4.4 Reflection, Refraction & Total Internal Reflection
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Reflection
When a wave hits a boundary between two materials, bouncing off the surface in a new direction.
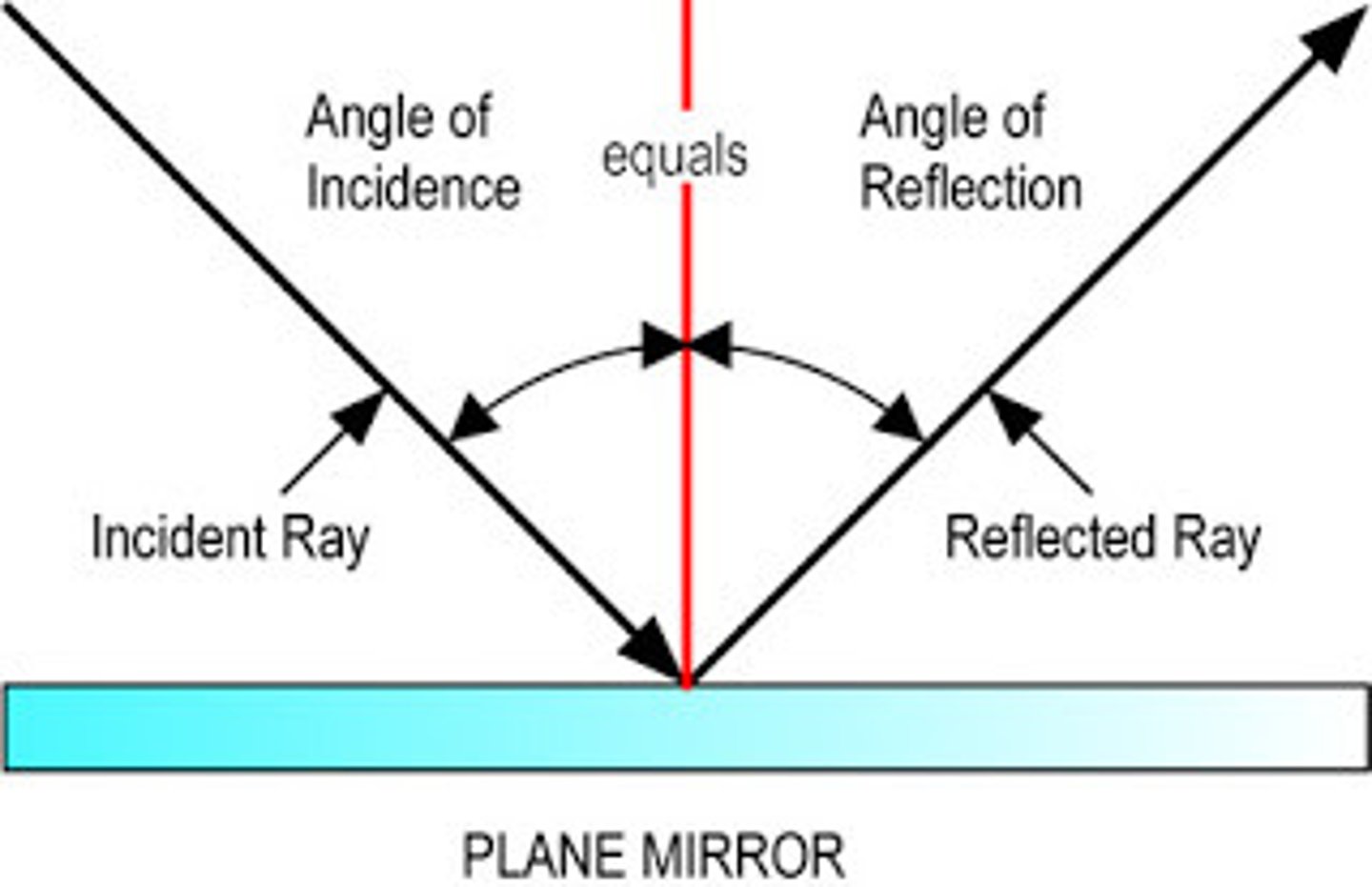
What does the law of reflection state?
angle of incidence = angle of reflection
Angle of Incidence (i)
The angle at which a wave strikes a surface.
