Chapter 5 - The Integumentary System
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Integumentary System
largest organ system of the body
accounts for 16% of body weight
composed of
skin
exocrine glands
hair, nails
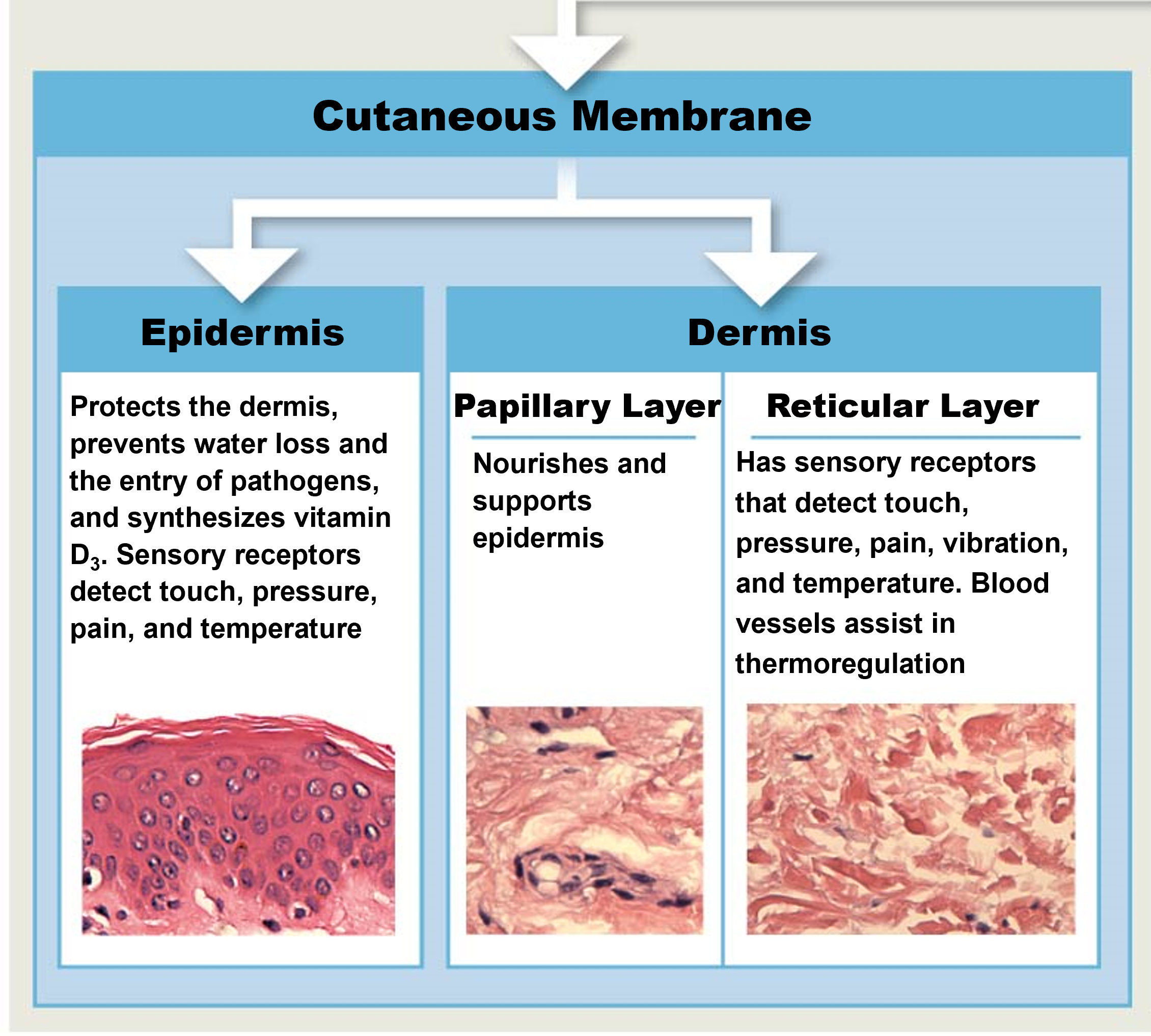
Cutaneous Membrane
Epidermis - superficial epithelium
Dermis - connective tissues
Papillary
Reticular
Epidermis
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
protects dermis, tissues, organs
excretion of salts, water, organic wastes through glands
maintenance of body temp (insulation & evaporation)
prevents water loss & entry of pathogens
production of melanin & keratin
synthesizes vitamin D3
storage of lipids
sensory receptors detect touch, pressure, pain, temp
Keratinocytes
contain large amounts of keratin
most abundant ells in epidermis
Melanocytes
containing pigment melanin
contribute to skin color
protect underlying tissues
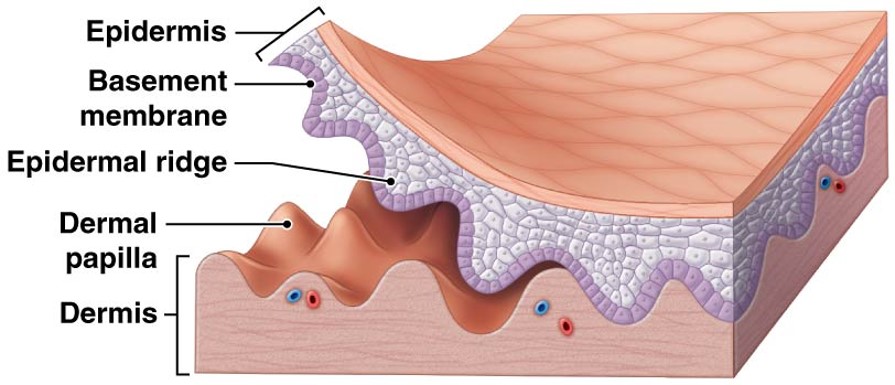
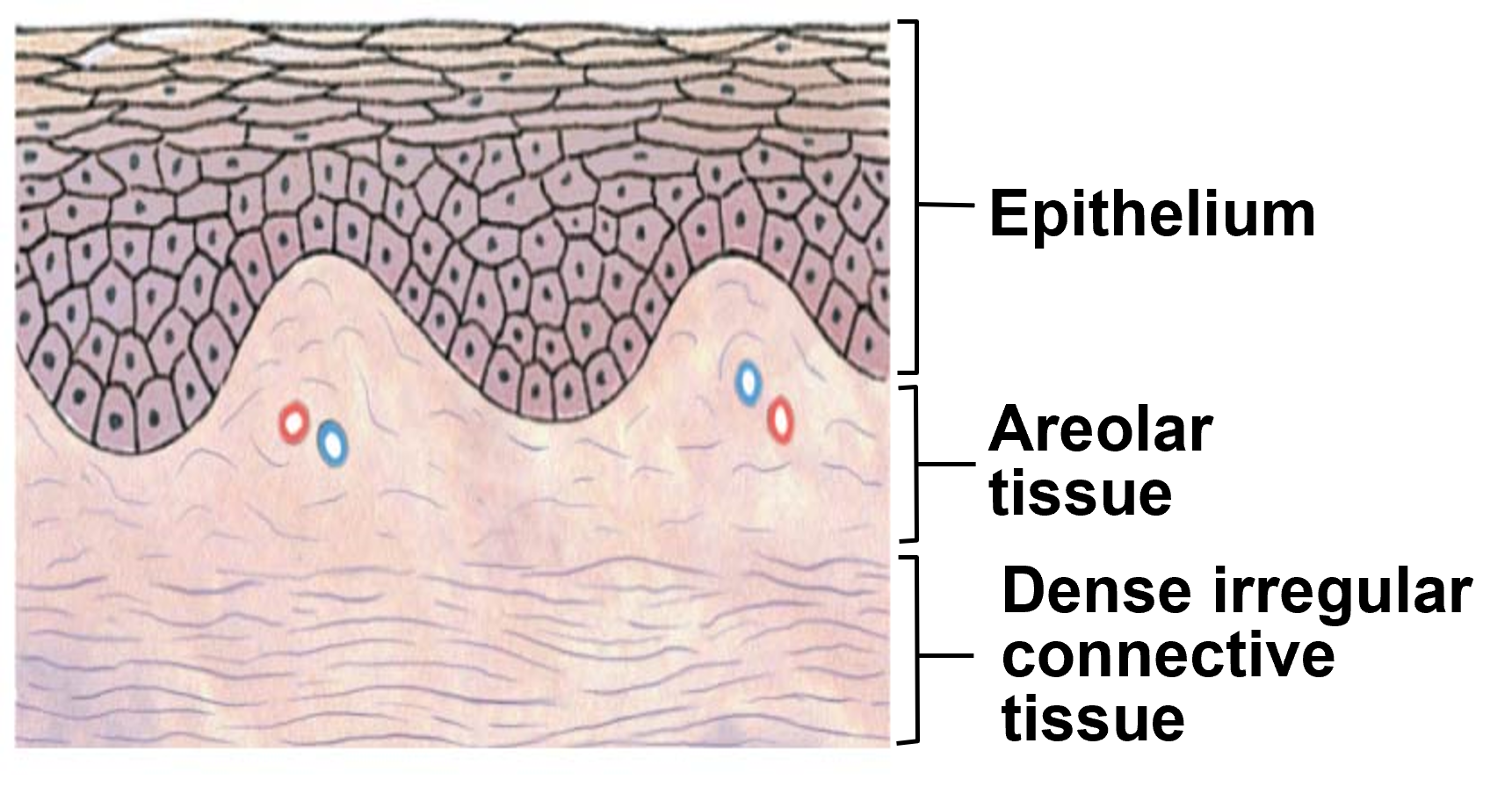
Papillary Layer
nourishes and supports epidermic from blood
areolar tissue
contains capillaries, lymphatics & sensory neuron endings
dermal papillae project between epidermal ridges
Reticular Layer
dense irregular connective tissue
has sensory receptors that detect touch, pressure, pain, vibration, temp
blood vessels assist in thermoregulation
