Near East & Egypt
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Sumer of the Sumerians
Moden day Iraq; 4100-1750 BCE
First in Neolithic Revolution & writing, irrigation, math, THE WHEEL TIME
City-state & theocracy → rulers were gods’ representation on Earth → god in charge of making political decisions the ruler/king
Wrote Epic of Gilgamesh - tale of Uruk King

“White Temple and Ziggurat” Uruk (Iraq); Sumerian; c. 3000 BCE
Context: located at center of city; pop. of over 40K; theocracy; like Templo Mayor
Bent Axis Plan
Control crowd & monitor entry - only for elites
Force the viewer to admire the architecture
Slae labor - like Inca
Ziggurat (plinth) - 2 functions
closer to the gods
separate from the profane world
Assuroam for“raised up”
like Templo Mayor and Lakshmana Temple
Made to look like nearby mountains where Gods supposedly lived
Lakshmana Temple
Spiritual belief: deity (most likely Anu of the sky) would descend into temple & talk to king to make political decisions (king goes in alone) -theocracy
Oriented towards cardinal points NSEW
INTERIOR:
Sacred Space
Small & Dark (controls light)
Foundation deposits of leopard and lion bones → indicated that there were likely animal sacrifices
Bitumen coated canals - flowing water into in center

“Eshnunna Votive Figures” c. 2700 BCE; Sumerian; Gypsum inlaid with shells and black limestone
Visual:
EYES are emphasized (for 2 theorized reasons)
eyes are alert & active to PRAY ALL DAY (pray for patron)
They are looking at deity itself
Beard & clothing indicate status
Function - worship by proxy
Hands holding “libations” to offer to the god
Context - buried beneath floor in Abu’s temple (fertility god)
references earlier practice of burying people under the house
Mat’ls, such as the shell, used in the eyes to make it them look wet and alive

Standard of Ur” Sumerian; c. 2500 BCE; Wod inlaid with shell, lapis lazuli, and red limestone
Context - found in tomb w/ treasure. lapis is symbol of status
Visuals - blue for royalty, hierarchy of the individual (larger, more ornate clothing), narrative organized by registers
Peace side and war side - dual nature of ruler
Babylon 1800 BCE - 1000 BCE
“Gate of the Gods”
Cite-State
Cuneiform writing
Largest city in world - 200000 people
Conquered territories thrived under Hammurabi

“Stele of Hammurabi” Babylon; Iran; c. 1750 BCE; Basalt stone
First code of laws - 292 in cuneiform → enforced social hierarchies
Hammurabi entering supernatural world (like Lady Xoc) and receiving the code from Shamash (sun god of justice, flames coming from shoulder
the one sittin is Shamash
Figures in high relief, composit stance
Rod and ring - building tools, power symbols
Early foreshortening - diagonal lines in beard
Cuneiform is written in Akkadian, the conquered language → shows dominance
Over 7 feet tall
Hammurabi is a pious theocrat, and these are not his laws, he is just the administer of divine justice
Copied several times & placed in conquered cities for PROPAGANDA
Displayed in temples honoring Shamash
Assyria circa 2500 BCE - 600 BCE
Takes over Babylon

“Lamassu” Citadel of Sargon II; Assyrian; Alabaster Stone; c. 720 BCE
Context: placed at entrance of city; anthropomorphic, part bull, part human
Function: Guard the city at the entrance
Monolith! → such a feat of engineering that they told stories of it in relief carvings
Contrast of smooth skin and textured wings/hair
Blends strength and beauty (dual nature of rulers)
5 legs -both rigid AND in motion
the rigid legs symbolize that is is judging you, and if it deems you worthy to pass, you can see the diagonal leg. The diagonal leg symbolizes that it is walking away
Iconoclasm - exploded by ISIS
Persian Empire
Conquers Babylon
AKA Archaemenid Empire
Persepolis is the citadel complex
Perspepolis monumental architecture to legitimize rule and assert dominance. It followed the hypostyle hall design because it was filled with columns
Cyrus the Great - unprecedented tolerance for conquered cultures
Kings and religion ould be kept, but the kings must have less authority than him

“Audience Hall of Darius and Xerxes” Persian; Persepolis, Iran; c. 520 BCE; Limestone
Context: situated on high plateau to overlook the plain
dominance and visibility
Xerxes sacks Athenian Acropolis, Alexander the Great retaliates by destroying Persepolis
Content - reliefs show all conquered cultures (23) coming together to offer goods to ruler → shows harmony and submission, not war
Terraced construction - just like Machu Pichu
Also - advanced rain irrigation + sewage
Processional during persian New Year
Wide Stairwell - receives conquered cultures
Audience Hall:
Content: apadana (audience hall) that could hold 10k people, 72 collosal columns, had a roof
large gathering area for conquered cultures
Capitals on top of columns influnced by Greek and Egyptian columns
Bull = royalty
23 subjugated nations shown in relief carvings - clothing indicated country of origin
Egypt - Old Kingdom
Nile River- great for irrigation for crops → success
Pharaohs are believed to be demi-gods or divine
Focused more on building than writing
Contextual practice - new pharaoh moves and builds new capital city
Polytheistic
Too powerful priests led to disorder & collapse

“Palette of King Narmer” Egypt; 3000 BCE; Greywacke
Narmer unifies North & South Egypt—interlocked necks of lions (interlocking and unification of Egypt)
also wears white (Upper Egypt) and red (Lower Egypt) crown
King is young, strong, calm victor among chaotic casualties (seen in Last Supper too)
Enemies show nude (debasement) and barbarous (like Night Attack)
Organized by registers to show the sequence of battle
Function - huge eyeliner palette used during a ceremony, but for display, not a utilitarian purpose
Presence of Horace = divine favor (god of war)
Divine Narmer= barefoot on sacred ground and sacred war approved by Horace
King NEVER set foot on gorund
Smiting pose = ultimate power

