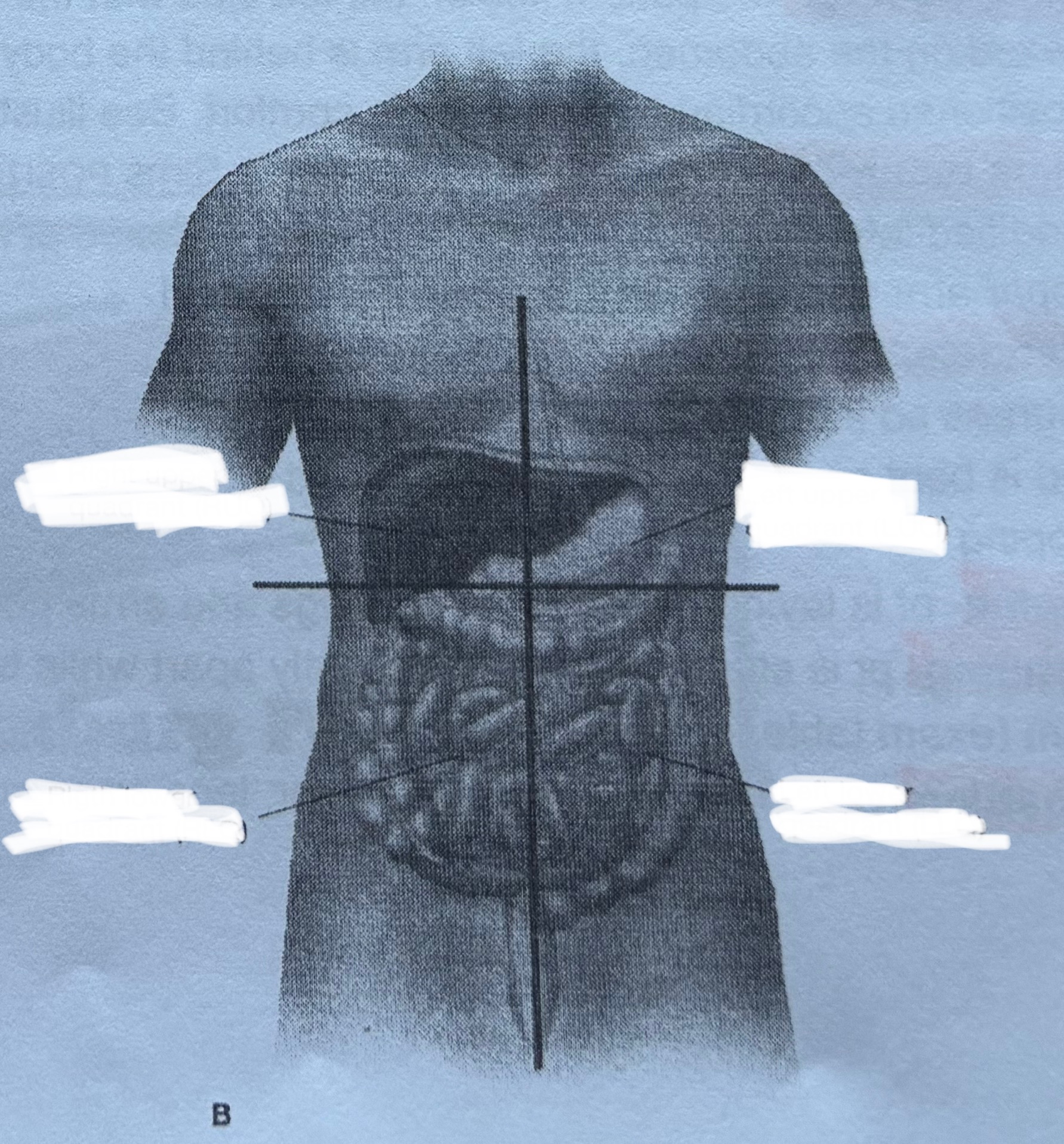
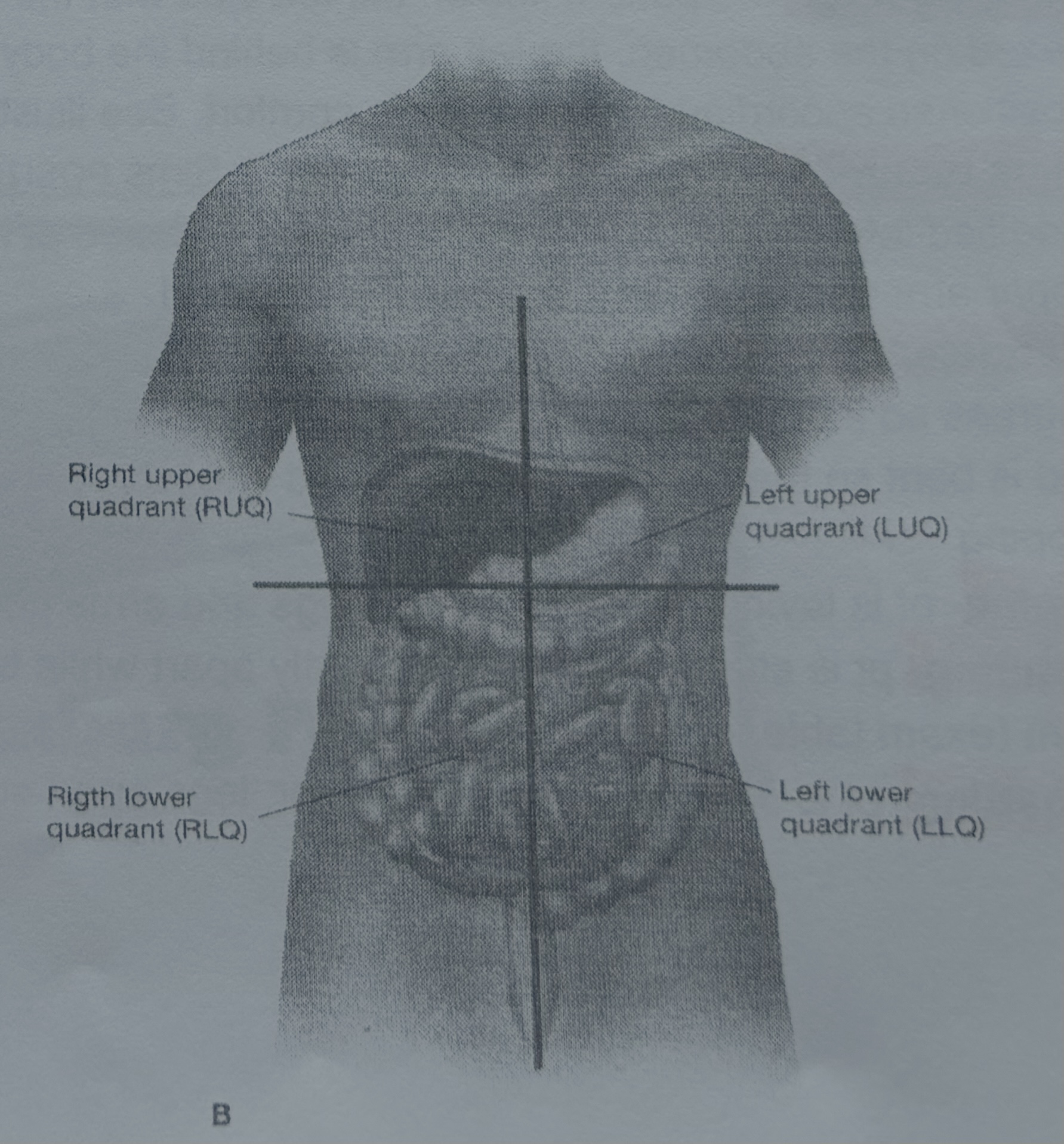
MOD-A Positions
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
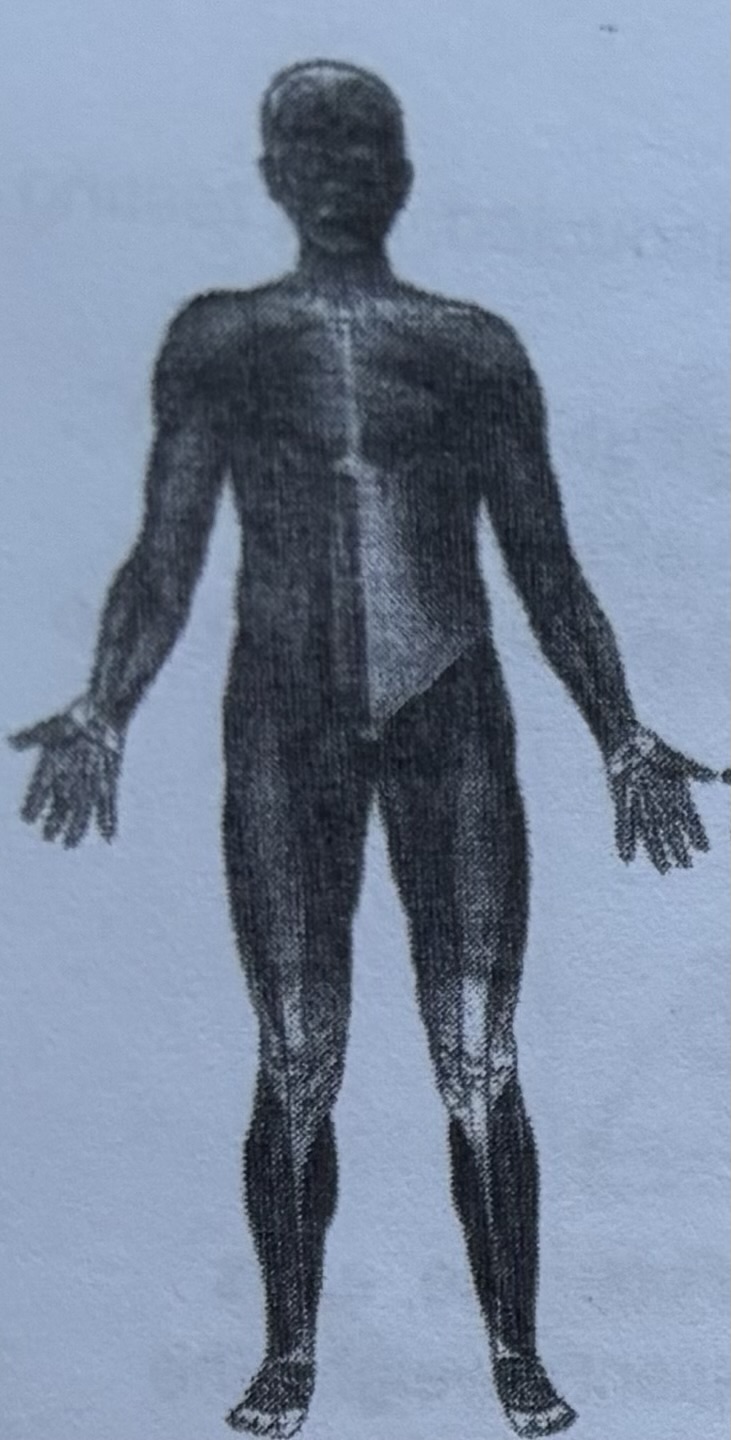
MUSCULAR SYSTEM
The muscular system consists of layers of muscles that cover the bones of the sKeleton, extend across joints, and can contract and relax to produce movement.
