ANAT 711 Back I & II + Vertebral Column Lecture
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
vertebral prominens
Landmark for C7
inferior scapular angle
Landmark for T7
scapular spine
Landmark for T3
Highest point of iliac crest
Landmark for L4
posterior superior iliac spine
Landmark for S2
kyphosis
-Primary curvatures of spine that occur before birth
-located at thoracic and sacral regions
Lordosis
-secondary curvatures of spine that occur after birth
- cervical (1st) and lumbar (2nd)
before birth
when does primary ossification occur?
bends occur after birth, throughout development
when does secondary ossification occur?
Osteoporosis
a condition in which there is a reduction in bone mass/strength
intervertebral foramen
where spinal nerves exit
vertebral body
structure in green
vertebral arch
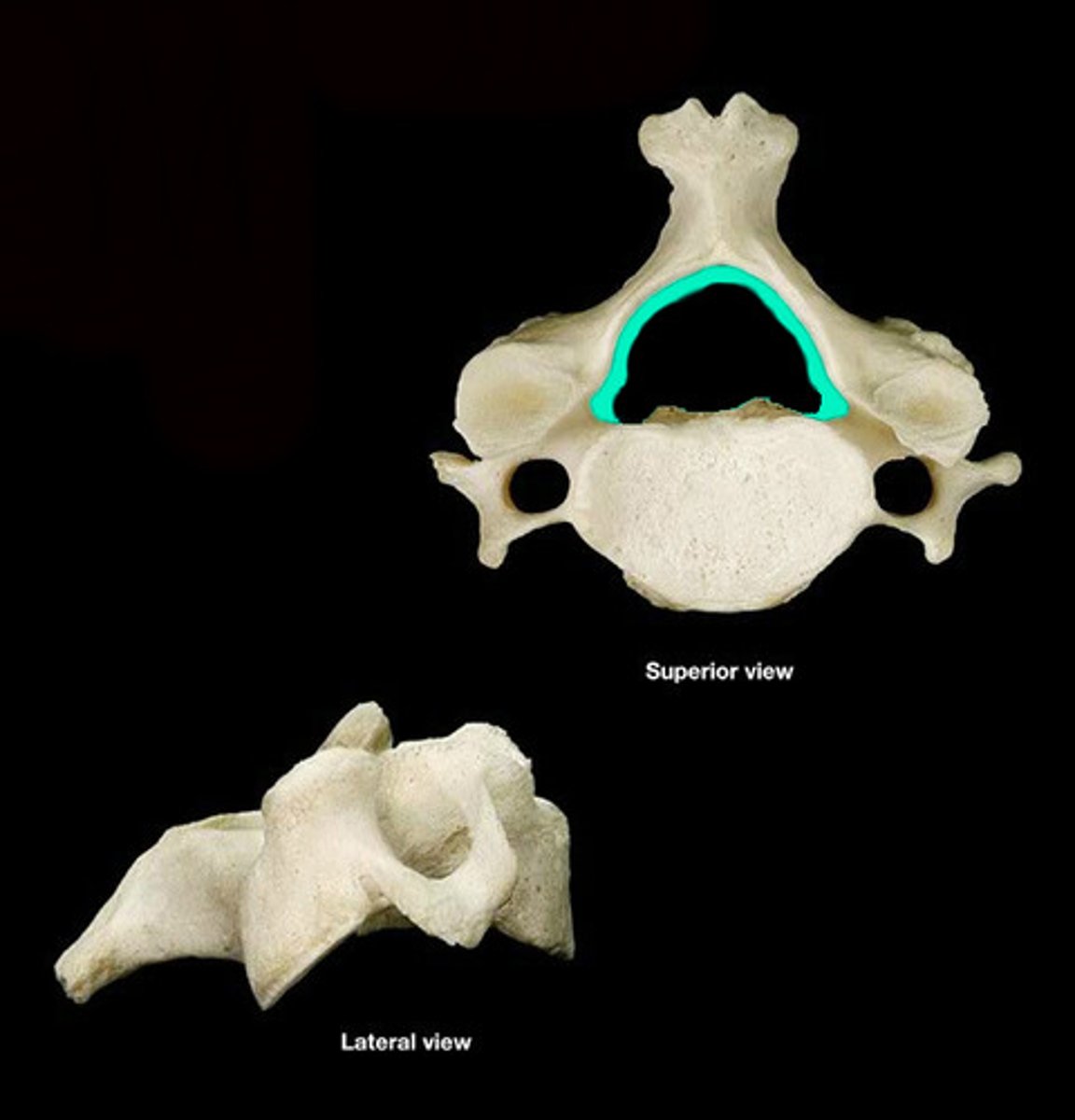
pedicle and lamina
what the vertebral arch is composed of
pedicle of vertebrae
Lamina of vertebra
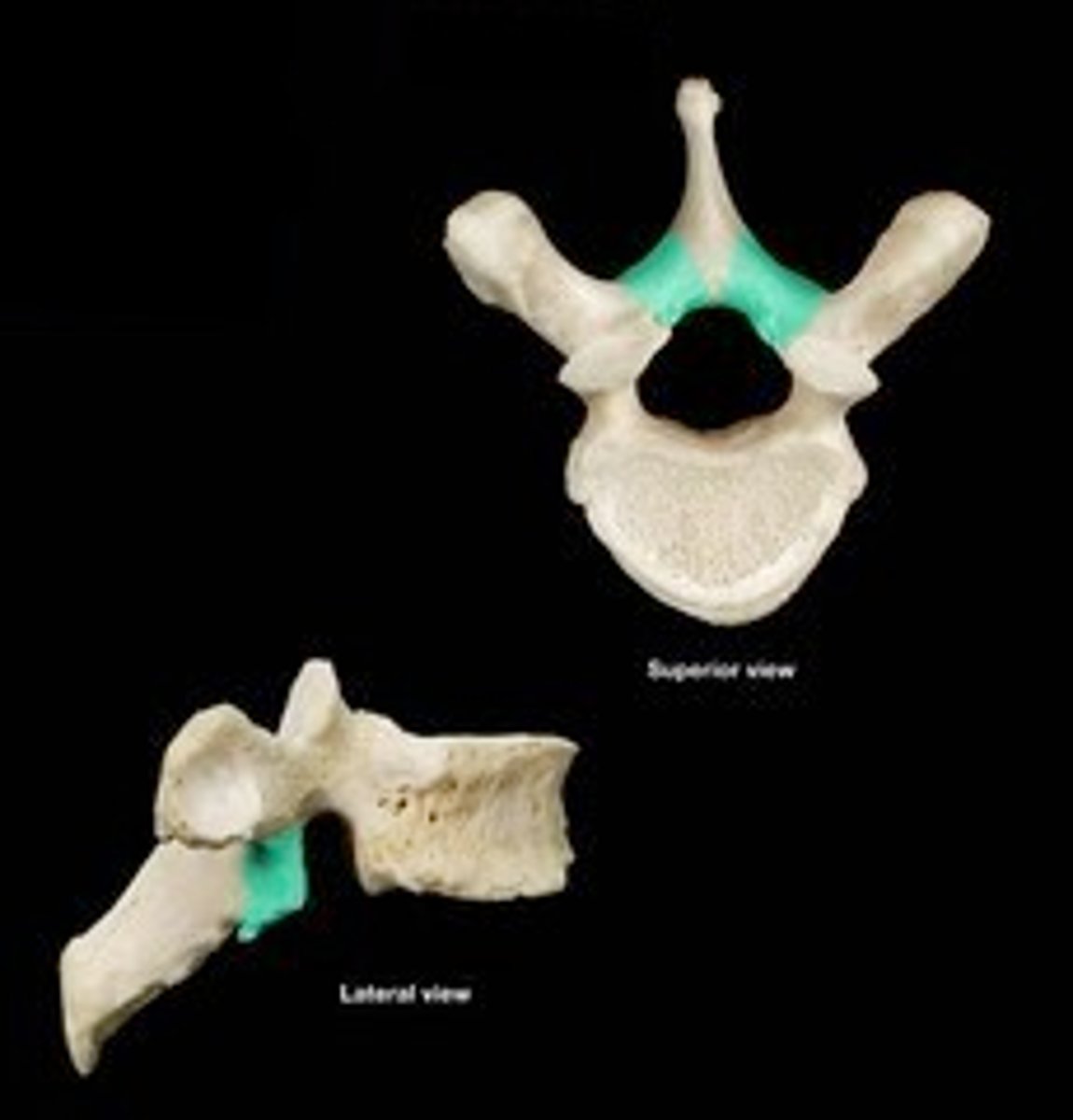
pars interarticularis
the area between the superior and inferior articulations of the vertebrae; common site of fractures due to spondylolysis
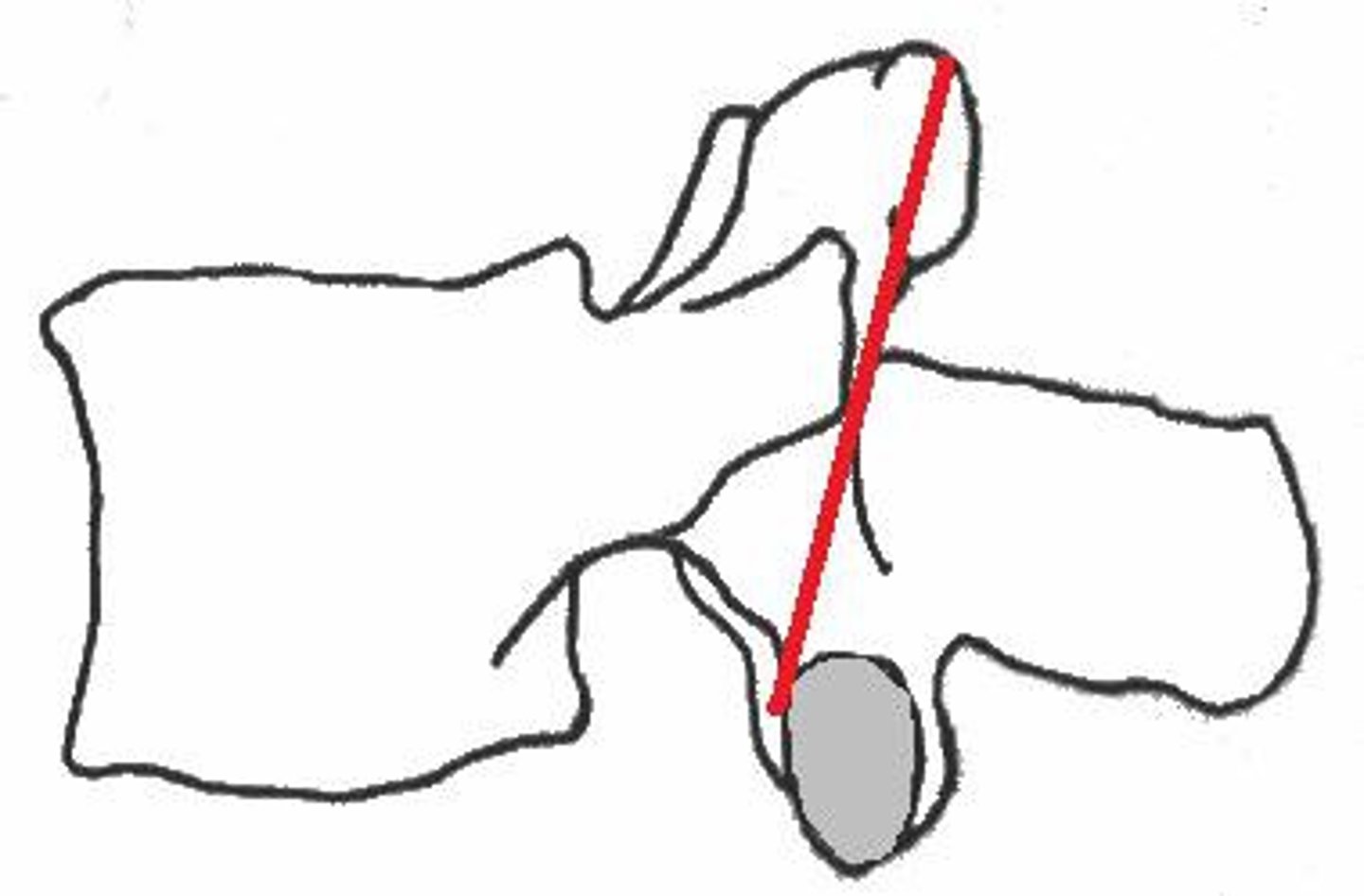
vertebral foramen
contains spinal cord and meninges
superior, inferior, transverse, posterior processes
4 projections from vertebral arch
spondylosis
osteoarthritis of the intervertebral joint
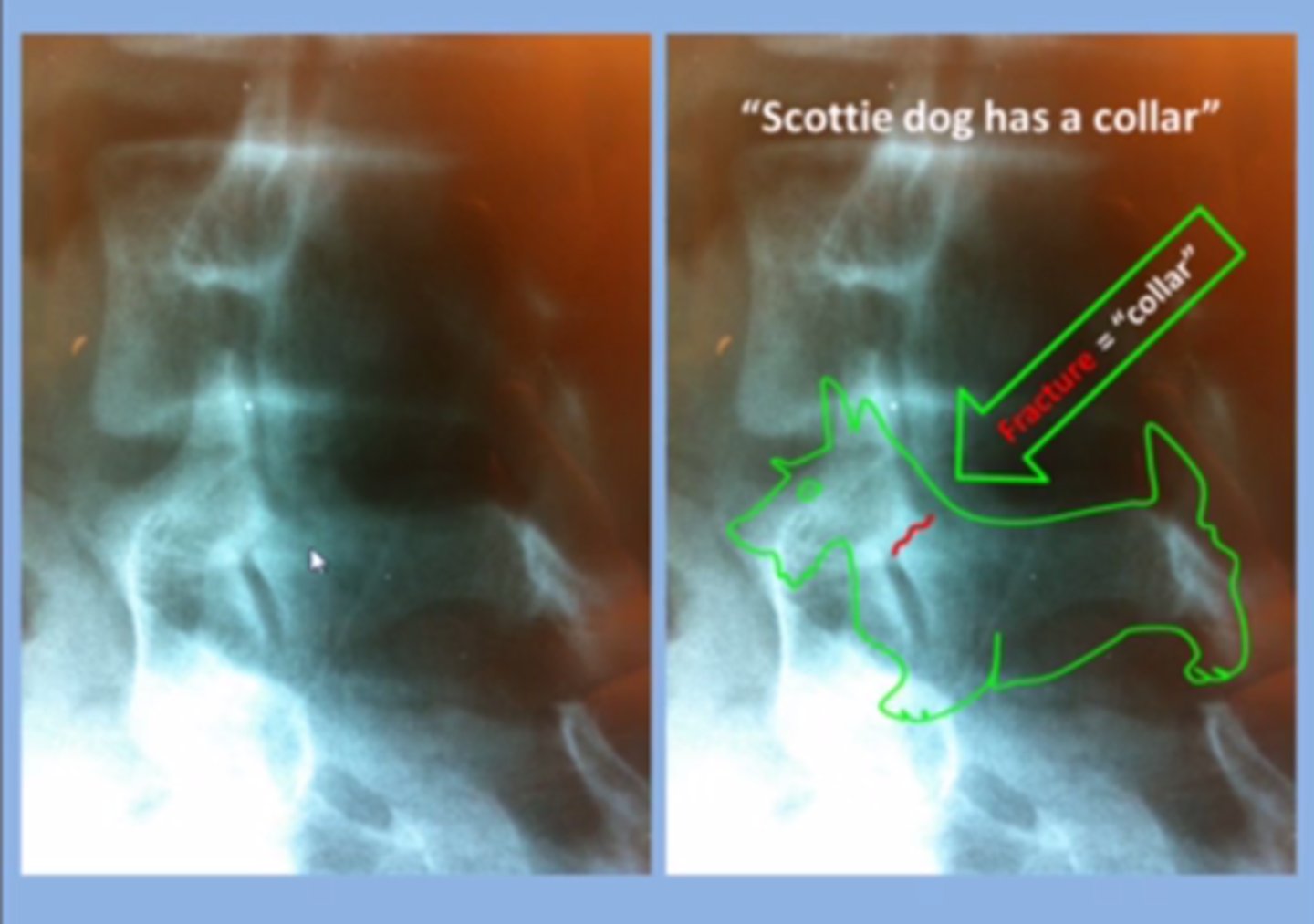
spondylolysis
stress fracture of the pars interarticularis
spondylolisthesis
anterior displacement of a vertebra
spondylolysis (image)
Scotty Dog indicates...
