Economics IA1 unit 3 definitions
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Absolute advantage
the ability of a nation to produce commodities more efficiently than another nation
Comparative advantage
the ability of a nation to produce a product at a lower opportunity cost of production than another nation
Competitive advantage (of a nation)
trade advantage obtained through the capacity of a nation’s industries to innovate and upgrade
Currency appreciation
an increase in the value of a currency relative to other currencies under a floating exchange regime
Currency depreciation
a decrease in the value of a currency relative to other currencies under a
floating exchange regime
Currency devaluation
a deliberate downward adjustment to the value of a country’s currency relative to another currency, group of currencies or standard under a fixed exchange rate
Currency revaluation
a deliberate upward adjustment to the value of a country’s currency relative to another currency, group of currencies or standard under a fixed exchange rate
delete
later
Exchange rate
the value of the currency of a nation expressed in terms of the currency of another nation
Exchange rate (fixed)
the value of a currency that is determined by the government fixing it to the value of another currency at a certain level, and guaranteeing to maintain that level
Exchange rate (floating)
the value of a currency determined by the forces of supply and demand in the foreign exchange market
Exchange rate (managed/dirty)
a floating exchange rate system where the central bank (the RBA in Australia) intervenes in the foreign exchange market by buying or selling a nation’s currency
Exchange rate appreciation
see currency appreciation
Exchange rate depreciation
see currency depreciation
Factor endowment
the supply of the factors of production (land, labour, capital and enterprise) that exists in a country
Free trade
trade of exports and imports in which government exerts little influence on the decisions of private firms and individuals; competitive market forces determine trade patterns
Globalisation
the growing integration of national economies to form a single interdependent global economy
Internal stability
a state of the economy in which there is full employment and acceptable levels of inflation
Sustainable economic growth
a rate of growth that, if maintained correctly, should not create any significant economic problems for future generations; it sustains a nation’s natural resources and the environment
Trade liberalisation
is a policy designed to promote free trade and reduce protection levels between nations
Terms of Trade
The measurement of the change in export prices relative to the change in import prices.
BOGS
balance of goods and services = total value of exports – total value of imports
Trade balance
The difference between a country's total value of exported goods and services and its total value of imported goods and services over a specific period
KAFA
Capital Account small part of the balance of payments, it includes capital transfers – mainly involves the transfer of assets when someone moves in or out of the AUS.
Financial account is the bigger part of the KAFA and is a component of a countries BOP.
BOP
Balance of payments is a record of all economic transactions between a country and the rest of the world over a specific period, such as imports, exports, and financial flows
. BOP must equal 0 so a surplus in the current account is equal to a deficit in the capital and financial account.
Current Account
has three components- net goods, net services and net secondary income.
Net goods: is total exported goods minus total debits paid for purchase of imported goods.
Net services is income earned by residents from the provision of factors of production.
Net secondary income: refers to one way transfers of money between Aus and the rest of the world wehre no good, service or asset is exchanged in return.
Positives of currency appreciation
Cheaper imports
increased purchasing power
decreased debt
foreign investment
inflation
negatives of currency appreciation
decreased competitiveness
negative effect on tourism industry
decreased economic growth
trade balance deficit (due to more imports)
positives of currency depreciation
export competition
increased employment
increased domestic production
increase economic growth
negatives of currency depreciation
decreased access to imports
decreased foreign investment
increased inflation on imports
foreign debt
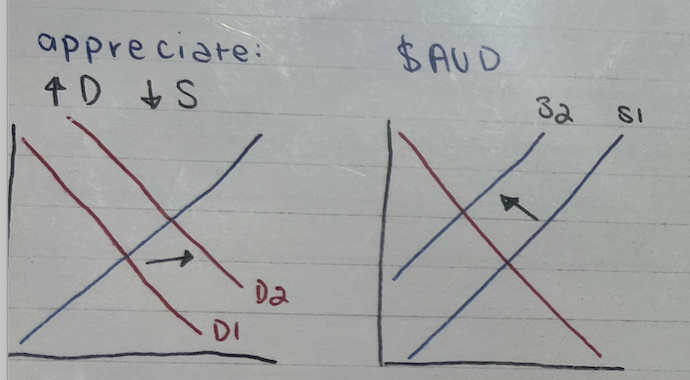
Appreciate AUD
increased demand decreased supply
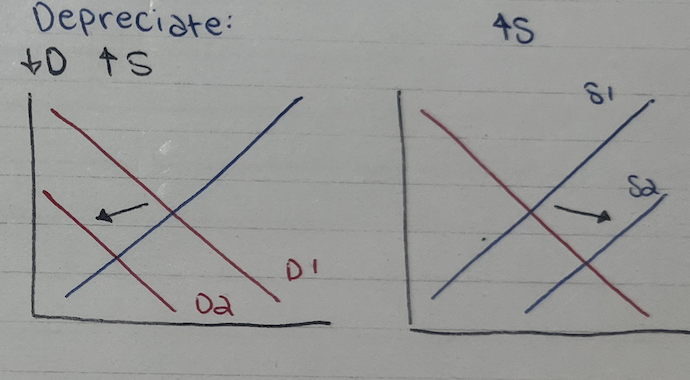
depreciate AUD
Decreased demand increased supply
advantages of fixed exchange rate
exchange rate stability
reduces inflation
encourages investment
disadvantages of fixed exchange rate
monetary policy indolence lost
balance of payments issue
maintaining is harder
positives of managed exchange rate
stability
flexibility
confidence for investors
negatives of managed exchange rates
policy mistake
limited long term stability
gov stability
foreign exchange market
(FOREX) market where intentional currencies are bought and sold
foreign reserves
assets held by countries central banking foreign currencies
positives of floating exchange rate
automatic adjustment
reflection of market condition
indépendant monetary policy
disadvantage of floating exchange rate
exchange rate volatility
short term investment
reduced investment confidence
benefits of feign investment
more capital investment
increase in exports
decrease in unemployment due to drive in economic growth
serves as an injection in circular flow of income
increased productivity by pushing curve out
increased technology and increased innovation
increase market output
costs of foreign investment
decreased control +owenership of industries/resources
higher returns on investment for external investors
increased profits = increased dividends + ROI (return on investment)
leakage to promot a foreign economy/market
types of foreign debt
public - gov owneed
private- individuals +businesses owed debt
costs of foreign debt
vunerable to change due to exchange rates
overseas currency appreciates making debt harder to pay
benefits of foreign debt
borrow from country with a favourable interest rate
capital investment - economic growth - develop economy
limited damage of fluctuations
foreign liabilities on the current account
borrow from abroad —→ inflow of capital recorded as credit on KAFA —→ interest repayments overseas —→ payments recorded as debits on the net primary income account and the current account