It is equal to the angle of reflection
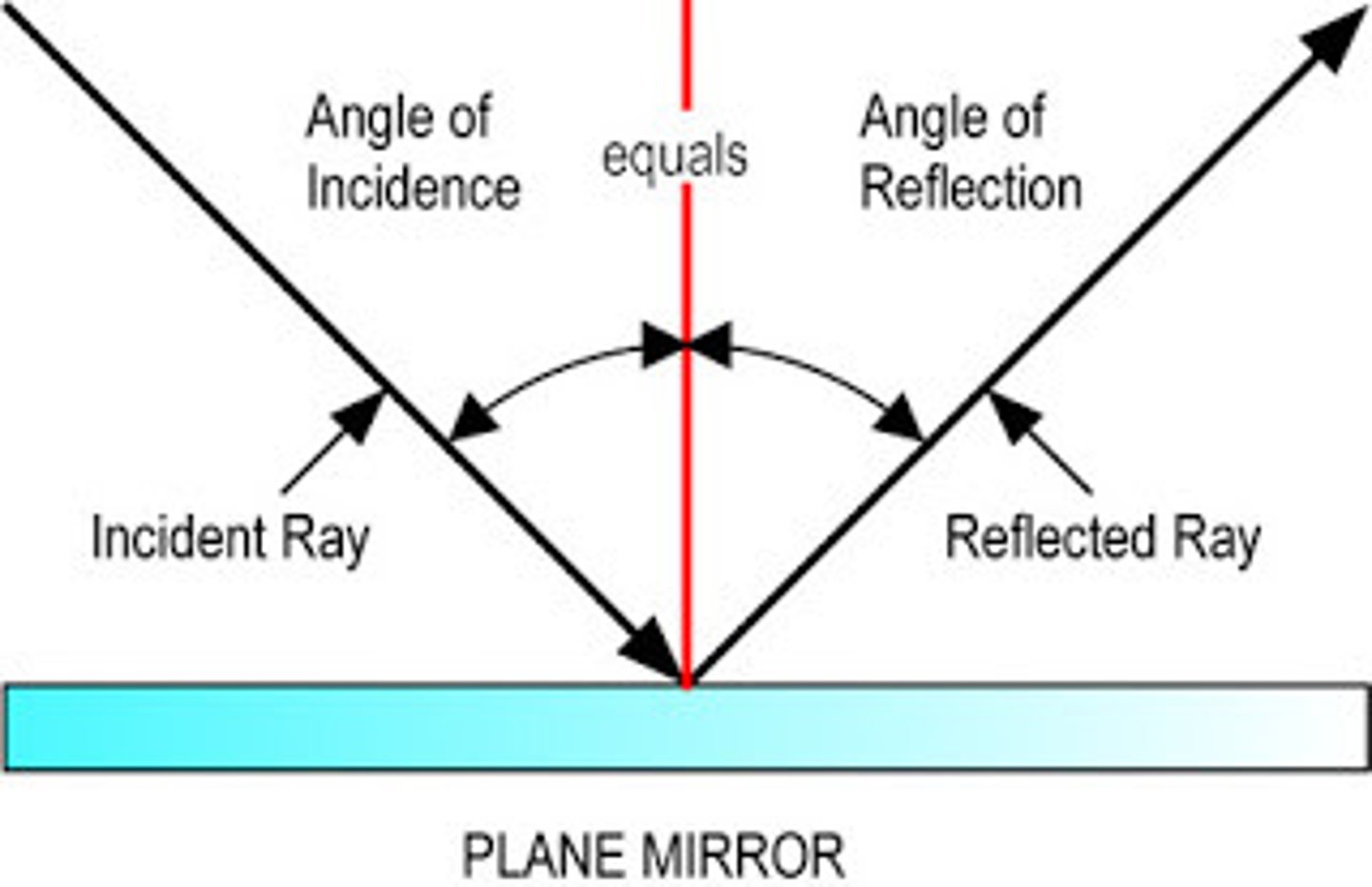
Angle of Reflection (r)
The angle at which a wave bounces off a surface
It is equal to angle of incidence
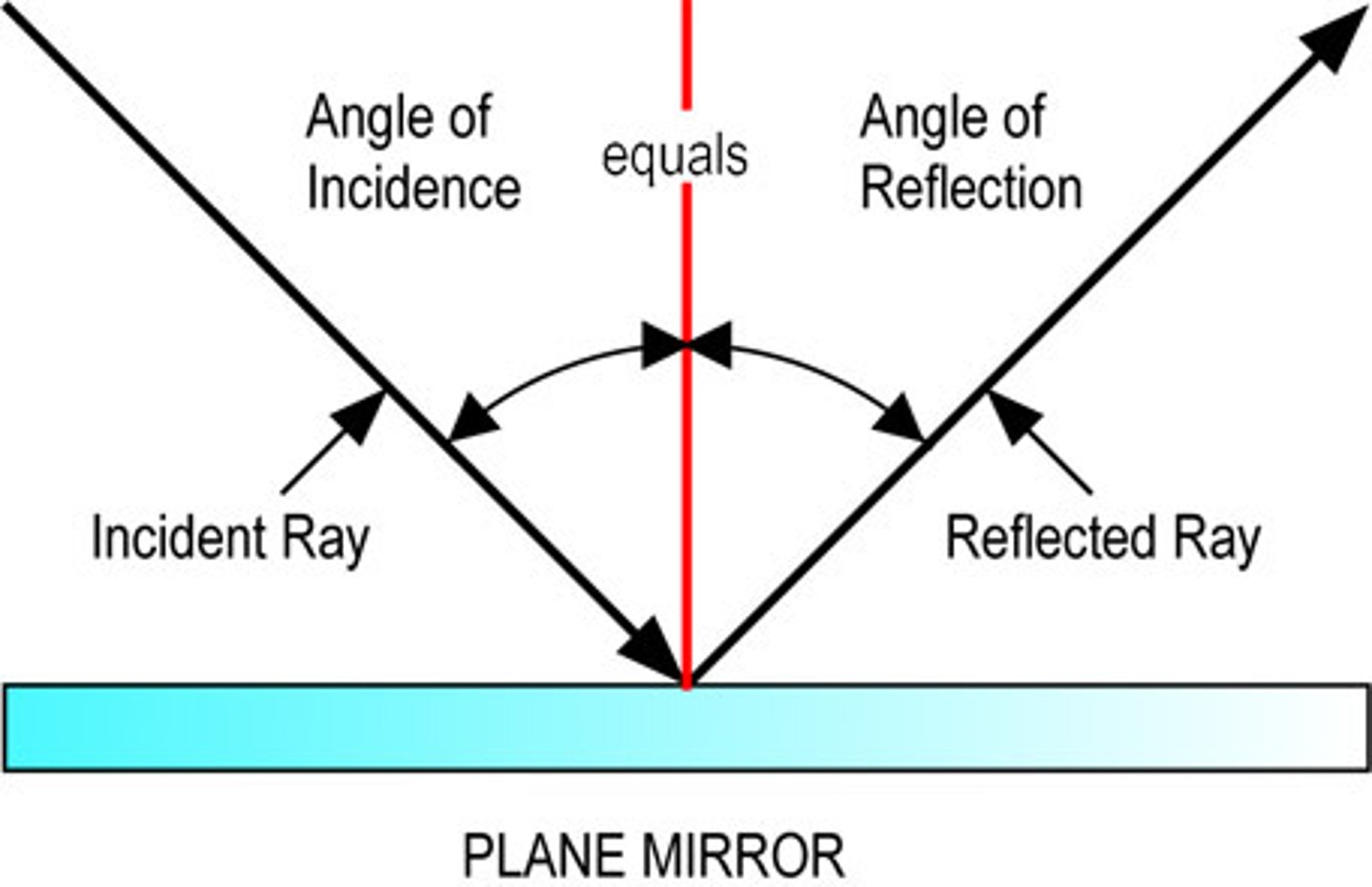
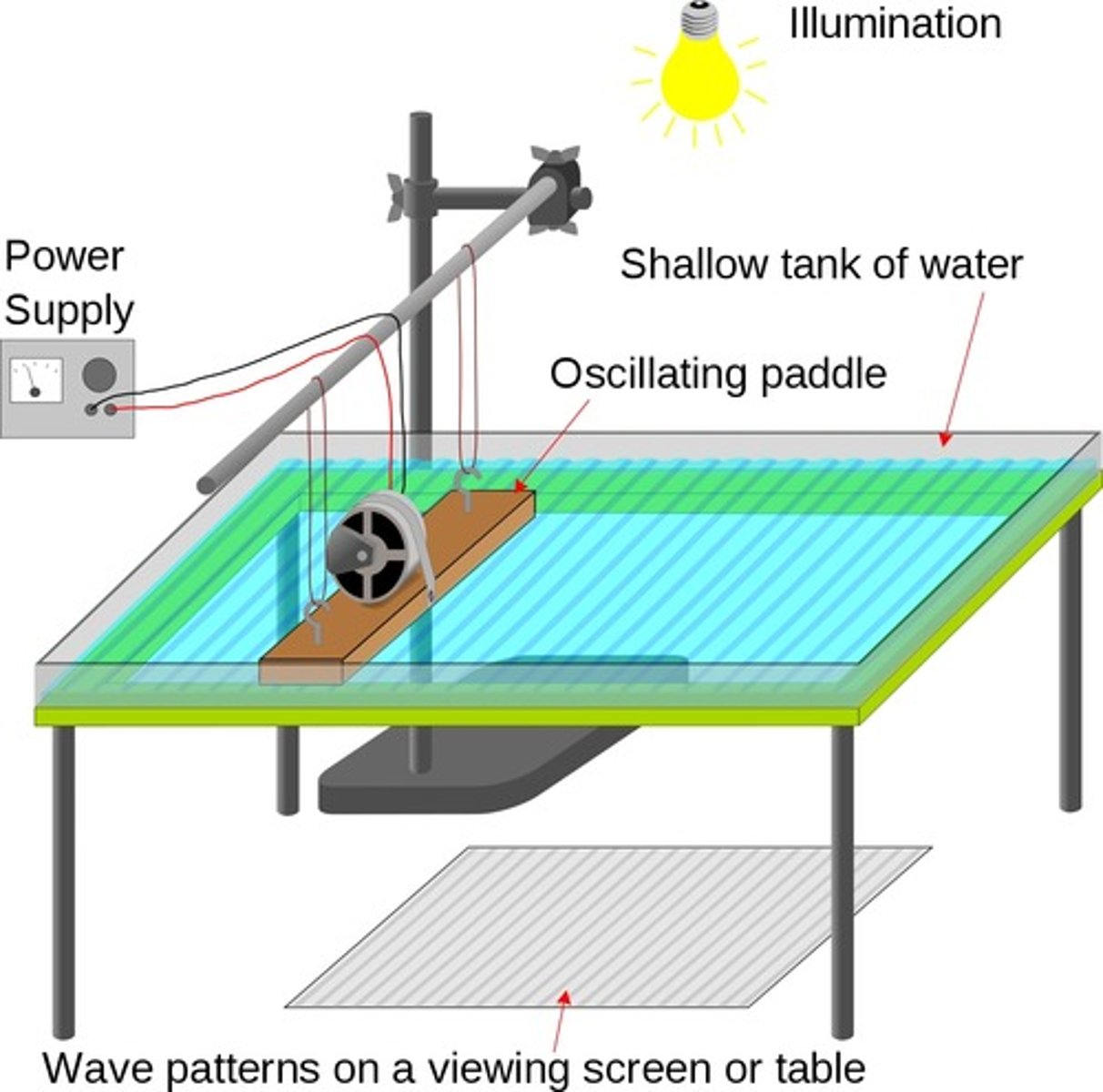
Observing Reflection - Water Waves
In a ripple tank, straight wavefronts reflect off a barrier. The waves bounce back at the same angle they hit the surface, showing that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. This demonstrates how reflection works for waves.
Observing Reflection- Ray Box
A ray box shines a narrow light beam onto a flat mirror. The incident ray reflects off the mirror, and the reflected ray is observed. The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, showing the law of reflection for light waves.
Refraction
When a wave changes speed and direction.
