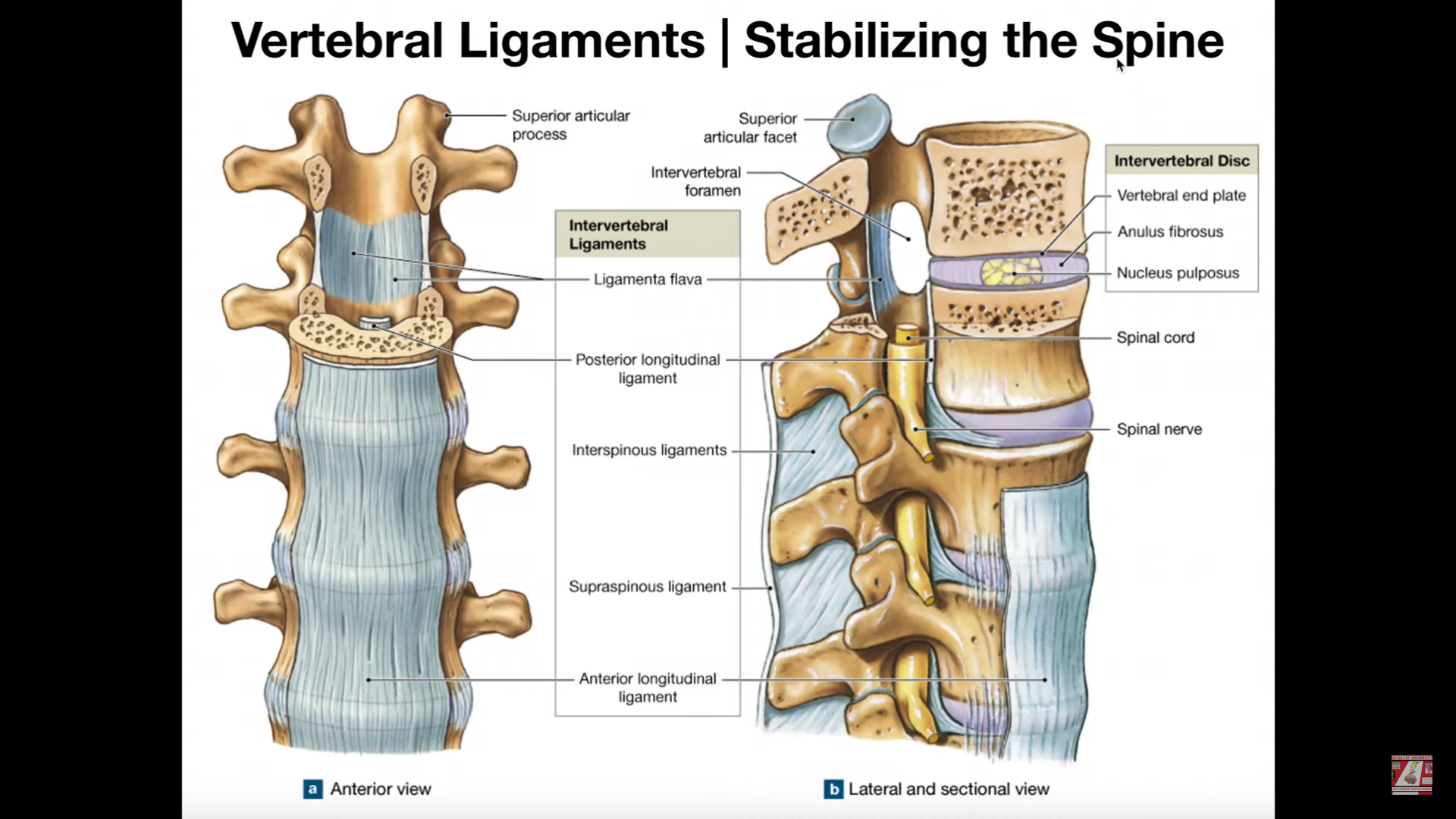
Ligaments of the Spine
Includes 5 of note:
Anterior longitudinal ligament
Posterior longitudinal ligament
Interspinal/-spinous ligament
Supraspinal/-spinous ligament
Ligamenta Flava
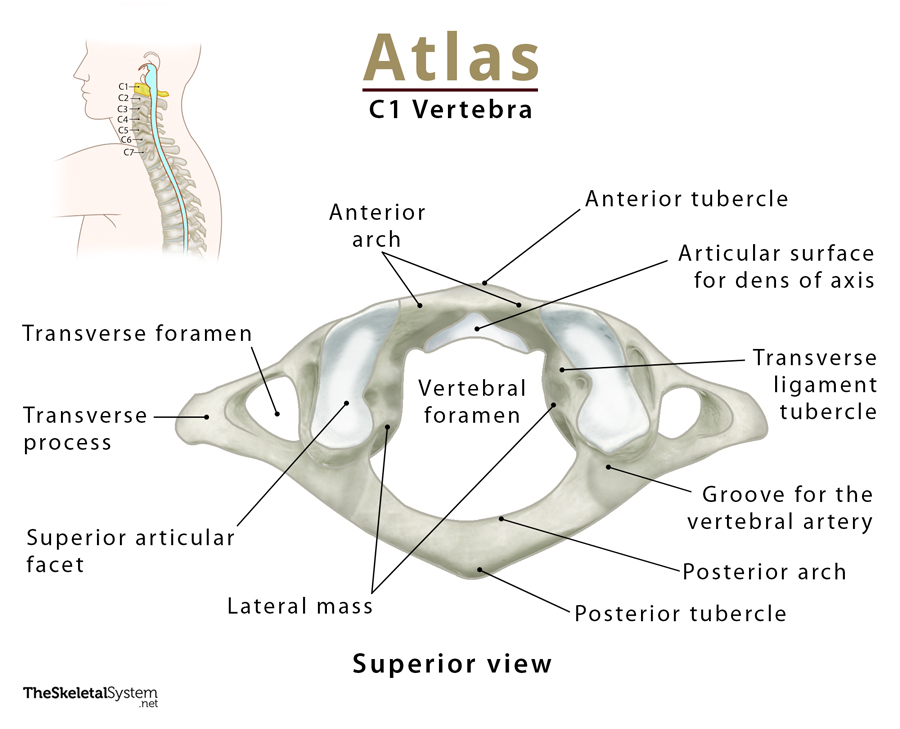
Atlas - C1
no body or spinous process
articulates with the skull. this articulation allows for flexion/extension of the head with the neck (nodding)
also responsible for rotation of the skull from side-to-side
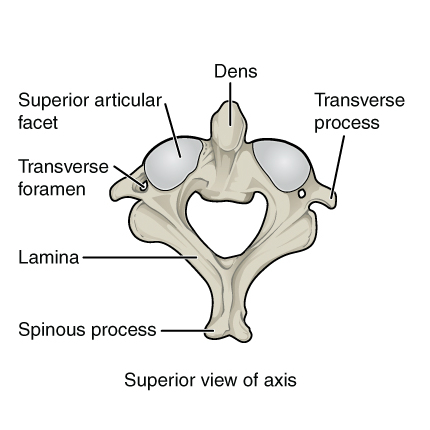
Axis - C2
provides a pivot point for atlas to rotate from side-to-side at the odontoid process/dens
Intrinsic Back Muscles
all innervated by dorsal rami of spinal nerves
deeper muscles, “true” back muscles
involved in movements of the vertebral column. help with posture and stability
