WEEK 8: Psychology of Humanistic and Existential Theories: Rogers, Sartre, Maslow
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
What is phenomenology in psychology?
A style of thought focused on individual consciousness and how one perceives phenomena and creates meaning from it.
Who proposed the phenomenological method?
Edmund Husserl.
What does Martin Heidegger's concept of 'throwness' refer to?
The predispositions and environmental factors influencing personality and the idea of 'free will'.
What does authenticity mean in the context of existentialism?
Being true to 'our' self rather than conforming to 'they' self (external expectations).
How does existentialism define 'being'?
'Being' is the essence of consciousness that arises in relation to something, not found in isolation.
What is Sartre's claim about existence and essence?
'Existence precedes essence' - we first exist, encounter ourselves, and then define who we are.
What is 'bad faith' according to Sartre?
Blaming circumstances for our actions, which undermines our freedom of choice and responsibility.
What are the two components that define a person's essence according to Sartre?
1. Their action (behavior) and 2. Intent.
What is humanistic psychology?
An aspect of phenomenological approach emphasizing individual perception and free will.
Why did humanistic psychology emerge in the 1950s?
As a reaction to the perceived pessimism of psychoanalysis and behaviorism.
What does humanistic psychology emphasize?
Looking at the whole individual, including inner states/drives and the external meaning of phenomena.
What are the key concepts stressed by humanistic psychology?
Free will, self-efficacy, self-esteem, and self-actualization.
What is the goal of positive psychology?
To study human flourishing, well-being, and the strengths and virtues of individuals.
What is the non-directive approach in Rogers' therapy?
Allowing clients to reflect on their thoughts, feelings, and behavior without direct guidance.
What is the role of the therapist in person-centered therapy?
To empathize and create a compassionate alliance with the client.
What are the three therapist-centered conditions necessary for a good therapeutic climate?
1. Genuineness, 2. Unconditional positive regard, 3. Empathy.
What does the therapeutic alliance refer to?
The equality and partnership between client and therapist in the therapeutic process.
How does existentialism view the capacity for good and evil in individuals?
No individual is inherently good or evil; all have the capacity for both based on free choice and past experiences.
What is the significance of graveyards in existential thought?
They remind us of our finiteness in life and force us to reflect on our existence.
What does the term 'self-actualization' mean?
The realization or fulfillment of one's talents and potential, often considered the ultimate goal of humanistic psychology.
What is the relationship between behavior and intent in defining essence?
Both behavior (actus reus) and intent (mens rea) are crucial in determining a person's essence.
What is the criticism of traditional psychological approaches by humanistic psychology?
They are seen as too deterministic, failing to account for free will and individual agency.
What is empathetic understanding in therapy?
The therapist strives to understand how the client perceives the world through active listening and empathetic concern.
What does genuineness mean in a therapeutic context?
The therapist is open, transparent, and speaks honestly, embodying their true self.
What is unconditional positive regard?
The therapist communicates a deep and genuine caring for the client as a person, regardless of their behavior.
What is the premise of Rational Emotive Behavioural Therapy (REBT)?
Humans are not disturbed by unfortunate circumstances but by how they construct their views of those circumstances.
What is the ABCD model in REBT?
A framework for reframing thoughts: A (Activating event), B (Beliefs), C (Consequences), D (Disputation of beliefs).
What is the significance of self-compassion according to CBT?
Self-compassion is key to overcoming negative thinking patterns and irrational beliefs.
What is attribution bias?
The tendency to attribute good outcomes to oneself and bad outcomes to external forces.
What does Roger's philosophy suggest about genuineness?
People can sense inauthenticity; genuine aspects of oneself are often admired.
What is the human potential movement?
It emphasizes that people have an ideal self and the drive to realize their potential.
What does Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs emphasize?
The importance of fulfilling psychological needs to achieve self-actualization.