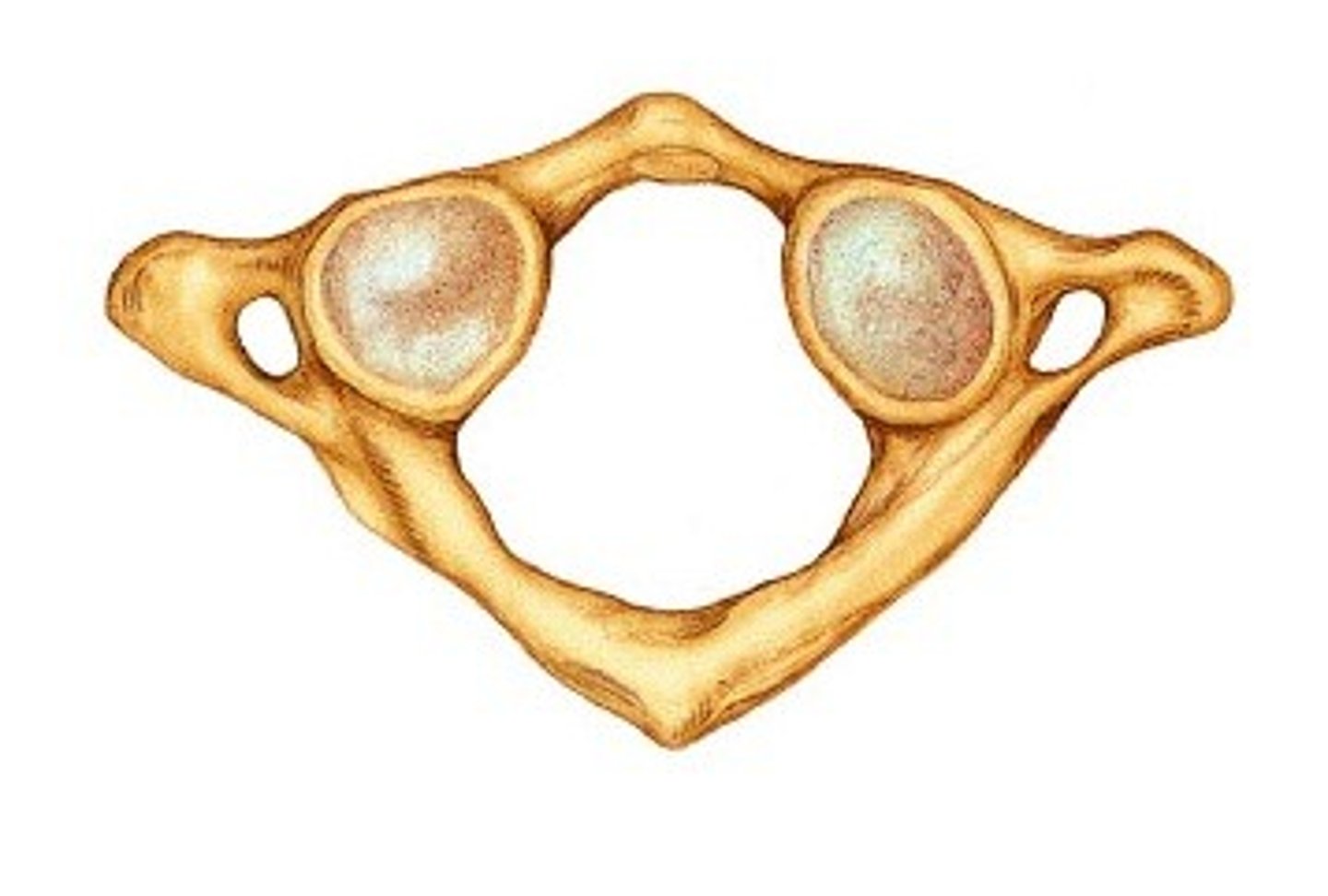
Atlas (C1)
Name the bone.
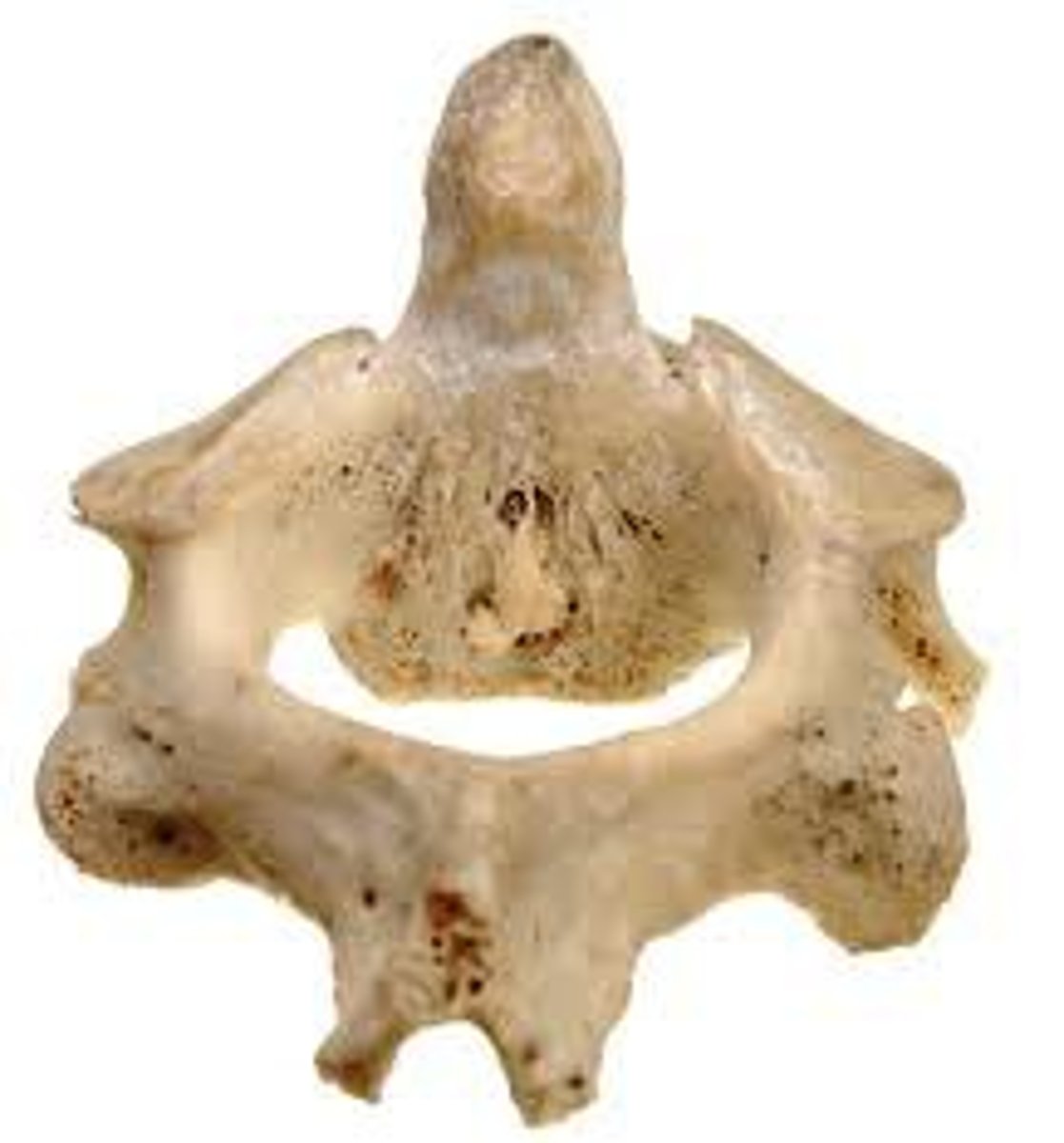
Axis (C2)
Name the bone.