Extrinsic Back Muscles
superficial muscles
connect spinal column to shoulders/upper limbs — involved in their movements + movement of the scapula
mostly innervated by the ventral rami of spinal nerves
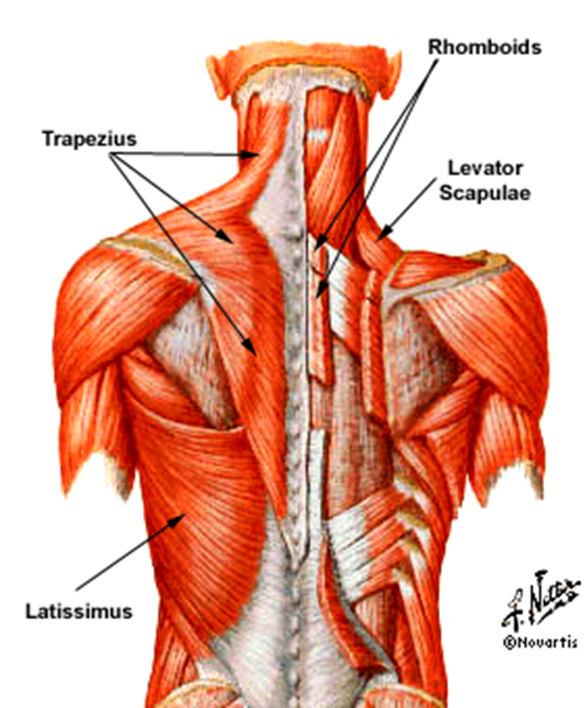
Superficial Extrinsic Back Muscles
Trapezius
Latissimus dorsi
Levator scapulae
Rhomboid minor
Rhomboid major
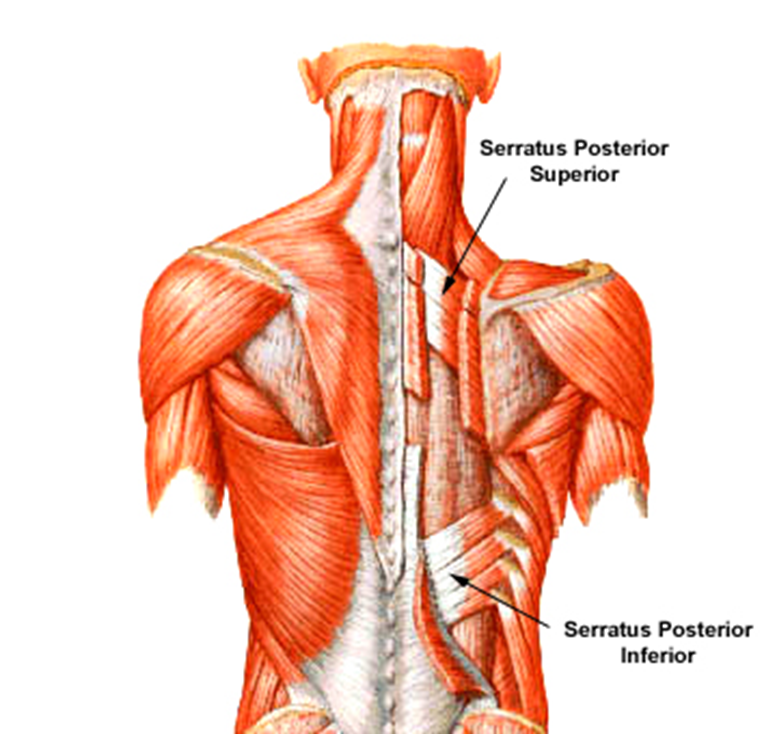
Intermediate Extrinsic Back Muscles
Serratus posterior superior
Serratus posterior inferior
both insert on ribs and assist with forced inspiration
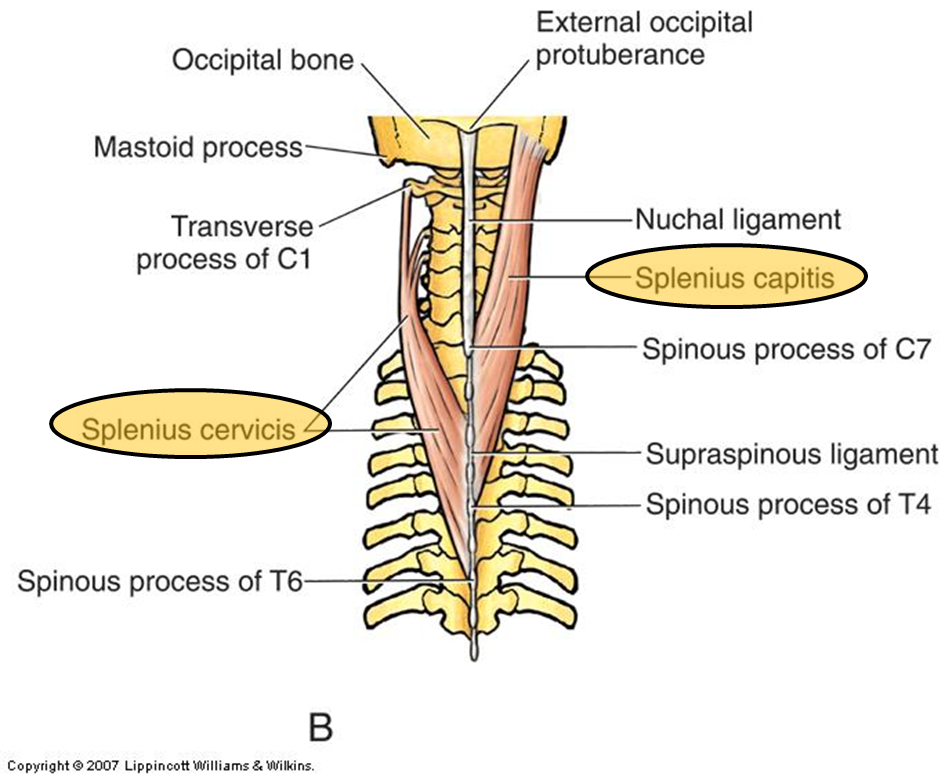
Superficial Intrinsic Back Muscles
splenius cervicis
splenius capitis
these muscles laterally flex / rotate the head to their respective sides when acting alone. they work together to extend the head and neck