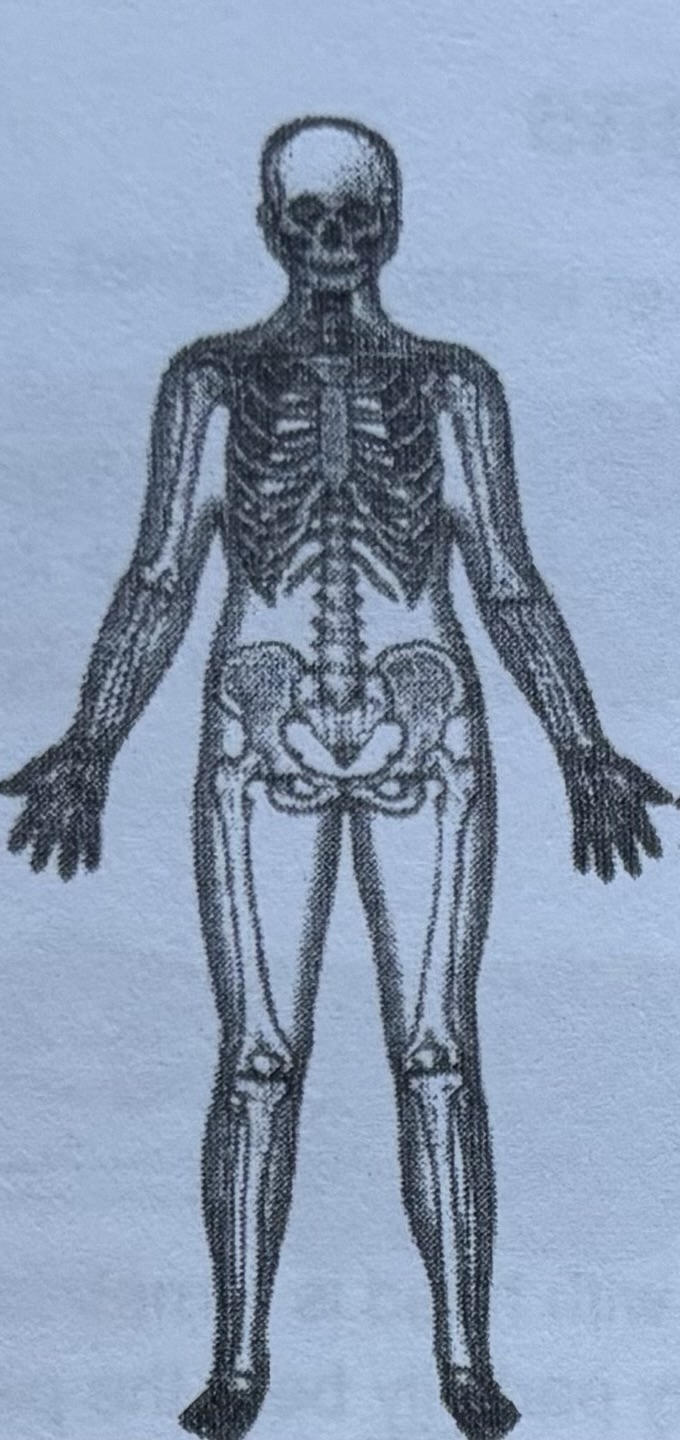
Skeletal system
The skeleton is a strong yet flexible framework of bones and connective tissue. It provides support for the body and function protection for many of its internal parts
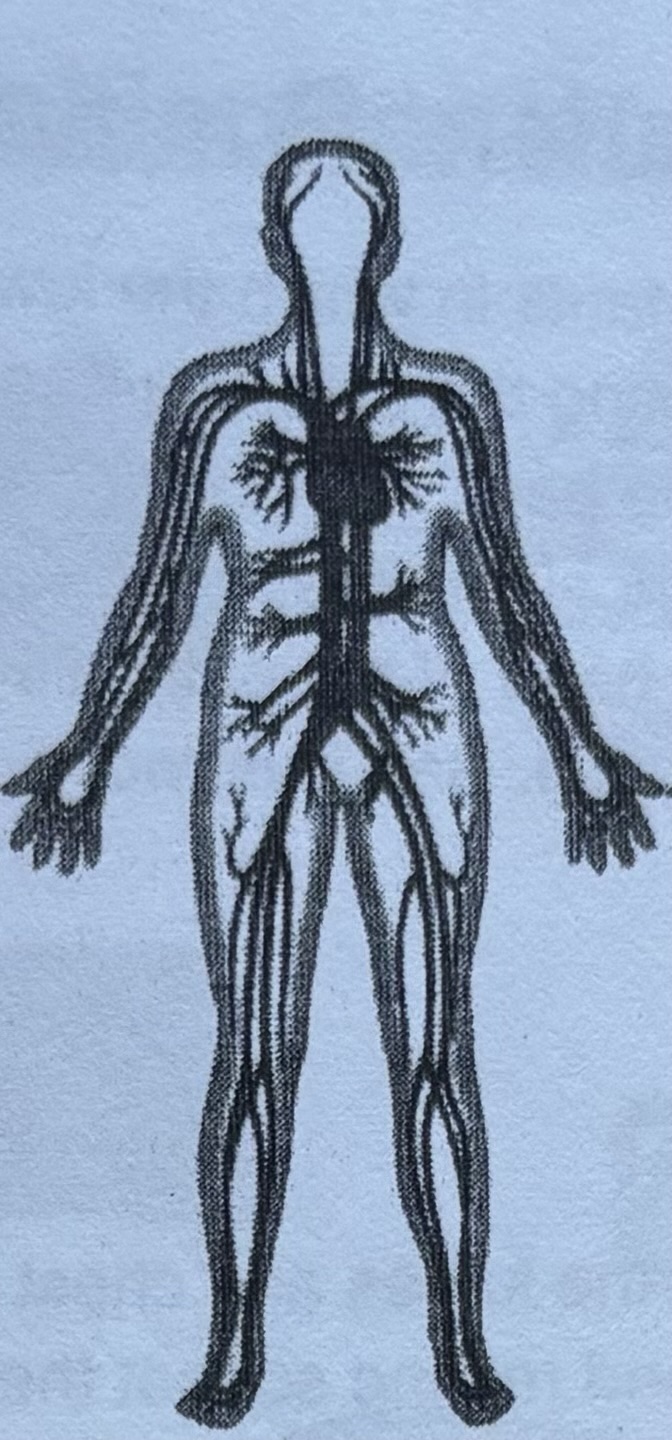
Circulatory system
This system consists of the heart and a network of vessels that carry blood. It supplies oxygen and nutrients to the body’s cells and removes waste products
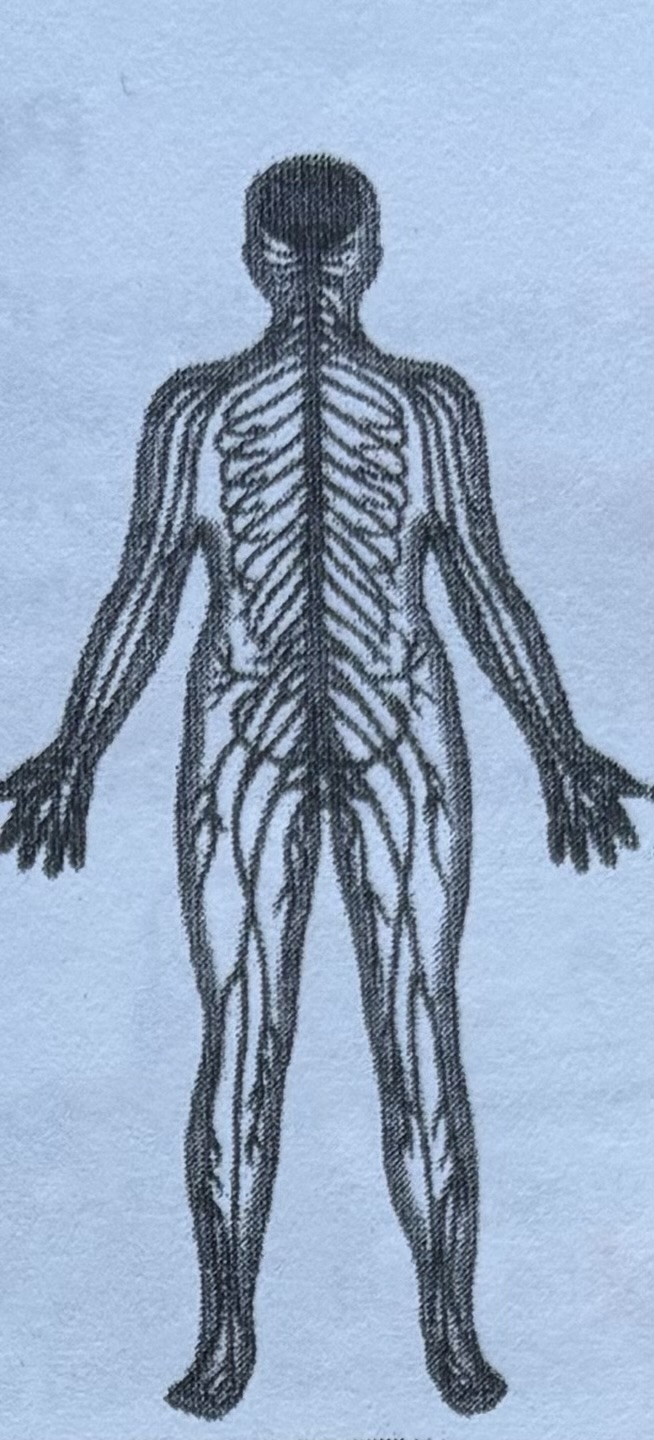
Nervous system
Is the body’s main control system it consists of the brain, the spinal cord, and a network of nerves that extend out to the rest of the body
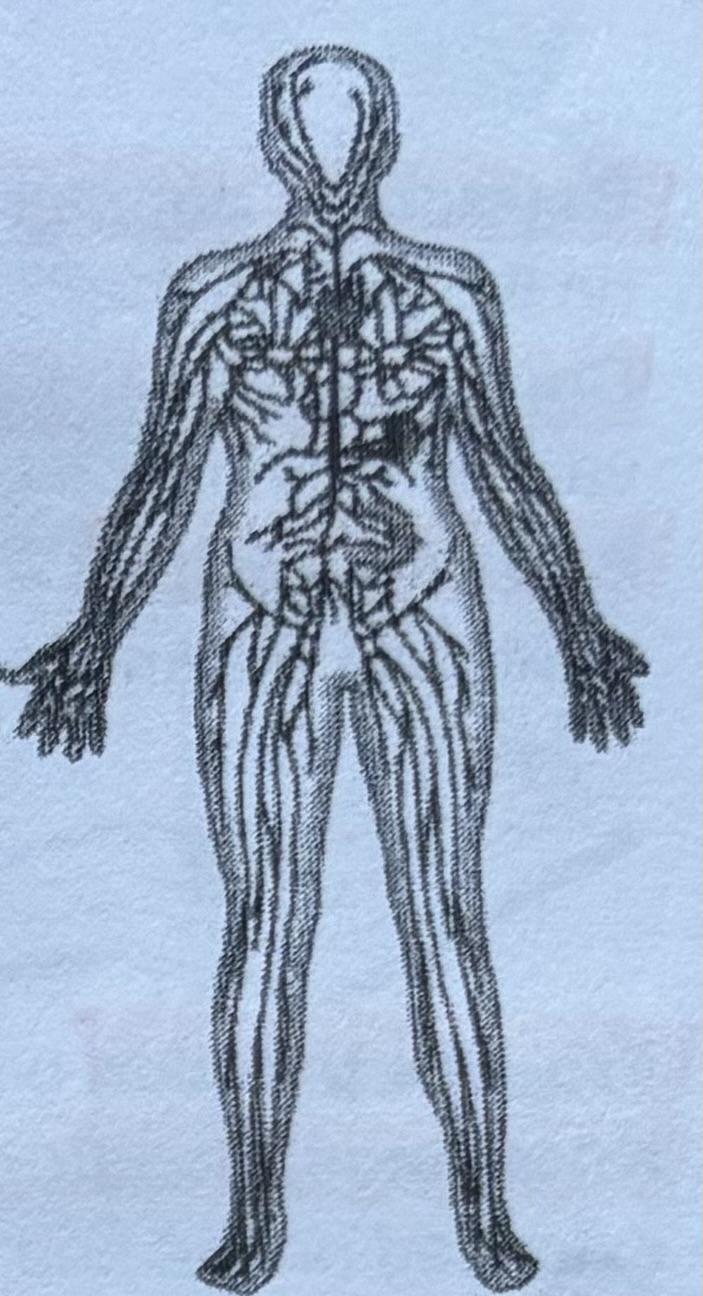
Lymphatic (immune) system
This system is a network of vessels that collects fluid from tissues and returns it to the blood. It also contains groups of cells that protect the body against infection.