contains larger blood vessels, lymphatics & nerve fibers
composed of collagen & elastic fibers
provides skin with flexibility & resilience properties
Cutaneous Membrane
Epidermis - superficial epithelium
Dermis - connective tissues
Subcutaneous Layer (Hypodermis)
elastic areolar & adipose connective tissue
provides stability for skin
site of subcutaneous injection
Types of Skin
depends of # of epidermal layers
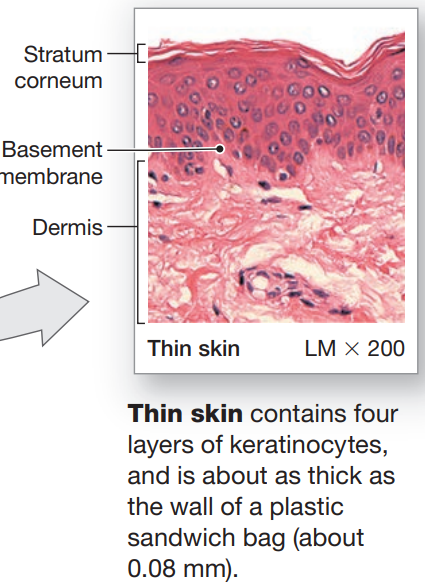
Thin
covers most of the body
4 layers of keratinocytes
Thick
covers palms of hands & soles
5 layers of keratinocytes
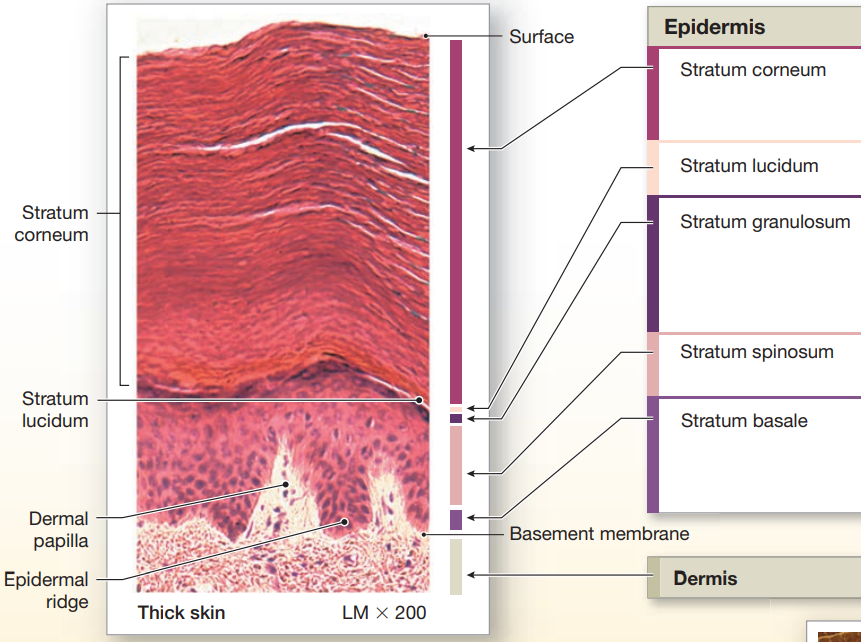
Layers of Thick Skin
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Lucidum
Stratum Granulosom
Stratum Spinosum
Stratum Basale
Layers of Thin Skin
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Granulosom
Stratum Spinosum
Stratum Basale
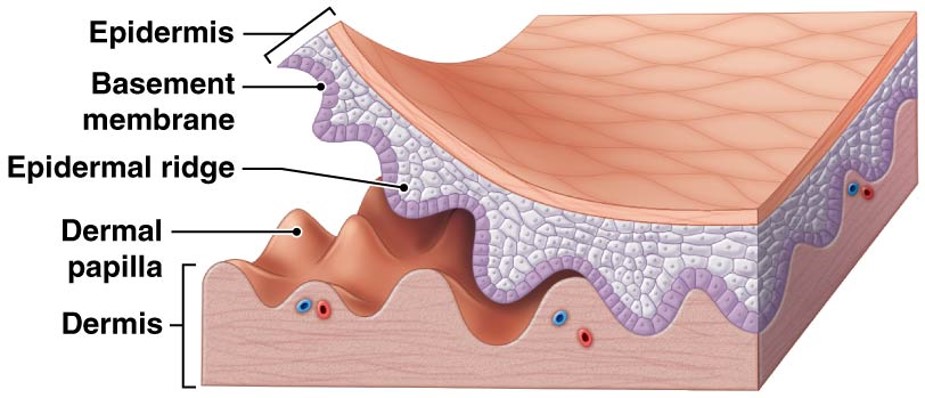
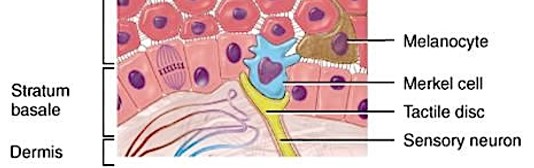
Stratum Basale
attached to basement membrane by hemidesmosomes
strong bond between epidermis & dermis
forms epidermal ridges (basis of fingerprints)
dermis forms dermal papillae (tiny mounds)
increases surface area of basement membrane
provides added strength between epidermis and dermis
Cells of Stratum Basale
keratinocytes
basal cells (germinative or stem)
Merkel cells
found in hairless skin
respond to touch
melanocytes