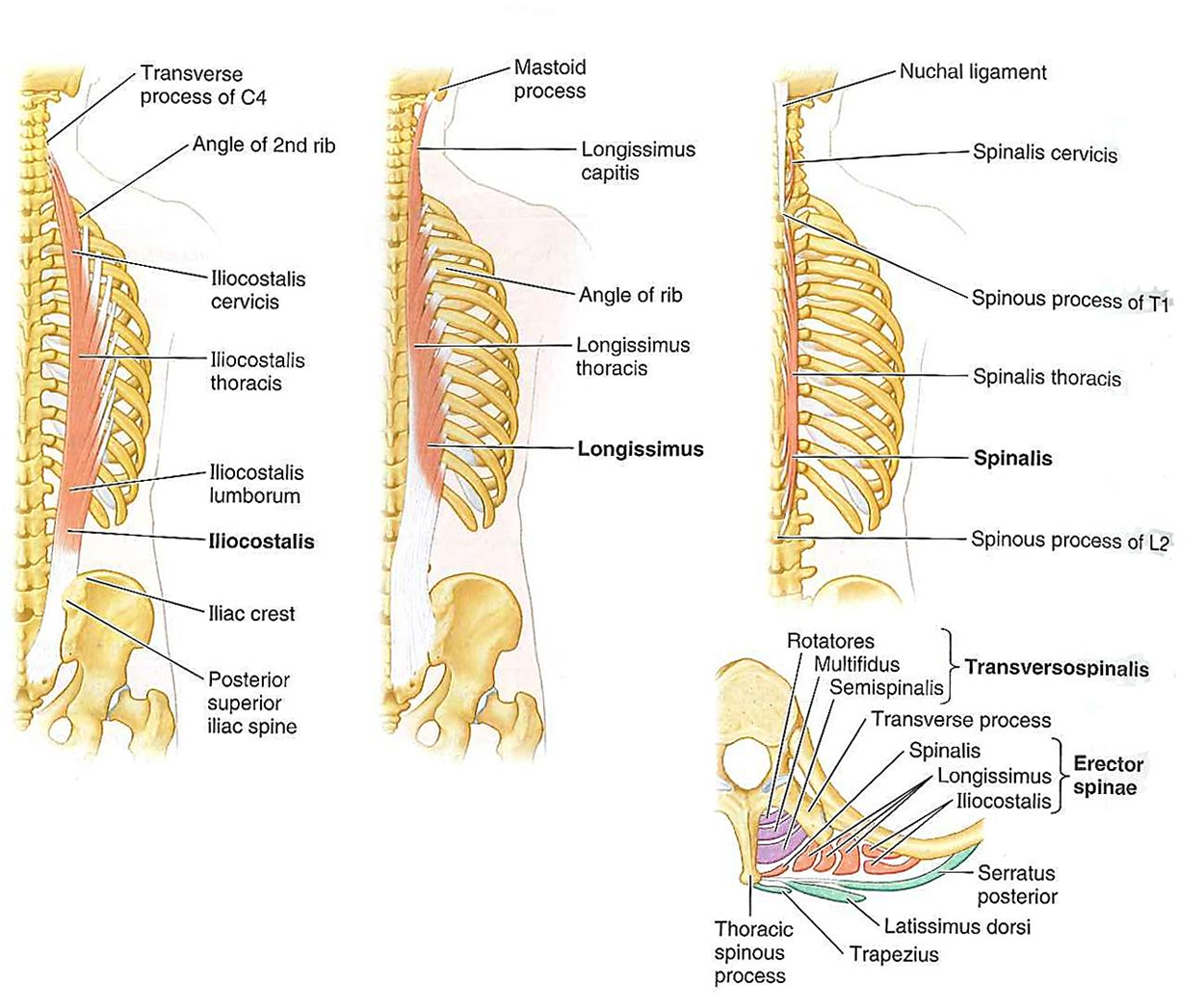
Intermediate Intrinsic Back Muscles
Erector Spinae Group:
Iliocostalis
Longissimus
Spinalis
these muscles are important in maintaining posture, vertebral extension, and lateral flexion
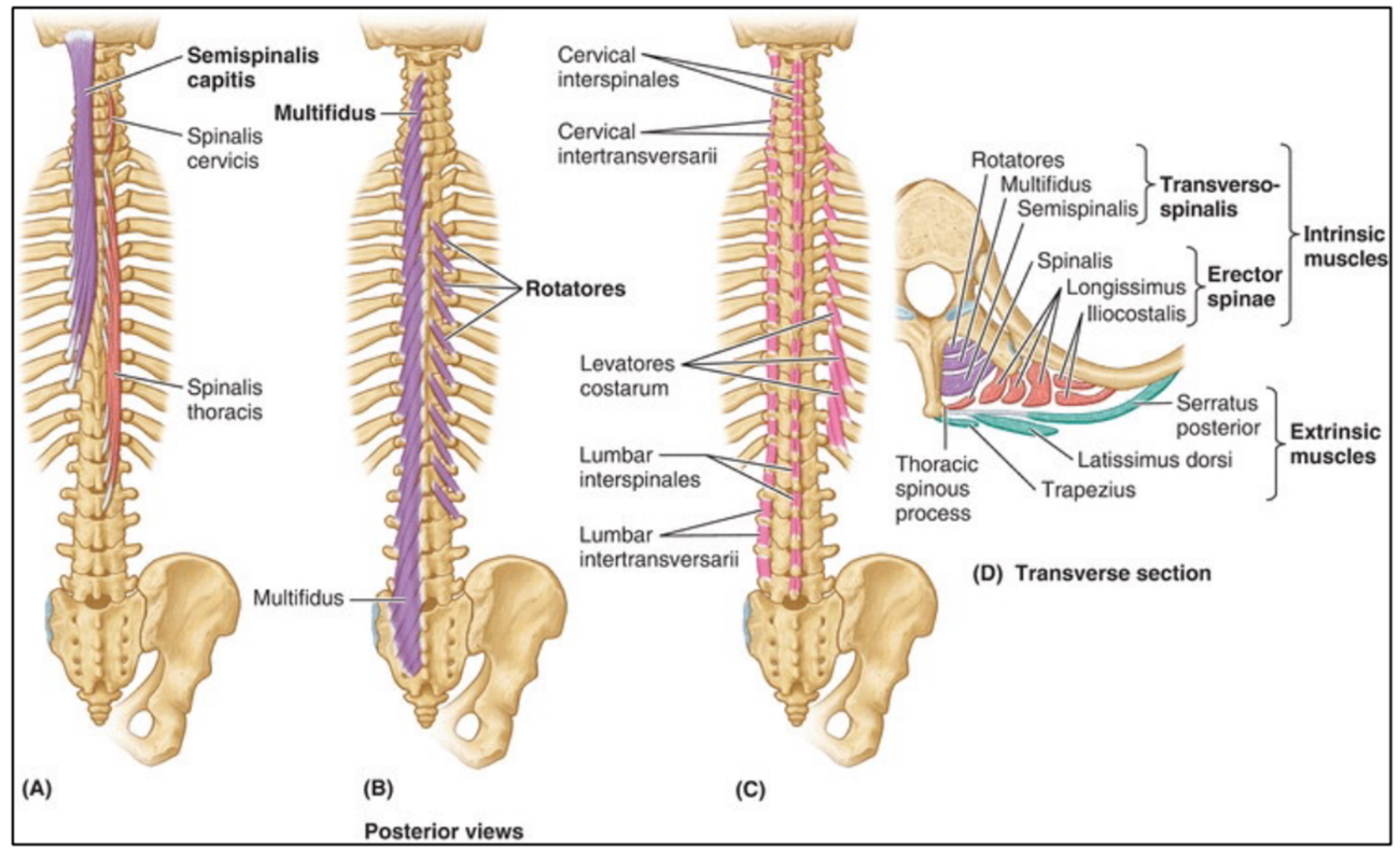
Deep Intrinsic Back Muscles
Transversospinalis Group:
Semispinalis (most superficial)
Rotatores
Multifidus
do not attach to the thoracolumbar aponeurosis
function in extension, rotation, lateral bending, and stabilize the vertebral column
these muscles generally run from transverse processes inferiorly to spinous processes superiorly
Trapezius
innervation: spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
vasculature: transverse cervical artery
Divisions
Upper: elevates shoulder, upward/superior rotation of scapula
