Rutgers University Functional Human Anatomy Lecture 18: Axial Musculature Overview
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Axial Skeleton
- skull and associated bones
- thoracic cage
- vertebral column
axial musculature
-muscles that position the head and vertebral column
-muscles that move the rib cage
appendicular musculature
- muscles that stabilize or move the appendicular skeleton
muscles are innervated by
nerves
4 groups of axial muscles
- Muscles of the head and neck
- Muscles of the vertebral column
- Oblique and rectus muscles
- Muscles of the pelvic floor
muscles of head and neck
muscles of:
- facial expression
- extra-ocular
- mastication
- tongue
- pharynx
- anterior neck
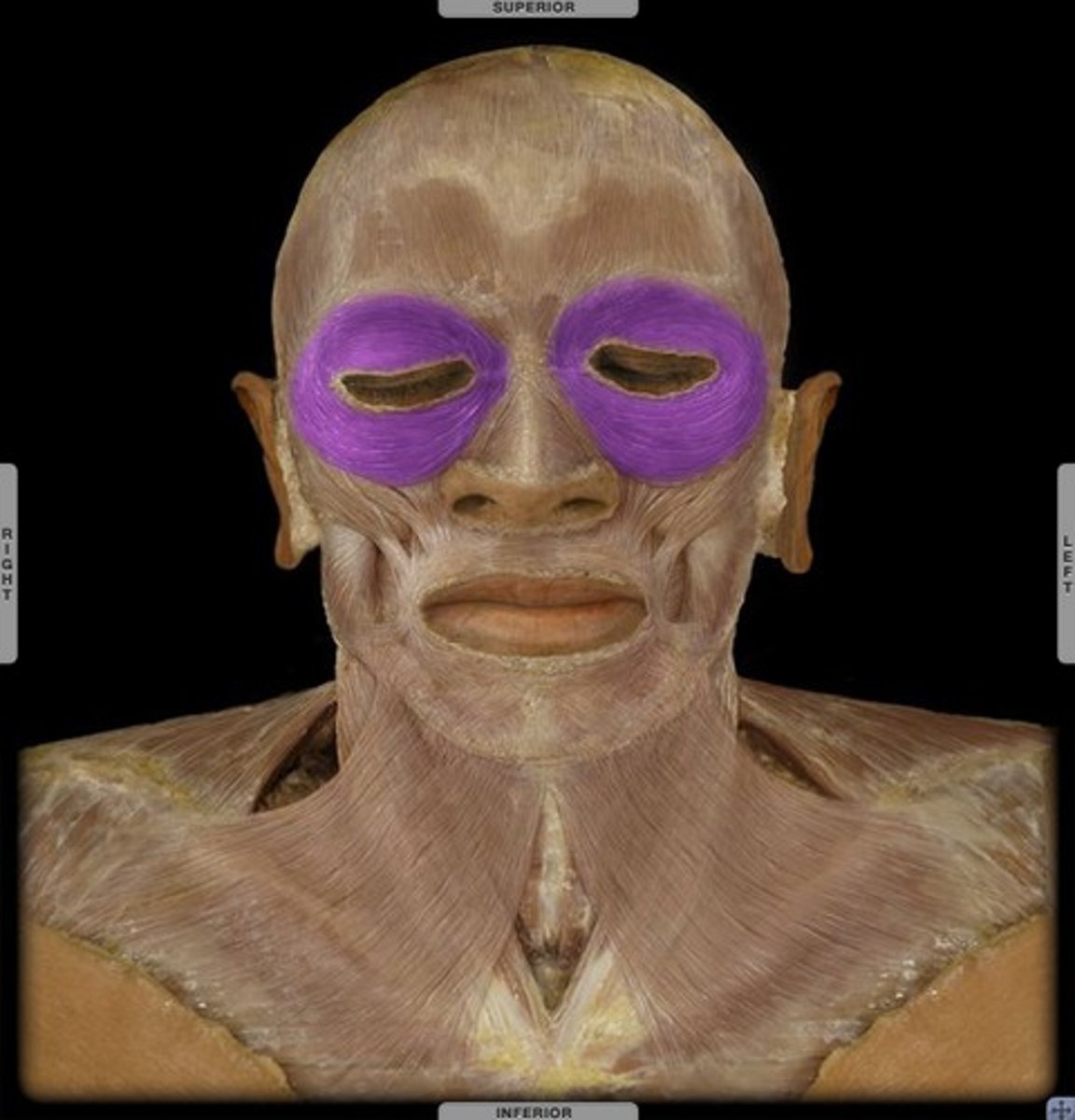
obicularis oculi (facial expression)
- close eyes
- aids flow of tears
- facial nerve
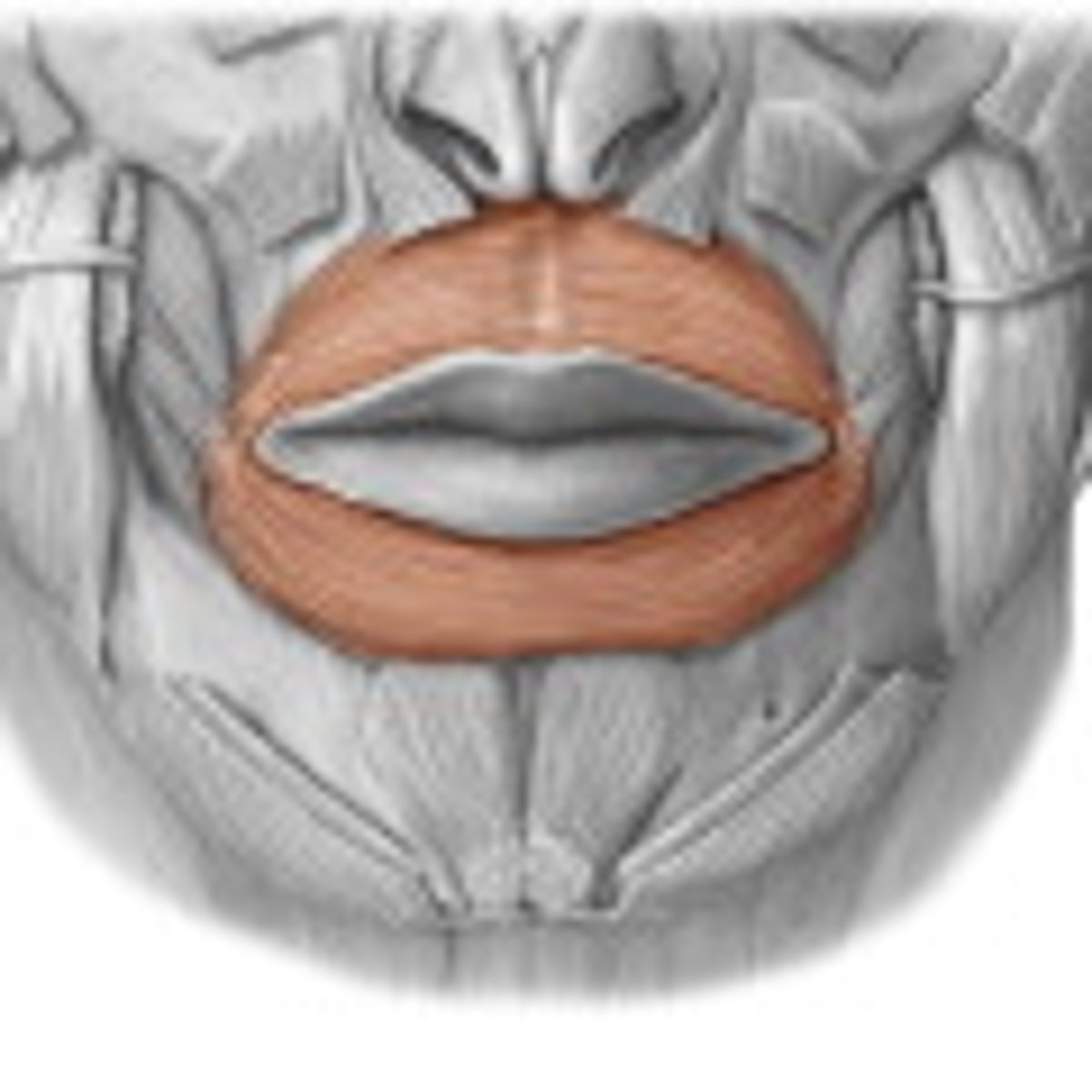
obicularis oris (facial expression)
- mucus membrane at margin of the lips
- pucker lips
- innervated by facial nerve
close mouth
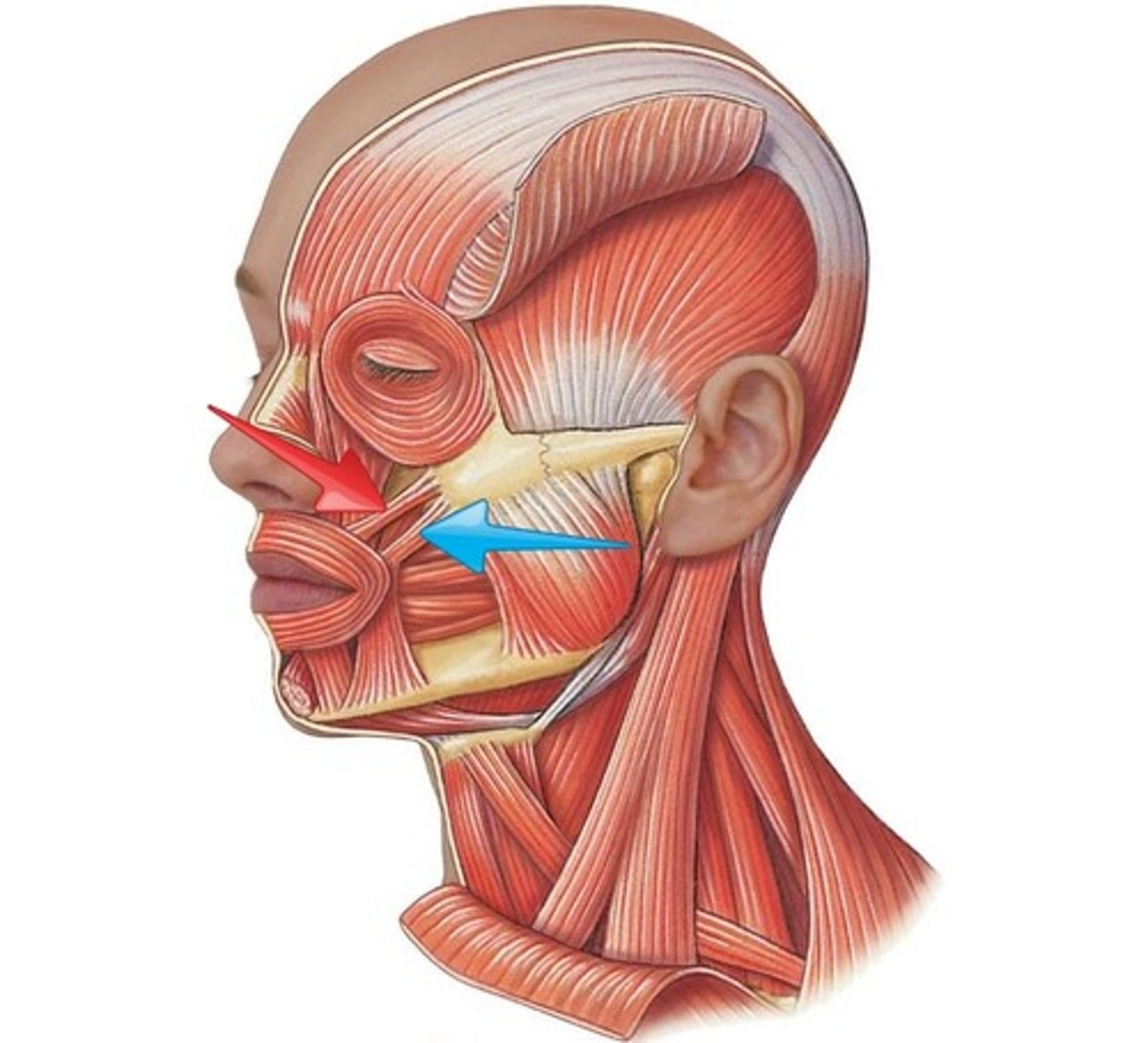
Zygomaticus major and minor (facial expression)