produce melanin
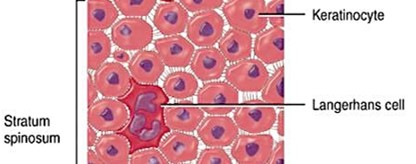
Stratum Spinosum
aka “spiny layer”
produced by stratum basale stem cell division
8-10 layers of keratinocytes bound by desmosomes
cells shrink untill cytoskeleton protrudes
contains dendritic (Langerhans) cells
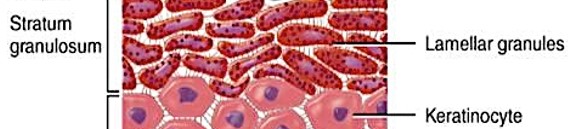
Stratum Granulosum
aka “grainy layer”
keratinocytes stop dividing
begin to produce protein fibers
keratin - tough, fibrous protein
keratohyalin - dense granules, cross-link keratin fibers
dehydrated & dies
form tightly interlocked layer of keratin surrounded by keratohyalin
Stratum Ludicum
aka “clear layer”
found only in thick skin
translucent cell layer
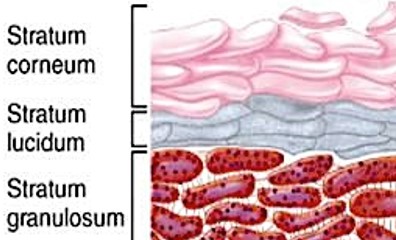
Stratum Corneum
aka ‘horn layer”
exposed surface of skin
15-30 layers of keratinized cells
water resistant
shed & replaced about every 2 weeks
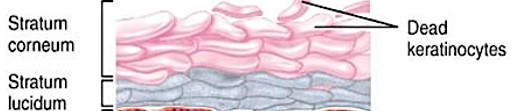
Keratinization (Cornification)
formation of a layer of dead, protective cells packed with keratin
relatively dry layer that is moistened by sebaceous glands
occurs on all exposed skin surfaces except eyes
takes up to 7-10 days for newly generated cells to migrate form stratum basale to stratum corneum
Types of Perspiration
Insensible - interstitial fluid lost by evaporation through stratum corneum
Sensible - water excreted by sweat glands
Dehydration of Skin
