Pediatrics
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
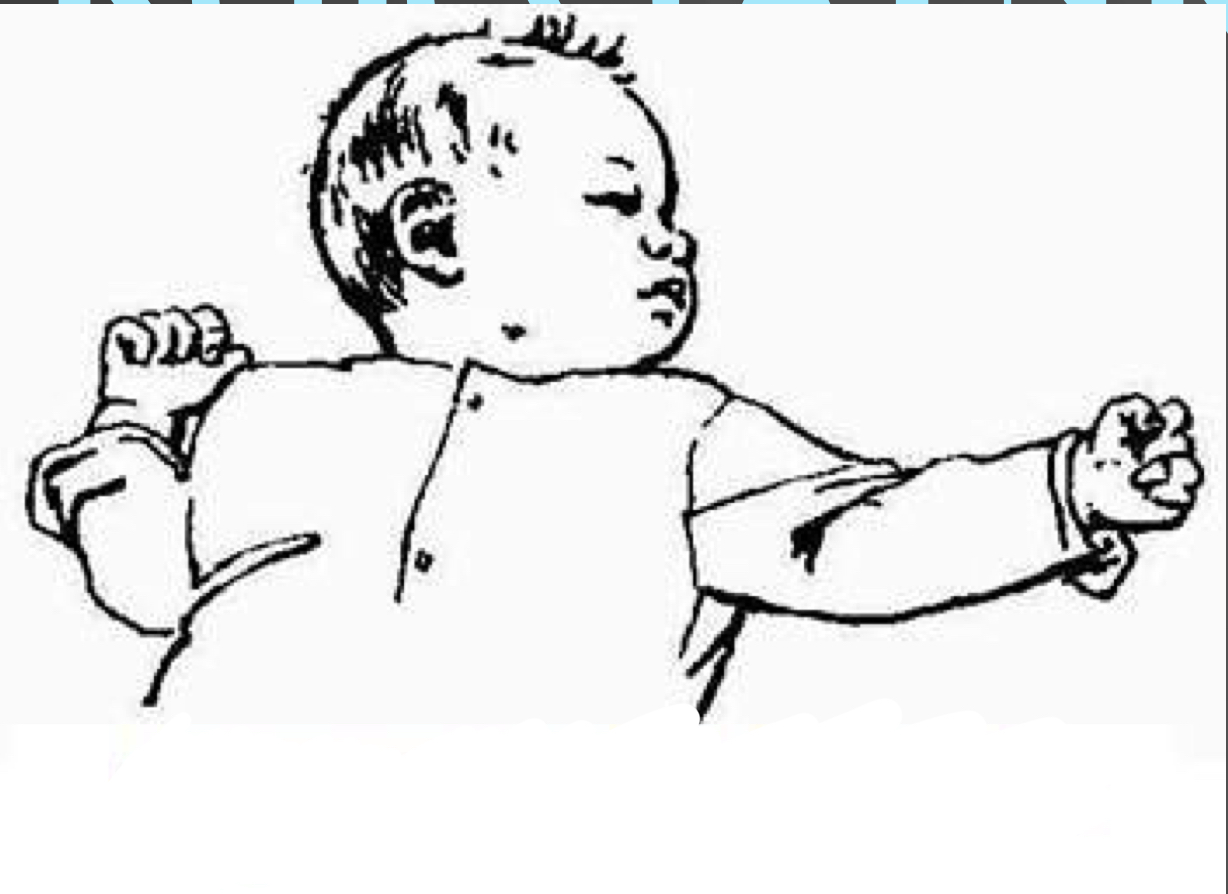

This is an example of what reflex…
Asymmetrical Tonic Neck Reflex (ATNR)
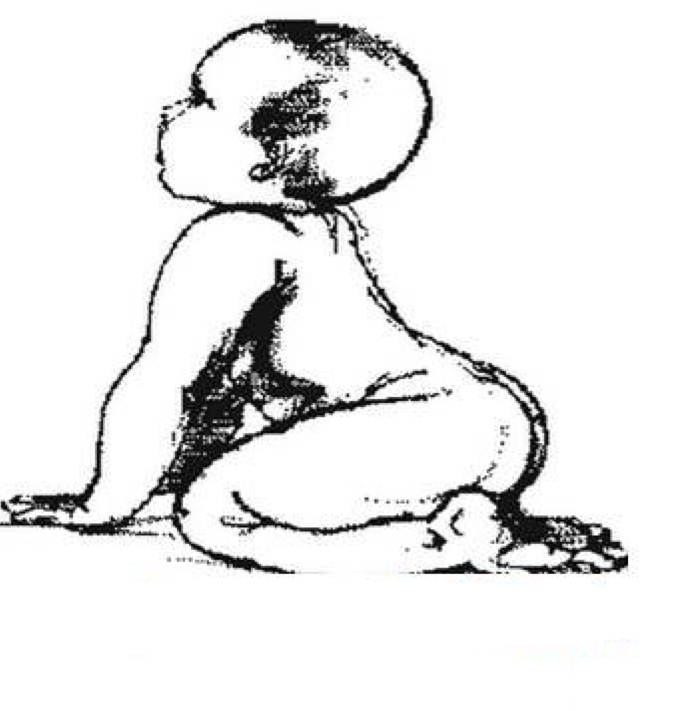

This is an example of what reflex…
Symmetrical Tonic Neck Reflex (STNR)
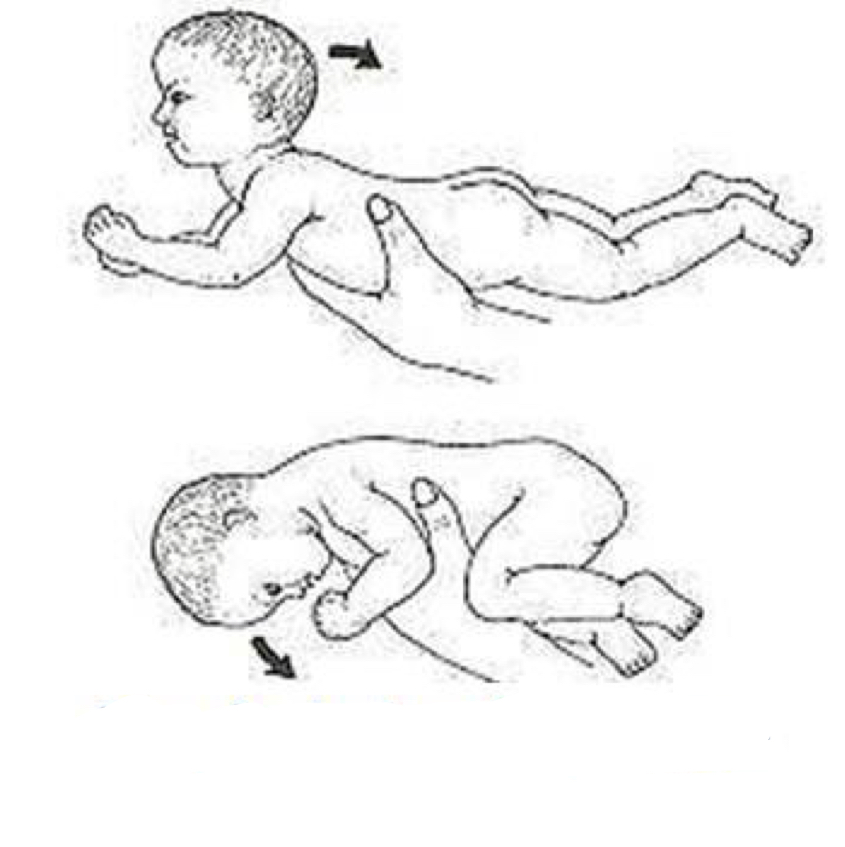
This is an example of what reflex…
Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex (TLR)
This is an example of what reflex…
Galant Reflex

This is an example of what reflex…
Rooting Reflex
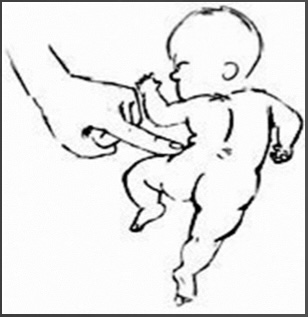
This is an example of what reflex…
Positive Support Reflex

This is an example of what reflex…
Palmar Grasp Reflex
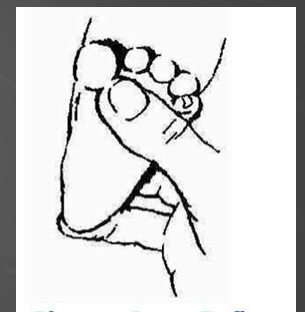
This is an example of what reflex…
Plantar Grasp Reflex

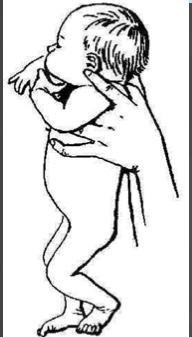
This is an example of what reflex…
Moro Reflex
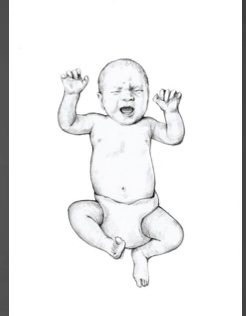
This is an example of what reflex…
Startle Reflex
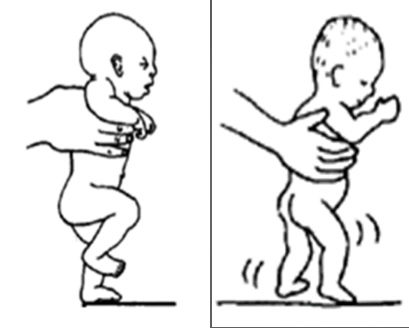
This is an example of what reflex…
Walking (Stepping) Reflex
Stimulus & Response:
Asymmetrical tonic reflex (ATNR)
Stimulus:
turn head to one side
Response:
same side arm/leg extend
Stimulus & Response:
Symmetrical tonic reflex (STNR)
Stimulus:
extend head/neck or flex head/neck
Response:
arms extend, legs flexed or legs extend
Stimulus & Response:
Doll-eye
Stimulus:
flex head
Response:
eyes looked up
Stimulus & Response:
Palmar grasping
Stimulus:
touch palm with object
Response:
hand closes
Stimulus & Response:
Moro
Stimulus:
shake head by tapping pillow
Response:
arms/legs extend, fingers spread, then arms/legs flex
Stimulus & Response:
Sucking
Stimulus:
touch face above or below lips
Response:
sucking
Stimulus & Response:
Babinski
Stimulus:
stroke sole of foot
Response:
toes extend
Stimulus & Response:
Searching, rooting
Stimulus:
touch cheek
Response:
head turns to stimulus
Stimulus & Response:
Palmar-mandibular (Babkin)