- skin & muscles of upper lips (minor)
- angle of mouth (major)
- elevate mouth
- lateral pull of mouth
SMILE
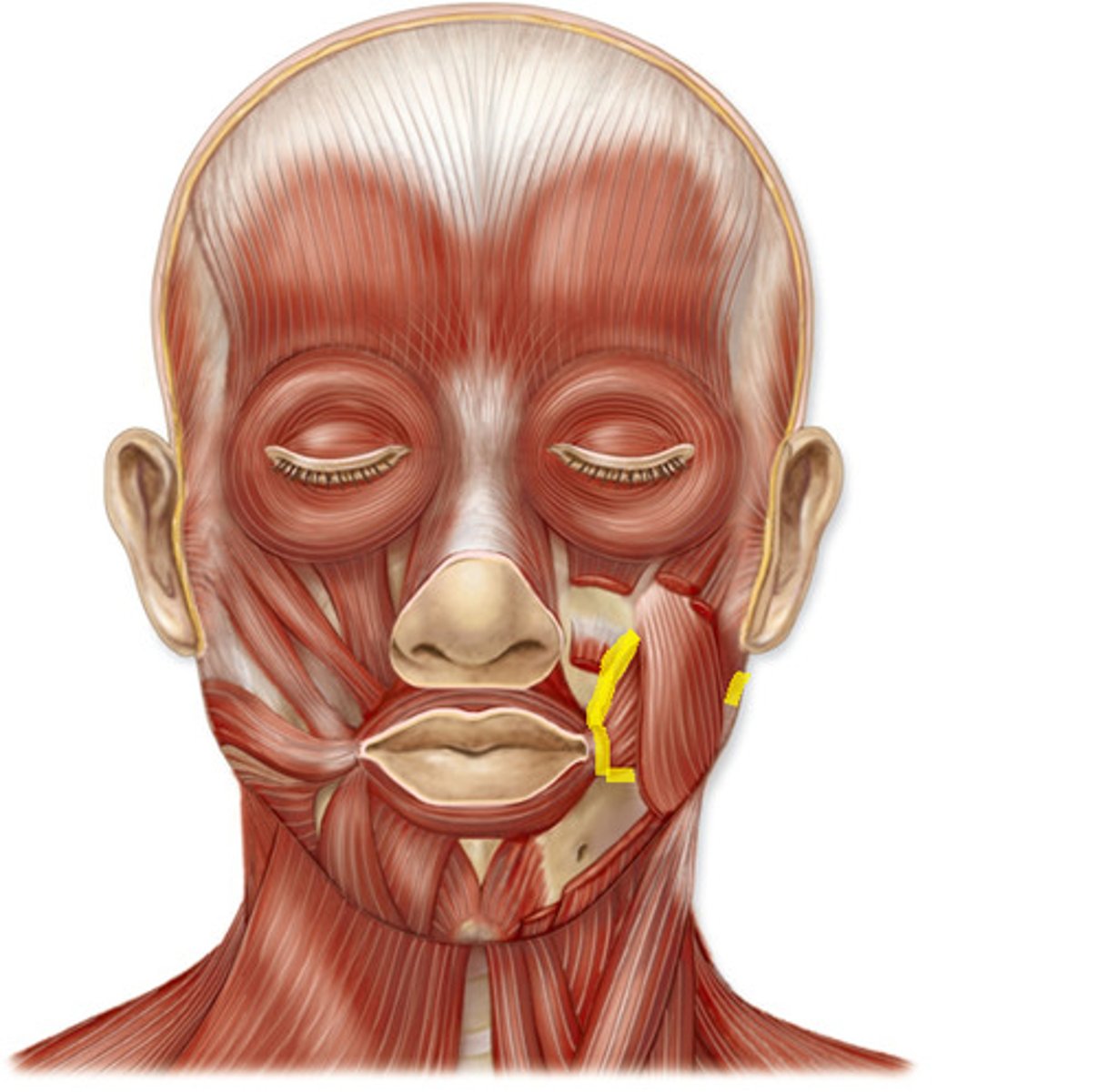
Buccinator (facial expression)
- pull mouth laterally & tightening cheeks
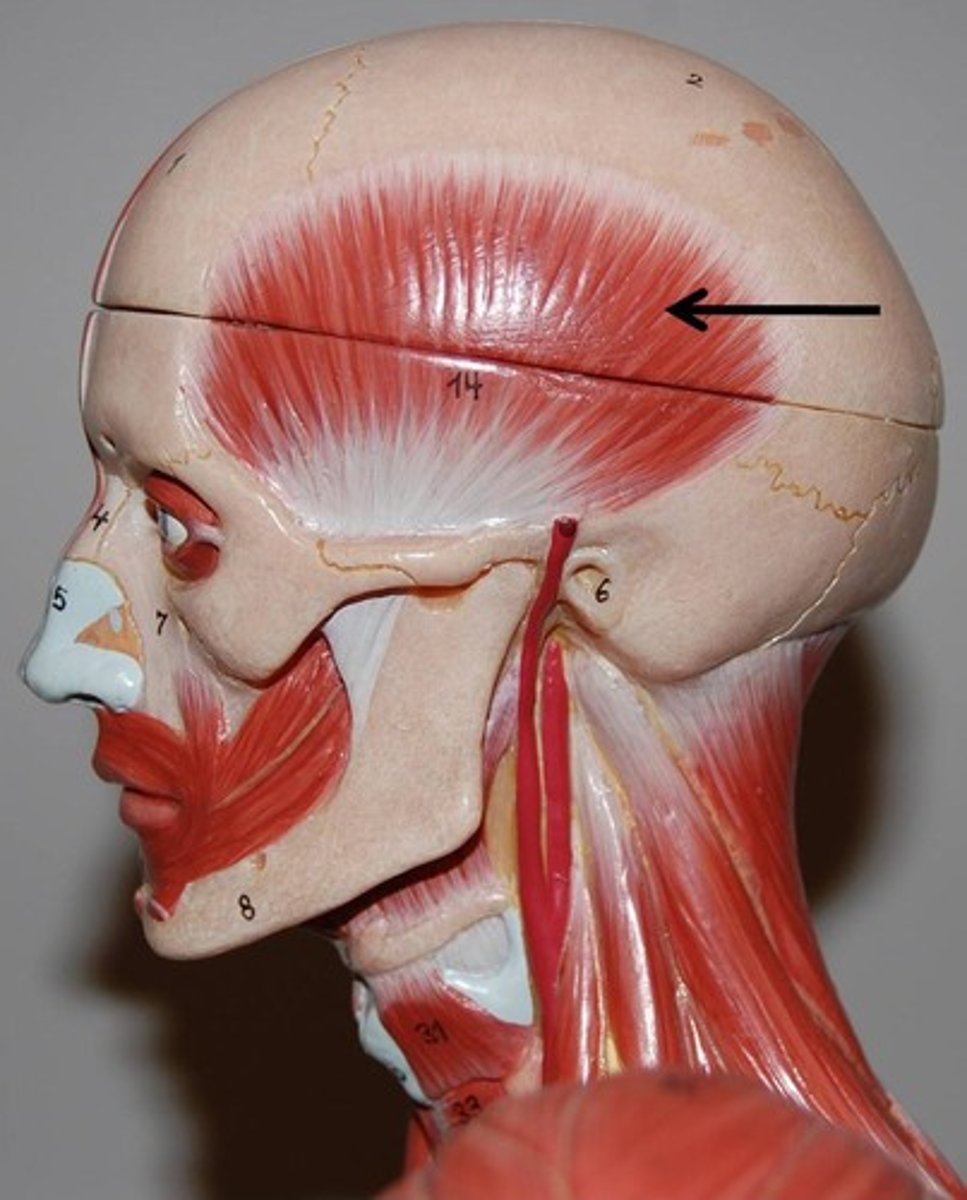
occipitofrontalis
- attach to cranial aponeurosis
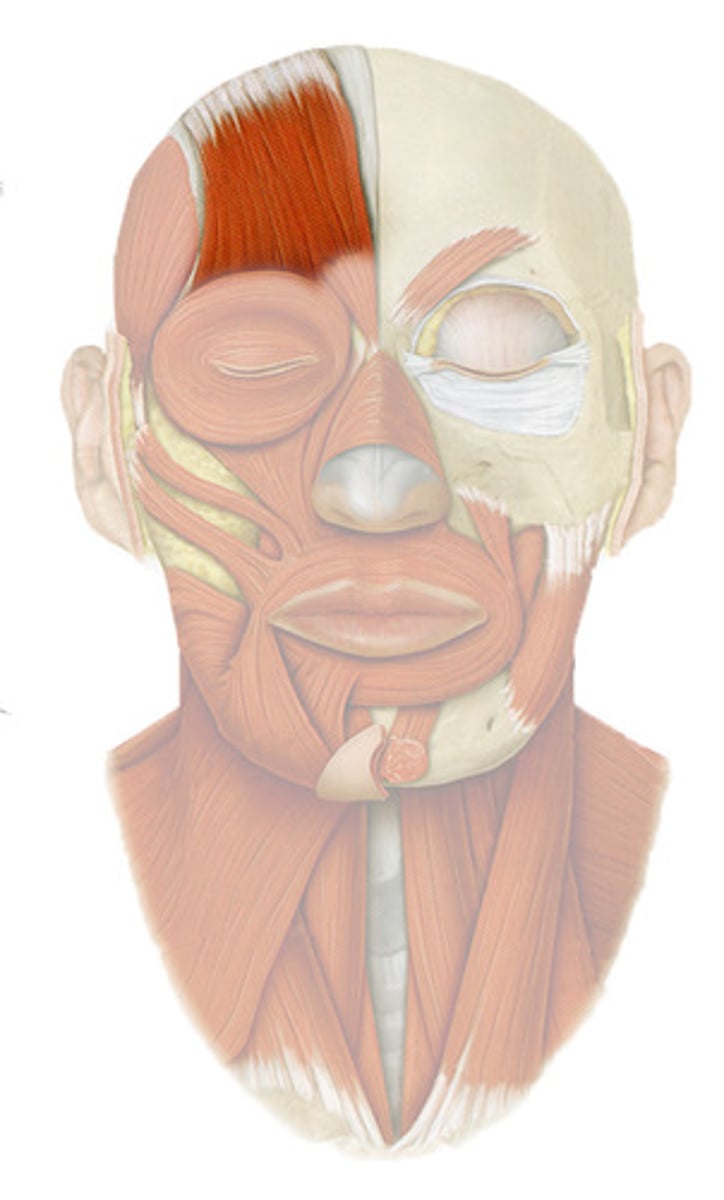
Temporoparietalis
-fascia around external ear
-epicranial aponeurosis
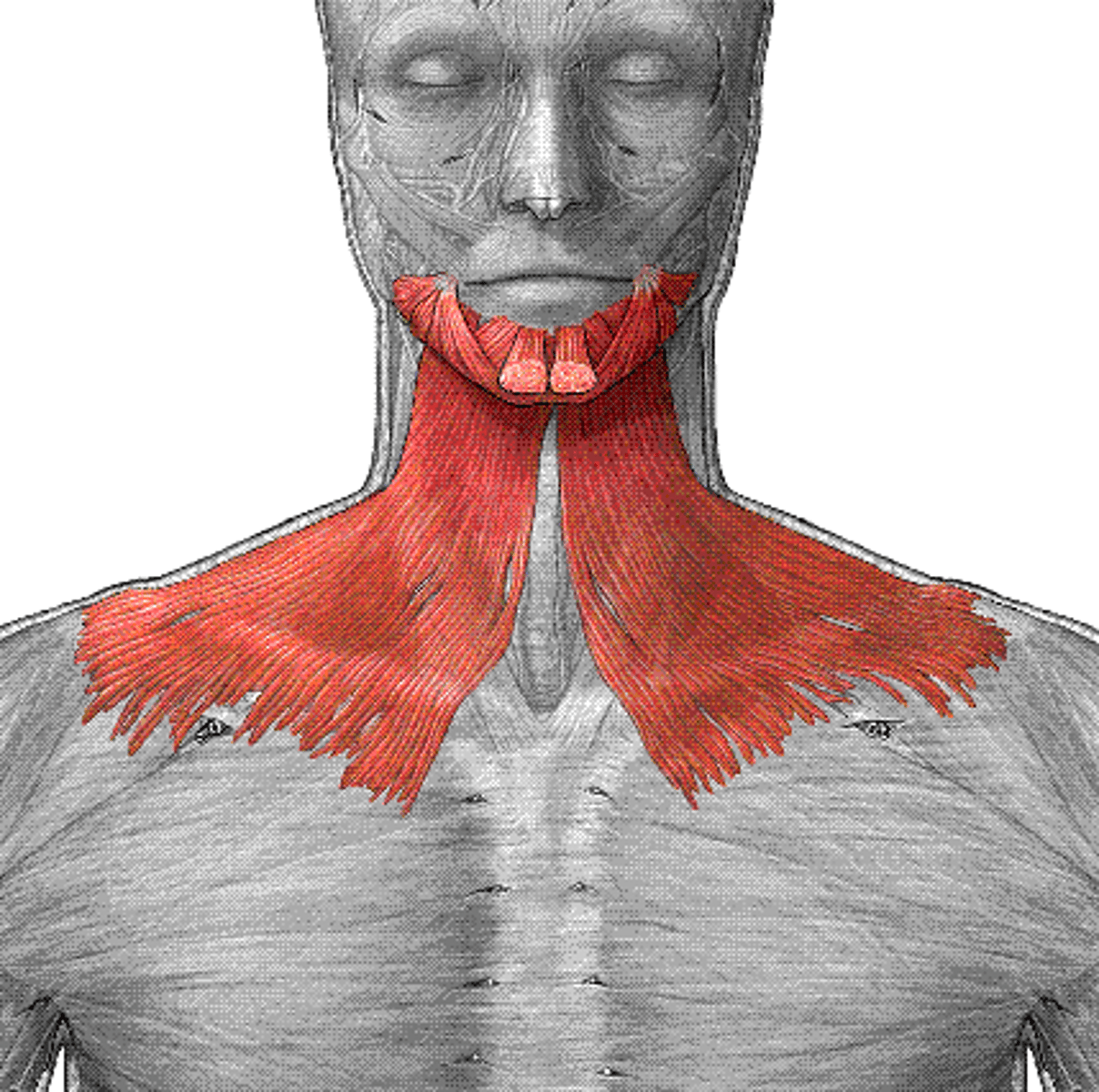
platysma
- originate near clavicle region
medial/lateral rectus muscles (extra-ocular)
- draw gaze medial/laterally
- medial, nerve 3
- lateral, nerve 6
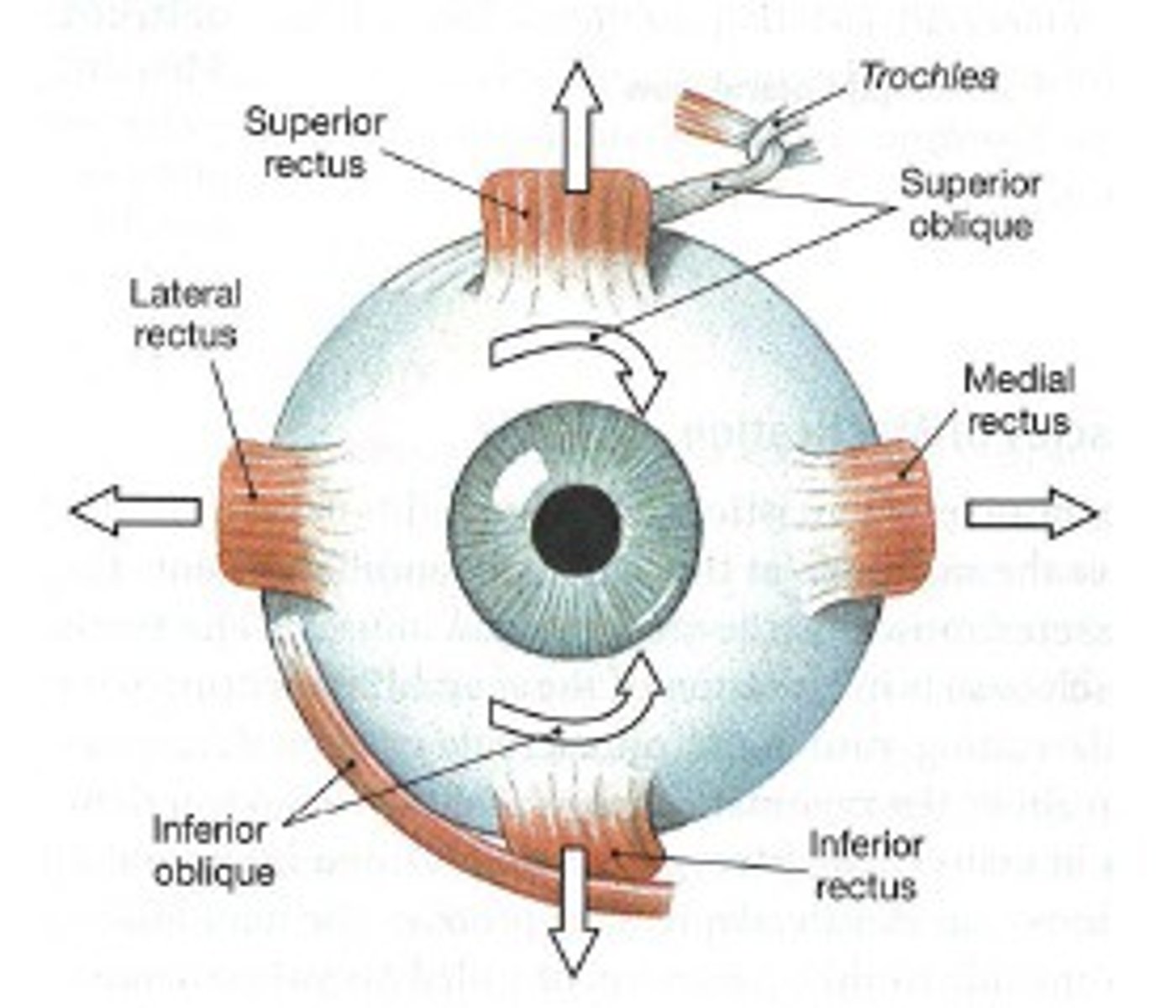
superior/inferior rectus (extra-ocular)
- draws gaze superior/inferior
- nerve 3
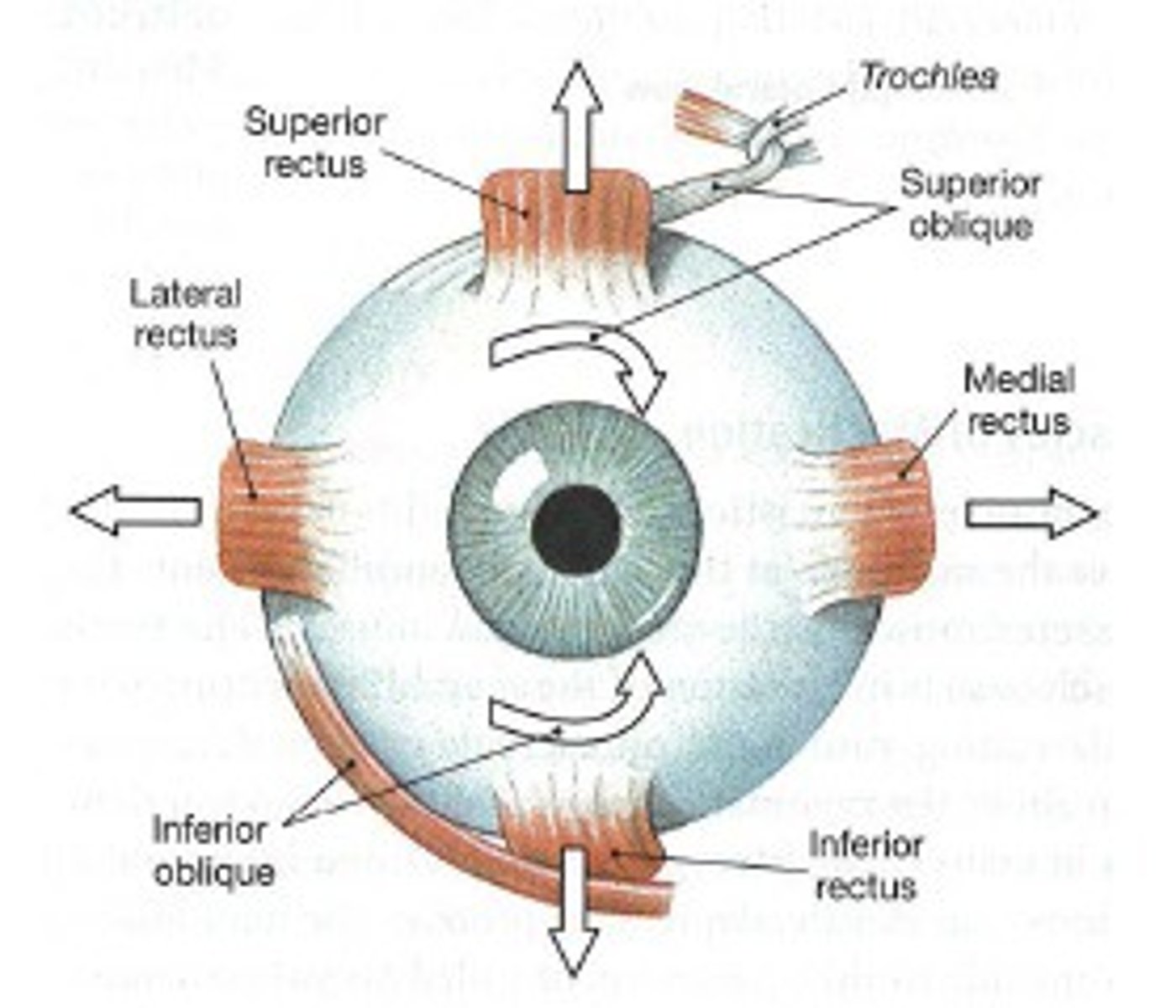
superior/inferior oblique (extra-ocular)
superior:
- draws gaze downward and laterally
- nerve 4
inferior:
- draws gaze upward and laterally
- nerve 3
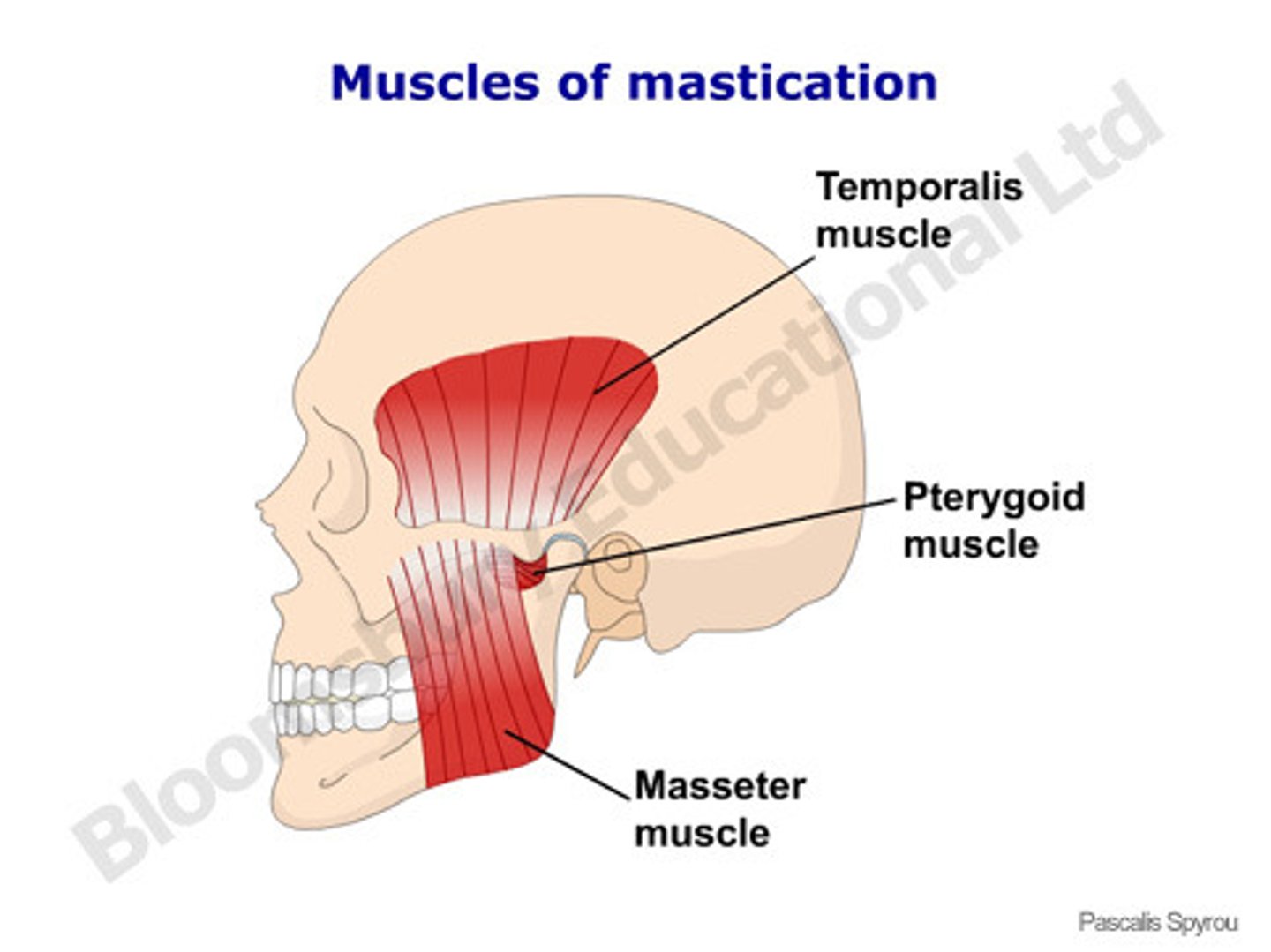
muscles of mastication
- innervated by CN 5
masseter:
- originate on zygomatic arch
- insert in mandible
- pull mandible