Vertebral artery and vein
passes through C1
cervical vertebrae
what part of the vertebrae has a transverse foramen?
nuchal ligament
-limits forward flexion of head & cervical spine. It also serves as the attachment for supraspinatus muscle
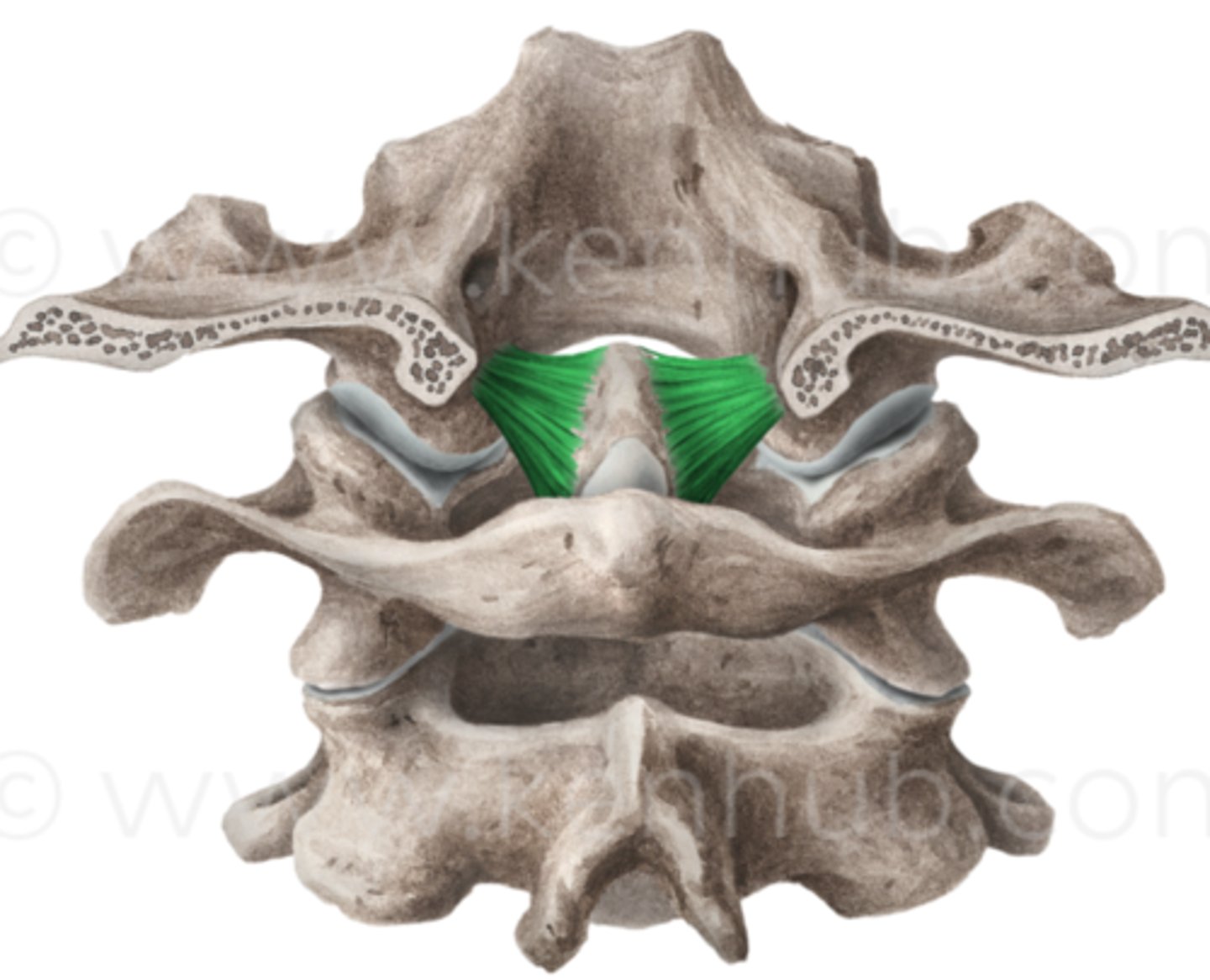
transverse ligament
forms the posterior support of the dens during head rotation
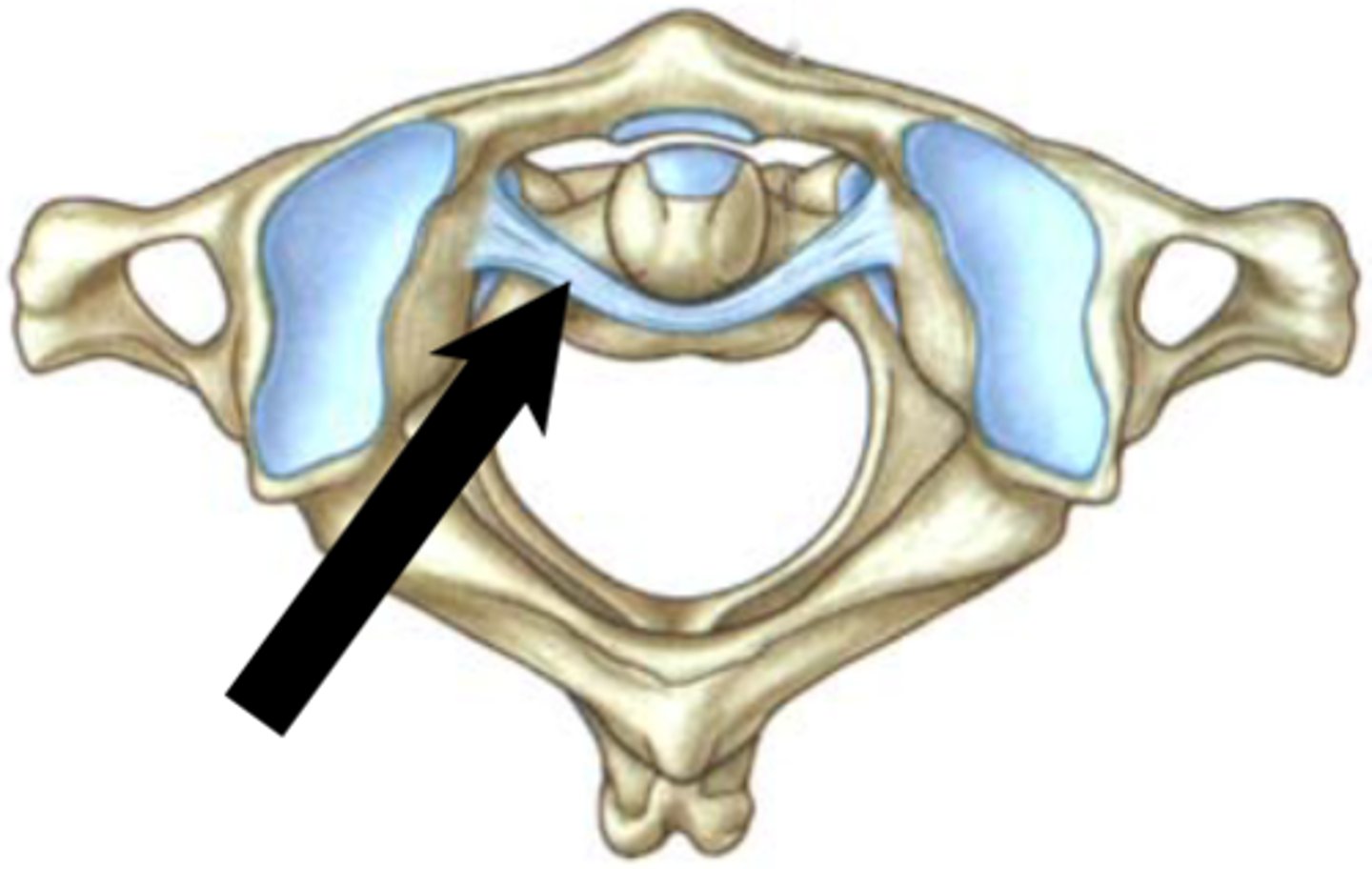
alar ligament
-extends from sides of the dens to occipital bone
-prevents head rotation
atlantooccipital joint
Condylar synovial joint involved in flexion, extension, and lateral flexion of the head.