damages stratum corneum
increases insensible perspiration
particularly dangerous for burn victims
Hydration of Skin
replenishes tissues
Pigments in Skin Color
Carotene
orange-yellow pigment
found in orange veggies (ex: carrots)
accumulates in epidermal cells & dermal fatty tissue
can be converted to vitamin A
Melanin
yellow-brown or black pigment
produced by melanocytes in stratum basale
melanosomes are transferred to keratinocytes
RBC
Melanocytes
found associated with stratum basale
long process extend from melanocyte into stratum spinosum
melanin is transferred to keratinocytes by means of pigment-carrying melanosomes
travels up via transcytosis
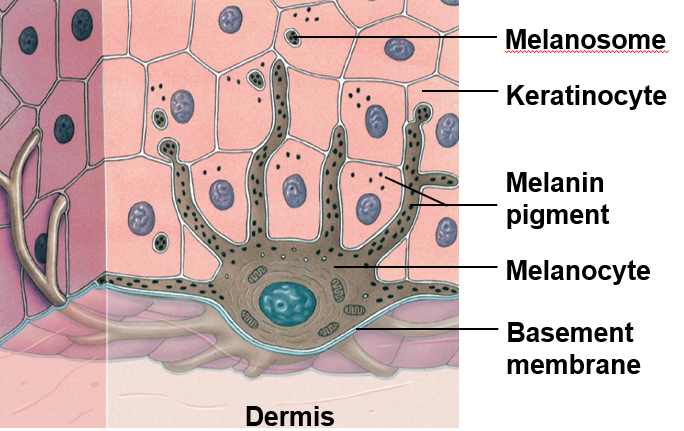
Contribution to Skin Color
melanin protects skin from sun damage
melanosomes shield nucleus of keratinocytes
Melanocyte Contribution:
level of melanin
melanin isoform expression
equivalent #s of melanocytes
RBC Contribution:
skin reddens when heat causes blood vessels to dilate
skin turns pale as blood flow decreases
skin developed bluish tiny due to severe reduction in blood flow or oxygenation
Jaundice
build-up of bile produced by the liver
yellowing of the skin
Pituitary Tumor
skin darkening due to excess MSH (melanocyte-stimulating hormone)
Addison’s Disease
skin darkening due to excess ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone)
