2023 RxPrep Ch. 2 Basic Science Concepts
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain & Spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Somatic (efferent & afferent)
- Autonomic (sympathetic & parasympathetic)
The acetylcholine released from the parasympathetic division acts on muscarinic receptors scattered all across the body. The acronym SLUDGE describes the general effects.
- Salivation
- Lacrimation
- Urination
- Defecation
- Gastric motility
- Emesis
Antagonism
Competitive inhibition
Antagonist binds to the SAME receptor at the SAME active site as the endogenous ligand
Antagonism
Non-competitive inhibition
Antagonist binds to the SAME receptor but at a DIFFERENT site than the endogenous ligand (allosteric site)
Describe the effect of muscarinic receptor agonism in the body
SLUDGE
Describe the effect of muscarinic receptor antagonism in the body
anti-SLUDGE
Describe the effect of nicotinic receptor agonism in the body
Elevated HR & BP
Describe the effect of nicotinic receptor antagonism in the body
NM blockade
Describe the effect of ⍺1 receptor agonism in the body
Vasoconstriction & elevated BP
Describe the effect of ⍺1 receptor antagonism in the body
Vasodilation & decreased BP
Describe the effect of ⍺2 receptor agonism in the body
Decreased sympathetic output (lower BP & HR)
Describe the effect of ⍺2 receptor antagonism in the body
Increased sympathetic output (elevated BP & HR)
Describe the effect of β1 receptor agonism in the body
Increased myocardial contractility, CO, & HR
Describe the effect of β1 receptor antagonism in the body
Decreased CO & HR
Describe the effect of β2 receptor agonism in the body
Bronchodilation
Describe the effect of β2 receptor antagonism in the body
Bronchoconstriction