Middle: retracts scapula
Lower: depresses scapula
Latissimus Dorsi
innervation: thoracodorsal nerve
vasculature: thoracodorsal artery
Levator Scapulae
originates on transverse processes C1-C4
innervation: dorsal scapular and cervical nerves
vasculature: dorsal scapular artery
also functions in inferior/downward rotation of scapula
Rhomboid Minor
Origin: Nuchal ligament and spinous processes of C7 and T1
innervation: dorsal scapular nerve
vasculature: dorsal scapular artery
retraction + downward rotation
Rhomboid Major
Origin: Spinous processes of T2-T5
innervation: dorsal scapular nerve
vasculature: dorsal scapular artery
rhomboids stretch from medial border @ spine to the inferior angle
Serratus Posterior Superior
Origin: Spinous process and supraspinous ligaments C7-T2
Insertion: Posterior aspect of ribs 2-5
Innervation: ventral primary rami T2-T5
Vasculature: intersegmental artery
Serratus Posterior Inferior
Origin: Spinous process and supraspinous ligaments T11-T12
Insertion: Posterior aspect of ribs 9-12
Innervation: ventral primary rami T9-T12
Vasculature: intersegmental artery
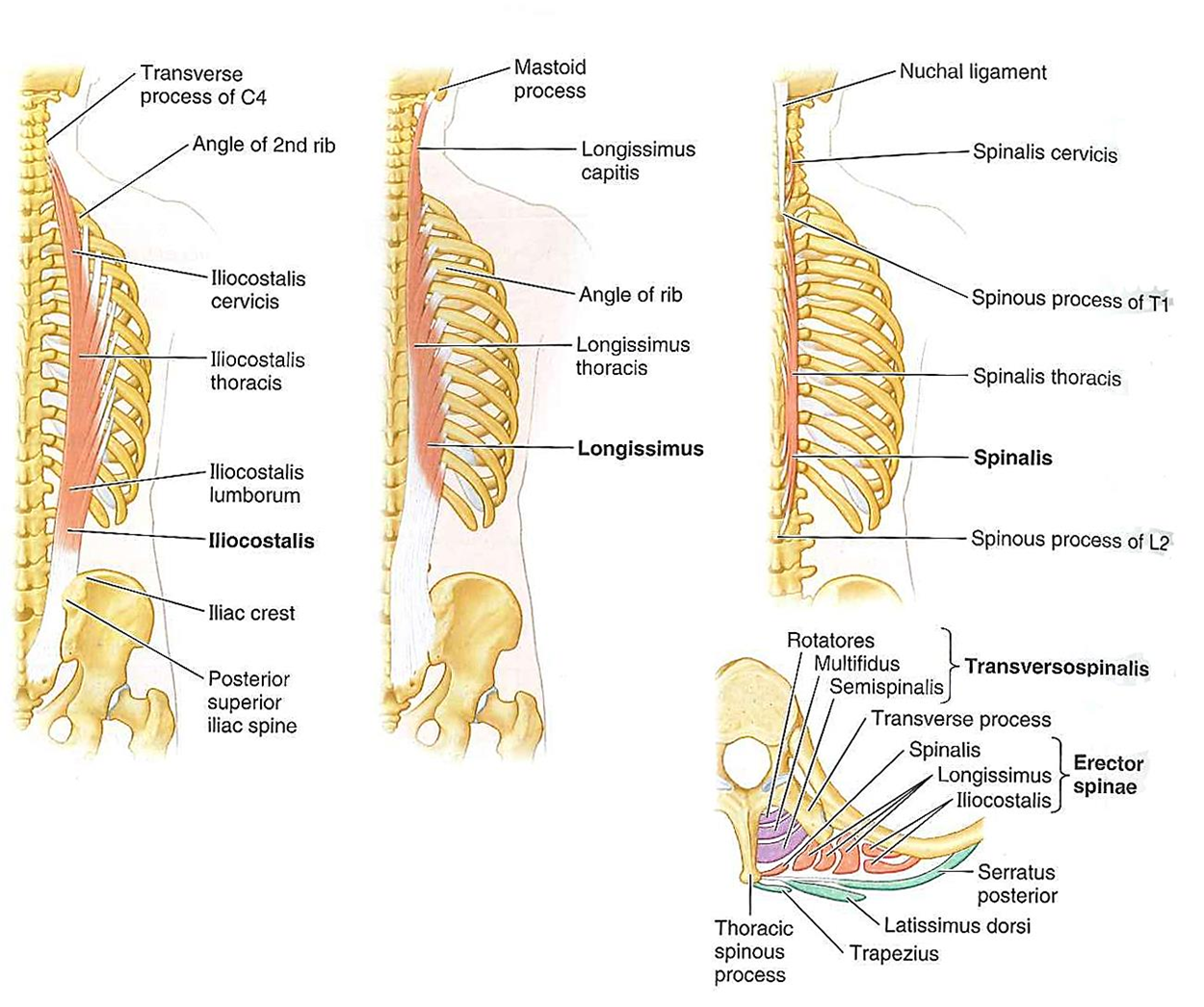
Erector Spinae Group NV
Innervation: Dorsal rami of spinal nerves
Vasculature: Dorsal branch of segmental artery
Insertions:
Iliocostalis (lumborum, thoracis and cervicis) - fibers run superiorly to angles of lower ribs, and to transverse processes of cervical vertebrae near top
Longissimus (thoracis, cervicis, capitis) - fibers run superiorly to ribs, angles towards thoracic/cervical transverse processes, and to mastoid process