When contraction happens it will elevate mandible
temporalis:
- originate at temporal bone
- insert in coronoid process of mandible
- pull mandible
Temporalis and masseter are elevating the mandible. This brings the biting surfaces of the teeth close to each other to allow the crushing of food.
pterygoid:
- elevate and laterally move mandible
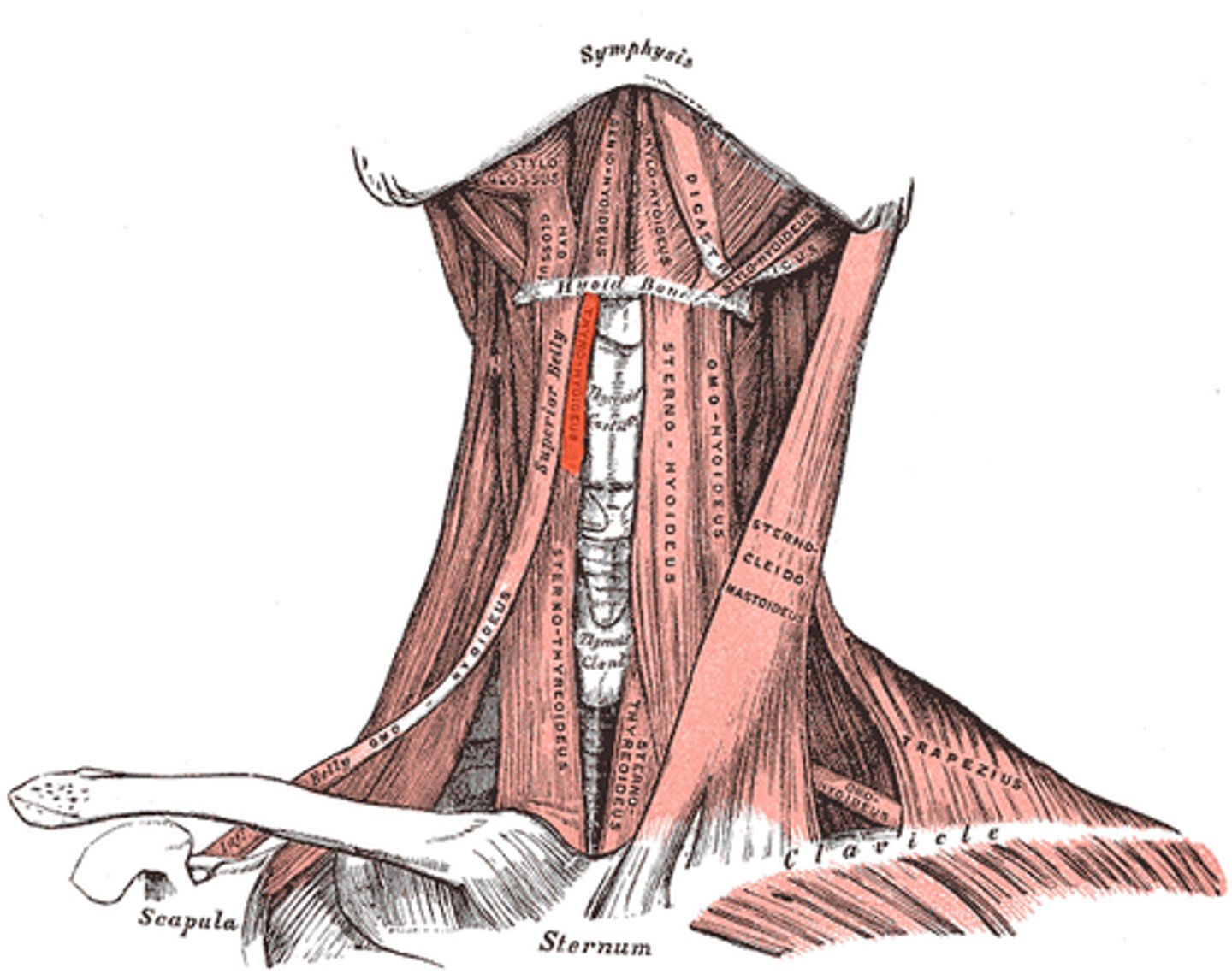
mylohyoid muscle (Anterior muscles of neck)
- forms floor of mouth
- from mandible to hyoid bone
- innervated by CN5
Geniohyoid (Anterior muscles of neck)
- from mandible to hyoid bone
- draws hyoid forward/depress jaw
- CN 12
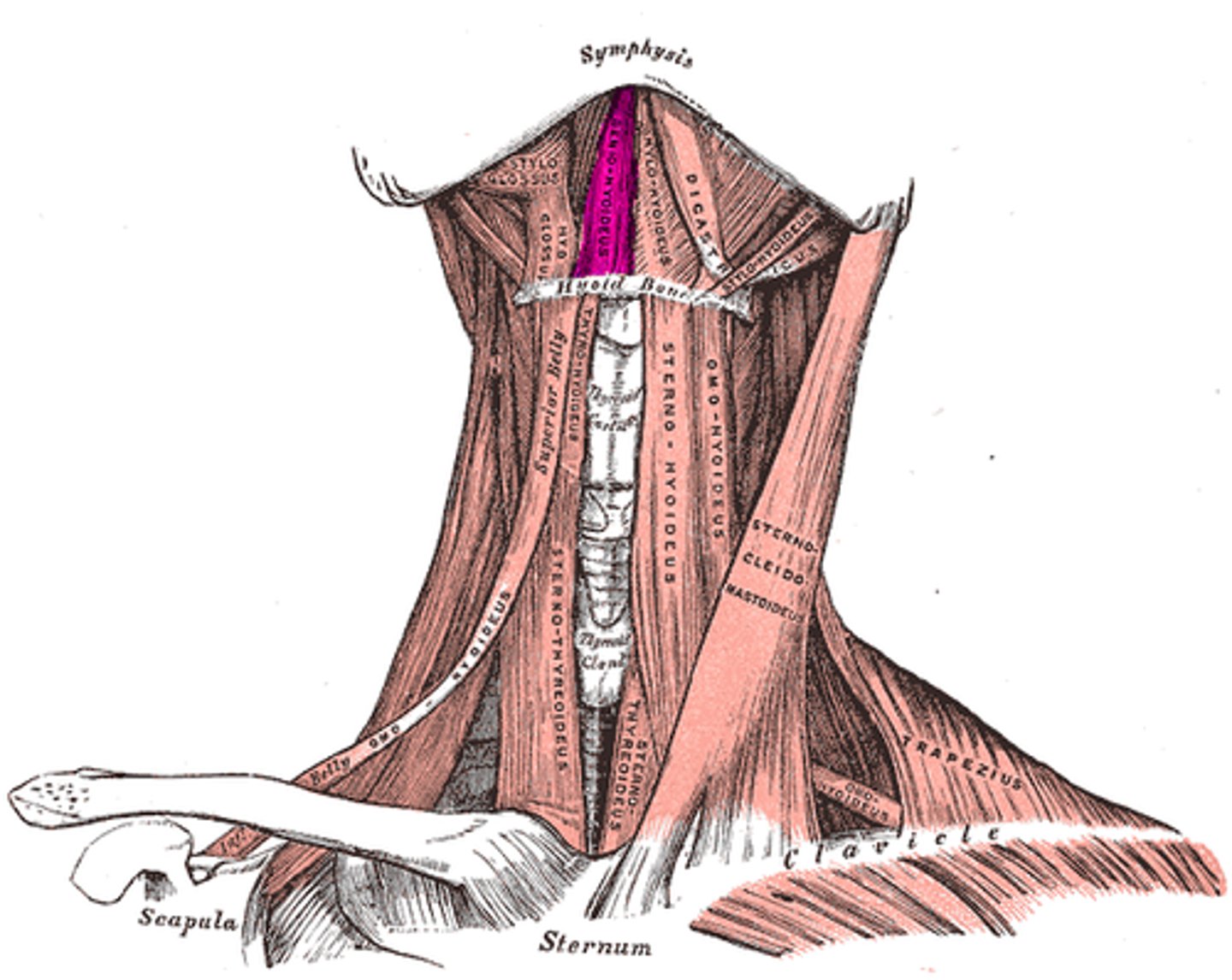
Stylohyoid (Anterior muscles of neck)
- from styloid process to hyoid bone
- lift hyoid for swallowing
- CN7
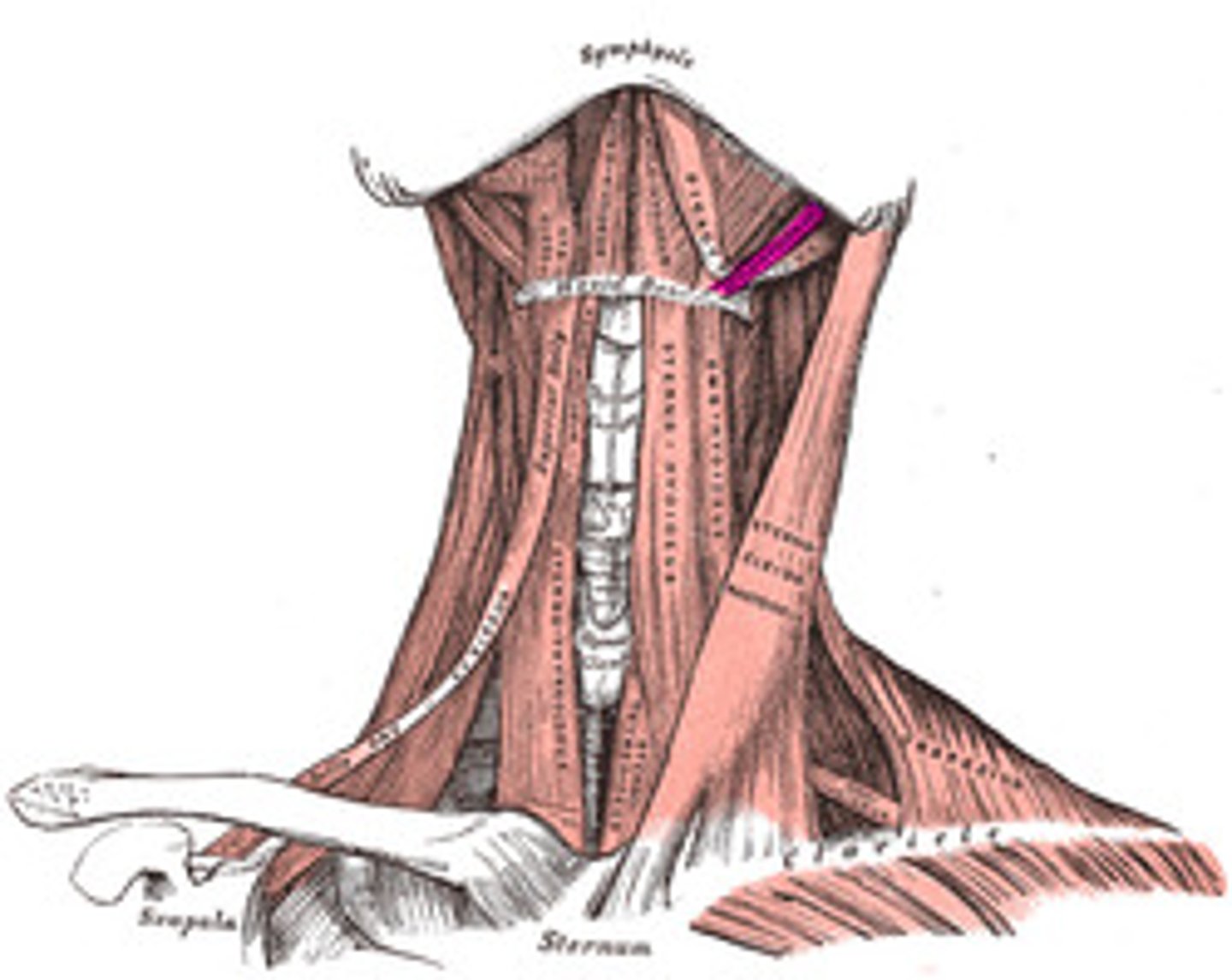
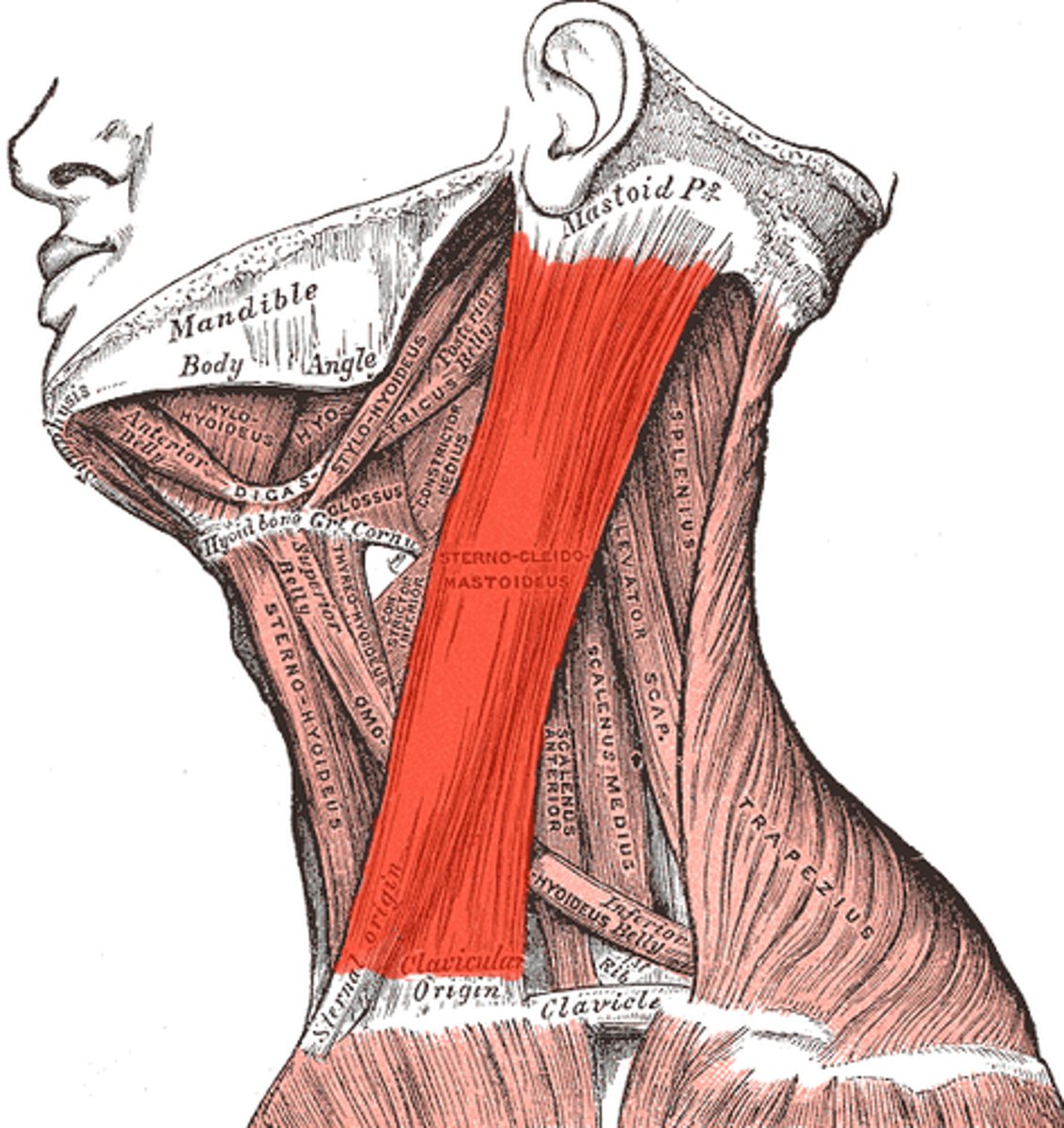
Sternocleidomastoid (Anterior muscles of neck)
- from sternum, clavicle to mastoid process
- lateral flexion of neck
- opposite side rotation
- CN 11
Origin - sternum of the clavicle
Insertion - mastoid process
When it contracts - laterally flex the neck to the ipsilateral side and turns the head to the contralateral side