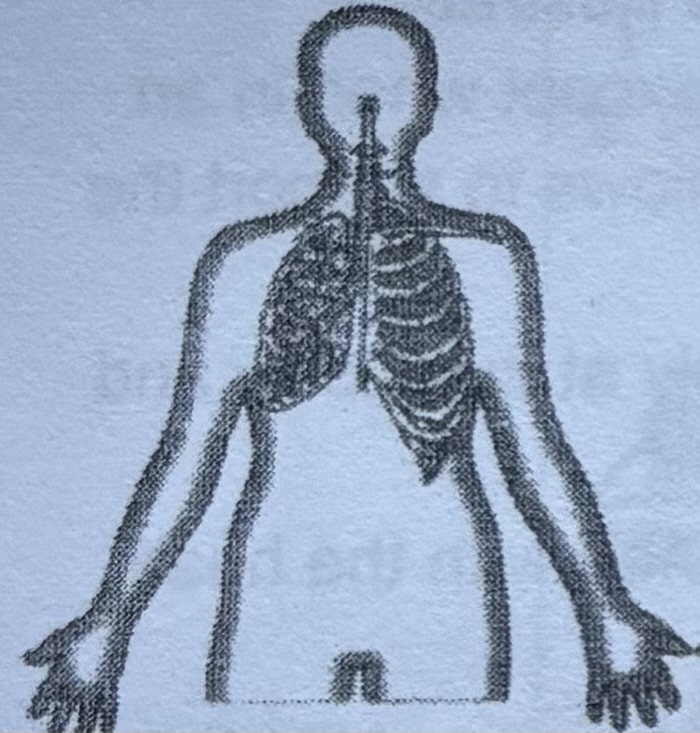
Respiratory system
The respiratory system is centered on the lungs, which work to get life-giving oxygen into the blood. They also rid the body of a waste product, carbon dioxide
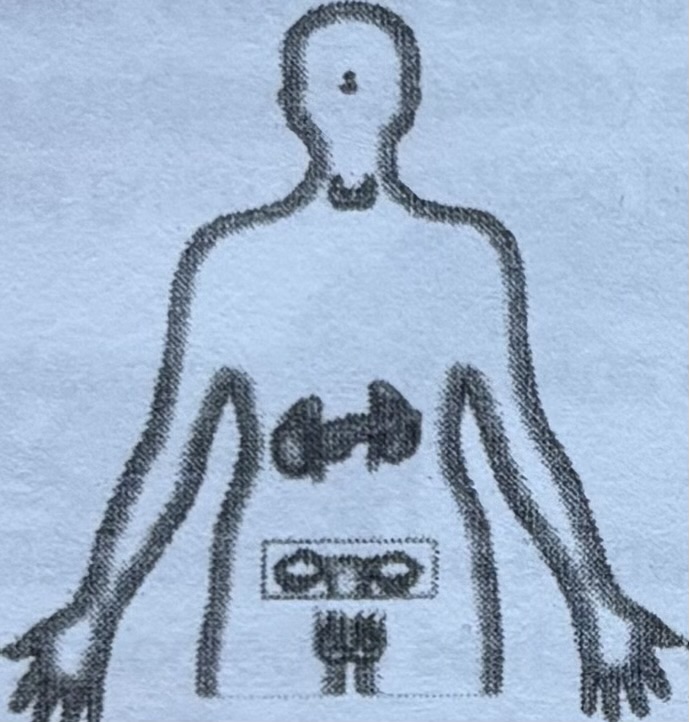
Endocrine system
Many body processes, such as growth and energy production, are directed by hormones. These chemicals are released by the glands of the endocrine system.
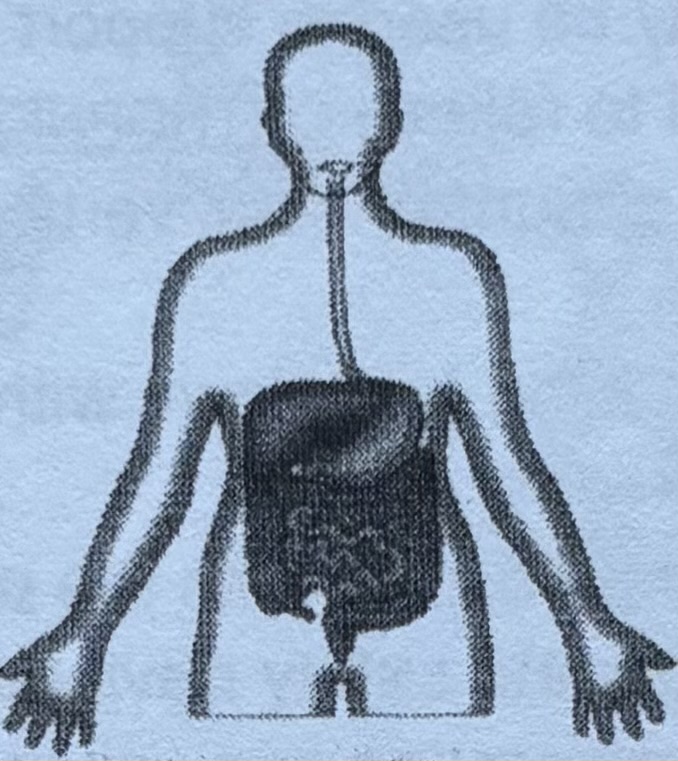
Digestive systems
The digestive system takes in the food the body needs to fuel its activities. it breaks the food down into units called nutrients and absorbs the nutrients into the blood.
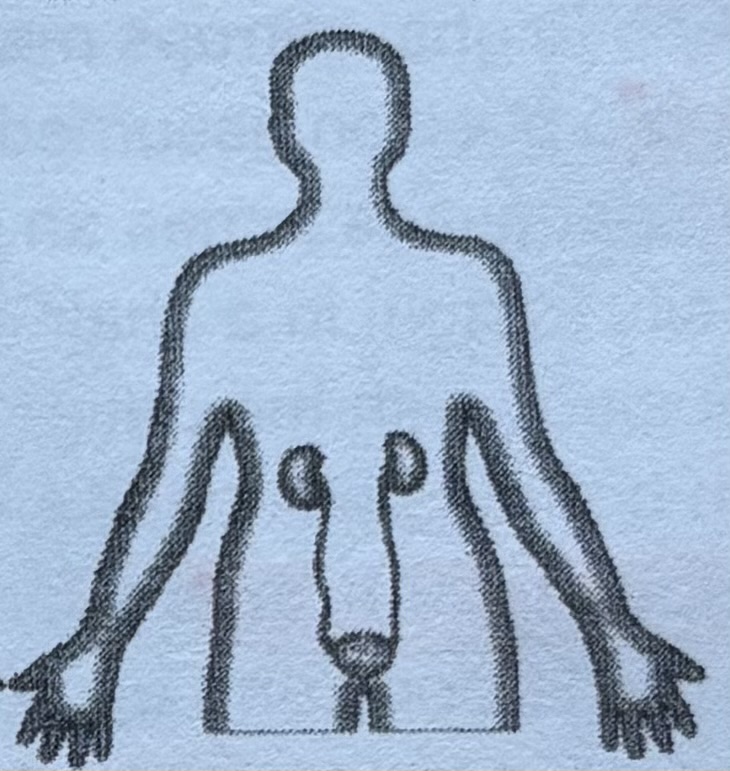
Excretory system
The body's cells produce waste products. many of which are eliminated in urine. The job of the urinary system is to make urine and expel it from the body.