If a wave speeds up it refracts away from the normal, if it slows down it refracts toward the normal
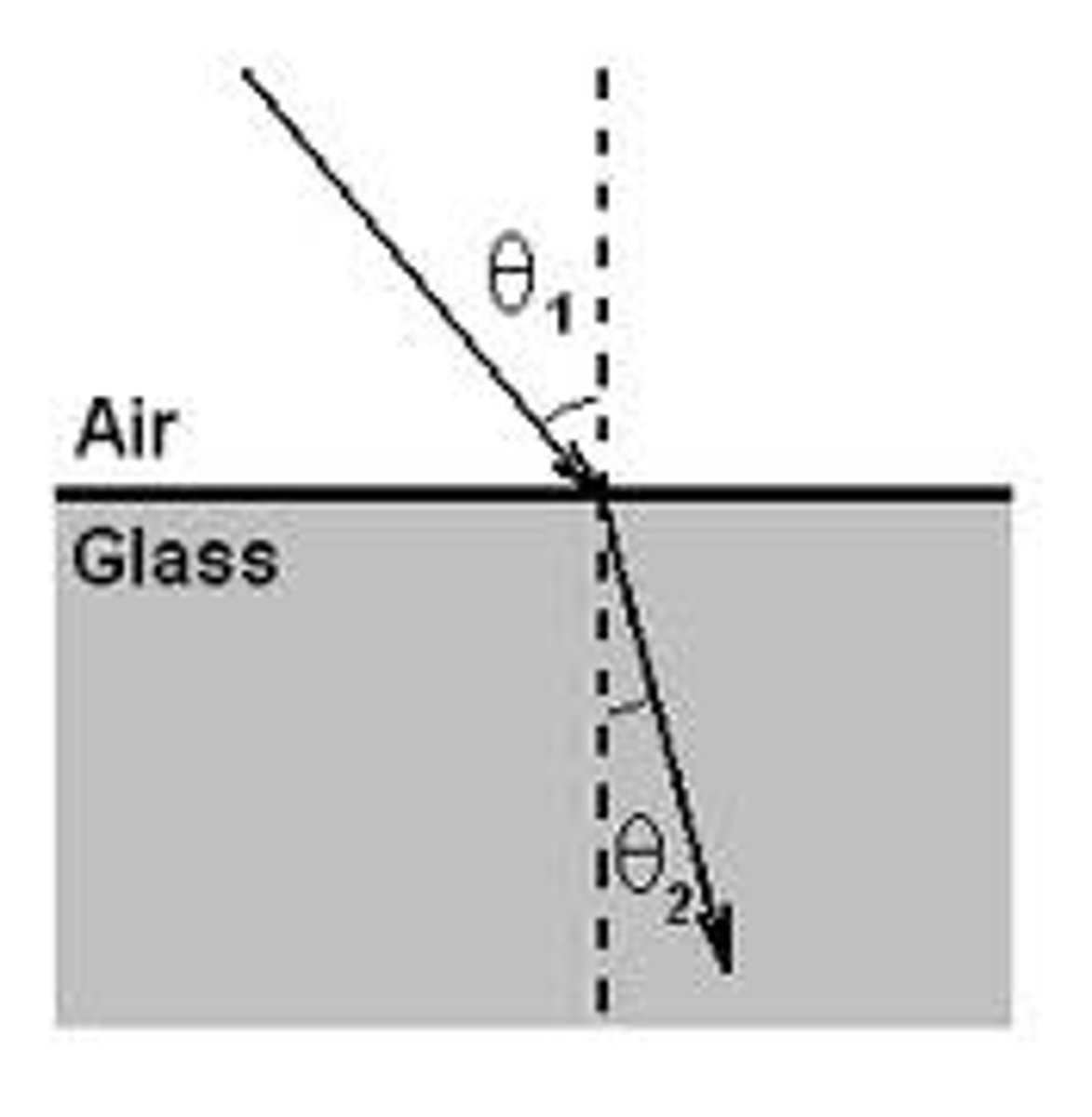
Snell's Law of Refraction
Snell's Law explains how light bends when it passes from one material to another.:
n₁ sinθ₁ = n₂ sinθ₂
Where:
n₁ and n₂ are refractive indices
θ₁ is the angle of incidence
θ₂ is the angle of refraction
It explains how light bends when moving between different materials.
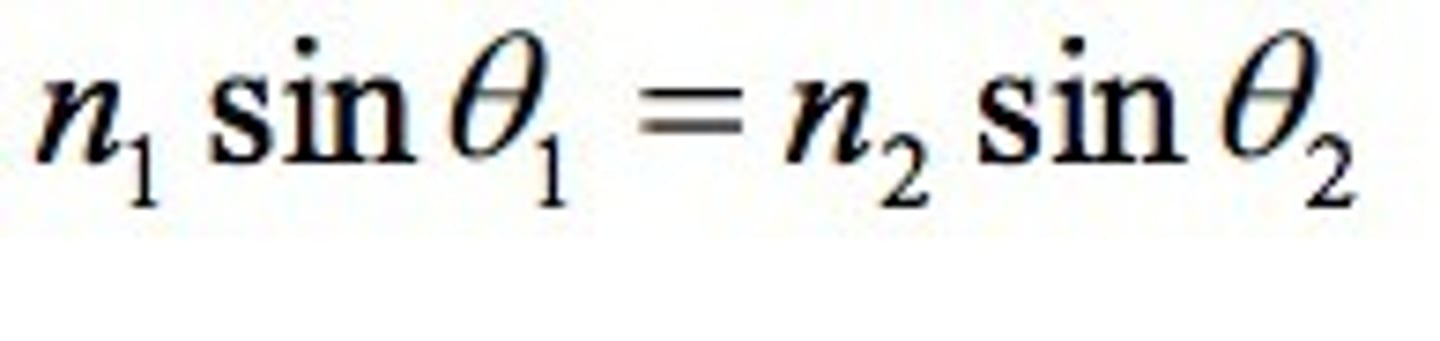
Refractive index equation
n = c/v
What is total internal reflection?