Innervated by CN XI (11)
omohyoid (Anterior muscles of neck)
- depress hyoid bone
- CN1-3
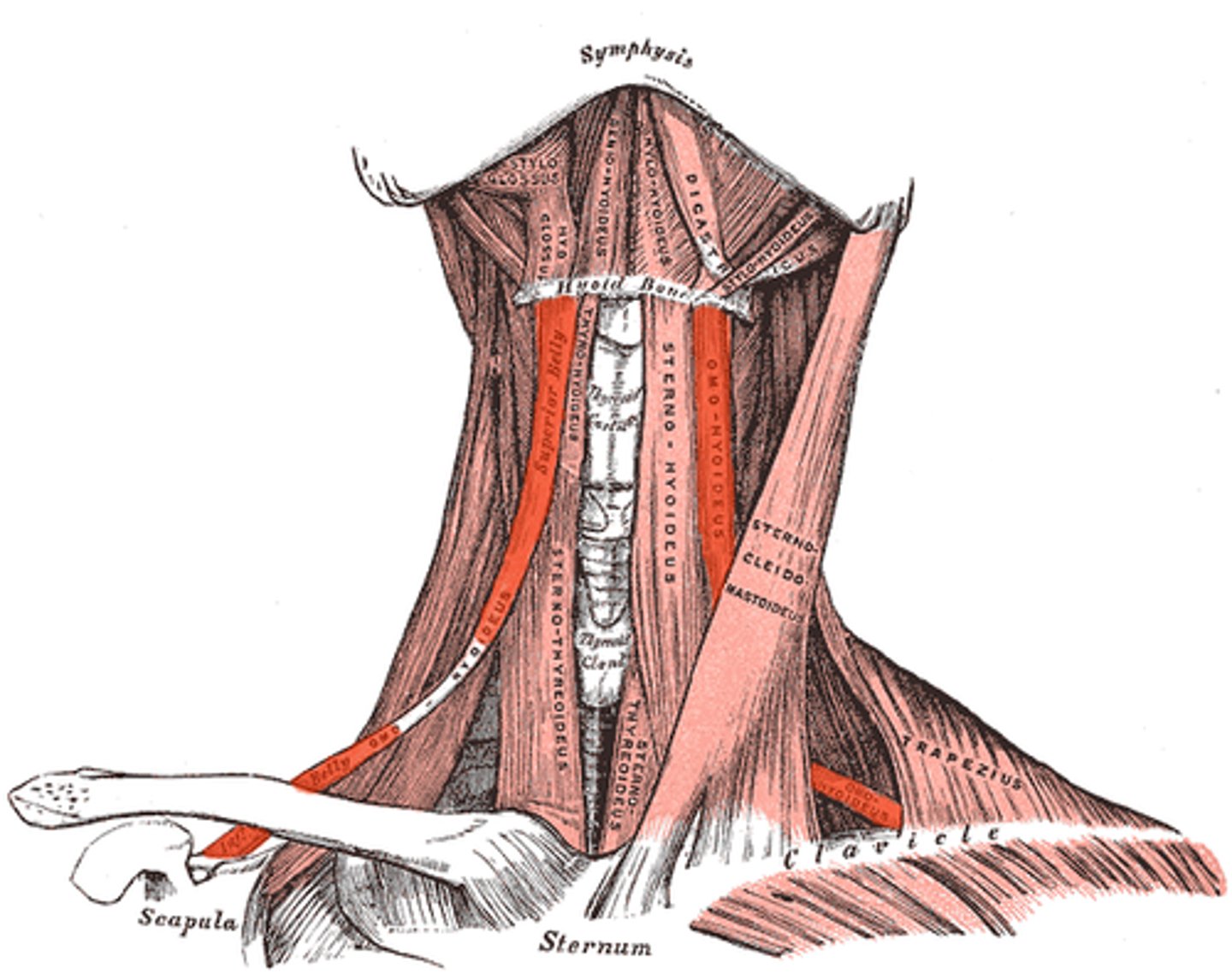
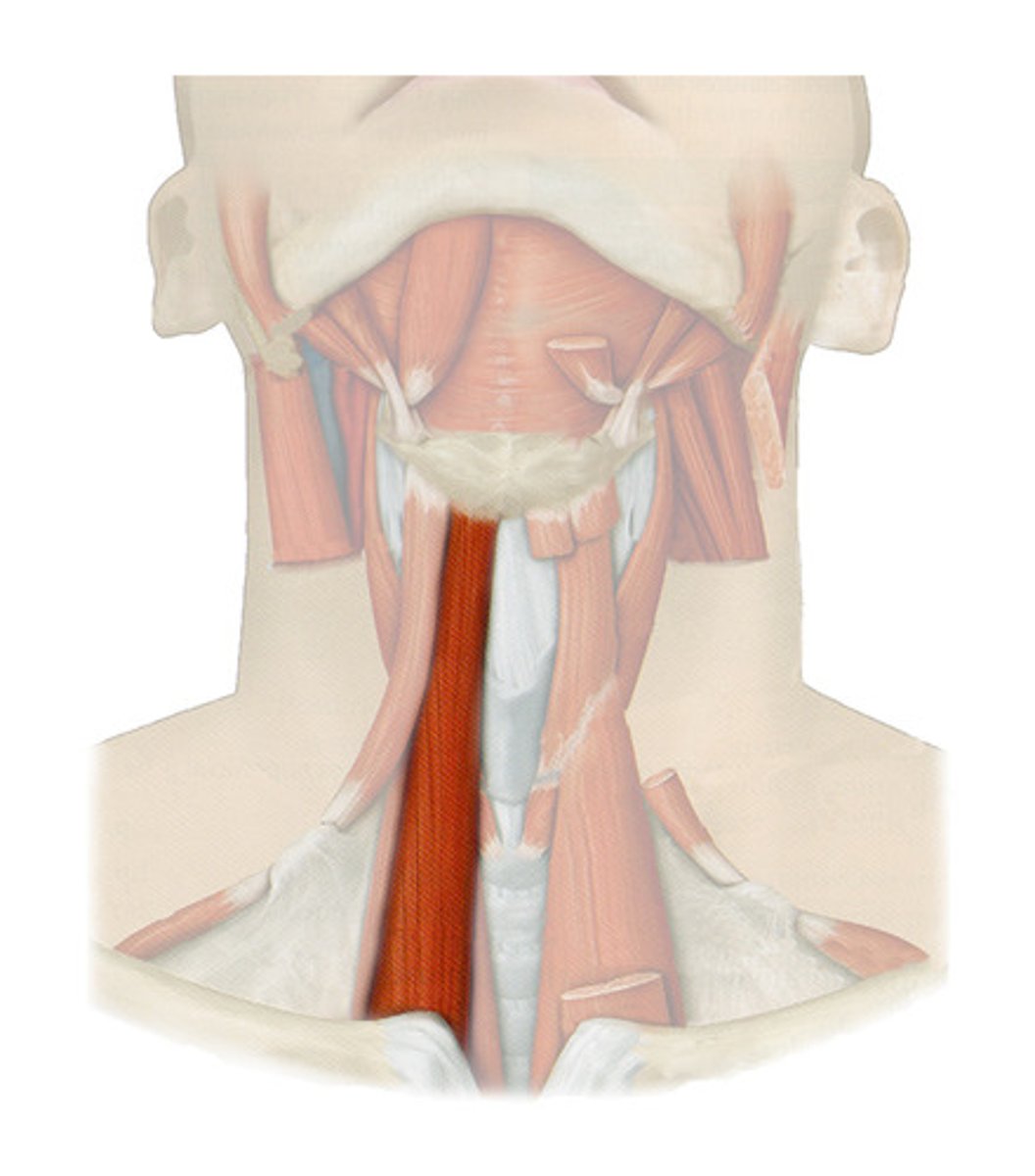
Sternohyoid (Anterior muscles of neck)
- from sternum to hyoid
- depress larynx for sound
- CN1-3
thyrohyoid (anterior muscles of the neck)
- from thyroid to hyoid
- elevate thyroid, depress hroid
- CN 12
Muscles of the vertebral column
- extension of vertebral column
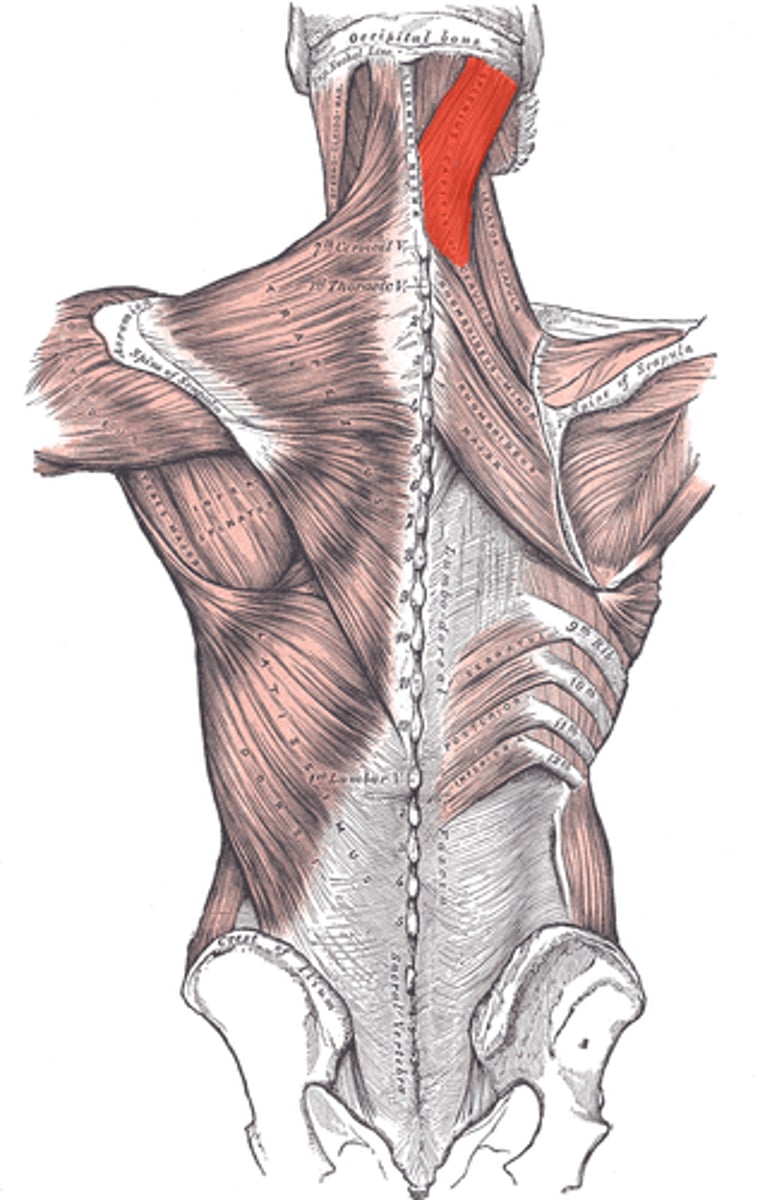
splenius capitis (Muscles of the vertebral column)
originate:
- lower cervical, upper thoracic spinous processes
insertion:
- mastoid process
- lateral occiput between superior/inferior nuchal line
- extend cervical spine (both side contraction)
- lateral flexion/ rotation (1-sided contraction)
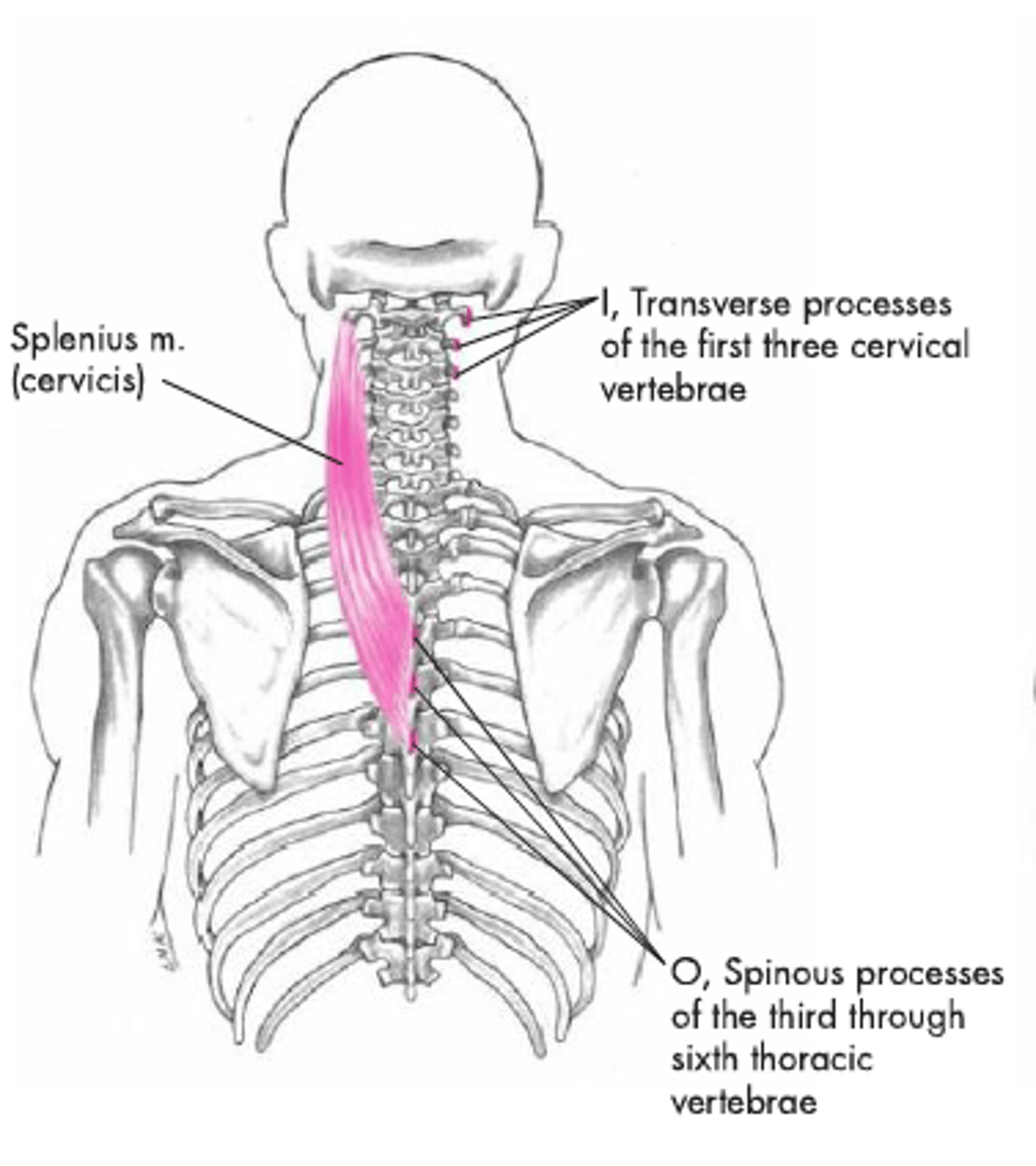
Splenius Cervicis (Muscles of the vertebral column)
originate:
- upper thoracic vertebrae spinous processes
insertion:
- transverse processes of C1-C3
- extend cervical spine (both side contraction)
- lateral flexion/ rotation (1-sided contraction)
