electricity
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
1
New cards
current is the rate of flow of charge round the circuit
what is current?
2
New cards
electrons usually carry the charge- they’re negatively charged particles
what carries the charge through the circuit?
3
New cards
current will only flow through a component if there is a voltage across that component
what is the one thing needed for currently to flow through a component?
4
New cards
voltage is the energy transferred per unit charge passed and the volt is a joule per coulomb
voltage is also know as potential difference or p.d
voltage is also know as potential difference or p.d
what is voltage?
5
New cards
resistance is anything in the circuit that slows the flow.
what is resistance?
6
New cards
there will be a higher resistance
if you add more components to the circuit what will happen to the resistance
7
New cards
ampere (amp) A
what is the unit for current?
8
New cards
volts V
what is the unit for voltage?
9
New cards
ohms
what is the unit for resistance?
10
New cards
more current
if you increase the voltage what will happen to the current?
11
New cards
less current and more voltage to keeps the same current flowing
if you increase the resistance what will happen to the current?
12
New cards
an ammeter measure the current in amps flowing through the components
an ammeter must be placed in series anywhere in the main circuit but never in parallel like the voltmeter
an ammeter must be placed in series anywhere in the main circuit but never in parallel like the voltmeter
wha is an ammeter?
13
New cards
a voltmeter measures the voltage in volts across the component
must be place in parallel
must be place in parallel
what is a voltmeter?
14
New cards
a.c
what is the name for main supply?
15
New cards
d.c
what is the name for battery supply?
16
New cards
approx 230 volts
what is the uk main electricity supply?
17
New cards
an a.c supply means alternating current which means the current is constantly changing direction
what is an a.c supply?
18
New cards
d.c is direct current which supply cell and battery and current flows in same direction.
what is d.c?
19
New cards

what is the formula for voltage?
20
New cards
shows you how the resistance of the component behave.
the steeper the graph the lower the resistance
the steeper the graph the lower the resistance
what does the gradient of an I-V graph show you?
21
New cards
a straight line graph has a constant gradient and shows a constant resistance.
if the graph curves it means the resistance is changing.
if the graph curves it means the resistance is changing.
what does a straight line graph shows you?
22
New cards
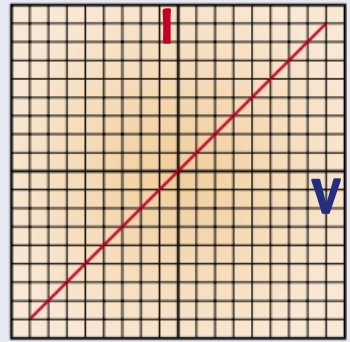
the current through a wire at a constant temperature is proportional to voltage
what is the graph for a wire?
23
New cards
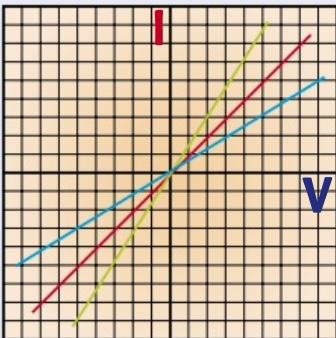
the current through a resistor at a constant temperature is proportional to voltage.
different resistors have different resistances hence the different slopes.
different resistors have different resistances hence the different slopes.
what is the graph for different resistors?
24
New cards
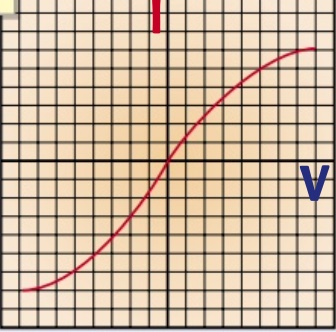
as the temperature of the lamp increase the resistance increases hence the curve
what is the graph for metal filament lamp?
25
New cards
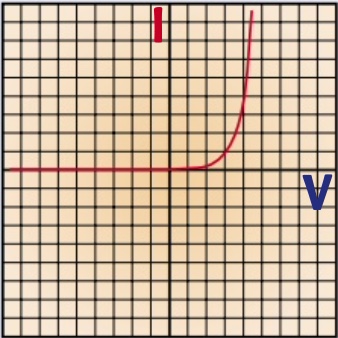
current will only flow through a diode in one direction
what is the graph for diode?