Stimulus:
apply pressure to both palms
Response:
mouth open, eyes close, head flexes
Stimulus & Response:
Plantar grasping
Stimulus:
stroke ball of foot
Response:
toes contract
Stimulus & Response:
Startle
Stimulus:
tap abdomen or startle infant
Response:
arms/legs flex
Reflex Timeframe:
ATNR
newborn - 4 months
Reflex Timeframe:
STNR
6 - 7 months
Reflex Timeframe:
Doll-eye
newborn - 2 weeks
Reflex Timeframe:
Palmar grasping
newborn - 4 months
Reflex Timeframe:
Moro
newborn - 3 months
Reflex Timeframe:
Sucking
newborn - 3 months
Reflex Timeframe:
Babinski
newborn - 4 months
Reflex Timeframe:
Searching, rooting
newborn - 1 year
Reflex Timeframe:
Palmar-mandibular (Babkin)
1 - 3 months
Reflex Timeframe:
Plantar grasping
newborn - 12 months
Reflex Timeframe:
startle
7 - 12 months
Age: Newborn - 1 month
Prone: lifts head briefly, heads to side, body flexion
Supine: body flexion, partially rolls to side
Sitting: head lag when pulling to sit
Reflex standing/walking
Age: 2 - 3 months
Prone: lifts head to 90 degrees, chest up with some weight on forearms, rolls to supine
Supine: ATNR, reciprocal leg kick
Sitting: head upright but unstable, requires full support otherwise
Age: 4 - 5 months
Prone: WB on extended UEs, pivot
Supine: rolls supine to side
Sitting: head stable, turns head, brief solo sitting
Standing: full WB in LEs in supported standing
Age: 6 - 7 months
Prone: rolls supine to prone, WB on one UE to reach with other UE
Supine: lifts head
Sitting: independent
Mobility: crawling backwards
Age: 8 - 9 months
Prone: can achieve quadruped
Supine: does not tolerate
Standing: stands with help from furniture, lowers to sitting
Mobility: crawls forward, cruises along furniture
Age: 10 - 11 months
Standing: brief unsupported standing, ½ kneeling to stand
mobility: walks with hand assistance, bear crawl
Age: 12- 15 months
walks without support
creeps upstairs
throws ball in sitting
Age: 16 - 24 months
walks up/down stairs