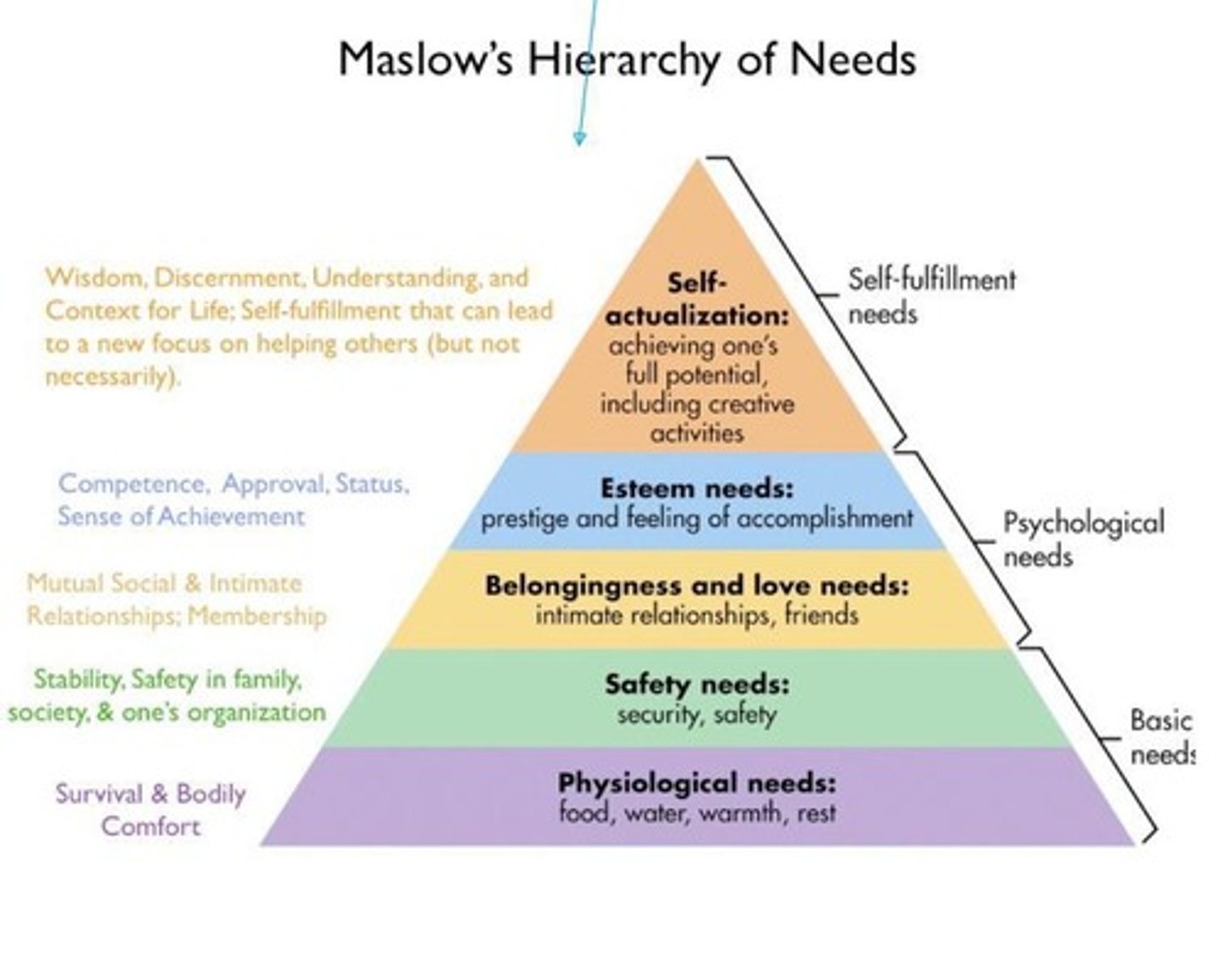
What characterizes self-actualizing individuals according to Maslow?
They accept themselves and others, are concerned for others, and respond flexibly to situations.
What is incongruence in humanistic therapy?
The psychological distress that occurs when there is a large discrepancy between the actual self and the ideal self.
What are the four cardinal virtues of Stoicism?
Wisdom, justice, courage, and temperance.
What does the virtue of wisdom entail in Stoicism?
The ability to discern good from evil and make rational decisions.
How does Stoicism define justice?
Fairness and righteousness in actions toward others, contributing to the common good.
What is the Stoic virtue of courage?
The strength to face fear and adversity with endurance and fortitude.
What does temperance mean in Stoicism?
Self-control or moderation, involving the restraint of desires and appetites.
What is the role of psychological flexibility in self-actualization?
It allows individuals to respond to unique situations rather than mechanically.
What is the significance of studying high-functioning self-actualized individuals?
It provides insight into personality and well-being beyond those with psychological problems.
What is the impact of perfectionism according to the notes?
Perfectionists may perform well academically but struggle in the workplace and often lack initiative.
What is the growth mindset?
A belief that emphasizes praising effort over accomplishment to foster resilience and growth.
What does the positive psychology movement focus on?
The nature of human strengths and virtues that contribute to well-being.
What is flow according to Csikszentmihalyi?
A positive state of consciousness characterized by focused attention and intrinsic enjoyment in an activity.
What are the outcomes of humanistic therapy?
Therapy aims to reduce incongruence between the actual self and ideal self, leading to greater psychological well-being.
What is the difference between the ideal self and the ought self?
The ideal self is concerned with hopes and desires, while the ought self focuses on duties and obligations.
What psychological issues arise from discrepancies between the ideal and actual self?
Disappointment and sadness from the ideal self, and fear and resentment from the ought self.
What is temperance in Stoicism?
Self-control or moderation, involving the restraint of desires and appetites.
What does 'Sommum Bonnum' mean in Stoicism?
It means to live your virtue (excellence).
What is 'Amor fati' in Stoicism?
It refers to the love of fate and the understanding of the impermanence of consciousness.
What is the significance of 'Premeditatio Malorum'?
It is a practice to reduce expectations and prepare for potential misfortunes.
What does 'Obstacle is the way' imply?
Obstacles show you the path to excellence.
What does 'Ego is the enemy' suggest?
Arrogance leads to willful blindness and the pursuit of unattainable perfection.
What does 'Interconnectedness' mean in Stoicism?
It emphasizes that what is bad for the hive is bad for the bee, highlighting the common good and selflessness.
What is 'Momento Mori'?
It is the reminder to live every day to its fullest, acknowledging that life is finite.
What is the overarching concern of existentialism?
It emphasizes existence, the human condition, and the search for meaning in life.
How does existentialism view life?
As suffering, with limited capabilities in a complex world.
What is the relationship between freedom and responsibility in existentialism?
With freedom comes great responsibility; individuals must take responsibility for their actions.
What is morality salience in the context of existentialism?
It tests the hypothesis that increased death anxiety leads to stronger commitment to cultural and political beliefs.
What does Terror Management Theory (TMT) address?
It explores how awareness of death influences behavior and the search for meaning.
What does TMT suggest about struggle?
Struggle provides meaning and resilience, motivating individuals to overcome challenges.
What are the limitations of phenomenological theory?
It lacks cultural diversity and relies heavily on subjective methods.
What is the importance of the therapeutic alliance in Rogerian theory?
It is considered the most important element in the interpersonal relationship between therapist and client.
What are some strengths of Rogerian theory?
It focuses on neglected aspects of human existence and provides effective therapeutic strategies.
What is a limitation of Rogerian theory?
It does not address phenomena outside of conscious experience.
How is self-concept measured in Rogerian theory?
It is often measured via traits, such as the Big Five personality traits.