whiplash injury
tearing of anterior longitudinal ligament and other soft tissue structures during hyper extension
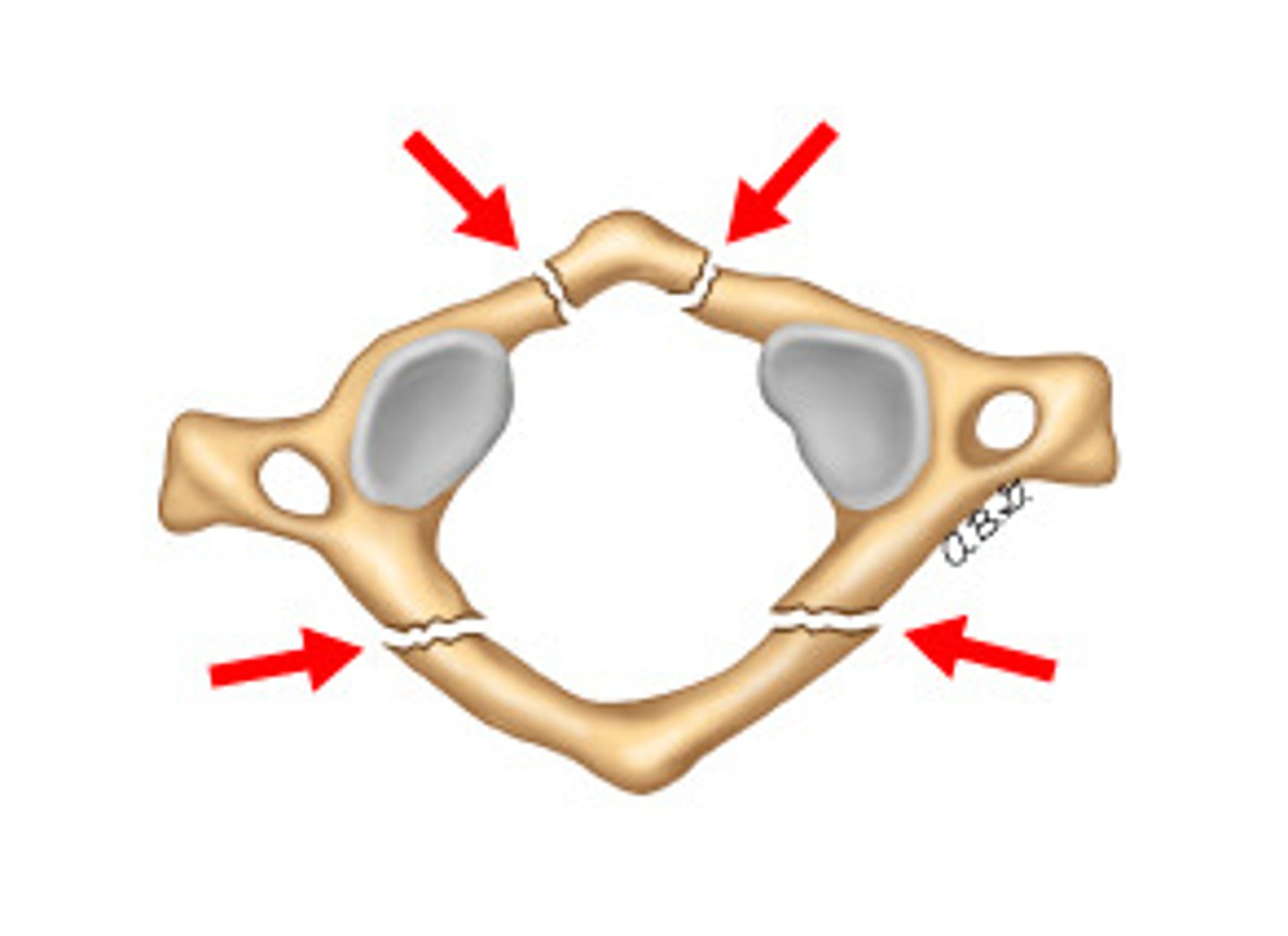
Hangman's fracture
-traumatic spondylolysis of C2
-Bilateral fracture of pars interarticularis of C2 due to hyperextension
-Associated with spinal cord injury
Jefferson's fracture
-excessive axial loading resulting from a blunt injury
-rare damage to spinal cord