Spinalis - (thoracis, cervicis, capitis) fibers run superiorly to spinous processes in upper thoracic region, and to cranium
Triangle of Auscultation
A small, triangular area on the back where breathing sounds can be heard most clearly. It is bounded by the following structures:
Laterally: Medial border of the scapula
Inferomedially: Lateral border of the latissimus dorsi muscle
Superomedially: Inferior border of the trapezius muscle
Fascia Functions
Structural Support: Fascia provides a supportive and flexible framework for muscles, helping to maintain their shape and alignment.
Force Transmission: When muscles contract, the fascia helps transmit the force generated to the tendons and bones, aiding in movement.
Separation and Protection: Fascia separates different muscles and muscle groups, preventing friction between them during movement. It also protects muscles and other structures from injury.
Pathway for Nerves and Blood Vessels: Fascia contains channels for nerves and blood vessels, ensuring they can reach muscles and other tissues.
Facilitating Movement: The fascia allows muscles to glide smoothly over each other, reducing resistance and enhancing movement efficiency.
Role in Sensation and Proprioception: Fascia contains sensory receptors that contribute to the body's ability to sense position, movement, and pain.
Thoracolumbar fascia
covers deep muscles of the back + has 3 layers
aka thoracolumbar aponeurosis
aka lumbodorsal fascia
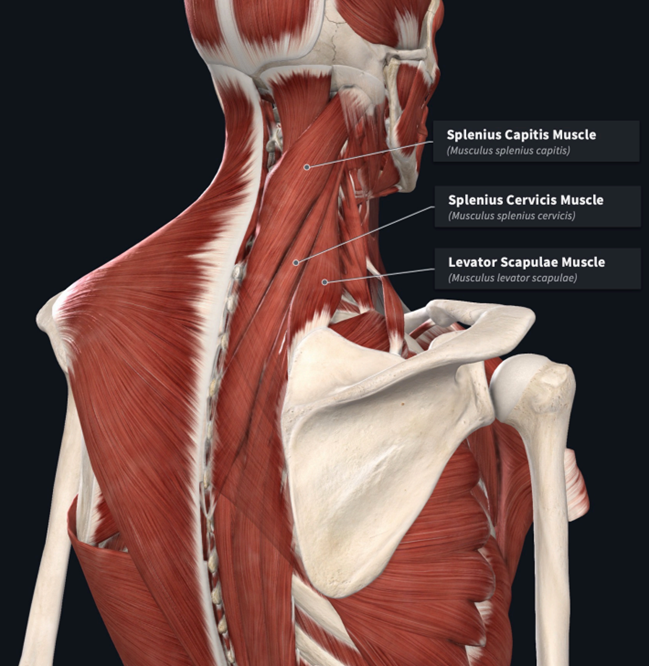
Splenius Muscles NV
innervation: dorsal rami of spinal nerves
vasculature: occipital artery