26
New cards
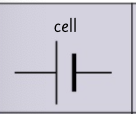
circuit symbol- cell?
27
New cards
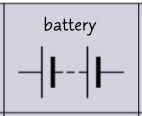
circuit symbol- battery?
28
New cards
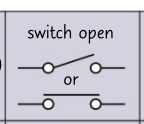
circuit symbol- switch open?
29
New cards
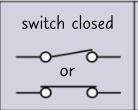
circuit symbol- switch closed?
30
New cards
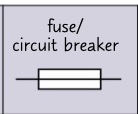
circuit symbol- fuse/circuit breaker?
31
New cards
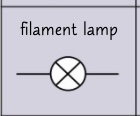
circuit symbol- filament lamp?
32
New cards
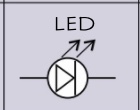
circuit symbol- LED?
33
New cards
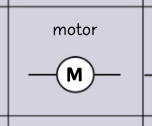
circuit symbol- motor?
34
New cards
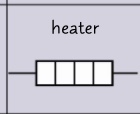
circuit symbol- heater?
35
New cards
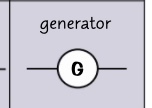
circuit symbol- generator?
36
New cards
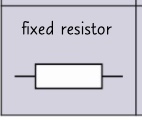
circuit symbol- fixed resistor?
37
New cards
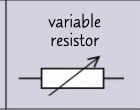
circuit symbol- variable resistor?
38
New cards
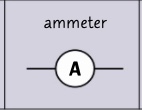
circuit symbol- ammeter?
39
New cards
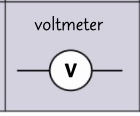
circuit symbol- voltmeter?
40
New cards
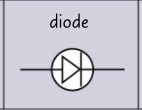
circuit symbol- diode?
41
New cards
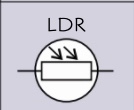
circuit symbol- LDR?
42
New cards
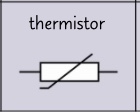
circuit symbol- thermistor?
43
New cards
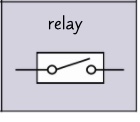
circuit symbol- relay?
44
New cards
light-emitting diodes:
* emit light when a current flows through them in the forward direction
* used for the numbers on digital clocks, traffic lights and in remote controls
* they don’t have a filament that can burn out
* emit light when a current flows through them in the forward direction
* used for the numbers on digital clocks, traffic lights and in remote controls
* they don’t have a filament that can burn out
what are LED’s?
45
New cards
a light dependant resistor is a special type of resistor that changes its resistance depending on how much light falls on it.
in bright light resistant falls
in dark light resistance is highest
LDR’s are great for electronic circuits and burglar detectors
in bright light resistant falls
in dark light resistance is highest
LDR’s are great for electronic circuits and burglar detectors
what is an LDR?
46
New cards
a thermistor is a temperature dependant resistor
in hot condition resistance decreases
in cold condition resistance increases
thermistor are useful in temperature detectors such as car engine temperature sensors, thermostats and fire alarms
in hot condition resistance decreases
in cold condition resistance increases
thermistor are useful in temperature detectors such as car engine temperature sensors, thermostats and fire alarms
what is a thermistor?
47
New cards
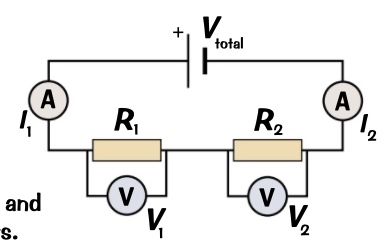
* different components are connected in a line end to end from positive to negative expect for voltmeter as it is in parallel
* if you remove a component the circuit is broken
* this is not good for example fairy light
* if you remove a component the circuit is broken
* this is not good for example fairy light
what happens in a series circuit?