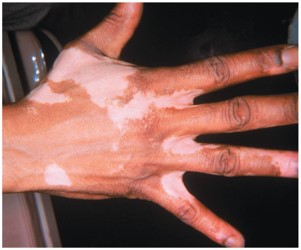
Vitiligo
loss of color in patches of melanocyte populations
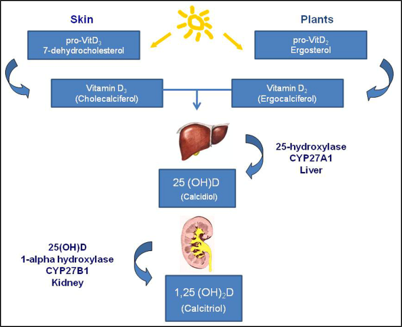
Vitamin D3 (aka Cholecalciferol)
produced in response to UV radiation or obtained from diet
converted to calcidiol by liver
converted to calcitriol by kidney
resulting in absorption of Ca + P
deficiency causes Rickets (weak & flexible bones)
Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)
potent peptide growth factor
produced through glandular secretions
submaxillary glands & glands in small intestine
promotes division of stratum basale stem cells
accelerates keratin production
stimulates epidermal repair & glandular secretion
Dermatitis
inflammation of papillary layer
caused by infection, radiation, chemicals, mechanical stimulation
symptoms include itch and pain
Skin Damage
reduction in skin elasticity caused by
dehydration, age, hormones, UV exposure
stretch marks
thickened tissue caused by excessive stretching
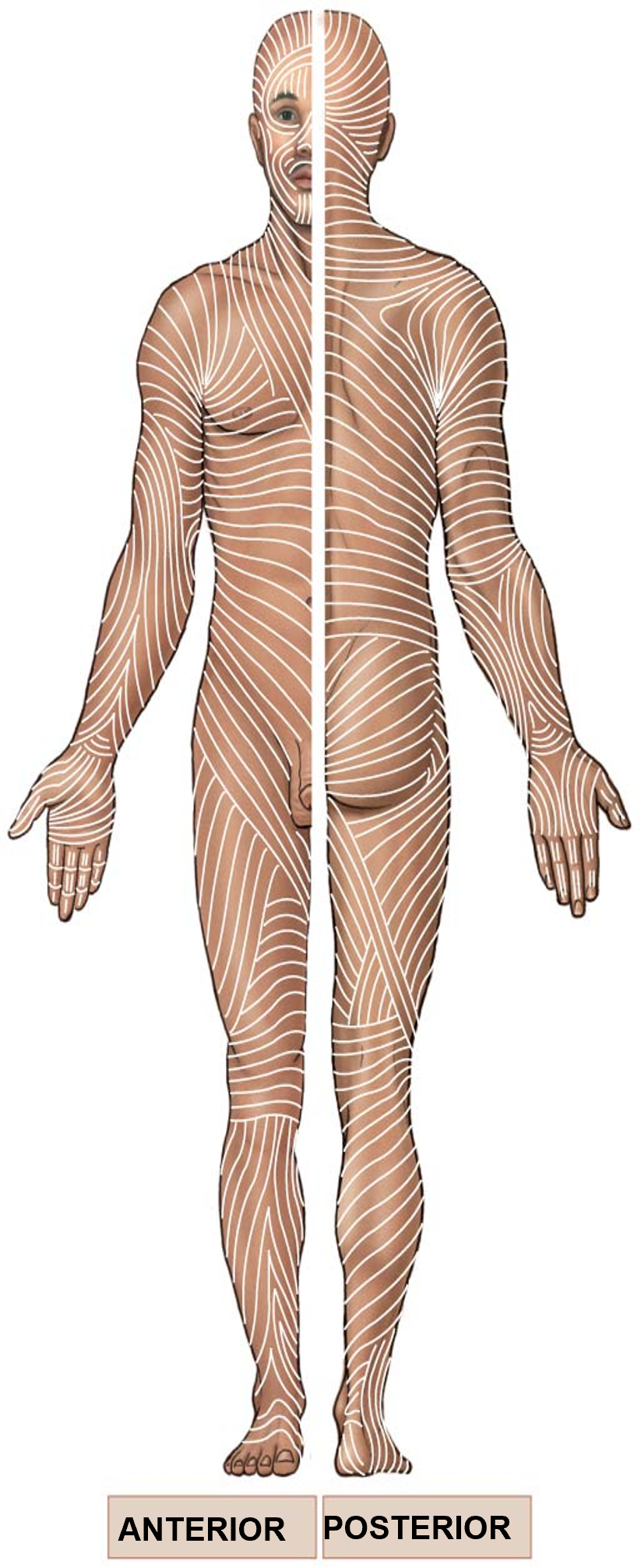
Cleavage / Tension / Langer Lines
collagen and elastic fibers arranged in parallel bundles
arrangement enables resistance of forced from specific directions
cut or incision parallel to bundles remain closed and heals well
cuts perpendicular to bundles causes wound to pull open and often results in scarring
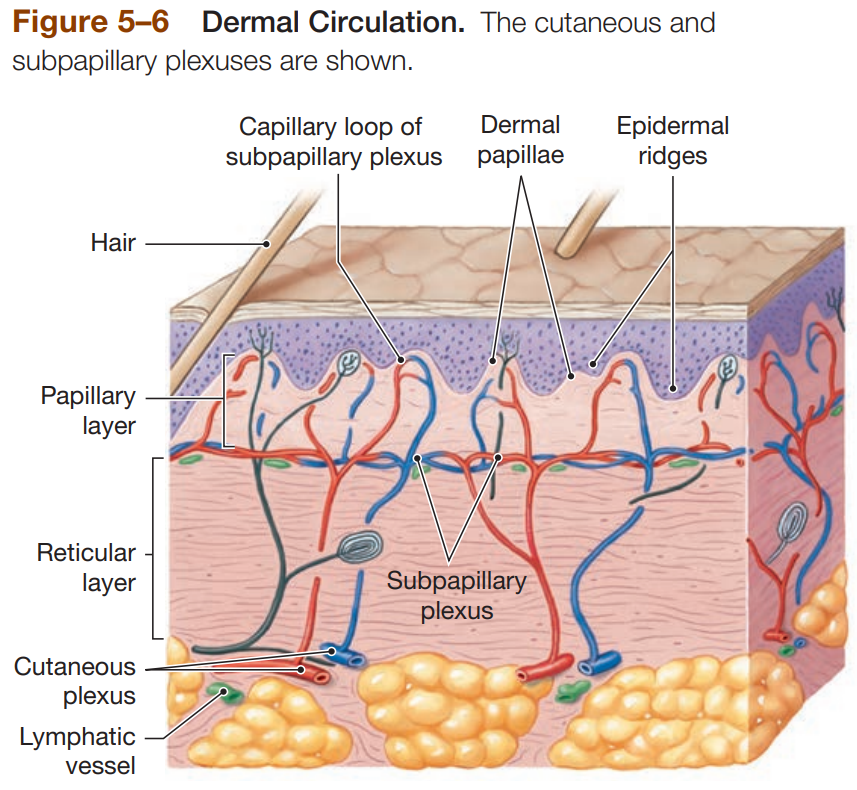