Capitis — inserts on mastoid process & lateral occipital bone
Cervicis — inserts on transverse processes of cervical vertebrae
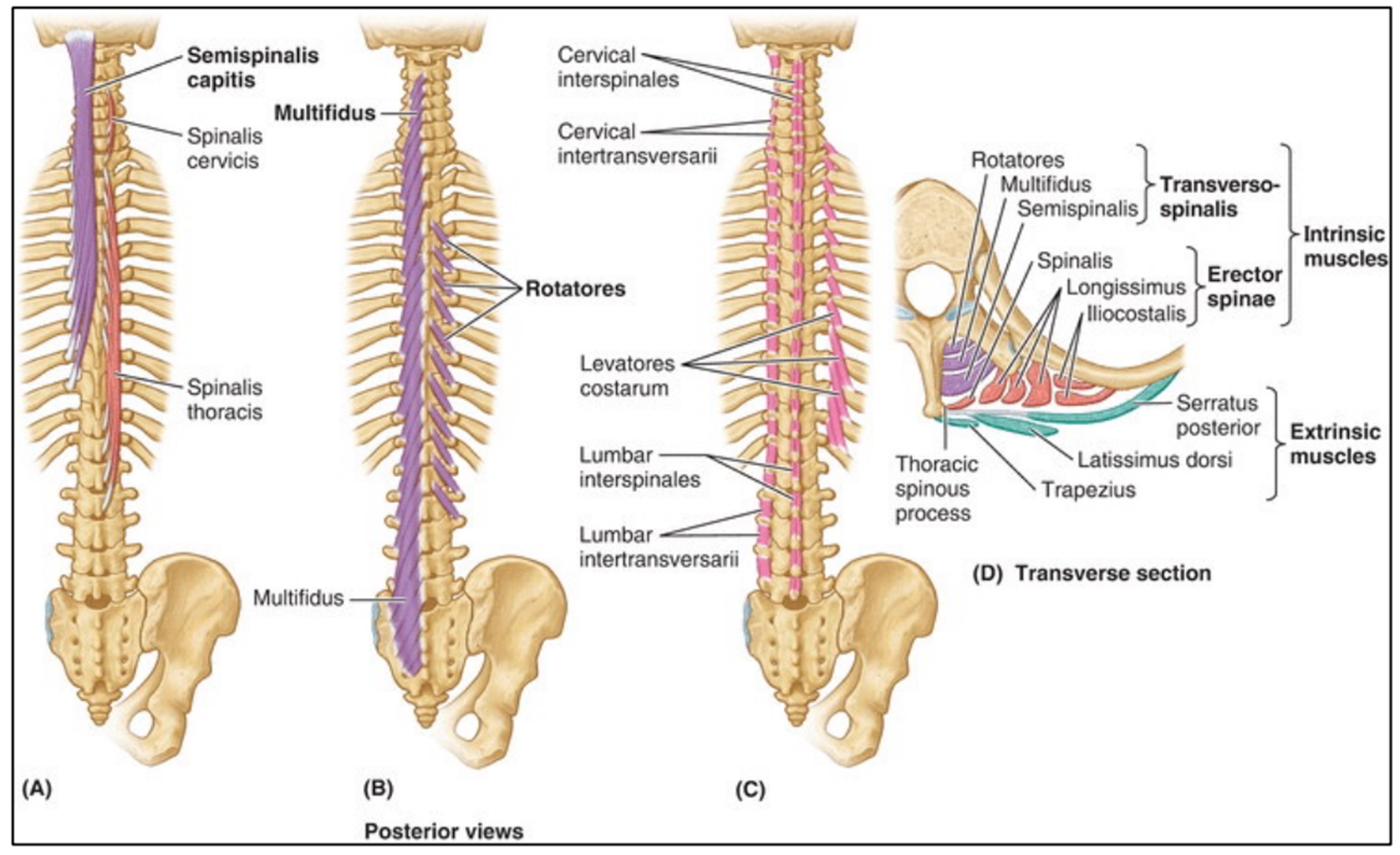
Transversospinalis Group NV
innervation: dorsal rami of spinal nerves
Semispinalis — inserts on occipital bone, spinous process in cervical/thoracic region going 4-6 segments superiorly
semispinalis capitis receives blood from occipital artery
Multifidus — thickest in lumbar region, spans all spinous processes and inserts 2-4 segments superiorly
Rotatores — inserts on junction of lamina/transverse process or spinous processes. Inserts either 1 (brevis) or 2 (longus) segments superiorly
Blood Supply to the Transversospinalis Muscles
Posterior Intercostal Arteries
Lumbar Arteries
Deep Cervical Artery
Vertebral Artery
Occipital Artery