48
New cards
* bigger supply p.d when more cells are in series
* current is the same everywhere
* total p.d of the supply is shared between components
* the p.d for each component depends on its resistance
* total resistance of the circuit depends on the number of components and the type of the components used
\
* current is the same everywhere
* total p.d of the supply is shared between components
* the p.d for each component depends on its resistance
* total resistance of the circuit depends on the number of components and the type of the components used
\
what happens to p.d, current and resistance in series?
49
New cards
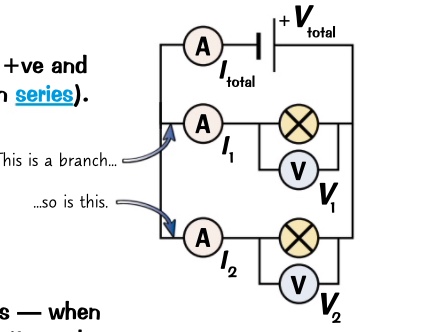
* each components is separately connected to the +ve and -ve of the supply
* if you remove a component circuit still works
\
* if you remove a component circuit still works
\
what happens in parallel circuit?
50
New cards
* p.d is the same across all branches
* current is shared between branches
* total current flowing around the circuit = to the total of all the currents through the separate component
* the current through a branch depends on the resistance of the branch
* the higher the resistance the harder it is for charge to flow
* total resistance decrease if second resistor is added in parallel
* current is shared between branches
* total current flowing around the circuit = to the total of all the currents through the separate component
* the current through a branch depends on the resistance of the branch
* the higher the resistance the harder it is for charge to flow
* total resistance decrease if second resistor is added in parallel
what happens to p.d, current and resistance in parallel ?
51
New cards

what is the formula relating charge current and time?
52
New cards
it transfers energy
* energy is supplied to the charge at the power source
* the charge gives up this energy when it falls thought any voltage drop in components
* the bigger the change in voltage the more energy is transferred
* a battery with a bigger voltage will supply more energy to the circuit for every coulomb of charge h
* energy is supplied to the charge at the power source
* the charge gives up this energy when it falls thought any voltage drop in components
* the bigger the change in voltage the more energy is transferred
* a battery with a bigger voltage will supply more energy to the circuit for every coulomb of charge h
what happens when a charge drops through a voltage?
53
New cards
energy transferred = charge x voltage
energy transferred = charge x current x resistance
energy transferred = charge x current x resistance
what are the 2 formulas for energy transferred?
54
New cards
live, neutral and earth
what are the 3 wires in a plug?
55
New cards
only live and neutral are usually needed but if something goes wrong the earth wire stops you from getting hurt
which 2 wires are mostly needed?
56
New cards
the live wire alternates between a HIGH +VE AND -VE VOLTAGE of 230v
what does the live wire alternate?
57
New cards
0V
what is the voltage for neutral wire?
58
New cards
through the live wire and the neutral wire
which 2 wires does electricity flow through?
59
New cards
for safety and they work together
what is the earth/fuse/circuit breaker for?
60
New cards
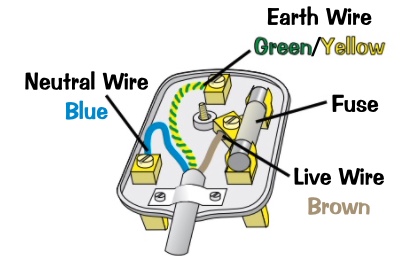
plug labelled with wires
61
New cards
must be ‘earthed’ to reduce the danger of electric shock.
must be attached to an earth wire
earthed conductor can never become live
must be attached to an earth wire
earthed conductor can never become live
what do all appliances with metal cases must have?
62
New cards
means that if the appliance has a plastic casing and no metal parts are showing
plastics are an insulator so it stops a current flowing.
anything with double insulation doesn’t need an earth wire- just a live and neutral
plastics are an insulator so it stops a current flowing.
anything with double insulation doesn’t need an earth wire- just a live and neutral
what does double insulated mean?
63
New cards
prevent fires and shock.
what do earthing and fuses prevent?
64
New cards
the case is earthed so a big current flows through the live wire, the case and the earth wire
if a fault develops in which the live wire touches the metal case what happens?