plays in squatting
kick, throw ball
tide-on toys
Age: 2 years
rides tricycle
runs on toes
walks downstairs with reciprocal pattern
catches large ball
hops on one foot
SS:
Arthtogryposis Multiplex Congenita
cylinder-like extremities with minimal definition
joint contractures
dislocation of joints muscle atrophy
PT Tx and Tx:
Arthtogryposis Multiplex Congenita
PT:
stretching
positioning
splinting
adaptive equipment
strengthening
Tx:
possible surgical intervention
SS:
Autism Spectrum Disorder
speech problems (non-purposeful, absence of speech)
diminished facial expressions
poor understanding of non-verbal cues
poor social interactions
lack of empathy
repetitive self-stimulating behaviors
routines/rituals
many have exceptional talents with music, art, and academics
PT Tx and Tx:
Autism Spectrum Disorder
PT Tx:
decrease non purposeful movements
sensory integration
Tx:
multidisciplinary
improve social communication
decrease non-purposeful vocalizations
S&S:
Cerebral Palsy
varies from mild/undetectable to severe loss of motor control and intellectual disability
abnormal muscle tone
impaired mobility
abnormal reflexes present
impaired modulation of movement
Pt Tx and Tx:
Cerebral Palsy
PT Tx:
stretching
strengthening
motor learning
developmental milestones
positioning
WB activities
mobility
Tx:
possible surgical intervention for orthopedic management and spasticity reduction
pharmacological intervention
SS:
Down Syndrome
intellectual disability
hypotonia
joint hypermobility
atlantoaxial instability
flattened nasal bridge
narrow eyelids
small mouth
feeding impairments
flat feet
scoliosis
congenital heart disease
vision and hearing loss
PT Tx and Tx:
Down Syndrome
PT Tx:
avoid compensatory patterns
tone management
increase strength, minimize laxity
maximize respiratory function
Tx:
pharmacological intervention
achieve max potential is overall goal
learning strategies
SS:
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