Blood Supply to the Dermis
Cutaneous Plexus - network of arteries along reticular layer
Subpapillary Plexus - capillary network arising from small arteries in papillary layer
Venous Plexus - capillary return deep to papillary plexus
Contusion - damage to blood vessels resulting in blood leaking into dermis, leaving bruising
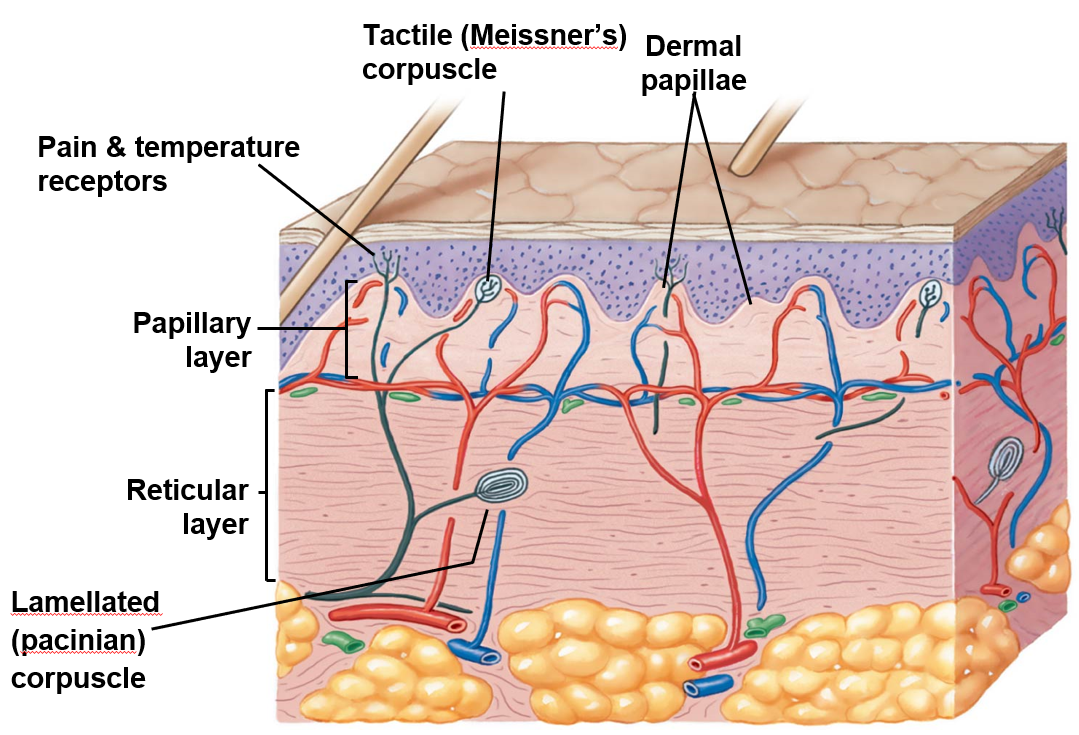
Nerve Fibers in Skin Control…
blood flow
glandular secretions
sensations
light touch - tactile (Meissner’s) corpuscles in dermal papillae
deep pressure & vibration - lamellated (Pacinian) corpuscles in reticular layer
pain & temp - sensory endings in epidermal & dermal layers
Accessory Structures
derived from embryonic epidermis
located in dermic
project through skin surface
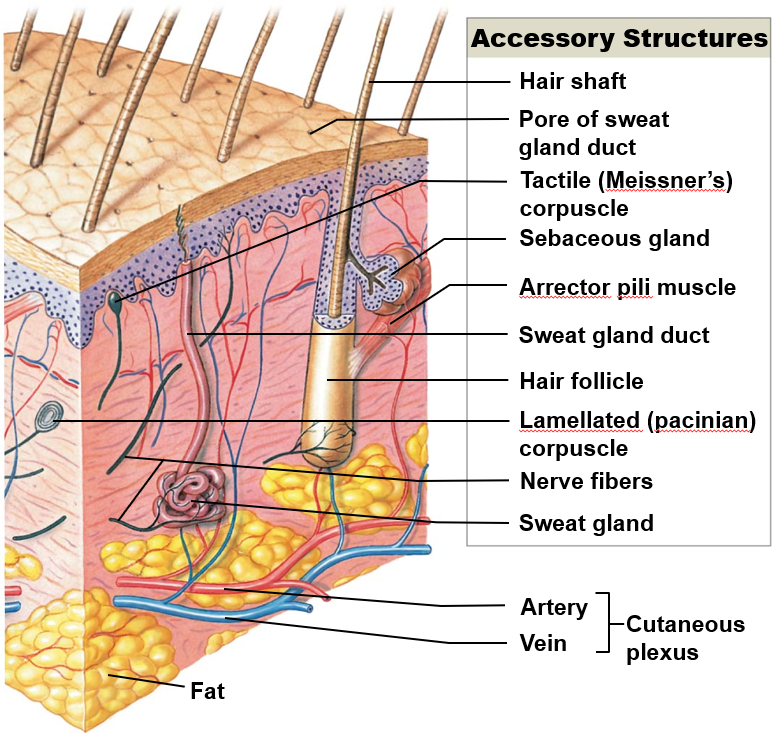
Functions of Accessory Structures
Hair Follicles
protect skull
provides delicate touch sensations on general body surface
Exocrine Glands
assist in temp regulation & waste excretion
Nails
protect & support tips of fingers & toes
Hair
dead, keratinized epithelial tissue
are active organs of skin
located in fermis
extends from epidermal surface to dermis (even to hypodermis)
epithelial cells wrap a dense connective tissue sheath
sensory nerve endings surround follicle base
Some regions are hairless
palm, sole, sides of fingers & toes, lips, portions of external genatalia