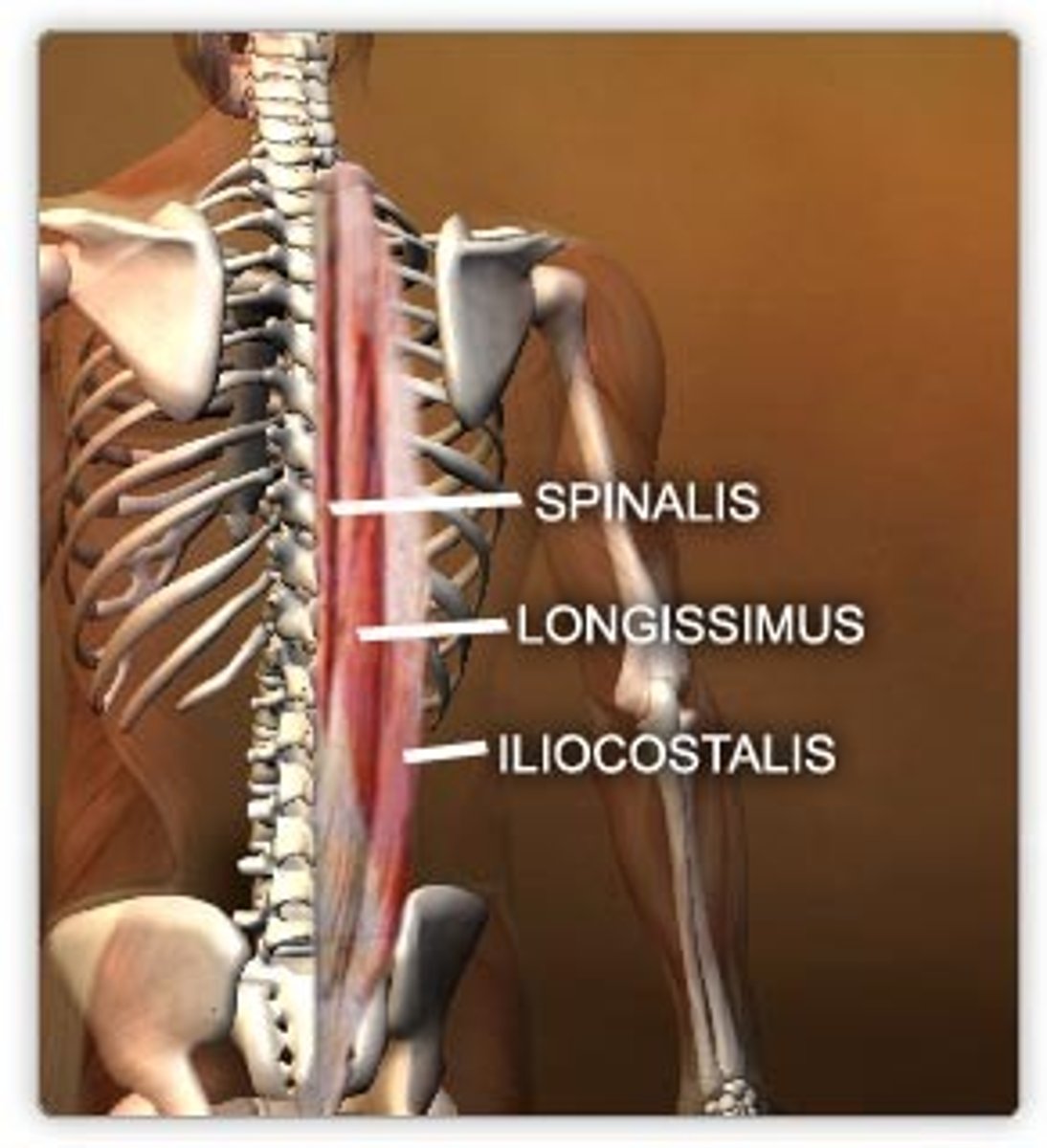
erector spinae (Muscles of the vertebral column)
- iliocostalis (lateral)
- longissimus
- spinalis (medial)
- extend spine
- same side rotation
- lateral flexion
- iliocostalis thoracis stabilizes throacic vertebrae in extension
- iliocostalis lumborum, extend vertebral column & depress ribs
- spinalis does no rotation
semispinalis group (Muscles of the vertebral column)
- capitits, cervicis, thoracis
- multifidus
- extension of vertebral column
- lateral flexion
- opposite side rotation
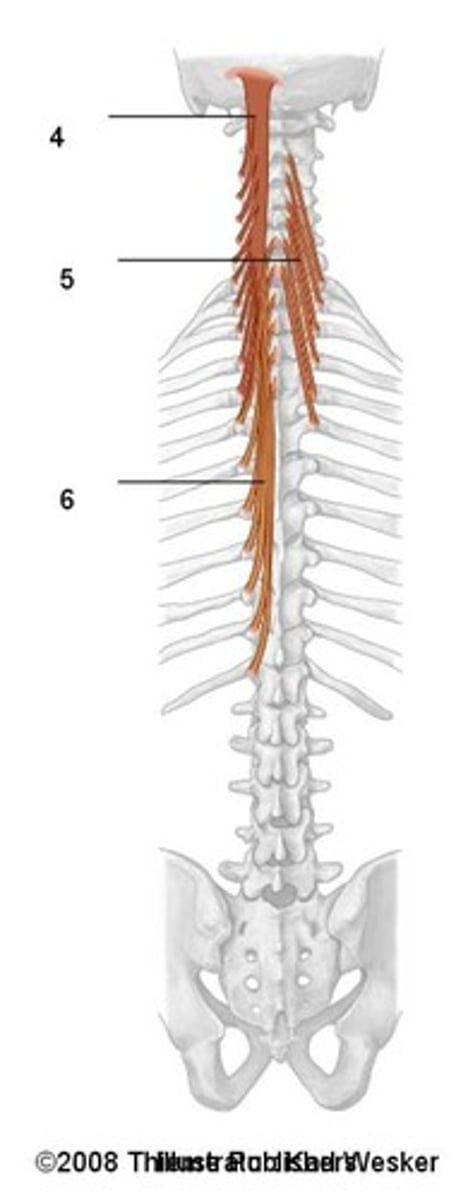
intervertebral muscles (Muscles of the vertebral column)
- rotatores
- intertransversarli
- interspinales (only performs extension)
- extension of vertebral column
- lateral flexion
- opposite side rotation
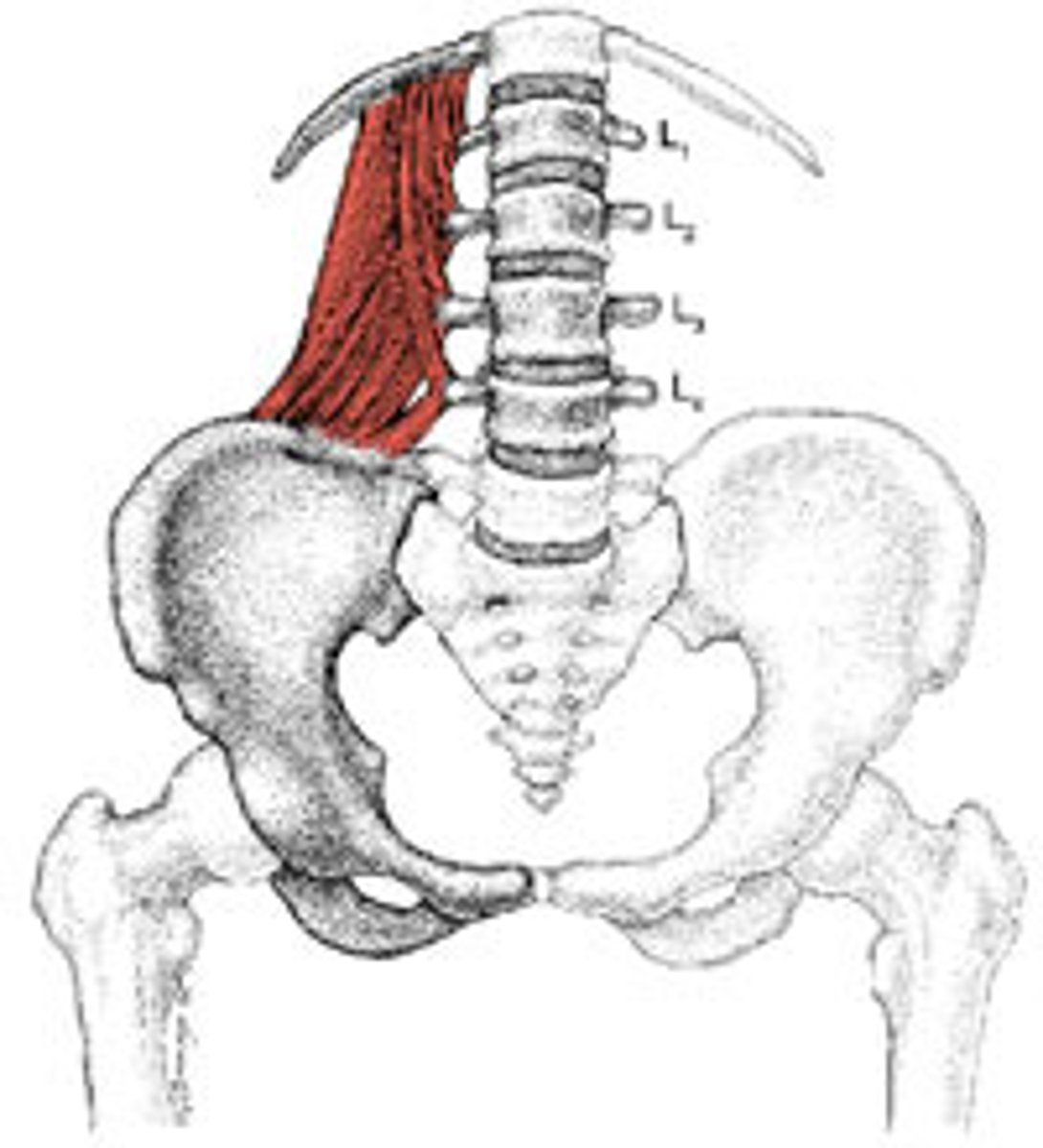
Quadratus Lumborum (Muscles of the vertebral column)
- from iliac crest & ilium lumbar ligament to last rib and lumbar vertebrae
- flexion of lower vertebral column
- depression of ribs
- lateral flexion
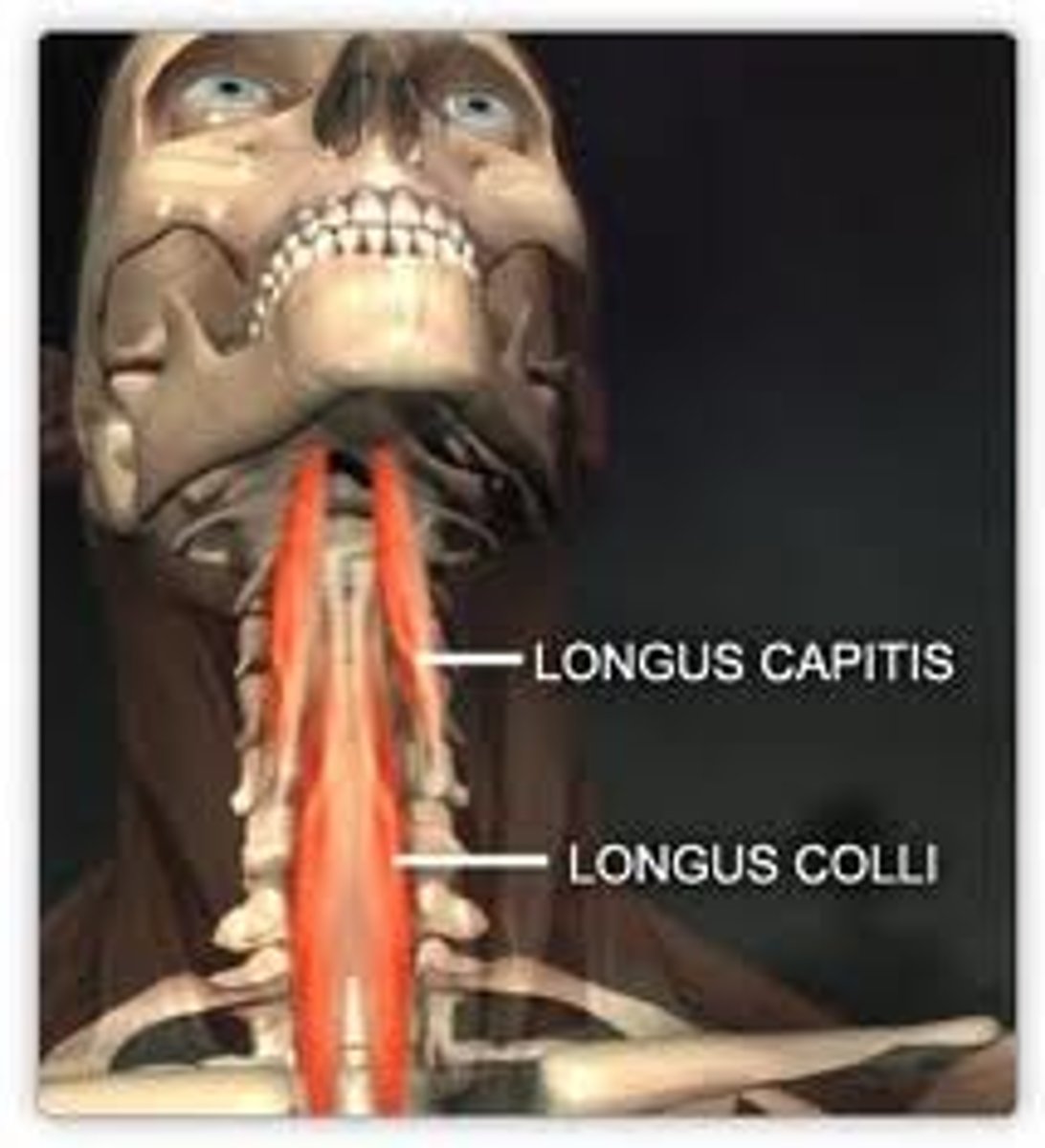
longus capitis/colli (spinous flexors)