progressive weakness
low interest in running
falling
toe walking
excessive lordosis
pseudohypertrophy of muscle groups
PT Tx and Tx:
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
PT Tx:
developmental milestones
maintaining strength
encourage mobiltiy
adapt to loss of function
promote family involvement in home program
Tx:
maintaining function as long as possible
pharmacological intervention
respiratory care
emotional support
SS:
Prader Willi Syndrome
small hands, feet and sex organs
hypotonia
almond-shaped eyes
obesity
constant desire for food
coordination impairments
intellectual disability
PT Tx and Tx:
Prader Willi Syndrome
PT Tx:
postural control
fitness
exercise
gross motor skill
Tx:
human growth hormone (HGH)
SS:
Spina Bifida
motor loss below lesion
sensory deficits
hydropcephalus
clubfoot
scoliosis
arnold-chiari type II malformation
osteoporosis
tethered cord syndrome
bowel and bladder dysfunction
learning disabilities
latex allergy
PT Tx and Tx:
Spina Bifida
PT Tx:
positioning
ROM
handling
developmental milestones
skin care
strengthening
balance
mobility
equipment management
Tx:
surgical closure of neural tube defect
medical management of bowel and bladder dysfunction
SS:
Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA)
progressive muscle weakness
muscle atrophy
diminished (or absent) DTRs
end-stage respiratory compromise
sensation intact
cognition intact
PT Tx and Tx:
Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA)
PT Tx:
positioning
visual/vestibular stimulation
mobility training
assistive devices
adaptive equipment
strengthening
SS:
Congenital Hip Dysplasia
asymmetrical hip abduction
tightness and and shortening of femur on affected side
PT Tx and Tx:
Congenital Hip Dysplasia
PT Tx:
stretching
strengthening
caregiver education
Tx:
open reduction
hip spica cast
harness
bracing
splinting
traction
SS:
Congenital Torticollis
lateral cervical flexion (to same side)