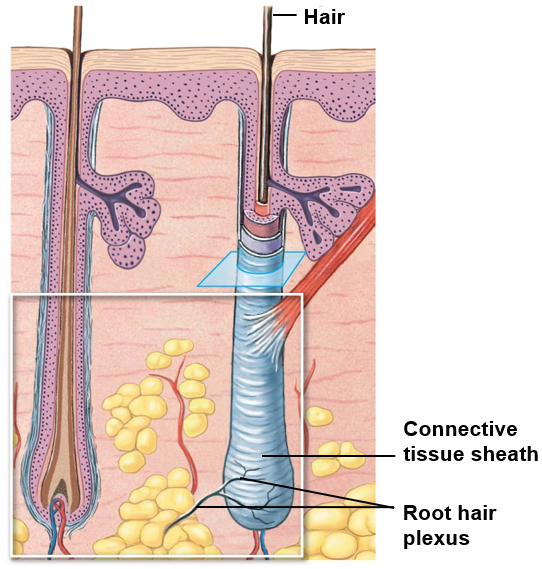
Arrector Pili
bundle of involuntary smooth muscle
extends from papillary layer of dermis to connective tissue sheath of follicle
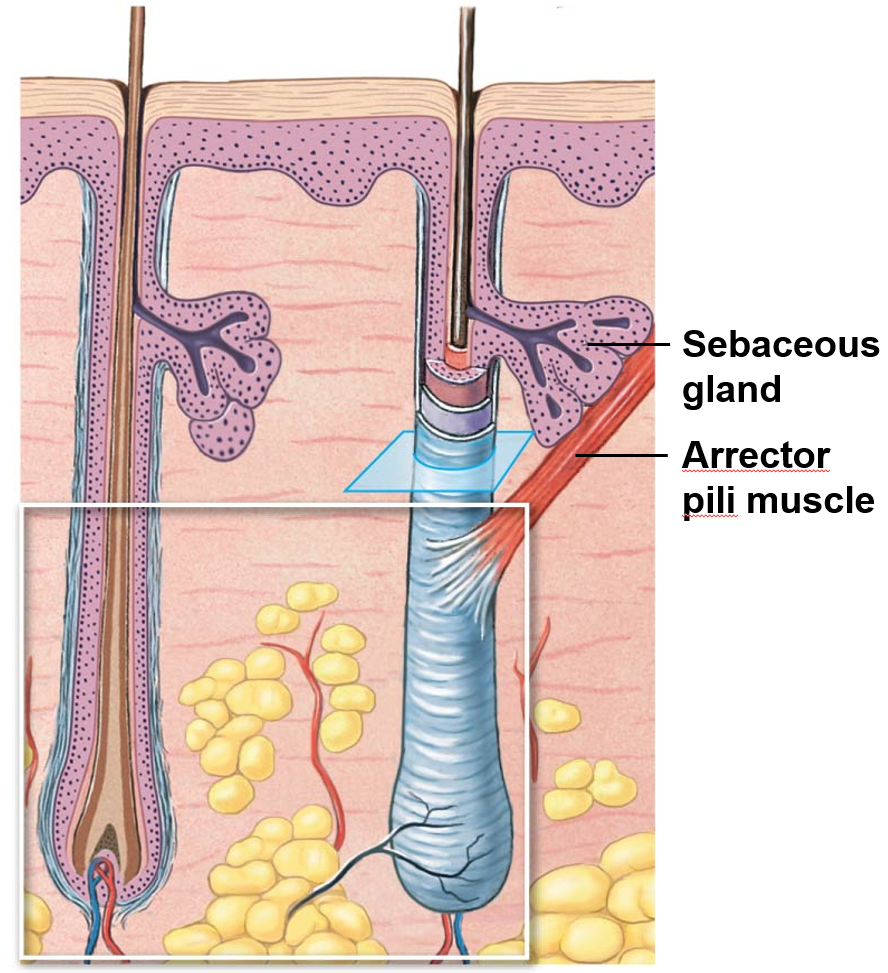
Sebaceous Glands
lubricates hair
conditions epithelial layers
inhibits bacterial growth
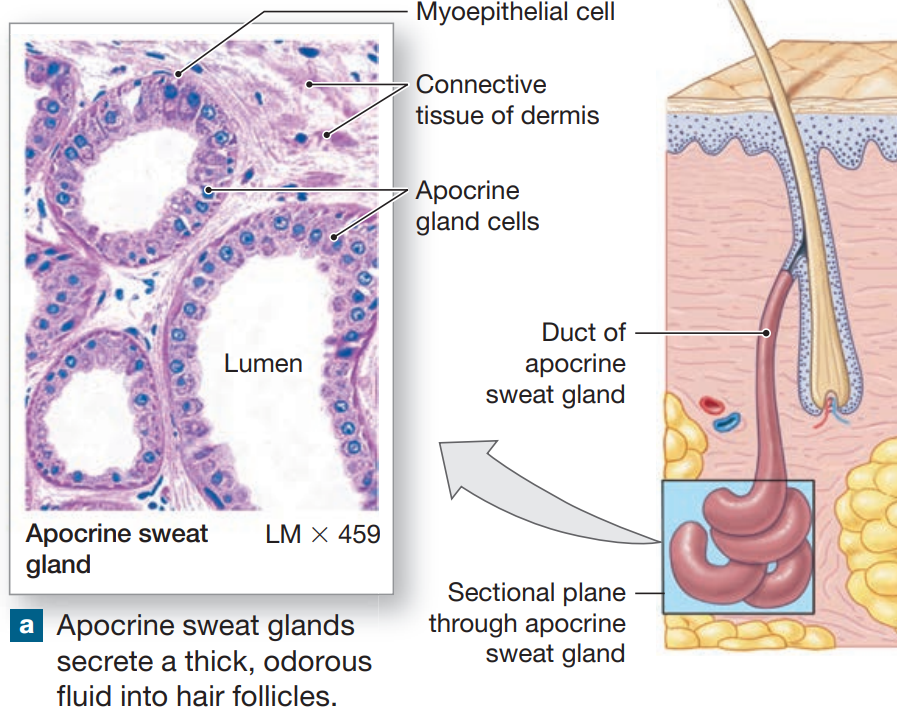
Apocrine Sweat Glands
coiled, tubular glands found in armpits, around nipples, pubic region that begin secreting at puberty
secret by apocrine secretion into hair follicles
produce sticky, cloudy secretions
breakdown of bacteria causes odors
surrounded by myoepithelial cells
squeeze gland, forcing secretion onto surface of skin
regulated by neural and endocrine systems
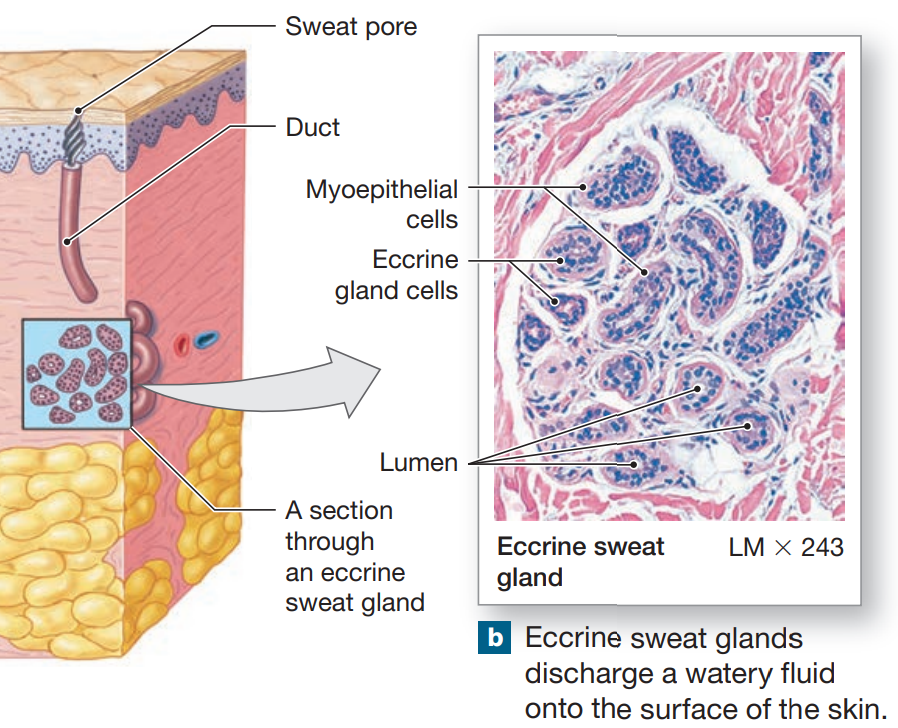
Merocrine (Eccrine) Sweat Glands
widely distributed on body surface
concentrated on pamls & soles
coiled, tubular gland
watery discharge directly onto skin
responsible for sensible perspiration
lose water, salt, & organic material
thermoregulation
maintains sensible perspiration
integrated nervous & cardiovascular system
flushes microorganisms & harmful chemicals from skin
controlled independent of other glands
localized stimulation of sweating
Ceruminous Glands
produce cerumen (earwax)
protects eardrum
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