Total internal reflection occurs when light moves from a more optically dense medium to a lower optically dense medium.
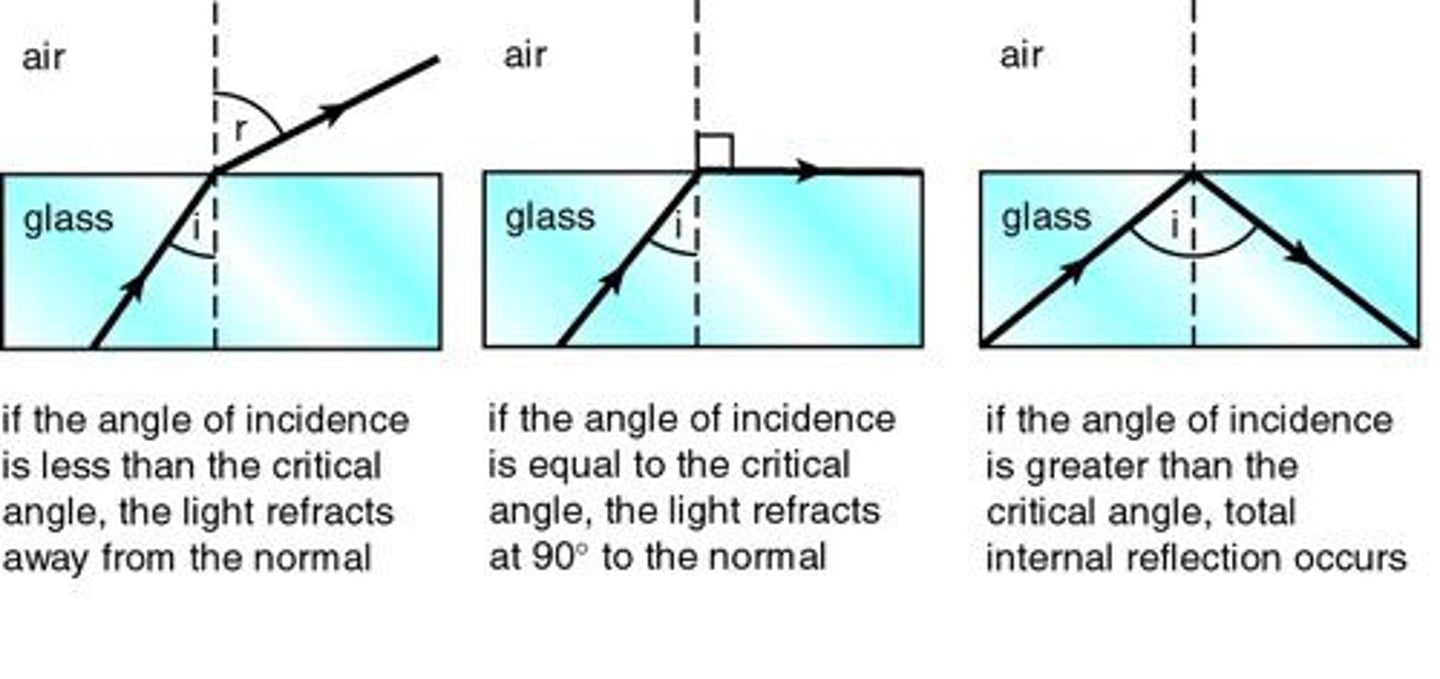
What happens if the angle of incidence is less than the critical angle?
Light refracts away from the normal as it enters the material with a lower refractive index.
What occurs when the angle of incidence is equal to the critical angle?
The light refracts at an angle of refraction of 90°.
What happens if the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle?
The light totally internally reflects and all light reflects back into the original medium.
What is the relationship between the angle of reflection and the angle of incidence?
The angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence.
How does the critical angle depend on the refractive index of the material?
As the refractive index (n) increases, the critical angle (θc) decreases.
What is the effect of higher refractive indices on critical angles?
Materials with higher refractive indices have lower critical angles for total internal reflection.
Critical Angle Equation
sinC= 1/n