Monoclonal antibodies
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
How are monoclonal antibodies able to target a specific chemical/ specific cells in the body?
The antibodies are specific to one binding site on one protein antigen and so are able to target a specific chemical or specific cells in the body
How are monoclonal antibodies produced?
By stimulating mouse lymphocytes to make a particular antibody. The lymphocytes are combined with a particular type of tumour cell to make a hybridoma cell. The hybridoma cell can both divide and make the antibody. Single hybridoma cells are cloned to produce many identical cells that all produce many cell identical cells that all produce the same antibody. A large amount of the antibody can be collected and purified.
What hormone do pregnancy tests detect?
A hormone called HCG which is found in the urine of women only when they are pregnant
How do pregnancy tests work?
A woman’s urine is applied to the absorbent pad of the test stick.
If present, the hormone hCG in the urine binds to mobile monoclonal antibodies that have blue beads attached.
These antibody–hCG–blue bead complexes move up the strip by capillary action.
At the test line, there are fixed monoclonal antibodies that also bind to hCG. This traps the complexes, producing a visible blue line (positive result).
At the control line, different fixed antibodies bind to the unused mobile antibodies with blue beads. This shows the test has worked properly.
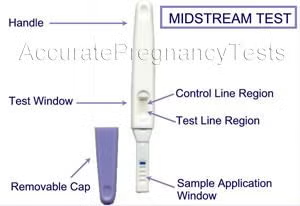
How do you tell if you’re pregnant/ not pregnant or if you have a faulty pregnancy test?
Two lines → pregnant (hCG present).
One line at control only → not pregnant (no hCG).
No control line → test invalid.
How are monoclonal antibodies used in diagnosis?
To measure hormone levels or other chemicals in blood.
To detect pathogens in blood samples.
To locate specific molecules in cells or tissues.
Monoclonal antibodies are made to bind to a specific molecule (e.g. a hormone, pathogen antigen, or cell marker)
In diagnostic tests, they bind to the target molecule if it is present, allowing the level or presence of the substance to be measured
How do monoclonal antibodies locate specific molecules in cells or tissues?
Monoclonal antibodies are made to bind to a specific molecule (e.g. a hormone, pathogen antigen, or cell marker).
Monoclonal antibodies are attached to a fluorescent dye.
If the target molecule is present, the antibody binds to it.
The dye allows the molecule to be detected under a microscope.
Explain how monoclonal antibodies are used to treat cancer (6 marks)
Cancer cells have antigens on their cell surface that are not found on normal cells.
Monoclonal antibodies are made to bind specifically to these cancer cell antigens.
The antibodies can be attached to a toxic drug, radioactive substance, or chemical.
When the antibodies bind to the cancer cells, they deliver the substance directly to them.
This kills the cancer cells.
Normal body cells are not targeted, so there are fewer side effects compared to chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
What are the disadvantages of using monoclonal antibodies?
1) Side effects, for example: fever, vomiting and low blood pressure.
2) Expensive to produce
What are the main advantages of using monoclonal antibodies?
They target specific diseased cells without damaging healthy cells (in conventional cancer treatments the drugs and radiotherapy also damage healthy cells.)