Posterior atlanto-occipital membrane
connects the posterior arch of the atlas with the occipital bone and is continuous with the lateral atlanto-occipital ligament
thoracic vertebrae
what has costal facets in their bodies and transverse processes with limited ROM
Thoracic
name the vertebral region
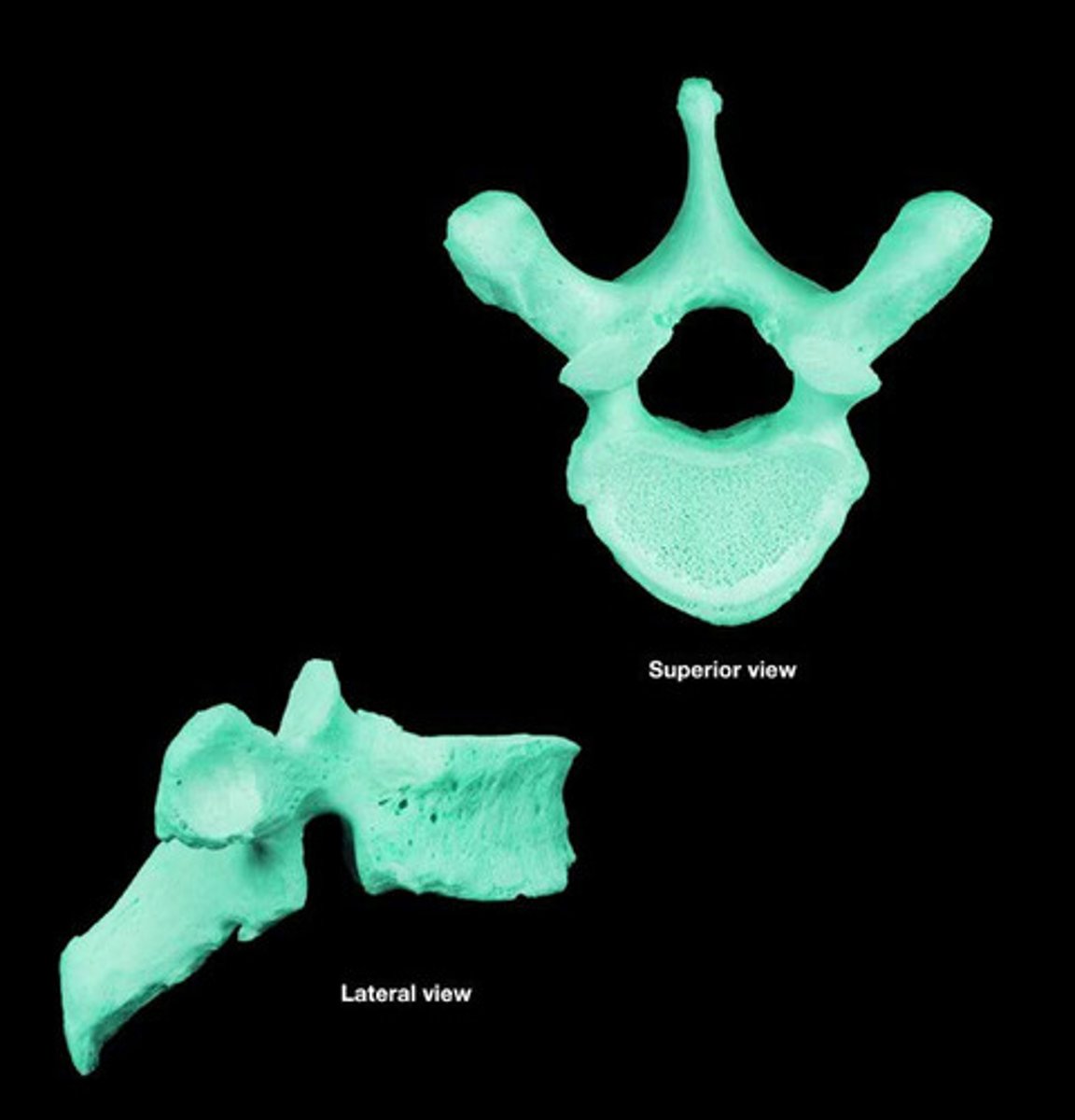
thoracic vertebrae
what contains long slender spinous processes that tilt inferiorly and form joints with ribs