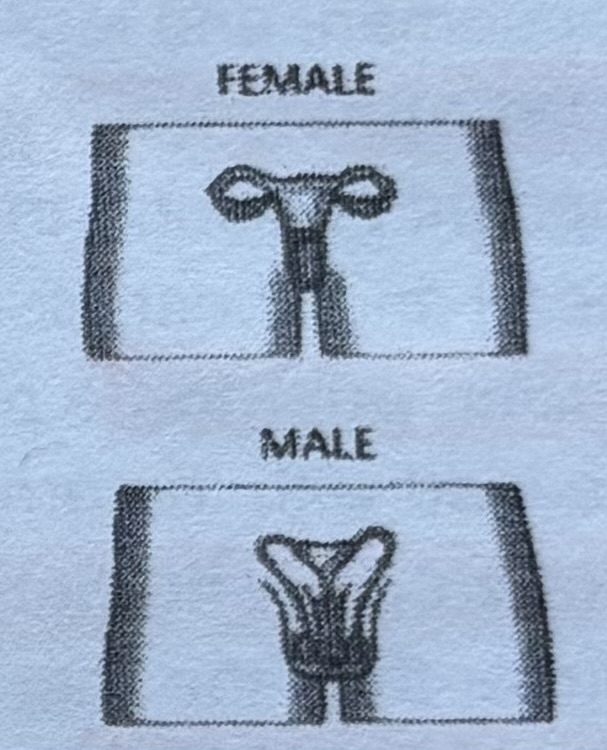
Reproductive system
The male and female parts of the reproductive system produce the sperm and eggs needed to create a new person. They also bring these tiny cells together.
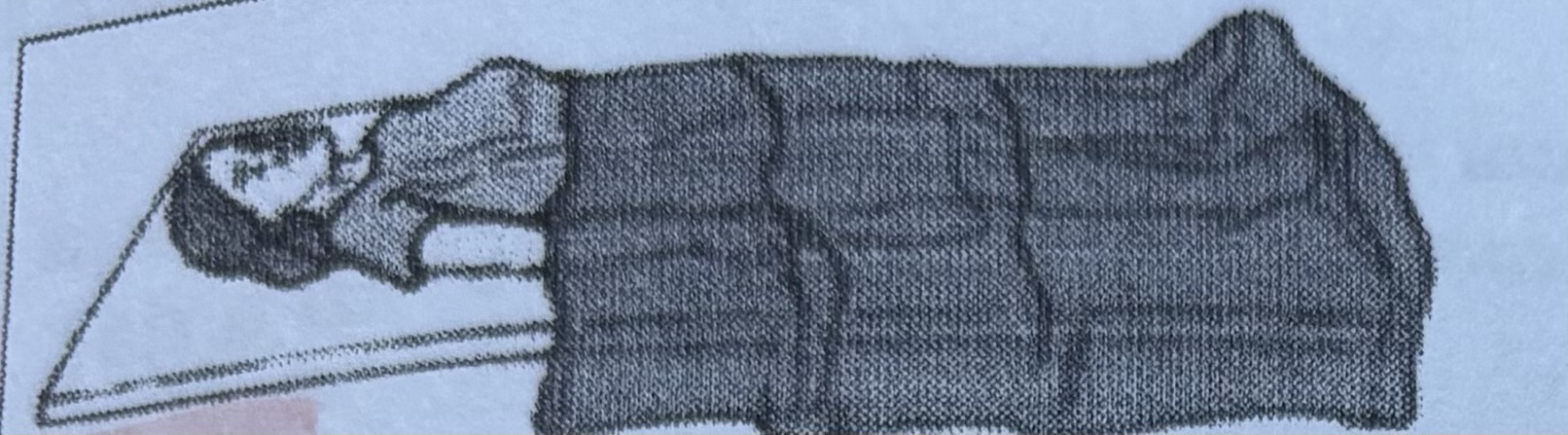

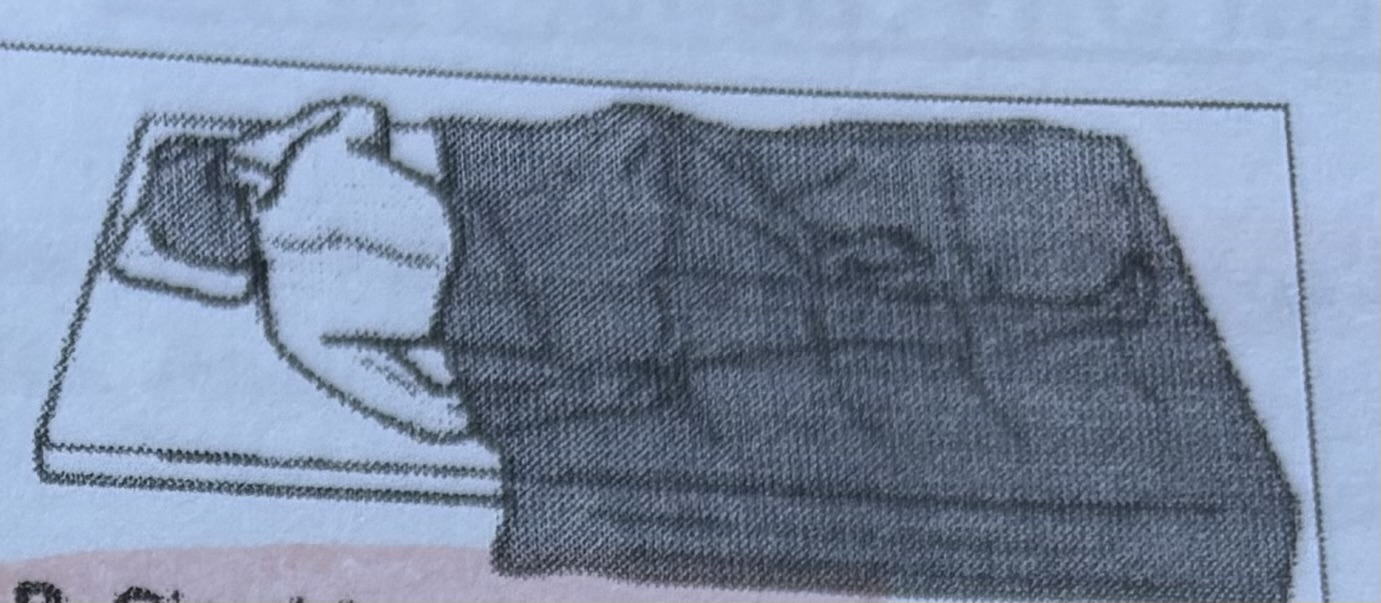
Supine
Sims’ (posterior view)
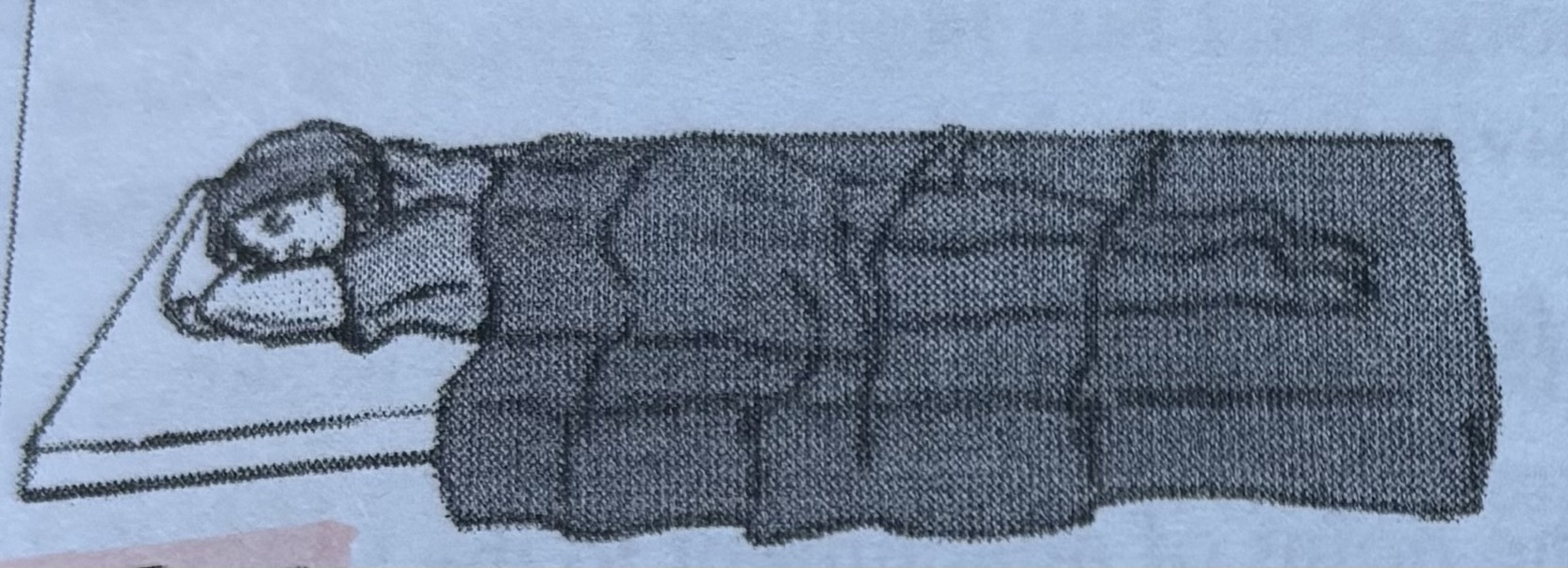
Prone