“Seated Scribe” Saqqara; Egypt; Old Kingdom; c. 2500 BCE; painted limestone with crystal inlay (eyes) and wood (nipples)
Context - found in Pharaoh’s Tomb (not sure which)
Visual Characteristics -
fat around the middle represents high status
naturalistic
Eyes emphasized with the gemstone inlay and eyeliner. The lapis lazuli and shell also make them look alive and alert
Function - Houses the Ka spirit & serves the Pharaoh in the afterlife

“Great Pyramids at Giza” Egypt; Old Kingdom; c. 2550 BCE; Cut Limestone
Context - shape based on triangle symbol (ben ben) for Sun God Re; improvement on mastaba stepped tombs
Sun rays = ladders pharaohs use to ascend to heaven
Function = tomb for deceased rulers, also A DISPLAY OF POWER (control a ton of resources and labor)
Tomb for pharaohs Khufu, Khafra, and Menkaura
Oriented NSEW and faces east to the rising sun, a reference to agriculture
Necropolis = royalty

“King Menkaura and Queen” Gize, Egypt; Old Kingdom; c. 2490 BCE; Greywacke
Contex - found in Menkaura’s tomb at Giza; pharaohs are part-god
Queen = MAYBE Queen Khamerernebty
Function - substitute home for ka (spirit) and serves as his body in afterlife
king = idealized; Queen = naturalistic
Gender roles define - strong masculinity w/ soft femininityRigid in motion - foot extended, attempt to appear active
Stance - even distribution of weight (problem)
Great Sphinx
Portrays King (Khafre) as the sun god Re
Human intelligence + strength of beast
Divine Rule
Egypt - NEW Kingdom
1570 BCE - 1069 BCE
Expand empire thorugh military conquest, gains wealth
New capital - Thebes
Old Kingdom - pyramid tombs
New Kingdom- temples to honor rulers and gods
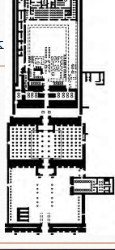
“Temple of Amun-Re” Karnak, Egypt; New Kingdom; c. 1550 BCE; Cut sandstone and brick
Statue f Amun (air) is bathed, dressed, given jewelry (like Shiva Nataraja & Jowo Rinpoche)
Central axis; Hypostyle hall
Created as a mound arising from sacred waters from beginning of time (like Borobudur temple)
Built by several different pharaohs over time, primarily Thutmose & Hatshepsut (like Forbidden City, which was built through Ming & Ching Dynasty)
Opet festival - agriculture exhausted gods and needed a fresh input of energy → surrounding area periodically flooded and people would get intentionally drunk
Problem - dark, sacred space with a lot of pillars and people are drunk → problem = people bump into columns
needs some light
SOLUTION - clerestory - windows at top allowing ofr illumination of the centre aisle, allowing ofr a focused light and not a flooding light because sacred spaces should be dark
Influence of the Clerestory seen in…
Forum of Trajan - Rome
Santa Sabina - Christianity
Southern Axis connects to Temple of Luxor Ram Heads Adorn Walkway (erase past ruler)
Relief carvings - Temple of Amun-Re
tradition of divine kings (youthful, calm victors)

“Mortuary Temple of Hatashepsut” New Kingdom Period, Egypt; 1470 BCE
One of the first female Pharaohs
New funerary ritual - temple to HONOR her, does NOT contain her body
Built into cliffside, symmetrical - stability/power
Central axis - order; oriented/points toward her addition to Temple of Amun-Ra in Karnak
Colonnade - row columns, tiny caves
Interior Artworks:
Divine rule - Horus present
Composite stance, idealized portraits
Holding libations for Gods
Shown both Masculine + feminine - goatee, flattened chest, softer face
Originally placed throughout kingdom for propaganda
New Kingdom - Armana Period
Context - Akhenaton takes thrown and THROWS AWAY all Egyptin tradition
Pharaoh portraiture becomes moe feminine and naturalistic (og = idealistic)
Declared one god - Aton (sun disc)

“Akhenaton and Family” NK Armana Egypt; c. 1340 BCE; Limestone
Traditional - divine pharaohs, relief carving; hieroglyphs
Innovation - intimate family portrait (more emotional), monotheistic - Aton sun, overlapping, no registers
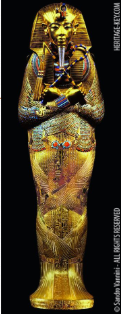
“Tutankhamun’s Tomb” NK c. 1323 BCE; Gold, enamel, precious stones
Context - Akhenaton is overthrown and Tut rules from 9-18
Return to tradition
Crook - shepard’s hook (shepard = pharaoh, sheep = ppl.)
Flail - weapon of submission
Flail + Crook = sigs of Osiris - god of afterlife
Dual nature of ruler
King Tut’s Death Mask:
Shows Pharaoh in his divine form
Believed to have gold skin, lapiz lazuli for hair, bones of silver
Coffin is covered with spell 151b from the Book of the Dead which guides the spirit through the afterlife

“Last Judgement of hu-Nefer” Page from the Book of the Dead; NK Egypt; c. 1275 BCE; Painted Papyrus Scroll
Context
Papyrus grew plentifully along Nile, tradition of writing on it
Scribes are high status
Function
Document Hu-Nefer’s worthiness
Historical document of ritual/belief