- originate on transverse processes c4-c6, insert at base of occiput (capitis)
- originate at transverse process of cervical vertebrae (colli)
- flexion of cervical region
- same-side rotation
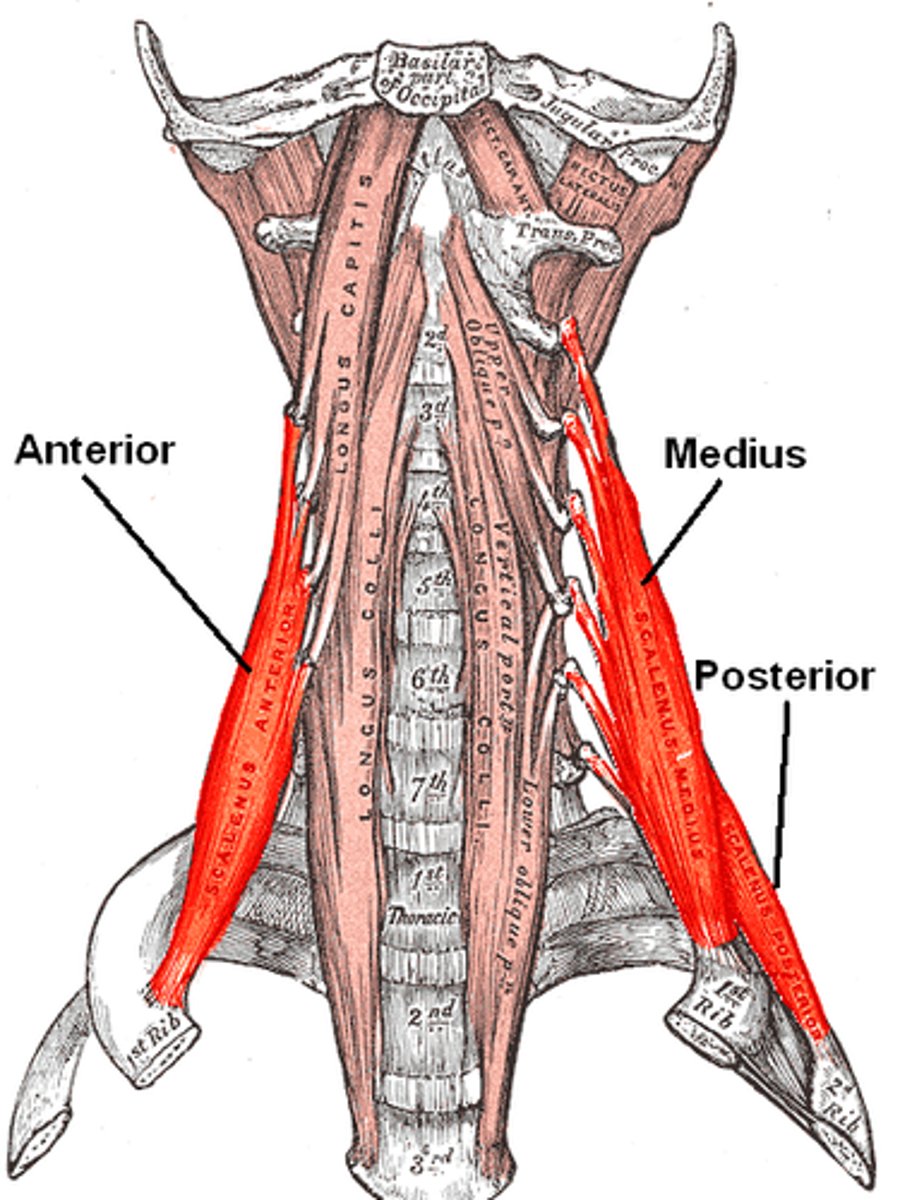
scalene (spinous flexors)
- from transverse vertebrae to ribs
- anterior, middle, posterior
- elevate ribs
- flex neck
- opposite side rotation (anterior)
- same side rotation (middles, posterior)
intercostal muscles (oblique & rectus muscles)
external:
- inferior border of rib to superior border of inferior rib
- expansion of rib cage (inhalation)
internal:
- superior border to inferior border of superior rib
- depress ribs (forced exhalation)
obliques (oblique & rectus muscles)
- compress abdomen
- depress ribs
- lateral flexion
external:
- from ribs 5-12 to aponeurosis and linea alba and iliac crest
- opposite side rotation
internal:
- from thoracolumbar fascia and inguinal ligament and iliac crest to ribs 8-12 and linea alba and pubis
- same-side rotation
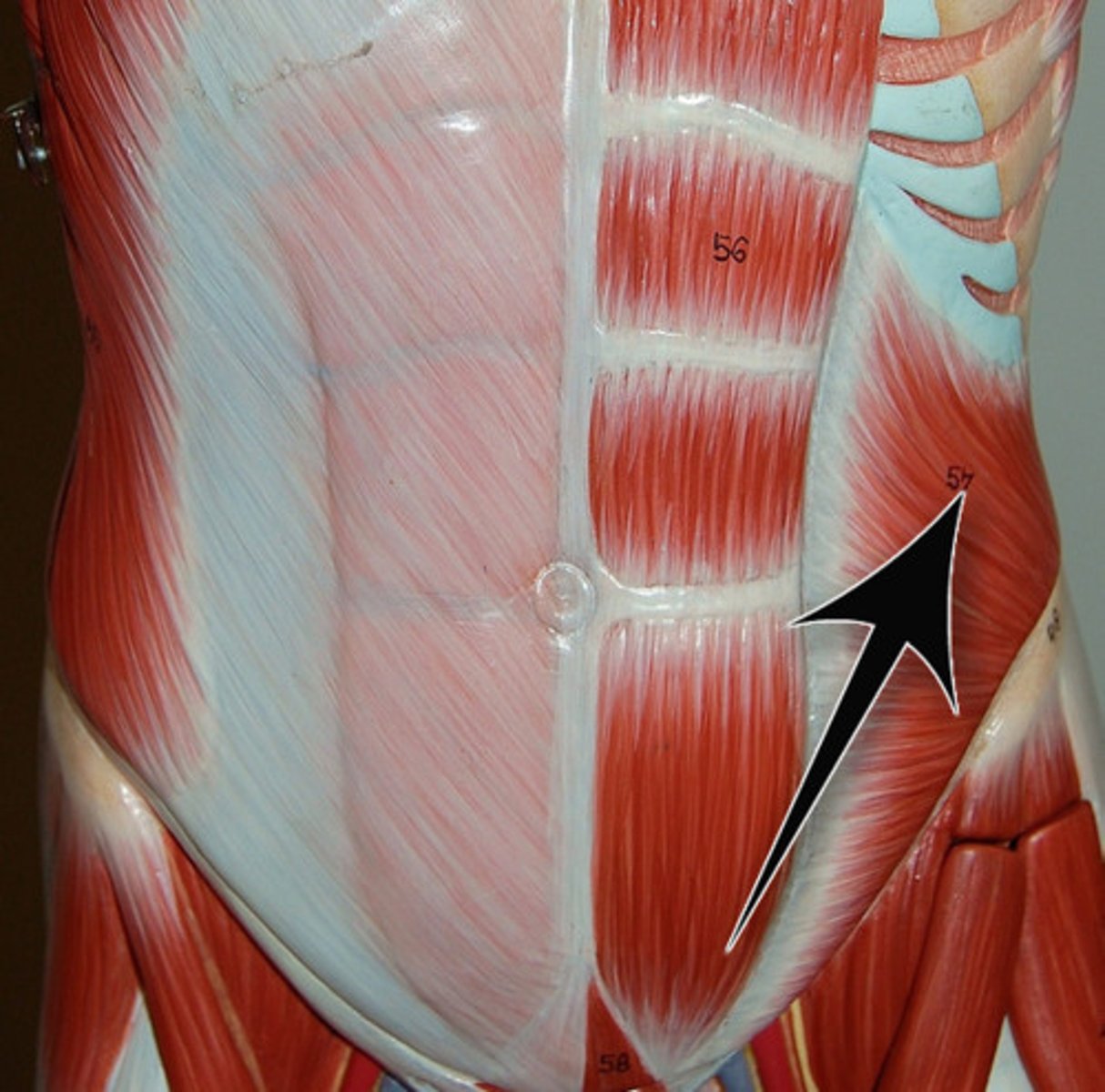
transverse abdominis (oblique & rectus muscles)