65
New cards
the surge in current blows and melts the fuse which cuts of the live supply.
this isolates the whole appliance making it impossible to get an electric shock .
prevents the risk of fire caused by the heating effect of a large current
this isolates the whole appliance making it impossible to get an electric shock .
prevents the risk of fire caused by the heating effect of a large current
what does the surge in the current do?
66
New cards
Circuit breakers are an electric safety device used in some circuits.
like fuses they protect the circuit from damage if too much current flow.
like fuses they protect the circuit from damage if too much current flow.
what are circuit breakers?
67
New cards
they break the circuit by opening a switch.
what happens when circuit breakers detect a surge in current in a circuit?
68
New cards
when an electric current passes through them.
\
\
when do resistors get hot?
69
New cards
* electrons collide with ion in the lattice that makes up the resistor
* this gives ions energy which causes them to vibrate and heat up
* heating effect increases resistor resistance
* less current greater voltage
* heating effect causes components in the circuit to melt circuit will stop working
* the circuit will melt and break if the current gets to high.
* this gives ions energy which causes them to vibrate and heat up
* heating effect increases resistor resistance
* less current greater voltage
* heating effect causes components in the circuit to melt circuit will stop working
* the circuit will melt and break if the current gets to high.
how do the resistor get hot?
70
New cards
electrical power is the rate at which an appliances transfers energy
what is electric power?
71
New cards
transfers a lot of energy in a short time.
an appliances with a high power rating transfers what?
72
New cards

watts W
what is power measured in? formula
73
New cards

electrically
\
\
how do electrical appliances transfer energy? formula
74
New cards
like charges repel opposite charge attract
what do like charges do?
75
New cards
conductors conduct charge insulators don’t
conductors are usually metal like copper and silver
insulators example like plastic and rubber
conductors are usually metal like copper and silver
insulators example like plastic and rubber
what do conductors do?
76
New cards
friction
what causes static charges?
77
New cards
* polythene and acetate rods being rubbed with a cloth duster
* electrons move from the duster to the rod
* rod becomes negatively charged and the duster is left with an = positive charge
* when acetate rod is rubber electrons move from the rude to the duster
* duster becomes -ve and rod has =+ve
* electrons move from the duster to the rod
* rod becomes negatively charged and the duster is left with an = positive charge
* when acetate rod is rubber electrons move from the rude to the duster
* duster becomes -ve and rod has =+ve
investigation of static electricity?
78
New cards
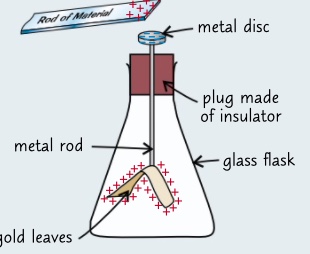
* you can see where a material is charged by using a gold leaf electroscope
* a gold leaf electroscope has a metal disc connected to the metal rod at the bottom of which are attached 2 thin pieces of gold leaf
* when a road with a charge is brought near the disc electrons will either attract or repel depending on the charge
* both gold leafs will have the same charge so they will repel each other causing them to rise
* when the rod is taken away the gold leaves will discharge and fall again
* a gold leaf electroscope has a metal disc connected to the metal rod at the bottom of which are attached 2 thin pieces of gold leaf
* when a road with a charge is brought near the disc electrons will either attract or repel depending on the charge
* both gold leafs will have the same charge so they will repel each other causing them to rise
* when the rod is taken away the gold leaves will discharge and fall again
gold leaf electroscope experiment?
79
New cards
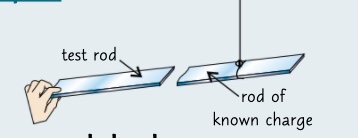
* suspend a road with a know charge on a thread and see if there is a repulsion or attraction when the rod you’re testing is brought close to it
* if there is an attraction then the test road has the opposite charge to the suspended rod
* if there is a repulsion then the test rod has the same charge as the suspended rod
* if there is an attraction then the test road has the opposite charge to the suspended rod
* if there is a repulsion then the test rod has the same charge as the suspended rod
suspending a charged rod experiment
80
New cards
a van de Graaff generator is sued to demonstrate electrostatic charge.
made of a rubber melt moving round plastic rollers underneath a metal dome
an electrostatic charge is built up.
the human body conducts charge like charges repel so the charges will spread out through your body and makes your hair stand up
made of a rubber melt moving round plastic rollers underneath a metal dome
an electrostatic charge is built up.
the human body conducts charge like charges repel so the charges will spread out through your body and makes your hair stand up
what is a van de graaff?