Describe the effect of DA receptor agonism/antagonism in the body
Renal, Cardiac, CNS effects, etc.
Describe the effect of 5-HT receptor agonism/antagonism in the body
Platelet, GI, Psychiatric effects, etc.
State the function of the following enzyme:
Acetylcholinesterase
Breaks down ACh
State the function of the following enzyme:
ACE
Converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II
State the function of the following enzyme:
COMT
Breaks down levodopa
State the function of the following enzyme:
COX
Converts arachidonic acid to prostaglandins (inflammation) & thromboxane A2 (PLT aggregation)
State the function of the following enzyme:
MAO
Breaks down catecholamines (DA, NE, EPI, 5-HT)
State the function of the following enzyme:
Phosphodiesterase (PDE)
Breaks down cGMP (smooth muscle relaxant)
State the function of the following enzyme:
Vitamin K epoxide reductase
Converts vitamin K to its active form that is required for the production of select clotting factors
State the function of the following enzyme:
Xanthin oxidase (XO)
Breaks down hypoxanthine & xanthine into uric acid
Hypertensive Crisis
Catecholamine excess
Serotonin Syndrome
Serotonin excess
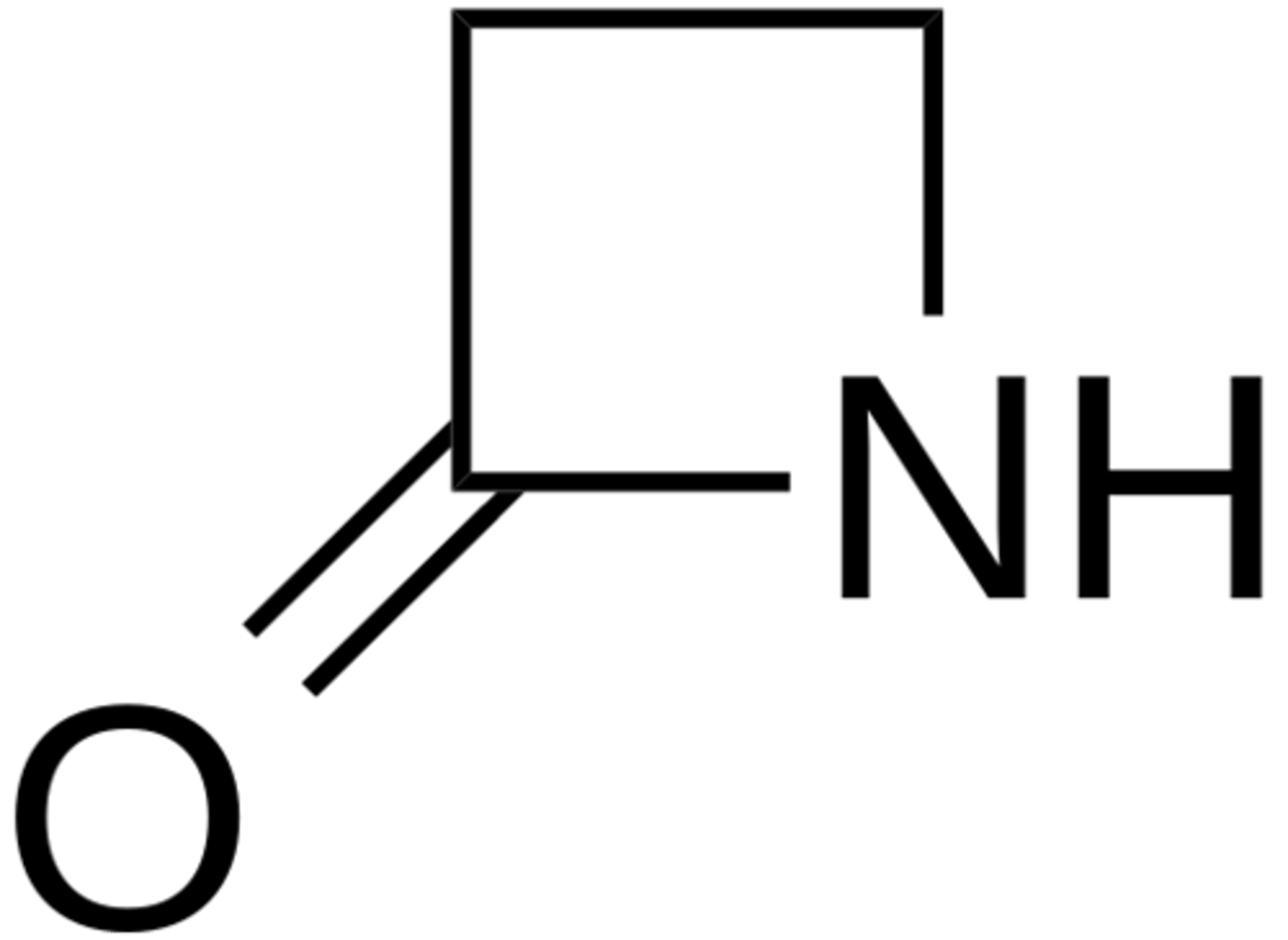
Beta-lactam structure
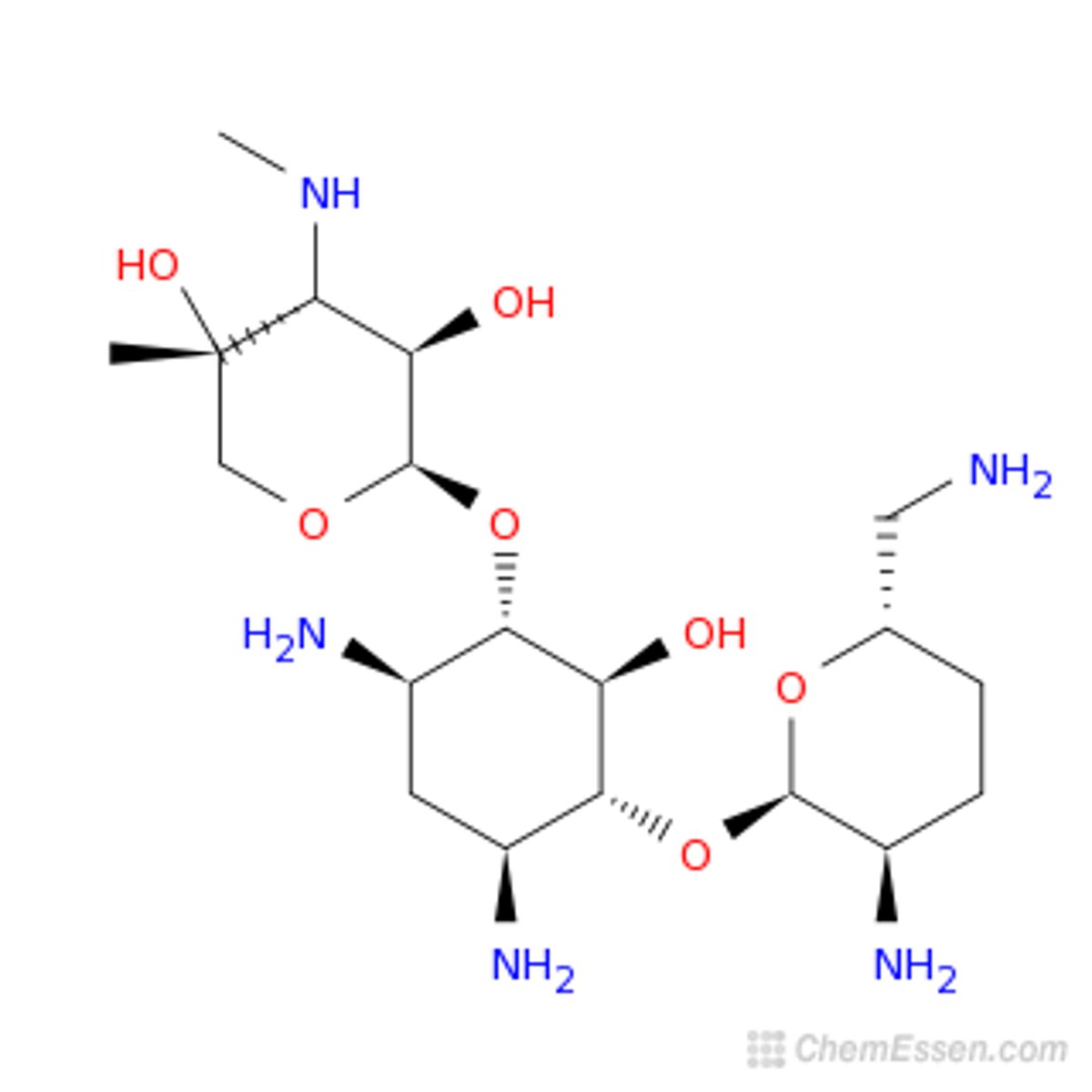
Gentamicin structure
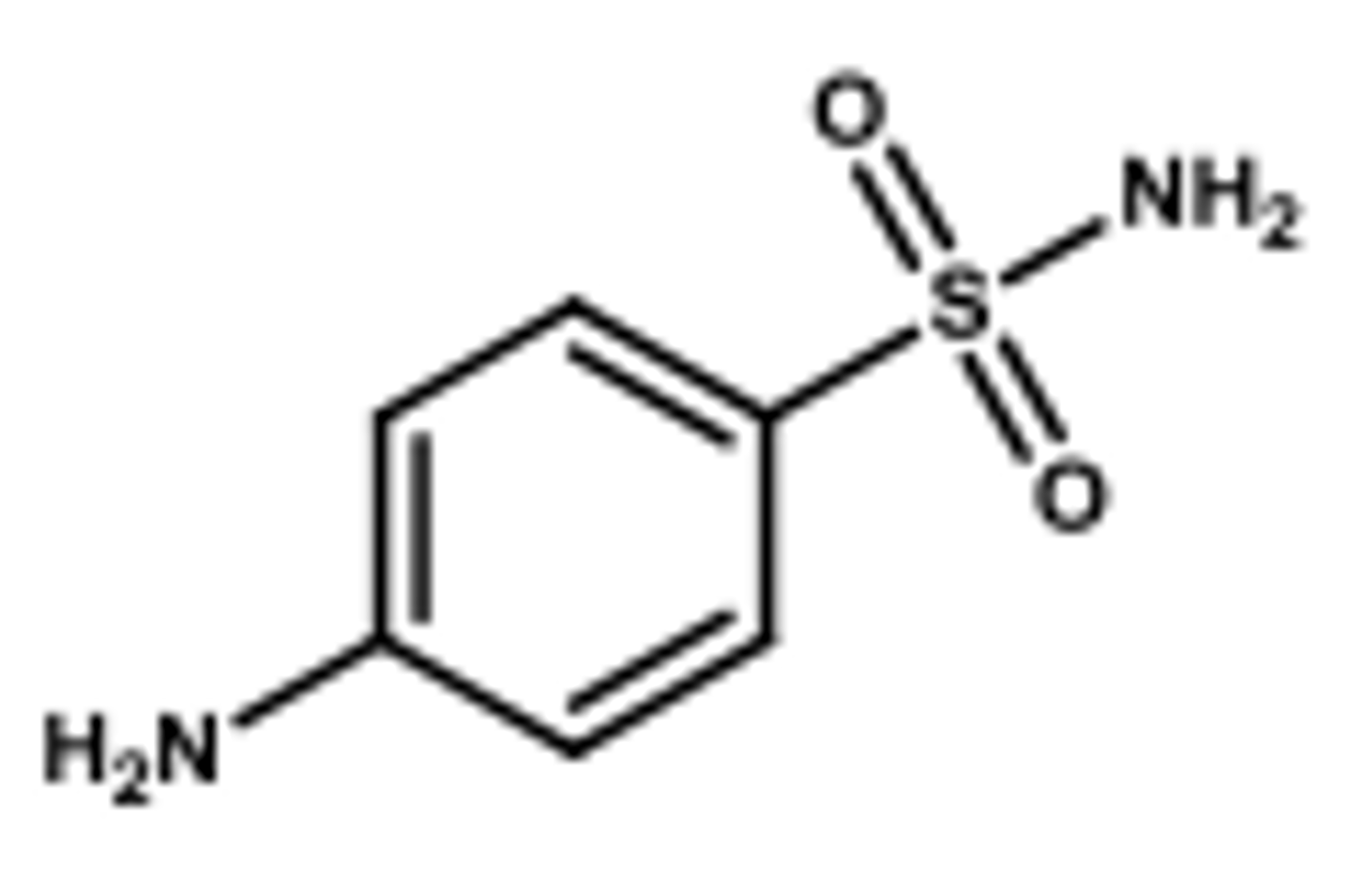
Sulfa drug structure