- from ribs 7-12 on cartilage from iliac crest & thoracolumbar fascia
- to linea alba & pubis
- compress abdomen
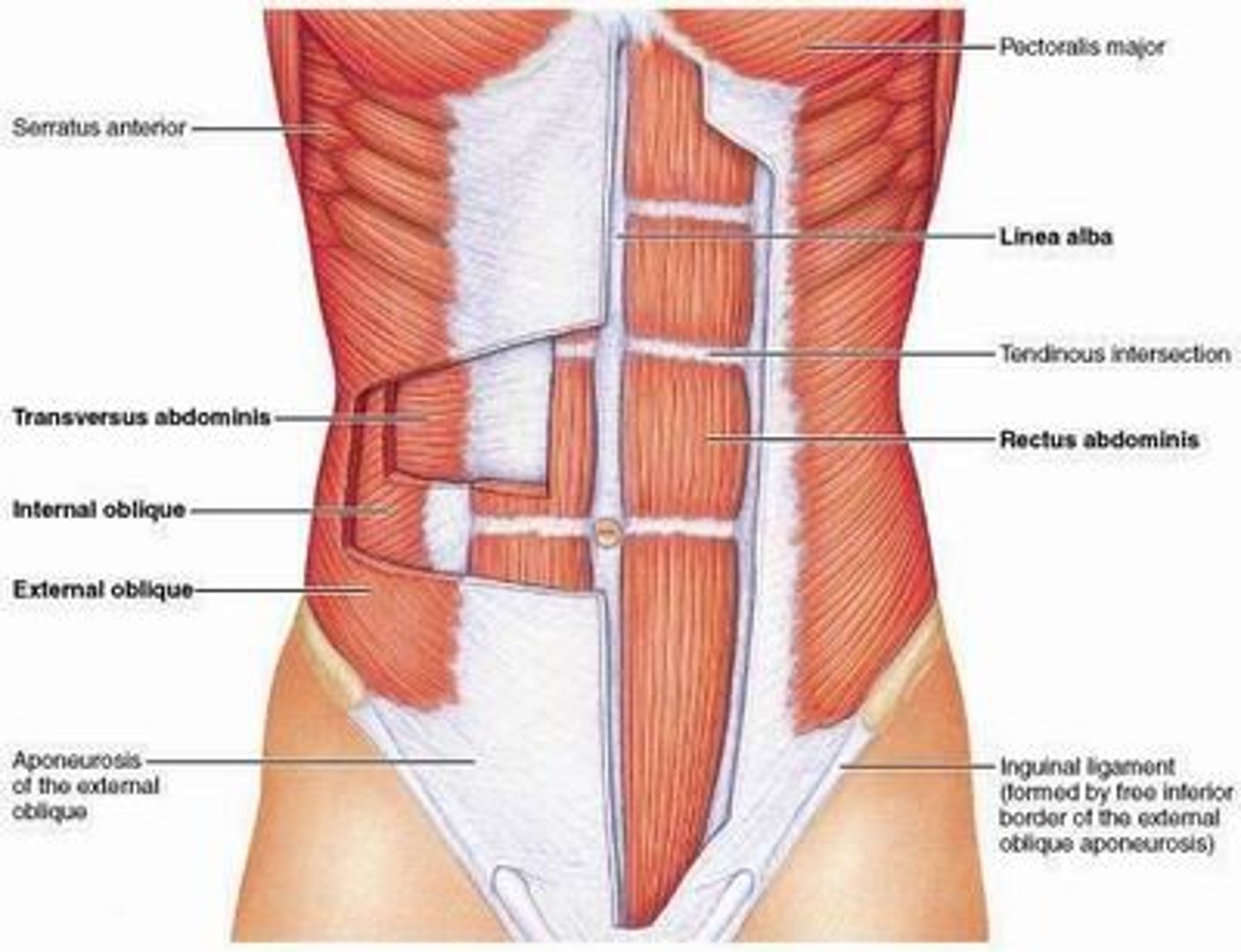
rectus abdominis (oblique & rectus muscles)
- from pubis to cartilage of ribs 5-7 & xiyphoid process of sternum
- depress ribs
- flex vertebral column
- compress abdomen
Diaphragm
- major muscle for ventilation
- separates thoracic & abdominal cavity
- from xiyphoid process to ribs 7-12 & anterior surface of lumbar vertebrae and insert in central tendon sheath
- curved upward in relaxed position (umbrella) (exhale)
- flatten when contracted
- innervated by phrenic nerve (Cn3-5)
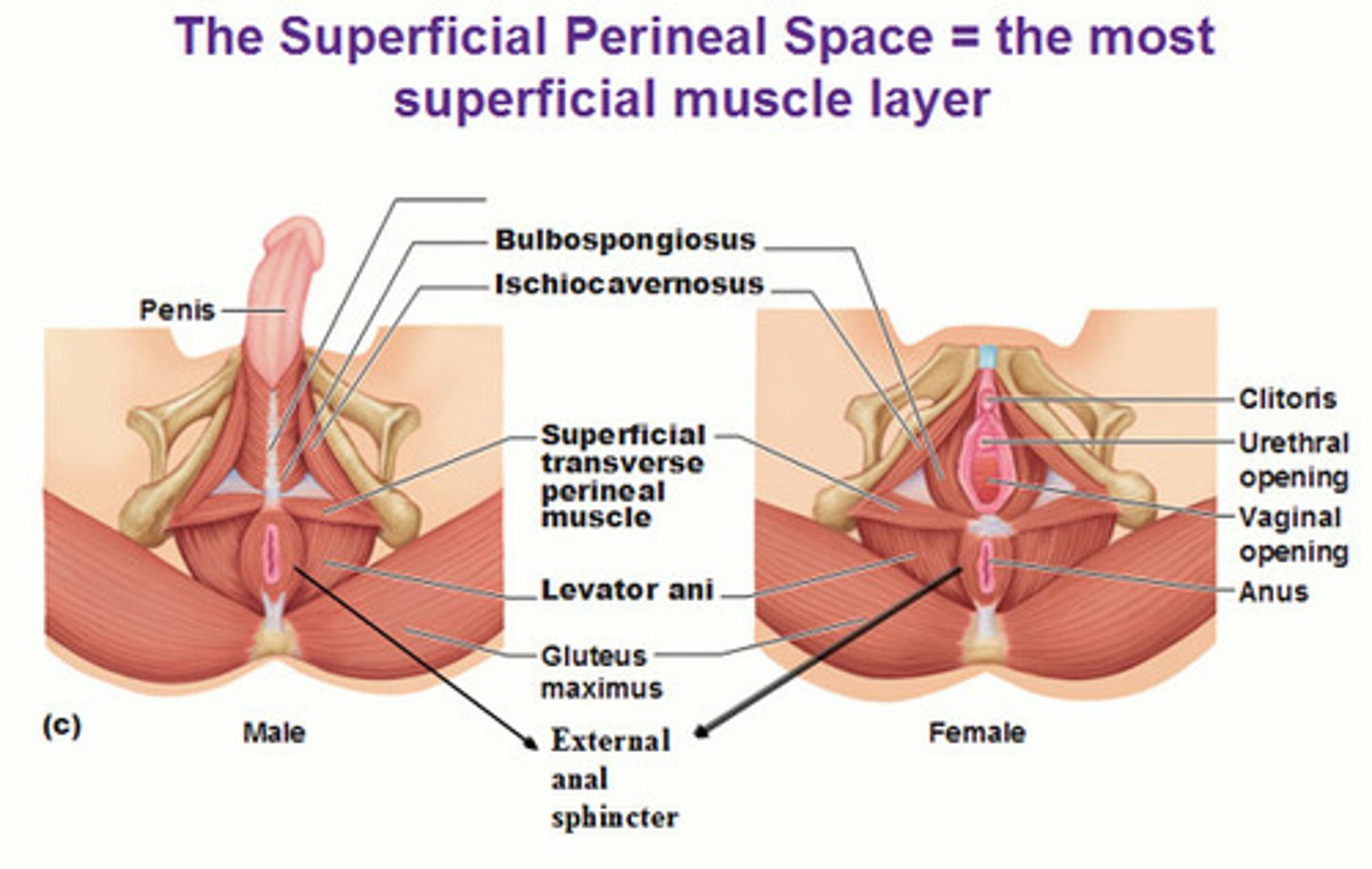
pelvic floor region (muscles of perineal region)
- urogenital & anal triangle
- separated by superficial transverse perineal muscle (stabilizer of central tendon of perineal region)
ischocavernosus (muscles of perineal region)
- contracts to compress & stiffen penis or clitoris
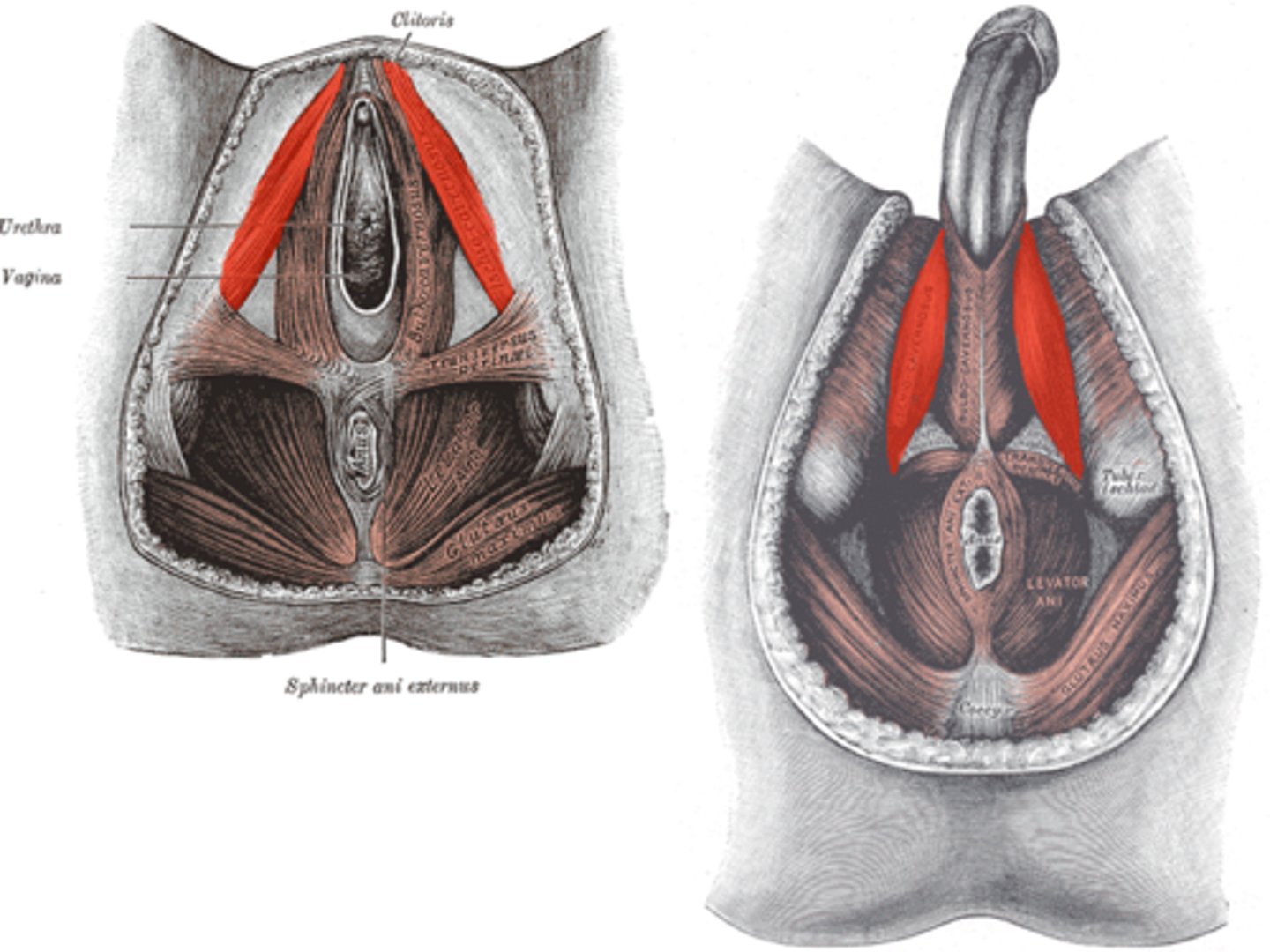
bulbospongiosus (muscles of perineal region)
- compress base of stiffen penis
- helps w/ ejection of urine/semen