81
New cards
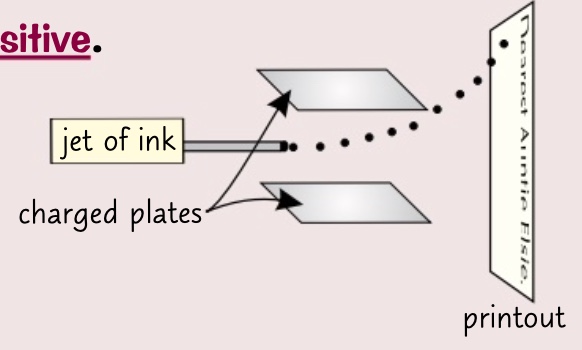
* tiny droplets of ink are forced out of a fine nozzle making them electrically charged
* the droplets are deflected as they pass between 2 metal plates
* a voltage is applied to the plates one negative and one positive
* the droplets are attracted to the plate of the opposite charge and repelled from the plate with the same charge
* the size and direction of the voltage across each plate change so each droplet is deflected to hit a different place on the paper
* lots of tiny dots make up your printout
* the droplets are deflected as they pass between 2 metal plates
* a voltage is applied to the plates one negative and one positive
* the droplets are attracted to the plate of the opposite charge and repelled from the plate with the same charge
* the size and direction of the voltage across each plate change so each droplet is deflected to hit a different place on the paper
* lots of tiny dots make up your printout
what happens an inkjet printer?
82
New cards
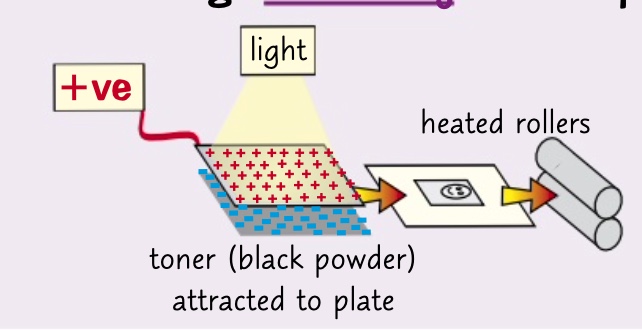
* the image plate is positively charged. an image of what you’re copying is projected onto it.
* whiter bits of what your copying make light fall on the plate and the charge leaks away in those places
* the charged bits attract negatively charged black powder which is transferred onto positively charged paper
* the paper is heating so the powder sticks
* and there is a photocopy
* whiter bits of what your copying make light fall on the plate and the charge leaks away in those places
* the charged bits attract negatively charged black powder which is transferred onto positively charged paper
* the paper is heating so the powder sticks
* and there is a photocopy
what happens in a photocopier?
83
New cards
when synthetic clothes are dragged over each other or over your heat electrons get scraped off leaving static charges on both parts which leads to the attraction and they stick together. little sparks and shock form as the charges rearrange themselves.
what happens when clothing crackles?
84
New cards
rain drops and ice bump together inside storm clouds knocking offf electrons and leaving the top of the cloud positively charged and the bottom of the cloud negative.
this creates a huge voltage and a big spark
this creates a huge voltage and a big spark
what happens in lightning?
85
New cards
as fuel flows out of of a filler pipe static can build up
this can easily lead to a spark and in dusty or fumy places
so do risk the hazard of a BOOM they make the nozzles out of metal so that the charge is conducted away instead of building up
there are also earthing straps between the fuel tank and the fuel pipe
this can easily lead to a spark and in dusty or fumy places
so do risk the hazard of a BOOM they make the nozzles out of metal so that the charge is conducted away instead of building up
there are also earthing straps between the fuel tank and the fuel pipe
what happens when someone is putting fuel in?