Aspirin structure
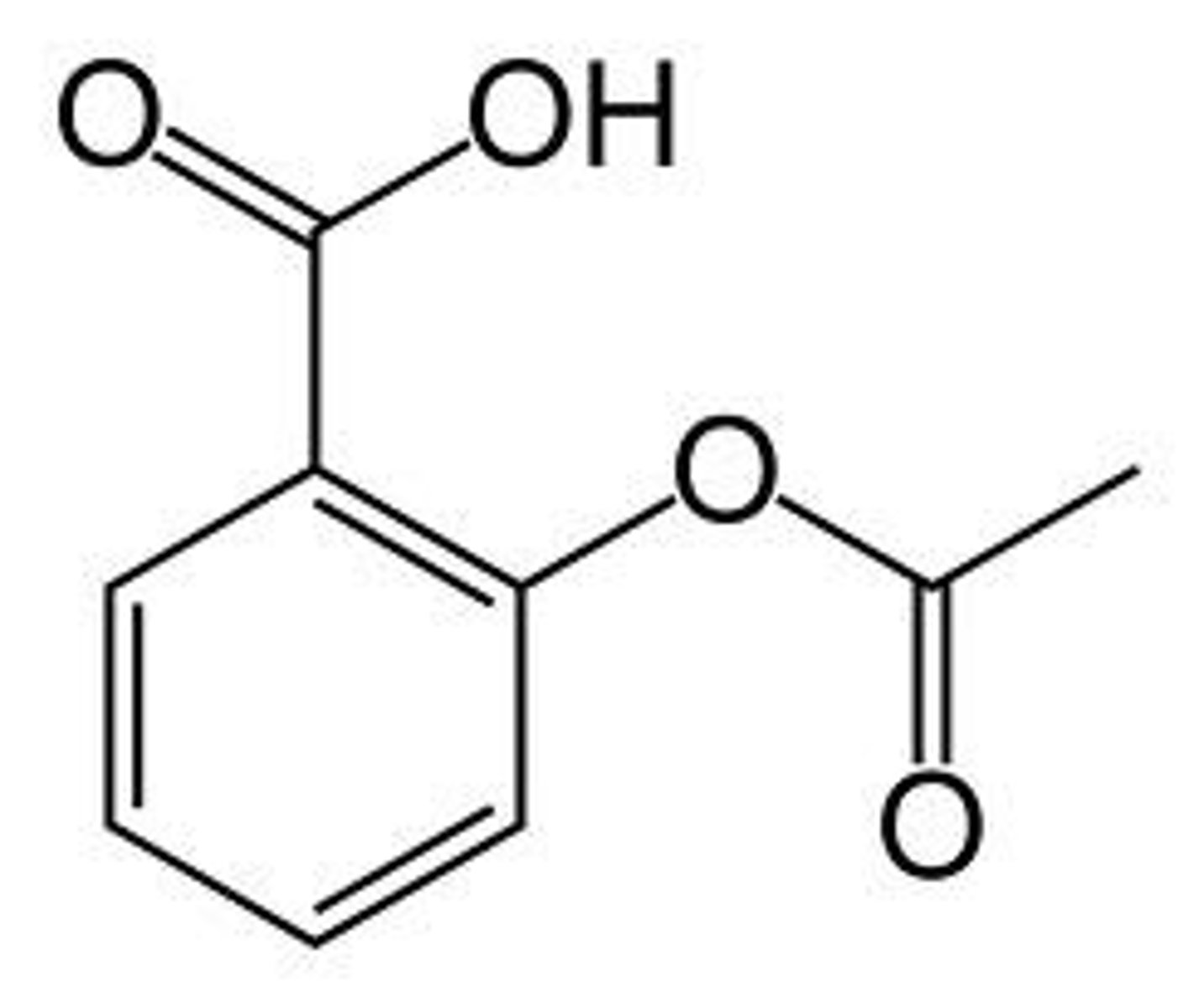
Ibuprofen structure
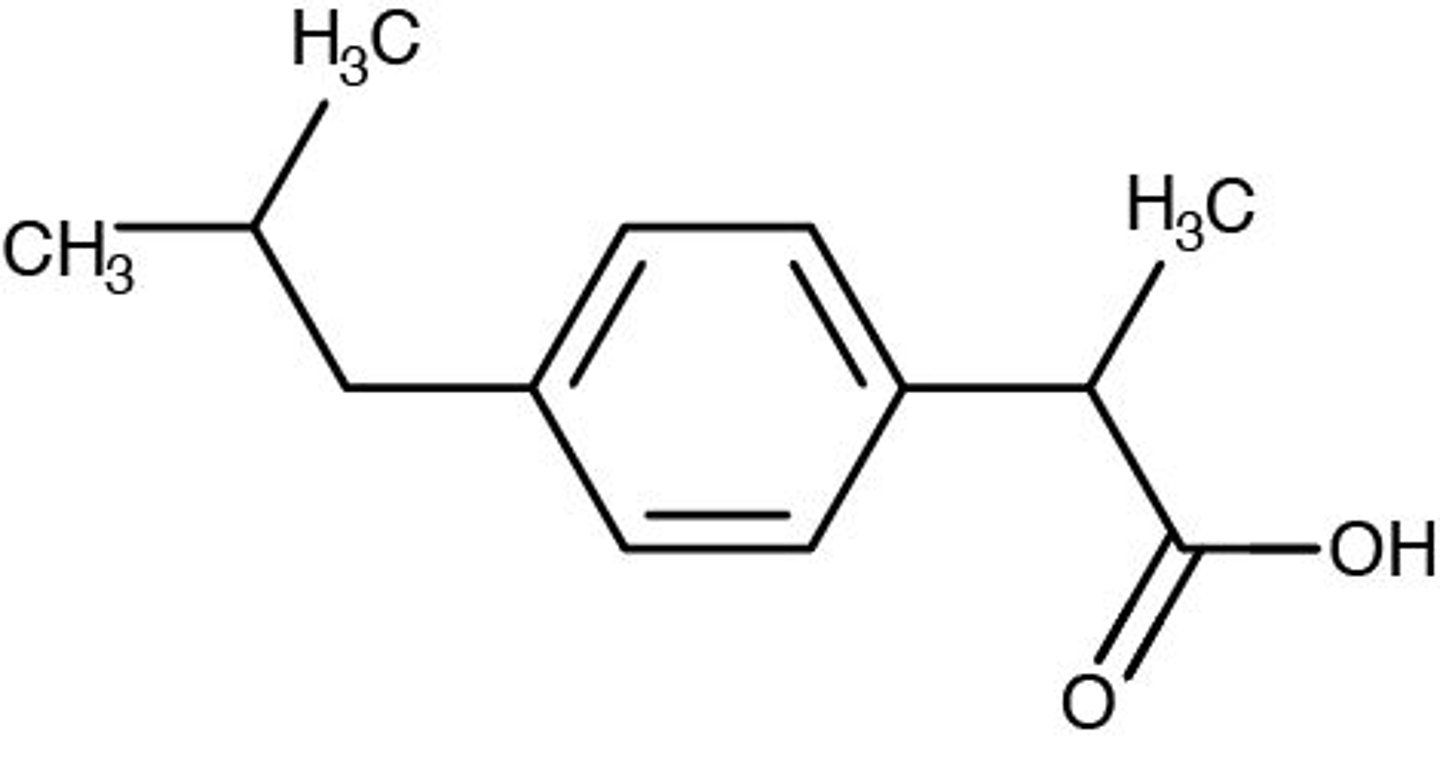
Levothyroxine structure
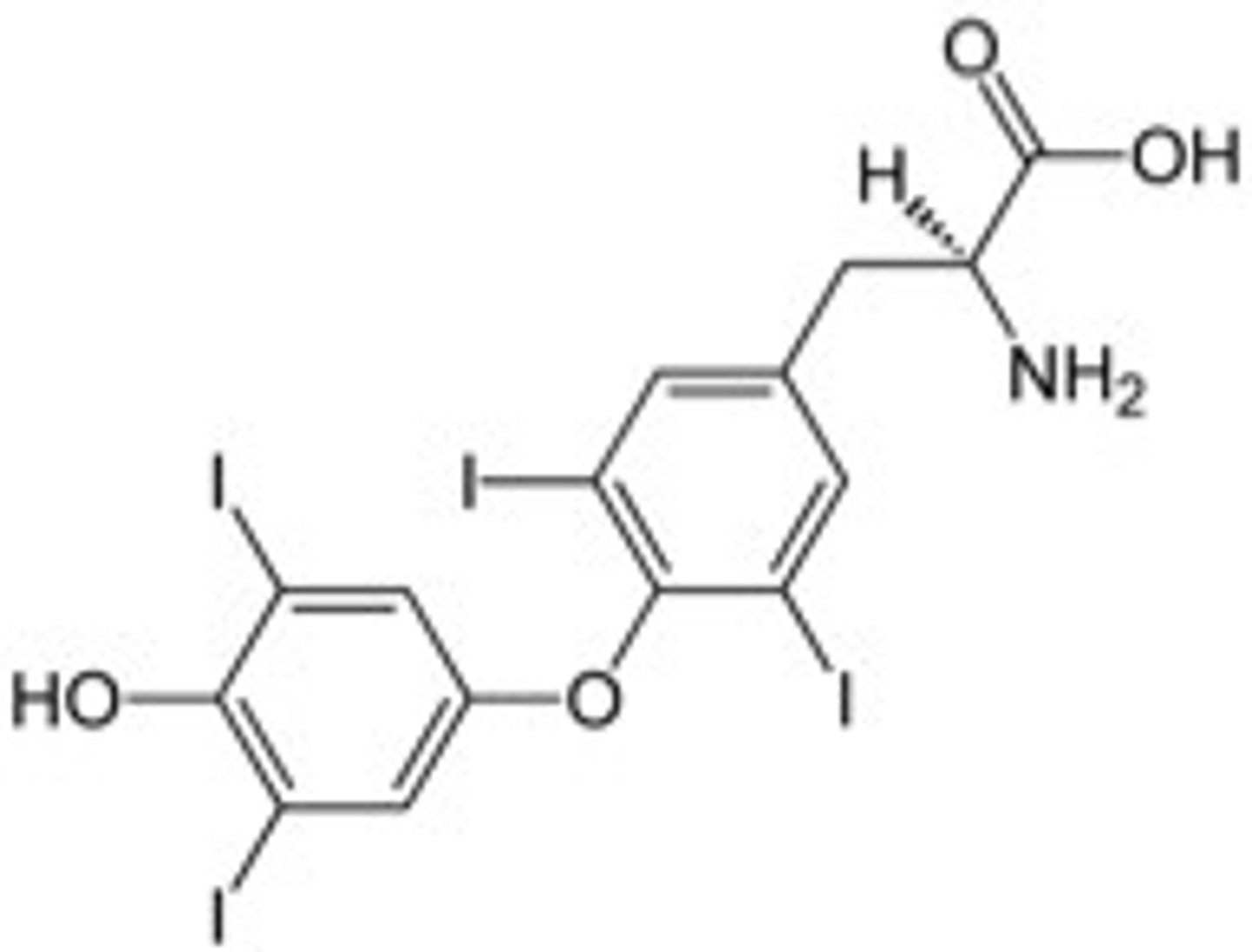
Amiodarone structure
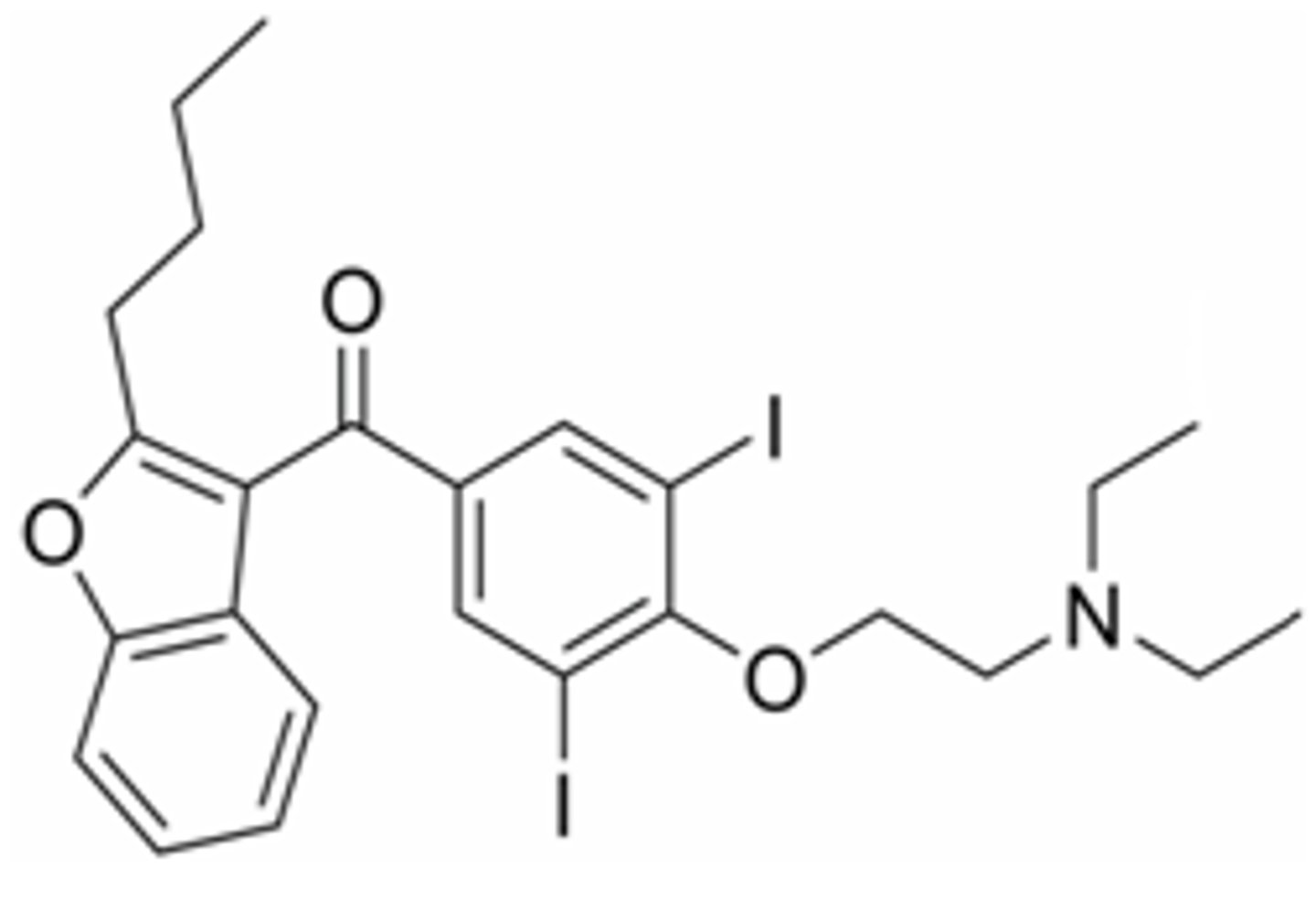
Fenofibrate structure
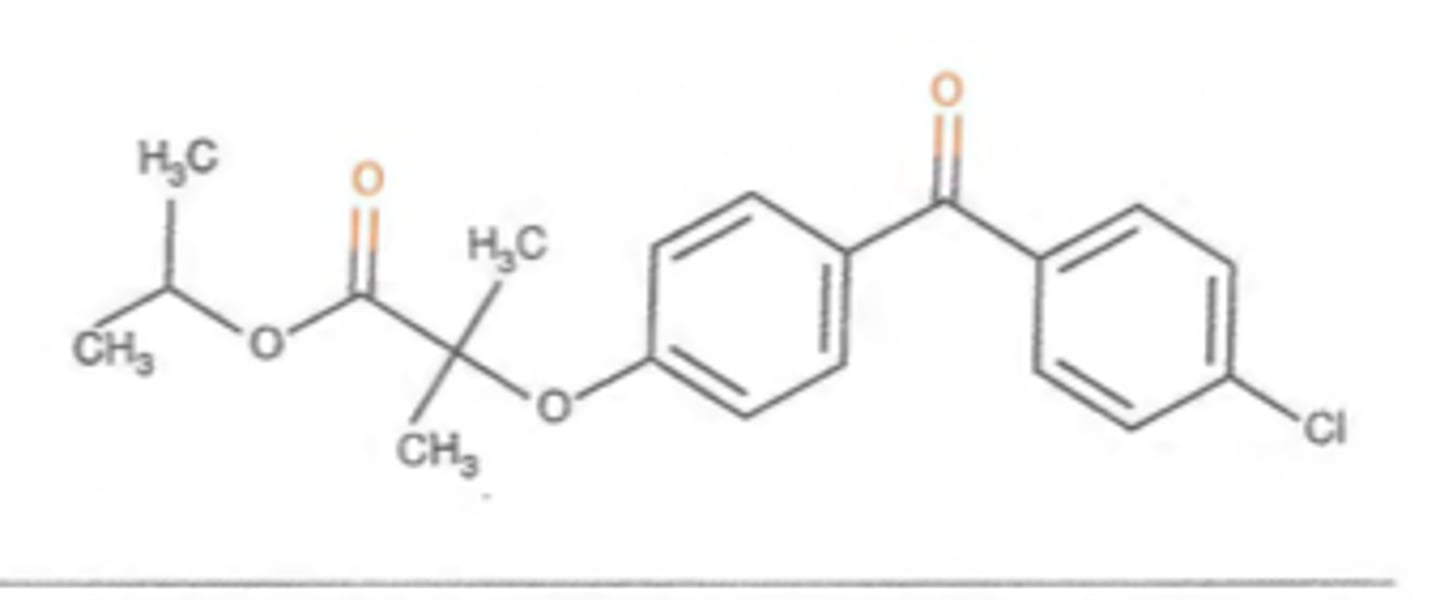
Amitriptyline structure
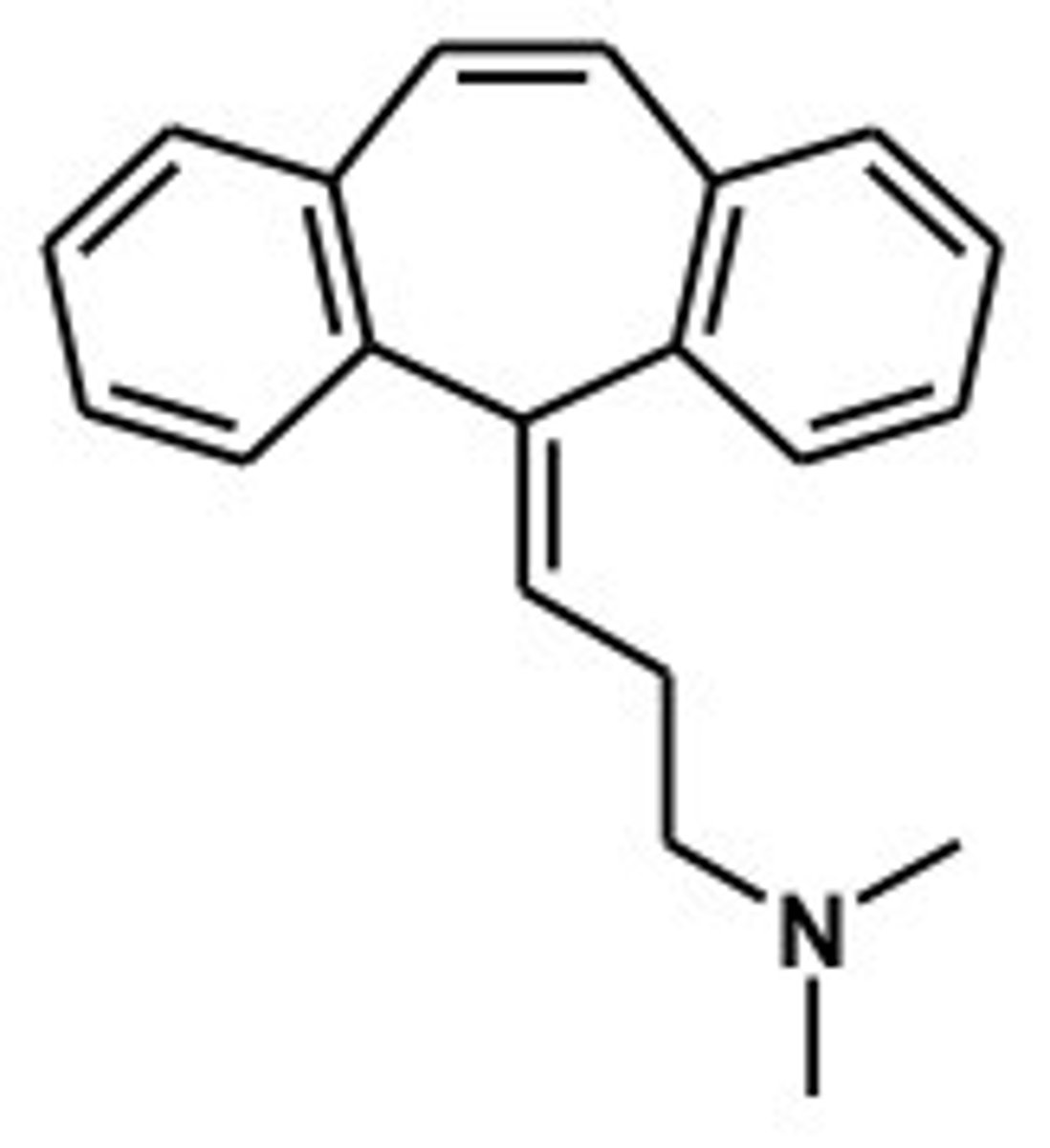
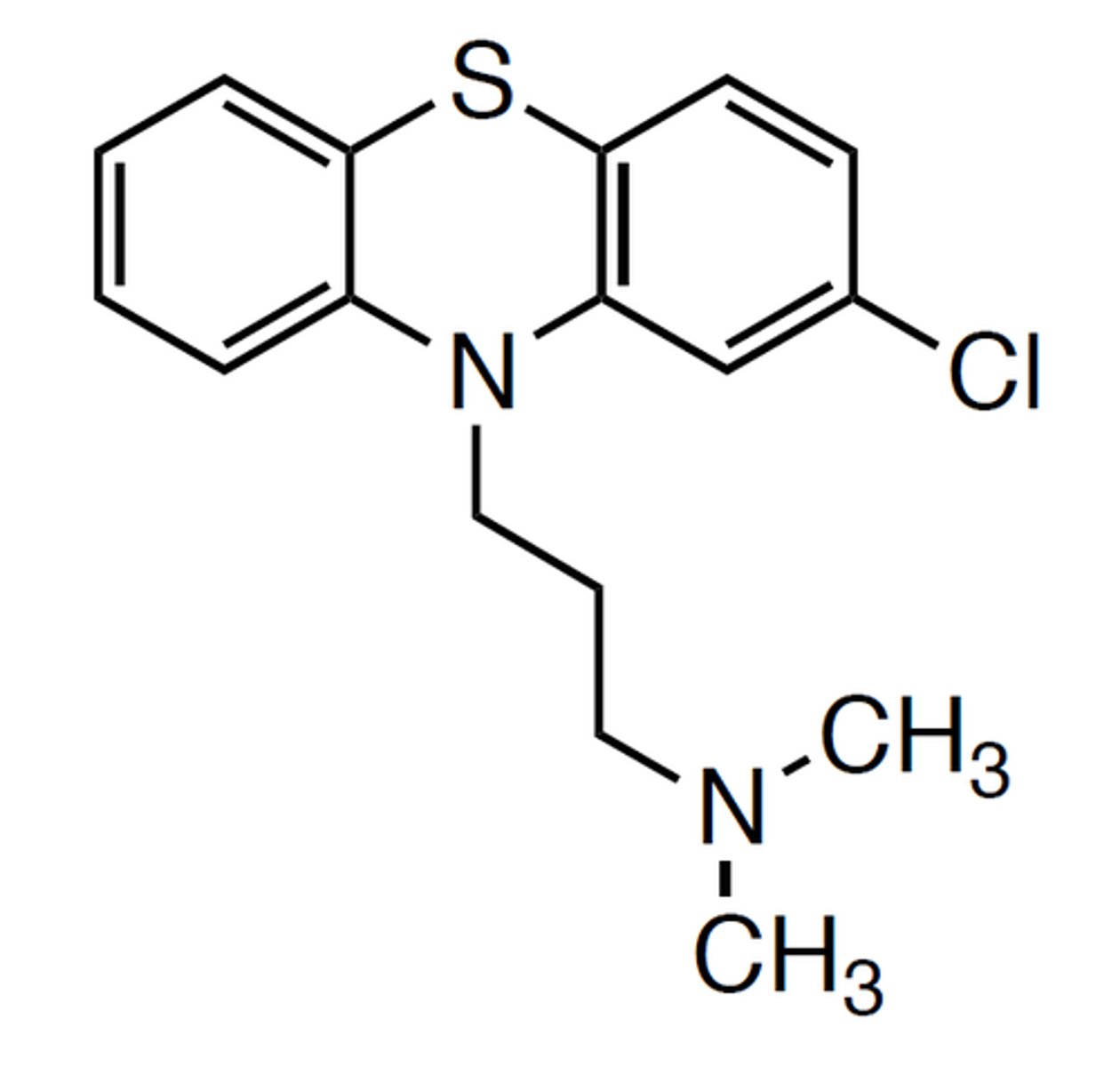
Chlorpromazine structure