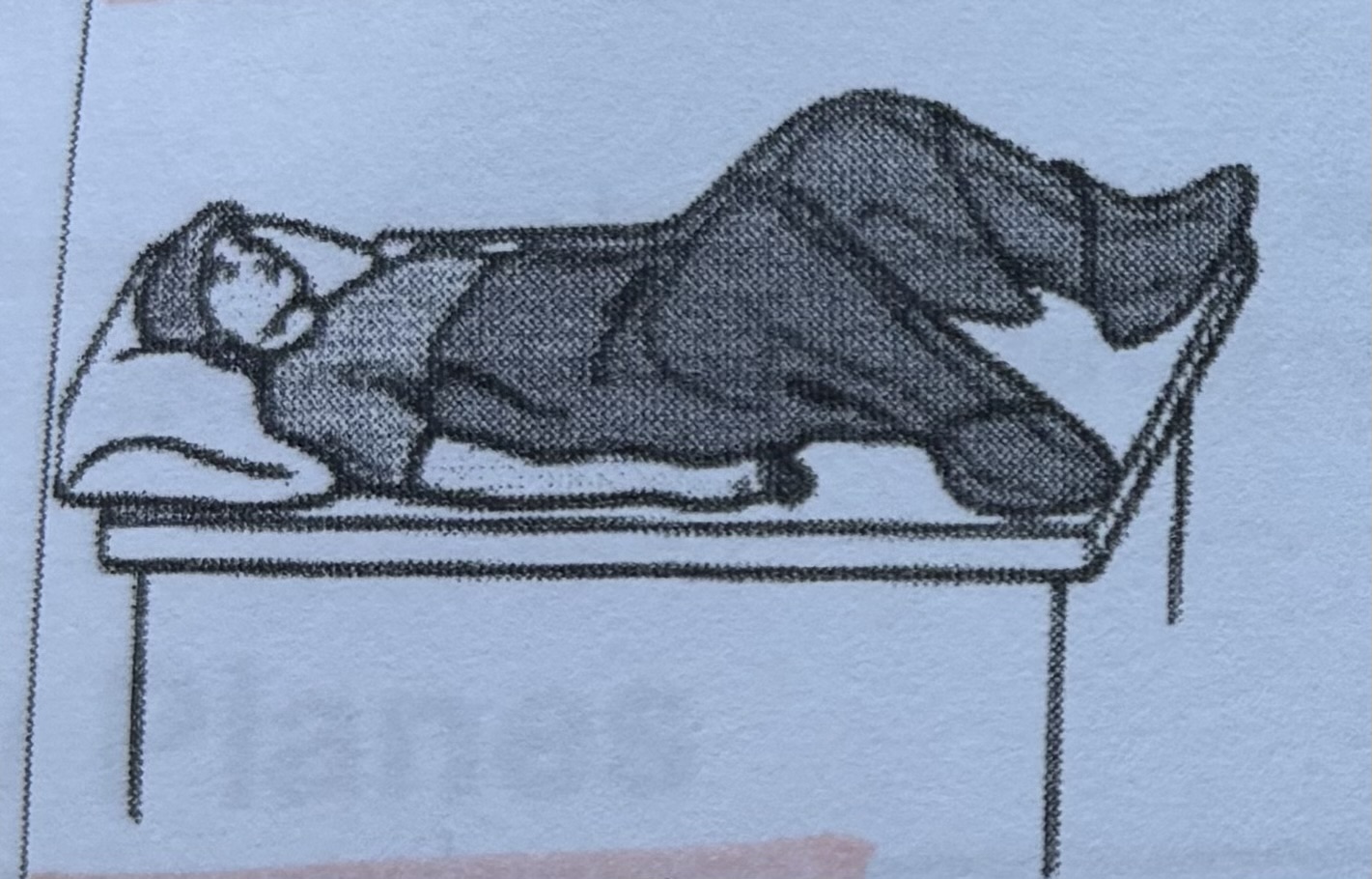
Dorsal recumbent
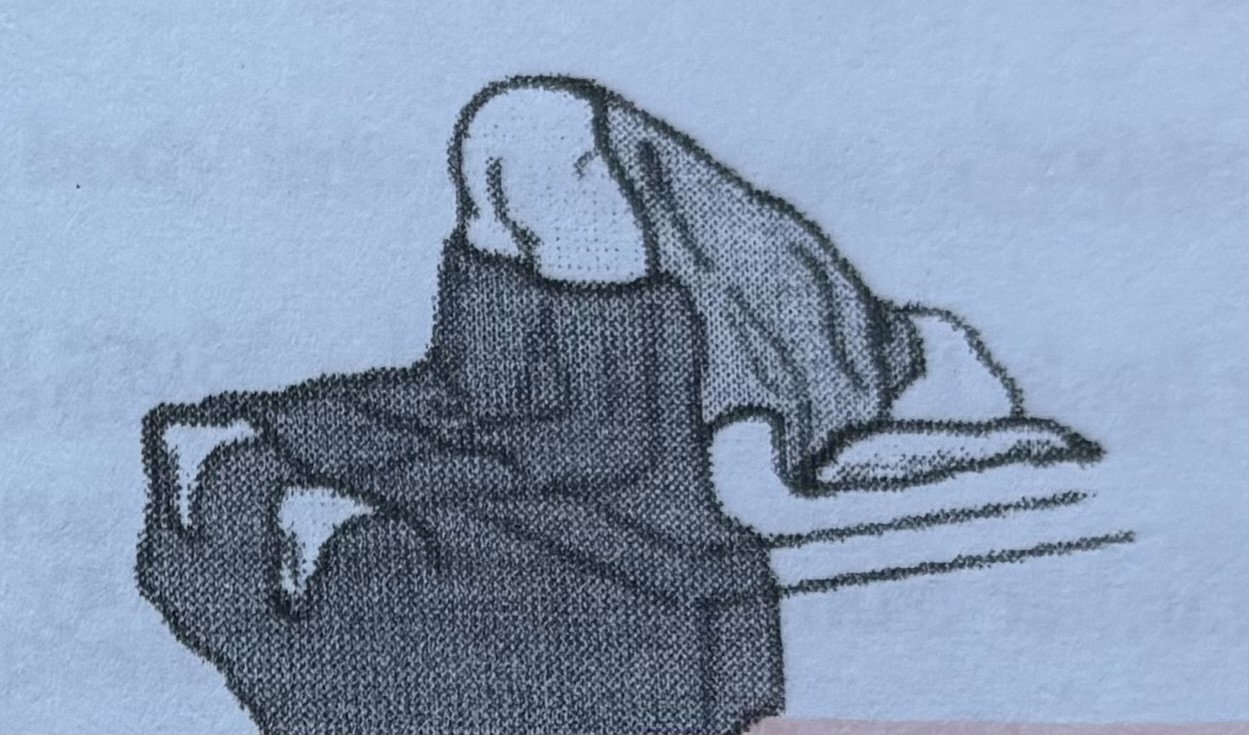
Knee-chest
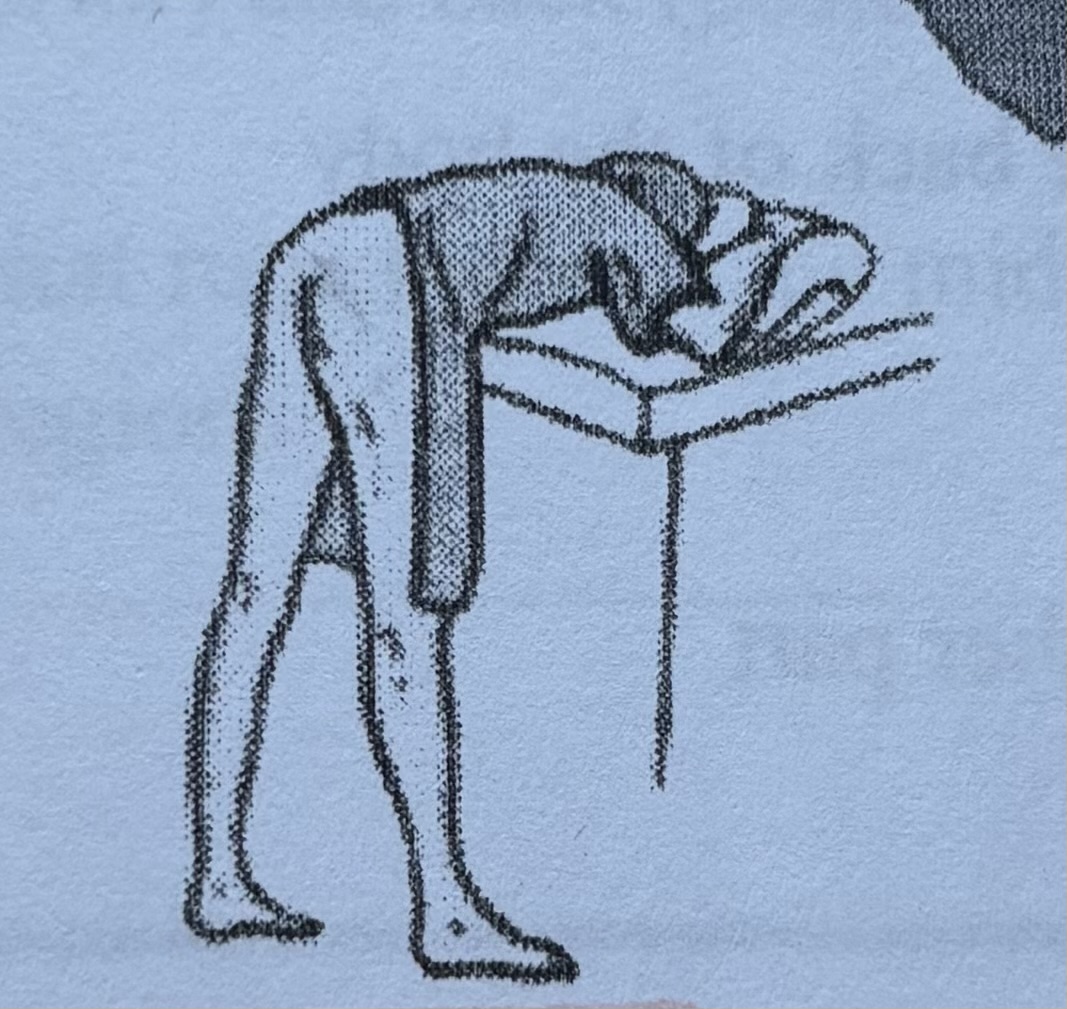
Standing
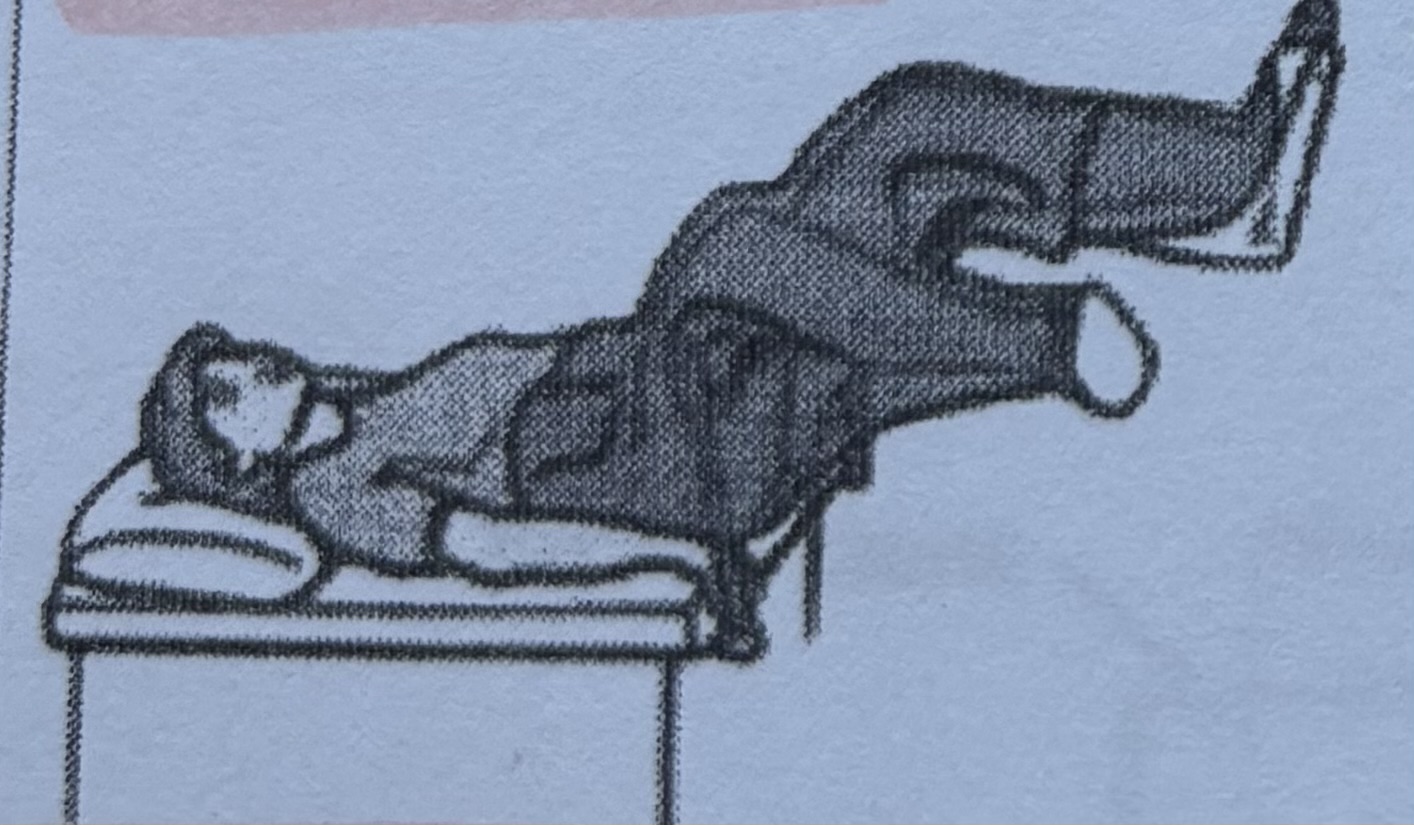
Lithotomy
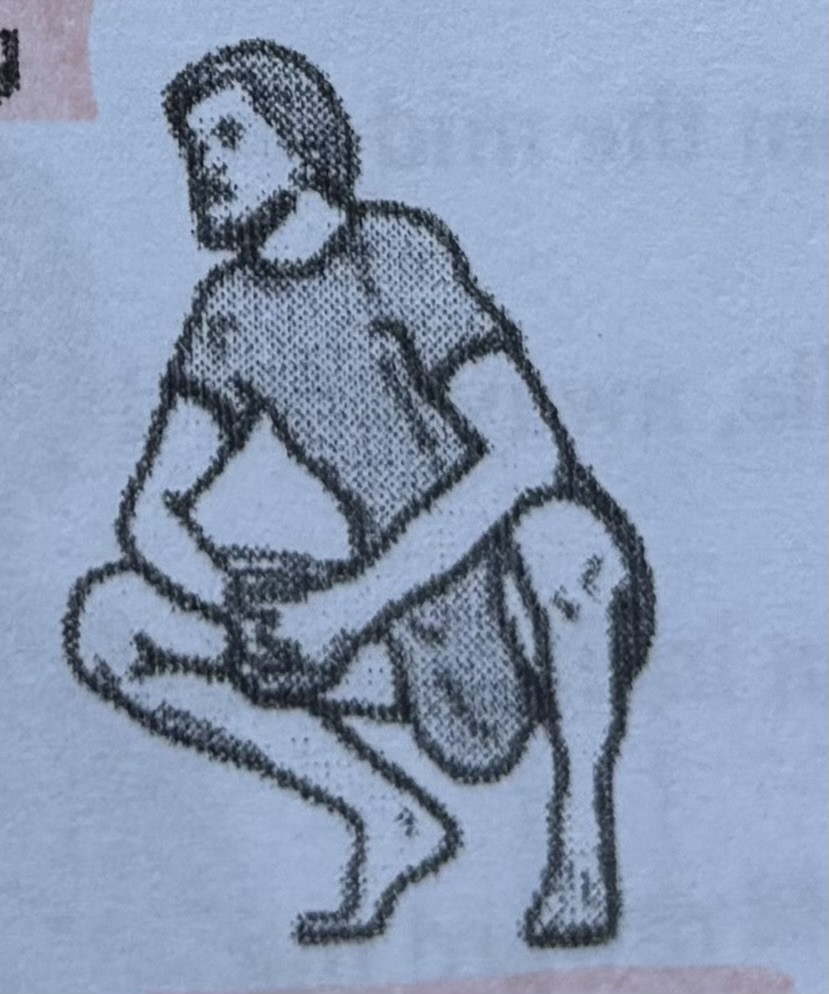
Squatting
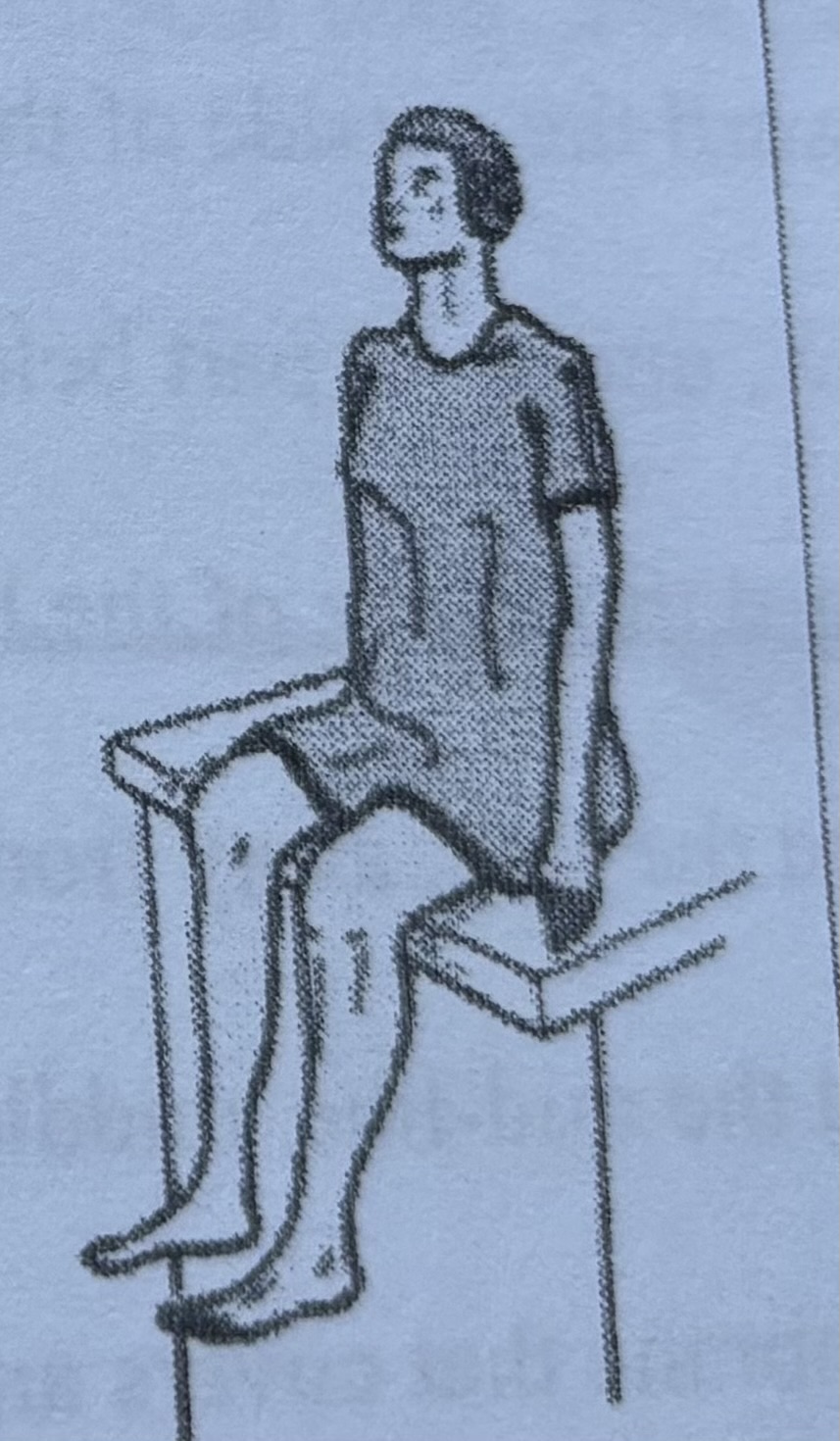
Sitting
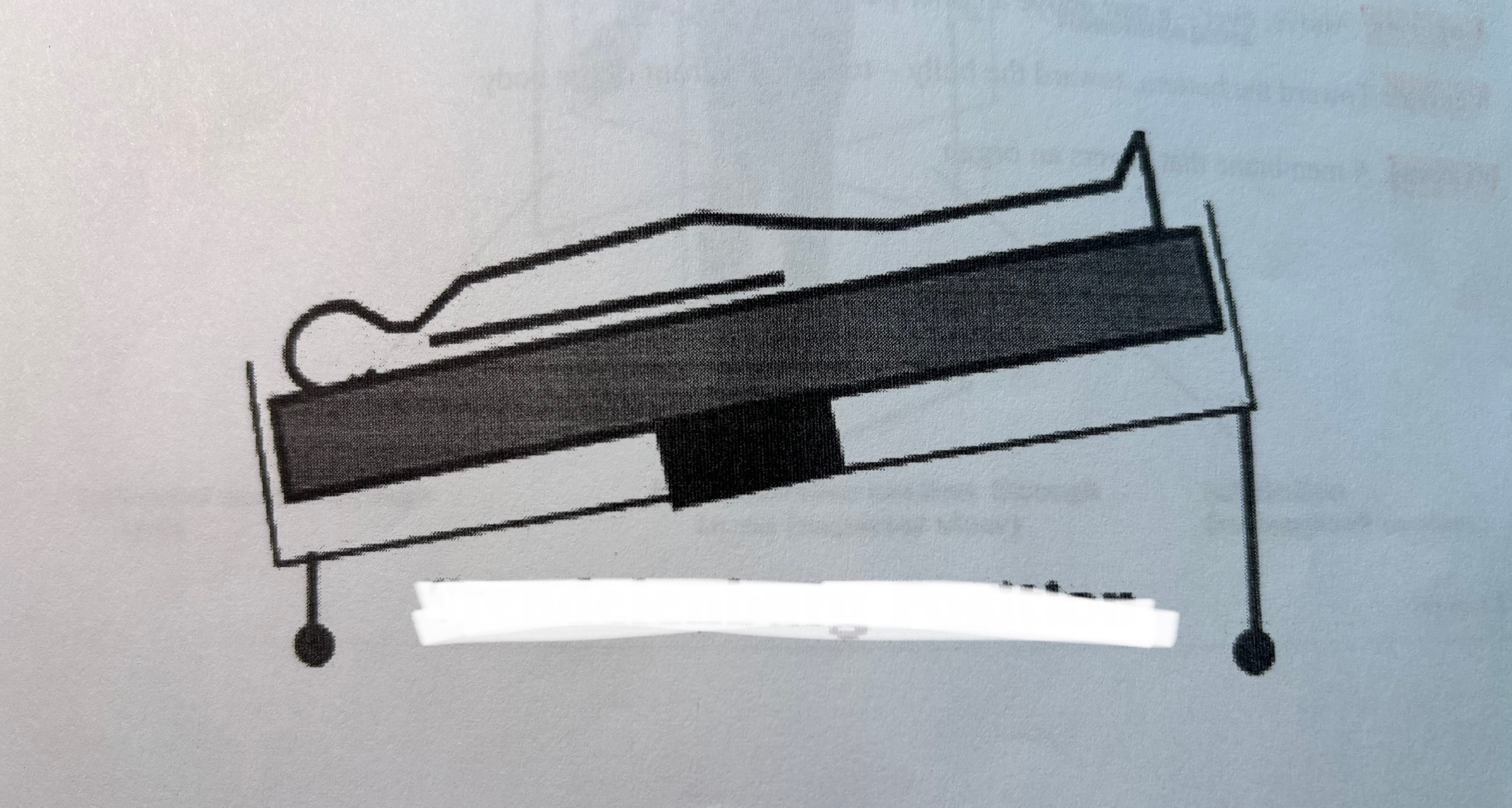
Trendelenburg position
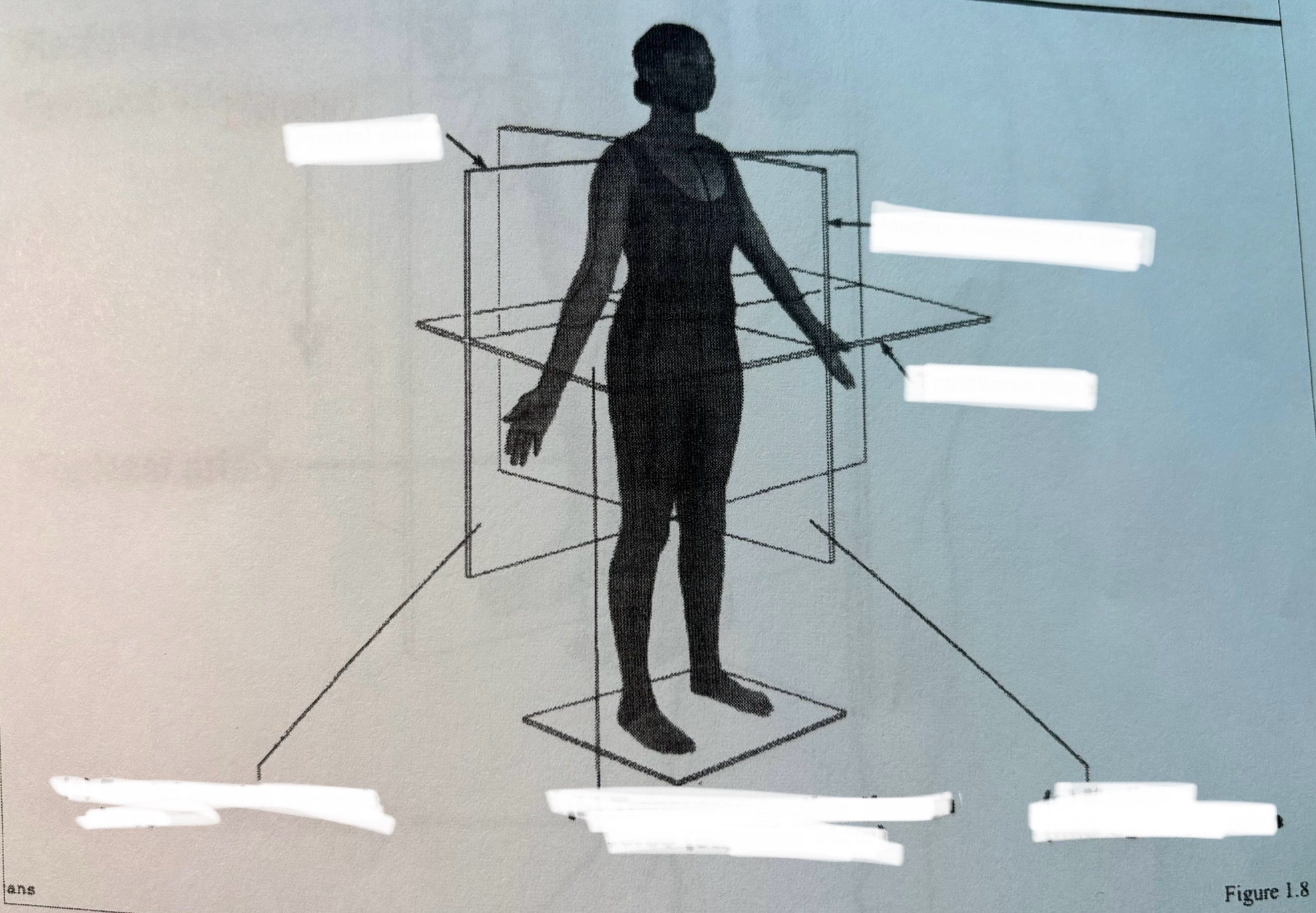