inferior, ribs
the alphanumeric designation of the __________ thoracic vertebra is the same as ________
lumbar
name the vertebral region
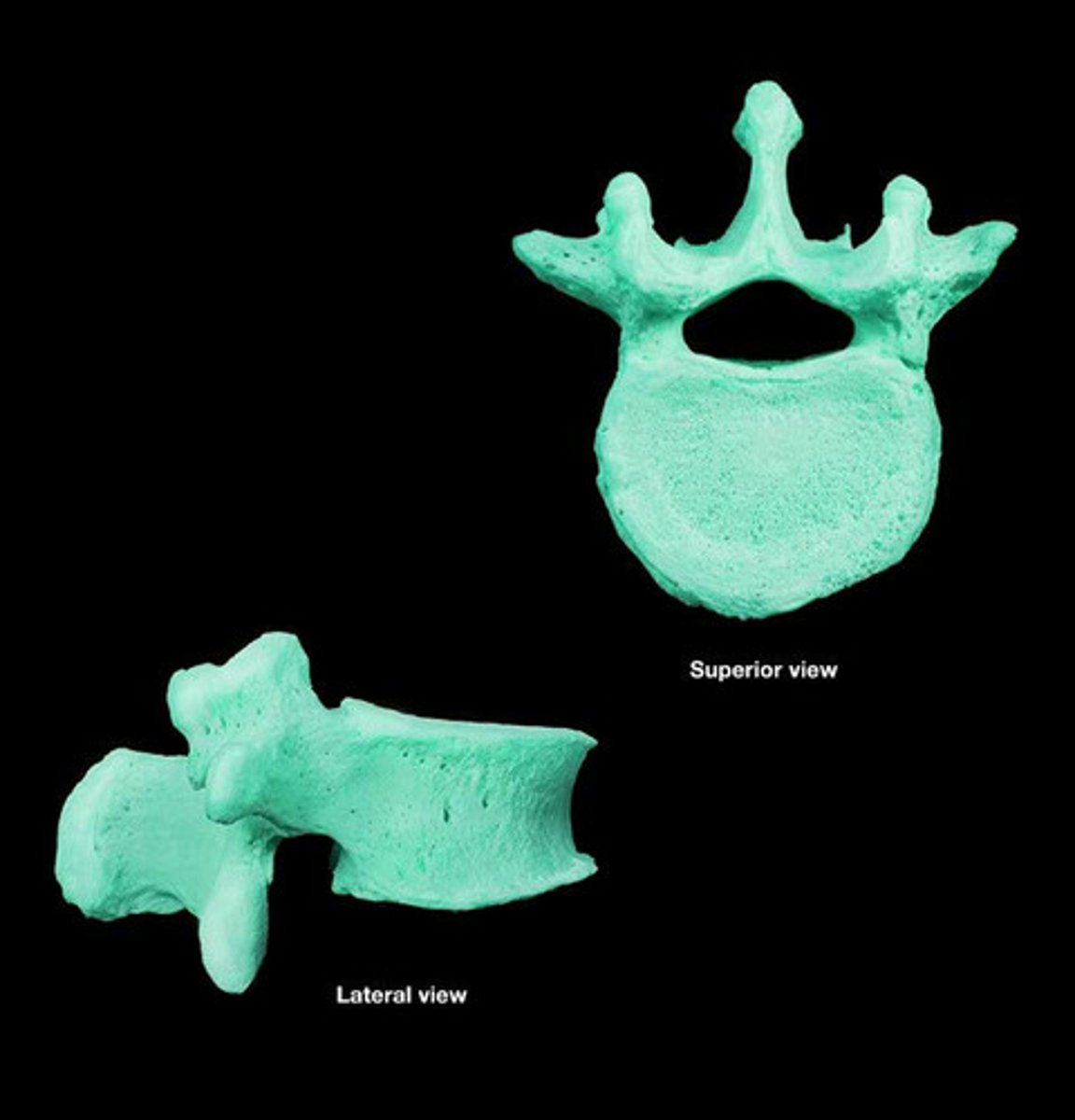
mamillary and accessory processes
these processes are associated with the lumbar region
lumbar vertebrae
large for stability and weightbearing
limited ROM
sacrum
name the vertebral region
Coccyx
the end of the spinal cord attaches here