- compress & stiffen clitoris
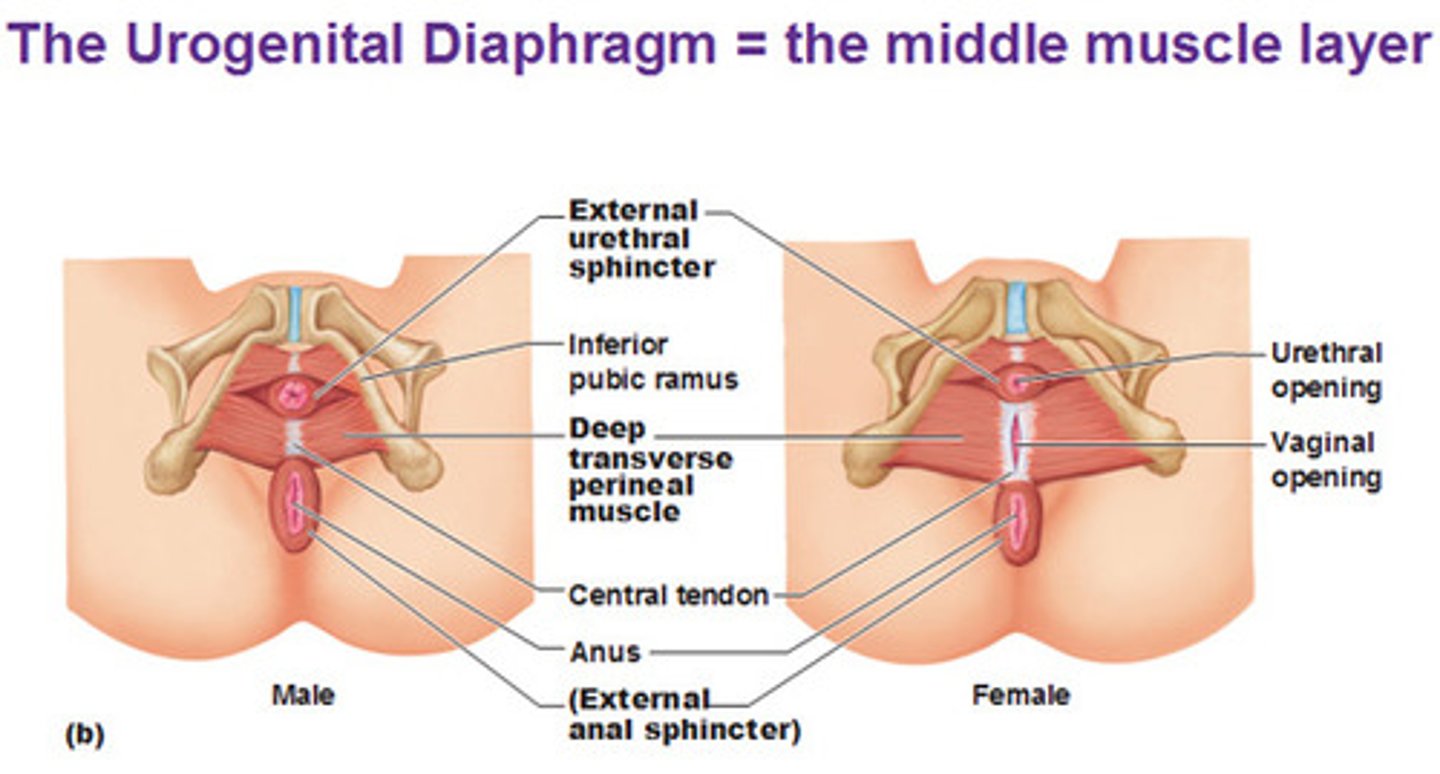
deep transverse perineal muscles (muscles of perineal region)
- muscles stabilizing central tendon
external urethral sphincter (muscles of perineal region)
male:
- compress urethra/prostate and bulb of urethral glands
female:
- closes urethra, compresses vagina & greater vestibular glands to lubrication
coccygeus (muscles of perineal region)
- flexion of coccygeal joint
- elevates pelvic floor
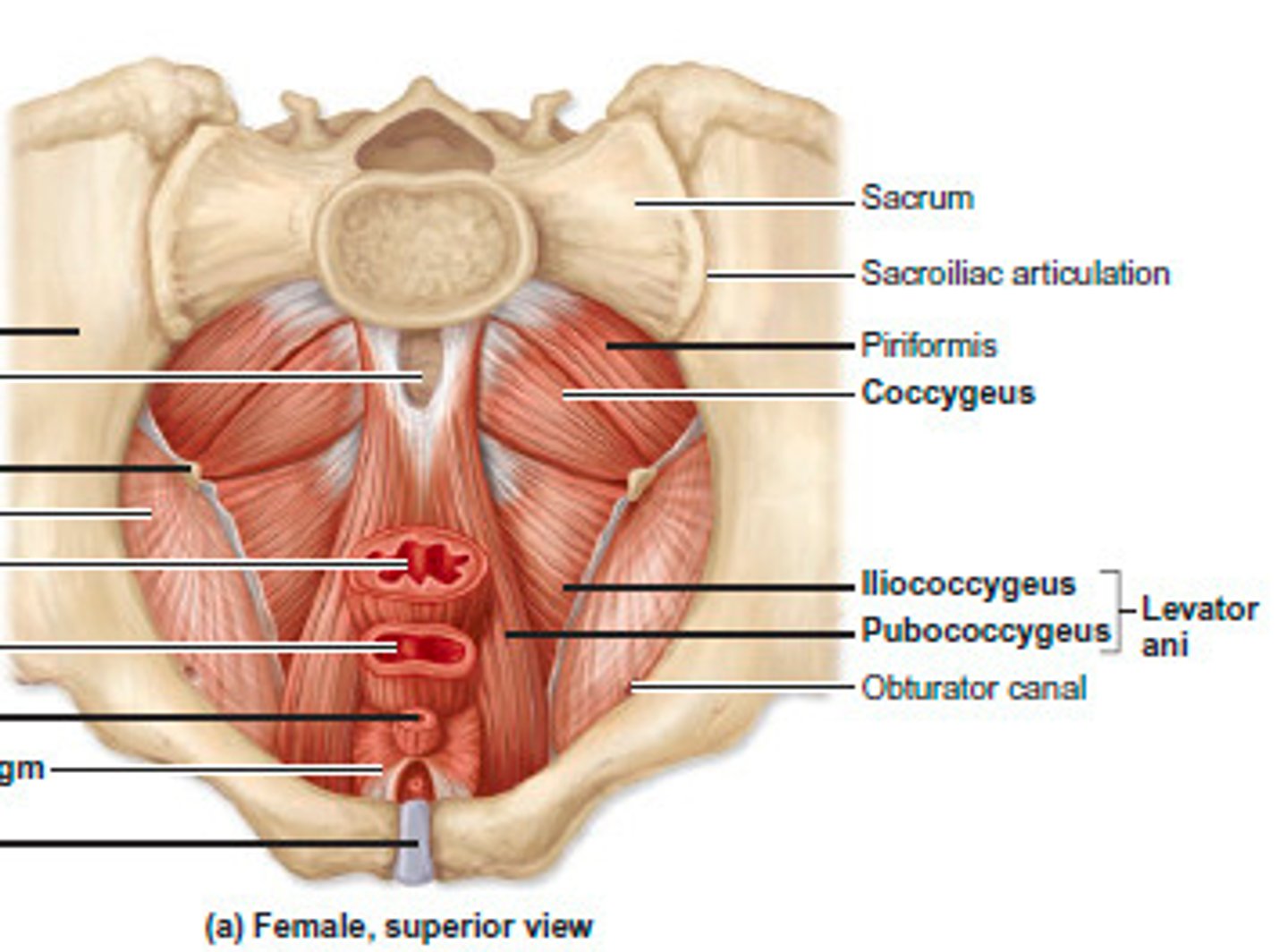
levator ani (muscles of perineal region)
pubo/illio coccygeus muscle:
- tenses pelvic floor
- supports pelvic organs
- elevates & retracts anus
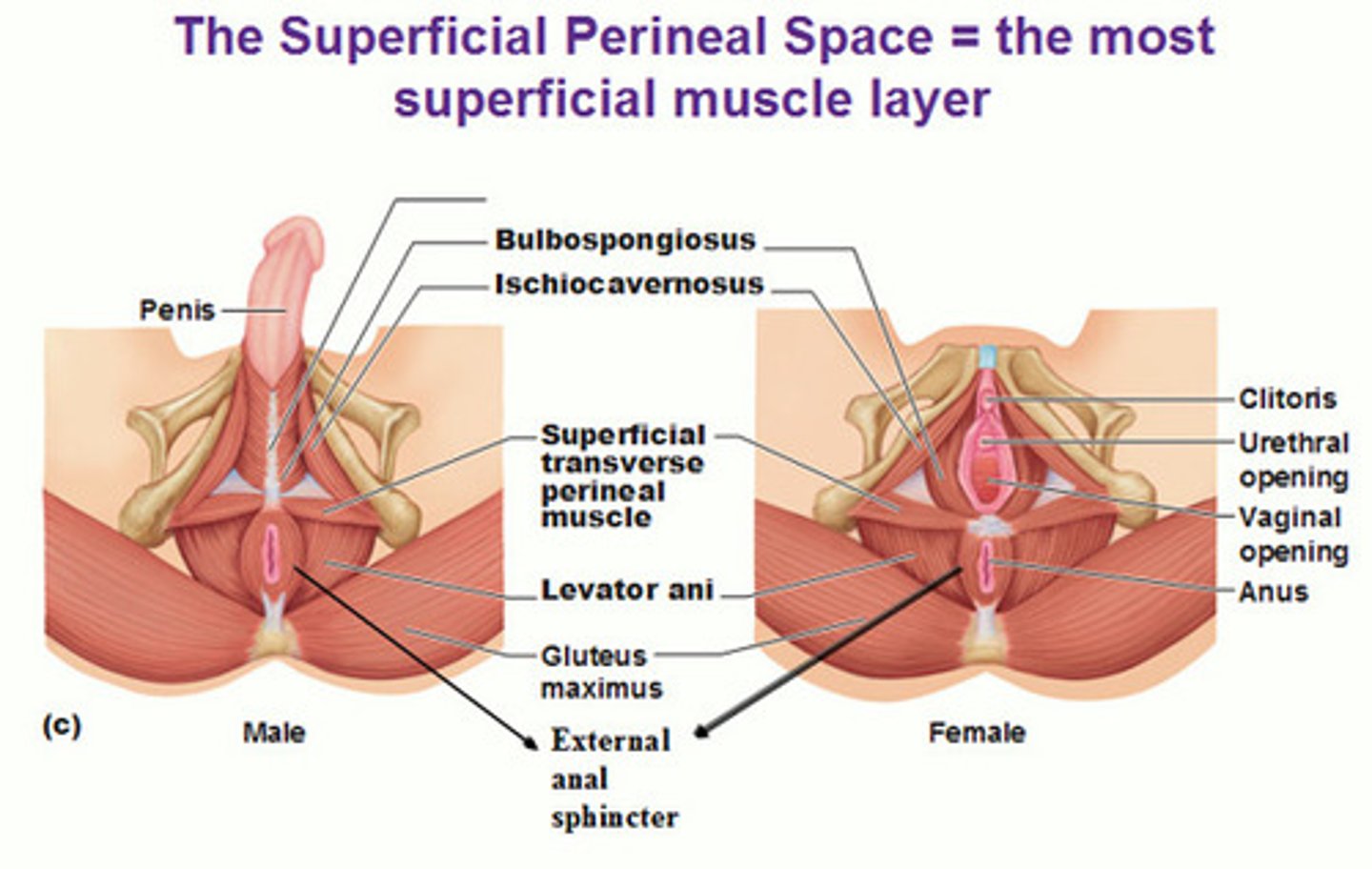
external anal sphincter (muscles of perineal region)
- closes anal opening
Contraction/relaxations of diaphran and respiration
During inspiration (breathing in), the diaphragm contracts and it descends to allow for lung expansion.
During expiration (breathing out), the diaphragm relaxes and it ascends to allow for lung contraction.
Weakness of the pelvic floor muscles can lead to urinary incontinence (urinary leakage).