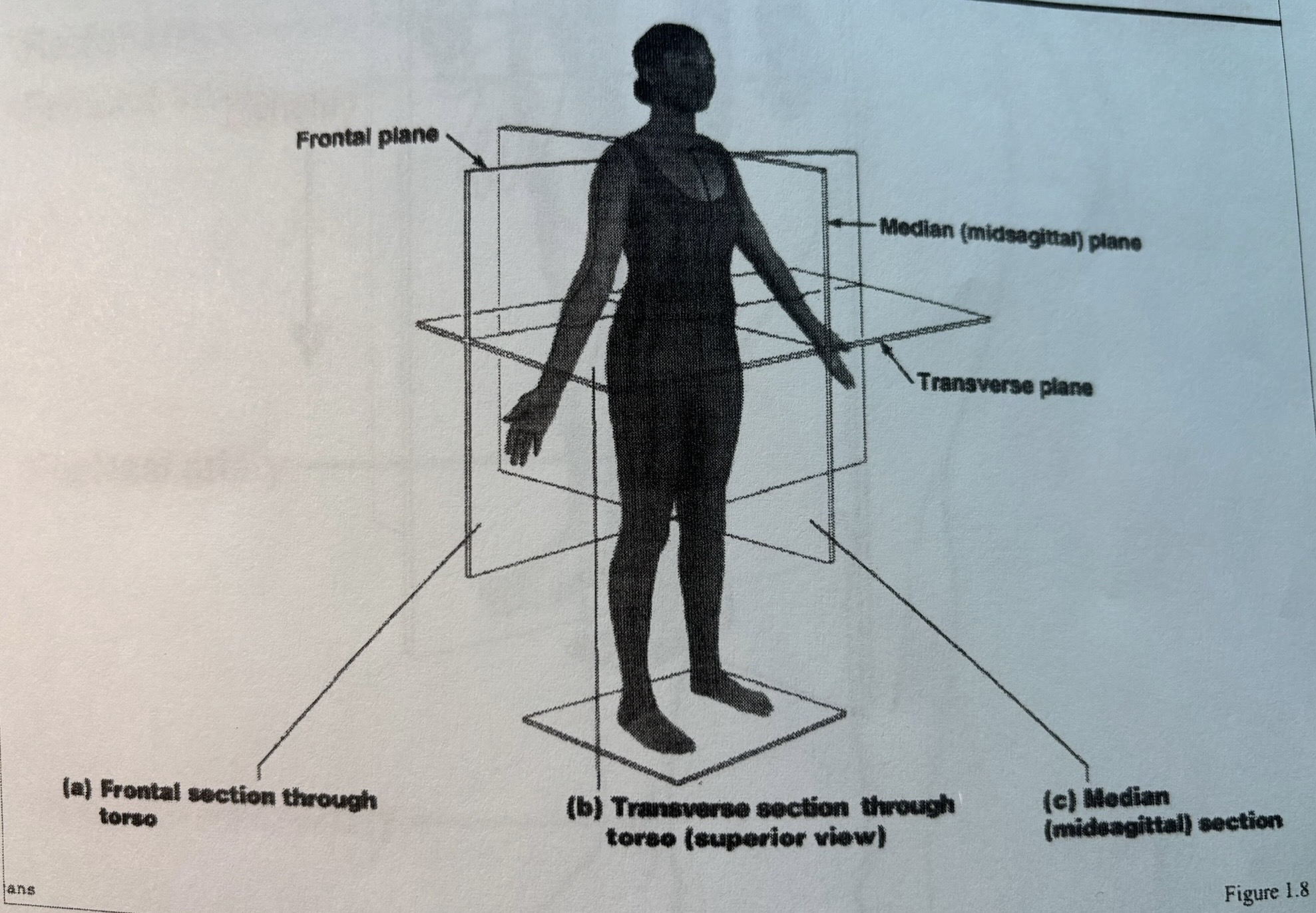
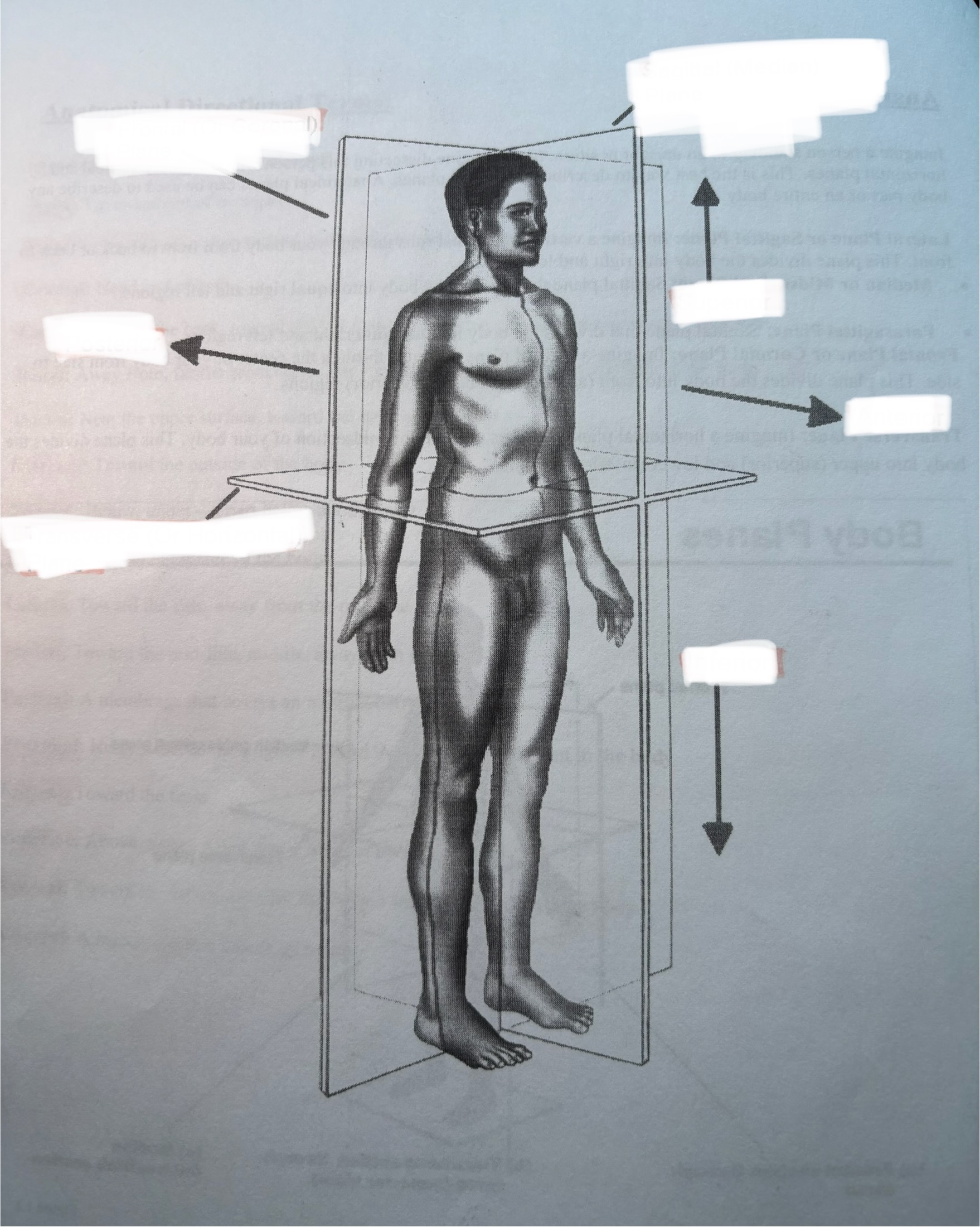
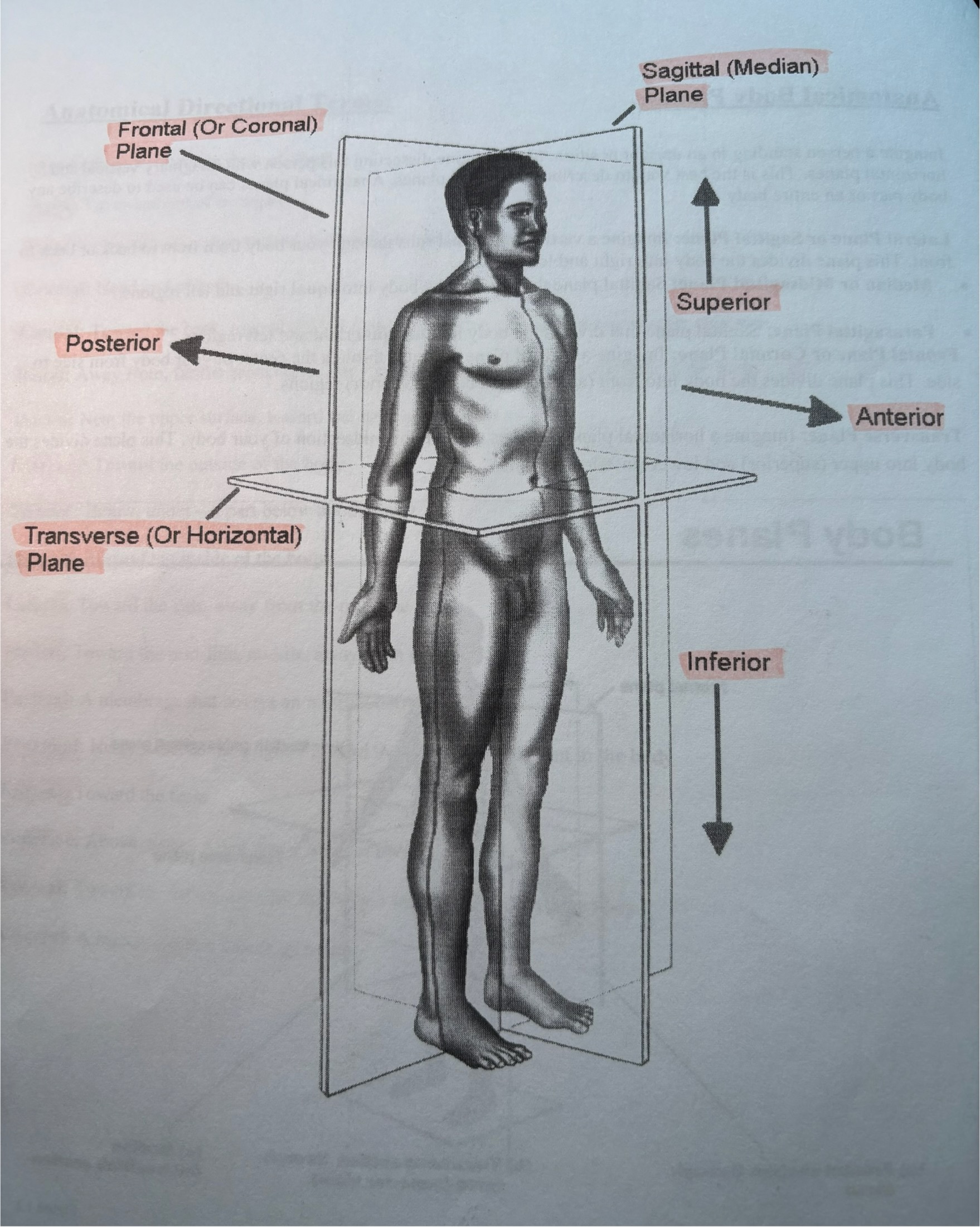
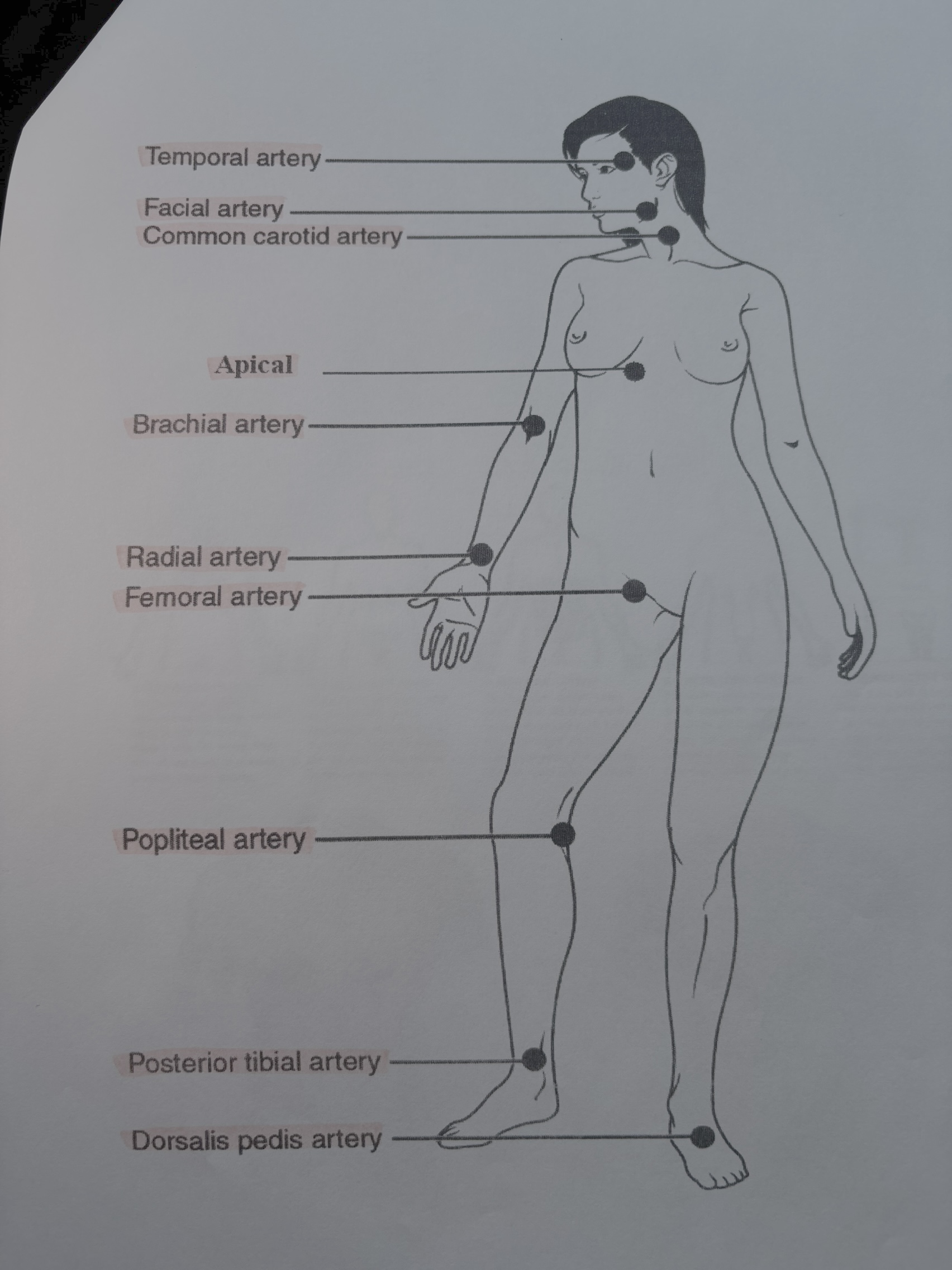
Anterior or Ventral:
In front of, front
Apex:
Tip or summit of an organ
Posterior or Dorsal:
After, behind, following, toward the rear
Cranial:
Head end of body
Caudal:
Toward the back, toward the tail - More toward feet or tail; below another structure
Distal:
Away from, farther from the origin - away from the point of attachment to the body
Dorsal:
Near the upper surface, toward the back of the body
External:
Toward the outside of the body
Inferior:
Below, under — a part below another part
Internal:
Toward the inside of the body
Lateral:
Toward the side, away from the mid-line
Medial:
Toward the mid-line, middle, away from the side
Parietal:
A membrane that covers an internal body wall
Proximal:
Near, closer to the origin - toward the point of attachment to the body
Rostral:
Toward the front
Superior:
Above, over - a part above another part
Ventral:
Toward the bottom, toward the belly - toward the front of the body
Visceral:
A membrane that covers an organ