cervical rotation (to opposite side)
facial asymmetries
PT Tx and Tx:
Congenital Torticollis
PT Tx:
stretching
AROM
positioning
caregiver involvement
SS:
Legg-Calve-Perthes
pain
decreased ROM
positive trendelenburg sign
antalgic gait
PT Tx and Tx:
Legg-Calve-Perthes
PT Tx:
stretching
splinting
aquatic therapy
traction
crutch training
Tx:
pain management
maintain femoral head
improve ROM
possible surgical intervention
orthotic devices
SS:
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
pathological fxs
osteoporosis
hypermobility
weakness
scoliosis
impaired respiratory function
bowing on long bones
PT Tx and Tx:
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
PT Tx:
AROM
positioning
functional mobility
fx management
use of orthotics/wheelchairs
SS:
Scoliosis
asymmetry of shoulders
possible rib hump
pain due to pressure/abnormal forces on other tissues
PT Tx and Tx:
Scoliosis
PT Tx:
muscle strengthening
flexibility exercises
shoe lifts
bracing
spinal orthosis for curves between 25 - 40 …
SS:
Cystic Fibrosis
salty tasting skin
persistent productive cough
frequent lung infections
wheezing
SOB
poor growth/weight gain
frequent greasty, bulky stools
PT Tx and Tx;
Cystic Fibrosis
PT Tx:
airway clearance
breathing
assisted cough
ventilatory muscle training
Tx:
medications (antibiotics, nutritional supplements, bronchodilators, etc)
lung transplants
SS:
Delayed Milestones/Prematurity
birth less than 37 weeks gestation considered premature
22 - 23 weeks is age of viability
PT Tx and Tx:
Delayed Milestones/Prematurity
PT Tx:
treat deficits so they catch up to peers
meet milestones
Tx:
respiratory function
feeding tube if needed
SS:
Hydrocephalus
enlarged head or bulging fontanelles
headache
vision changes
seizures
alteration in appetite, vomiting
incontinence
PT Tx and Tx:
hydrocephalus
PT Tx:
treats deficits
be aware of signs and symptoms of shunt malfunction
Tx:
medical intervention to alleviate excessive fluid
shunt placement