involuntary control of sebaceous & apocrine sweat glands
all glands effected concurrently
Repairing the Integument
injury occurs with bleeding & inflammatory response is triggered
blood clotting occurs, scab stabilizes & protects wounded area
stem cells migrate around wound
macrophages clean area
fibroblasts & endothelial cells migrate to area
producing granulation tissue (scar tissue)
inflammation decreases, clot disintegrates
raised keloid may form
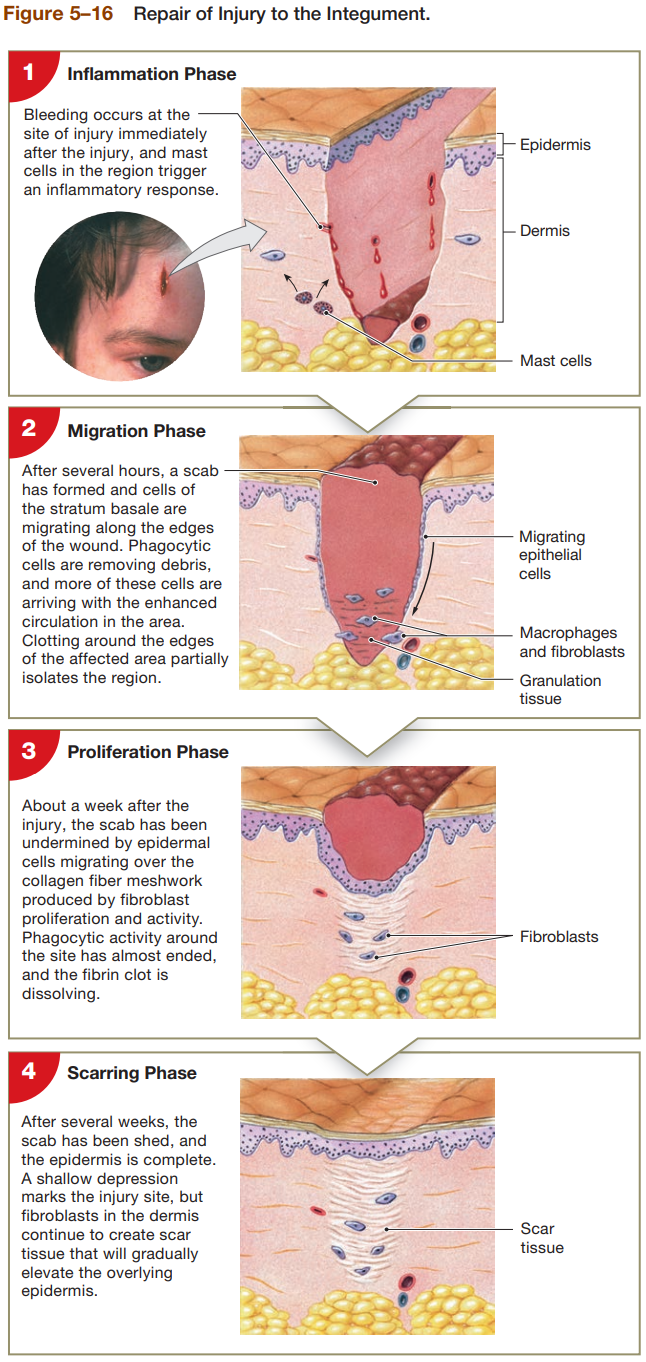
4 Phases of Repairing the Skin
Inflammation Phase
bleeding occurs at site immediately after injury
mast cells in region trigger inflammatory response
Migratory Phase
scab will form after several hours, cells of stratum basal are migrating along edges of wound
phagocytic cells remove debris, and more arrive due to enhanced circulation of area
clotting around edges of affected area particularly isolates region
Proliferation Phase
after a week, scab has been undermined by epidermal cells migrating over collagen fiber meshwork produced by fibroblast proliferation & activity
phagocytic activity around site has almost ended
fibrin clot is dissolving
Scarring Phase
after several weeks, scab shed and epidermis is complete
shallow depression marks injury sit, but fibroblasts in dermis continue to create scar tissue that will gradually elevate overlying epidermis