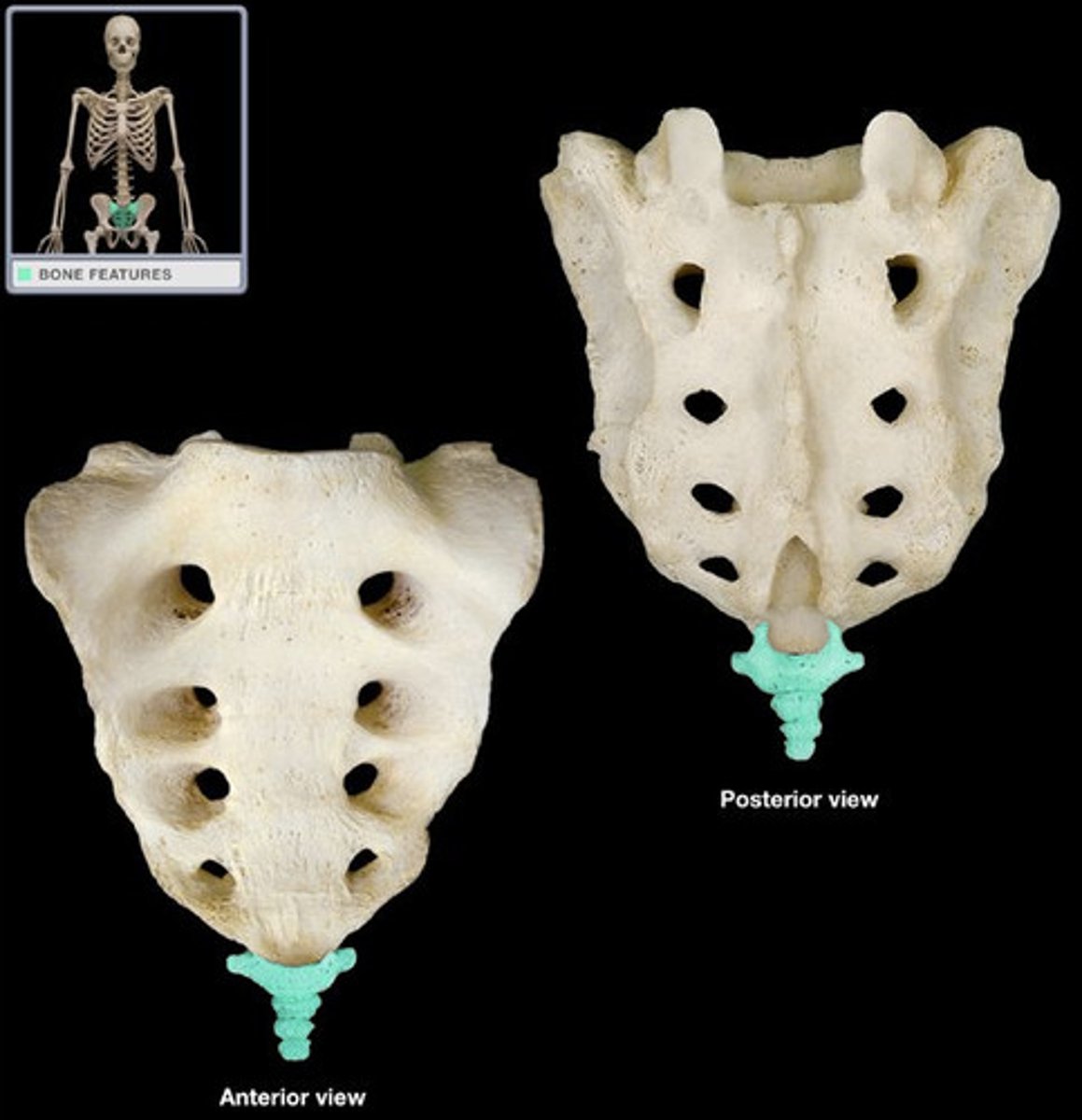
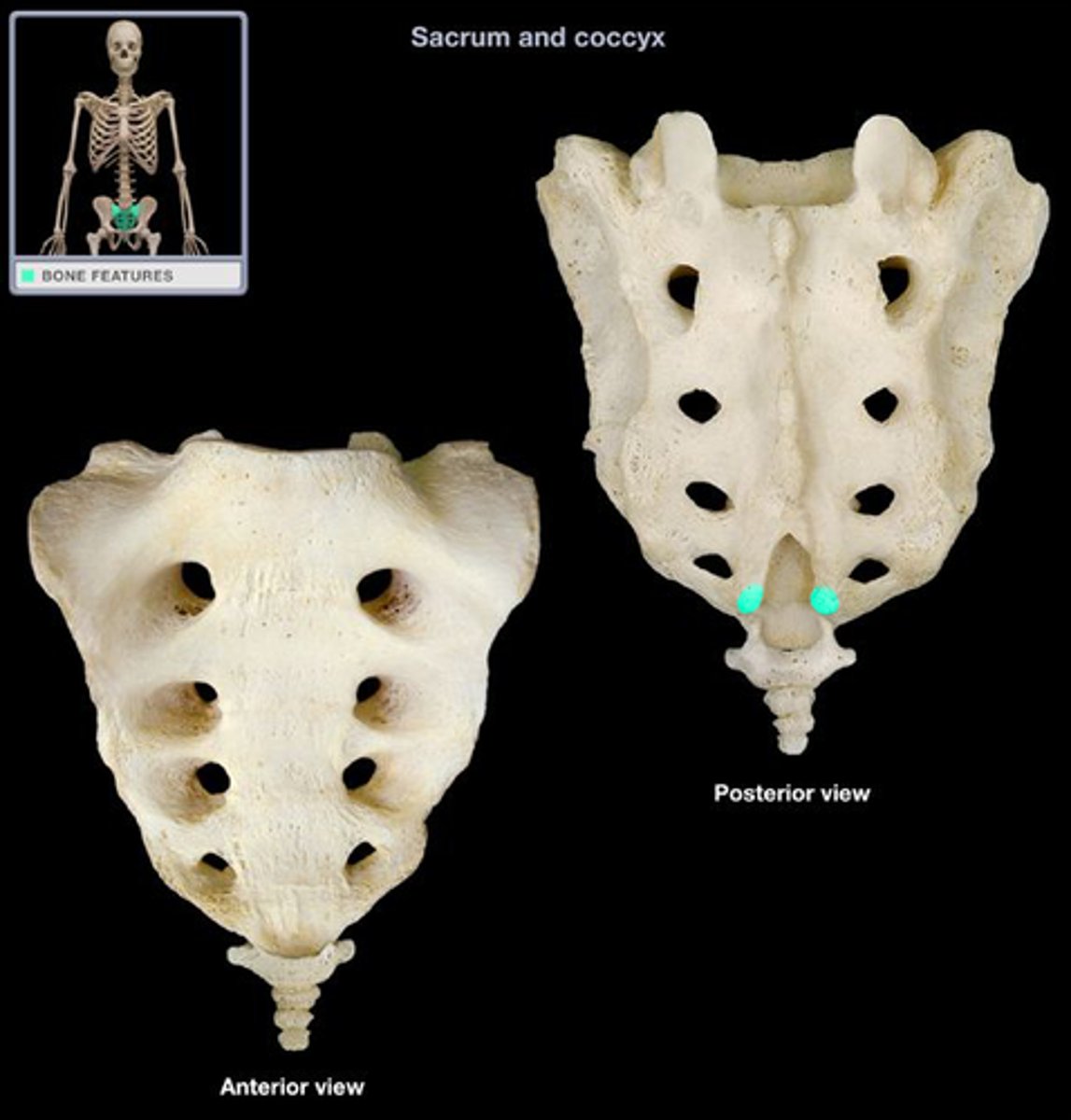
sacral hiatus
used for administration of caudal (extradural) anesthesia
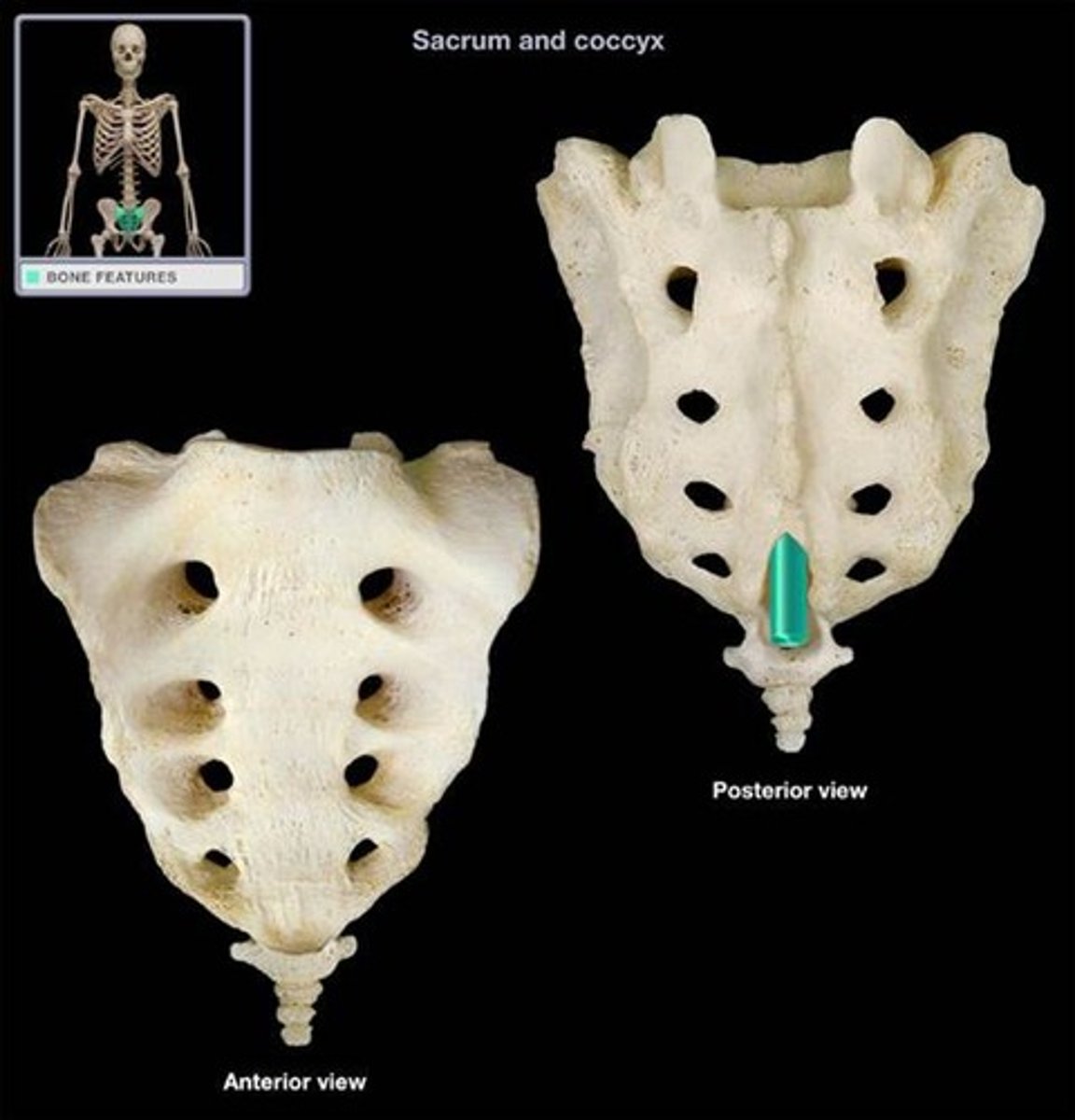
posterior and anterior sacral foramina
spinal nerves exit here
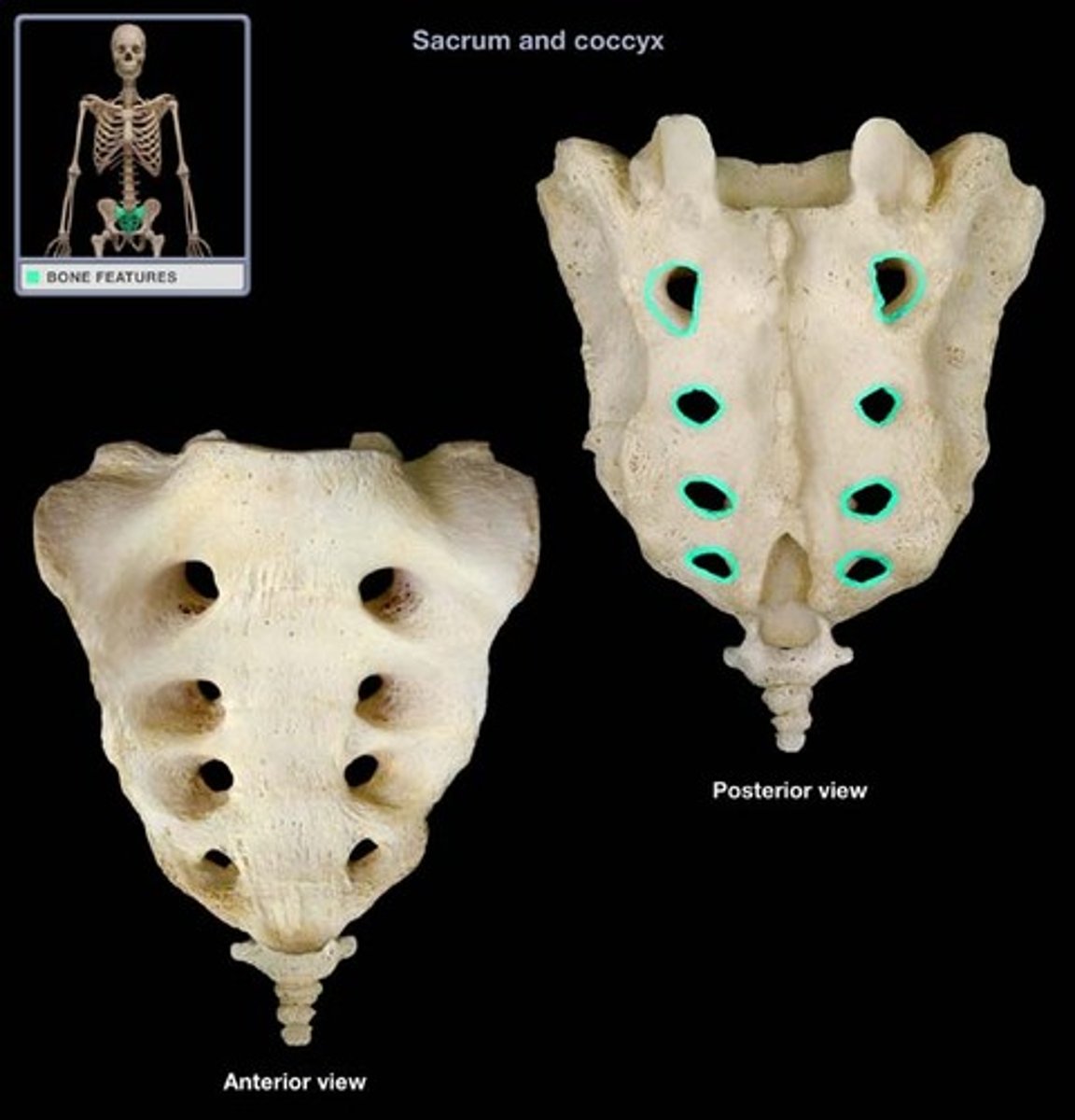
sacral cornu
formed by pedicles of 5th sacral vertebrae
used to find the hiatus
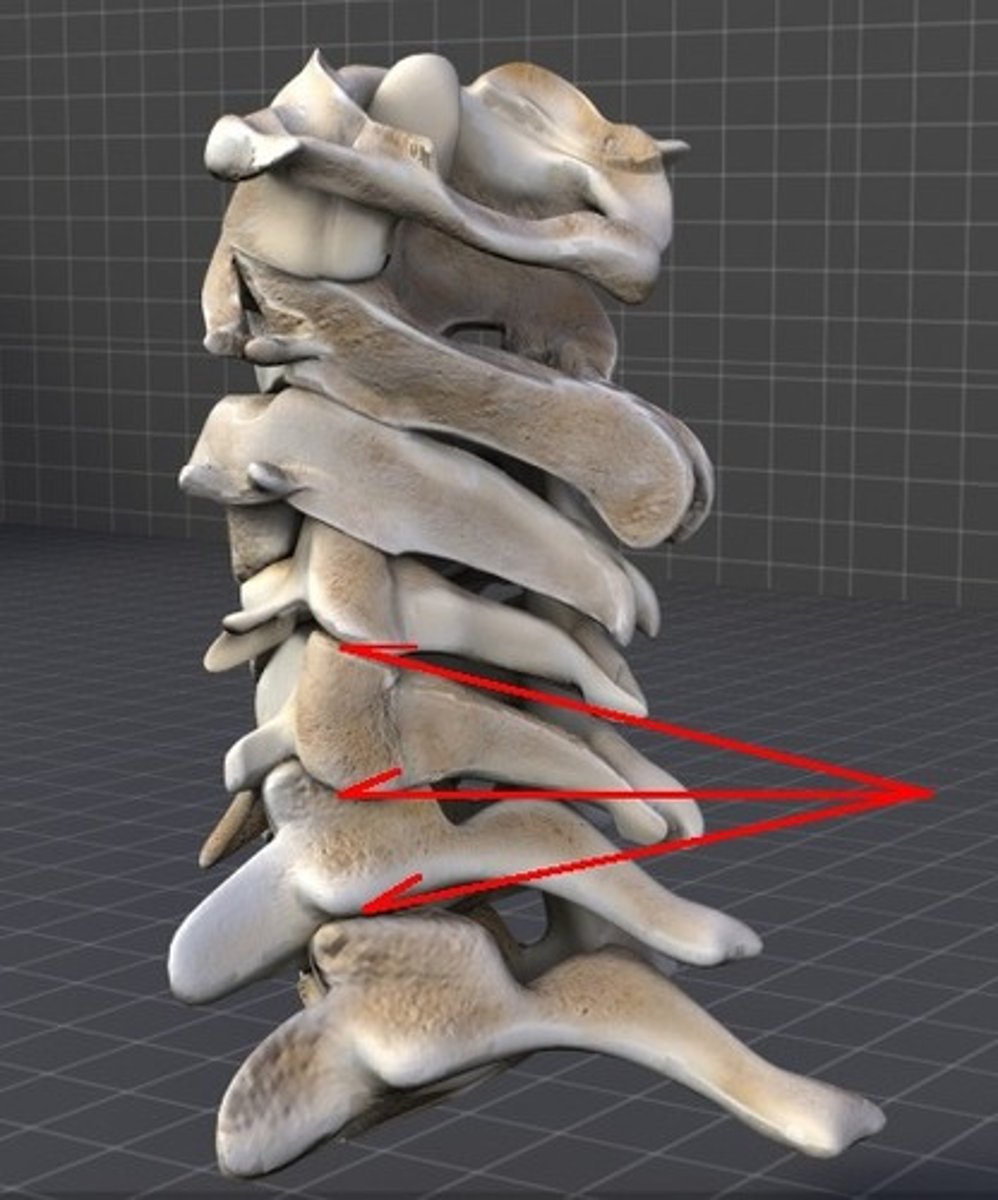
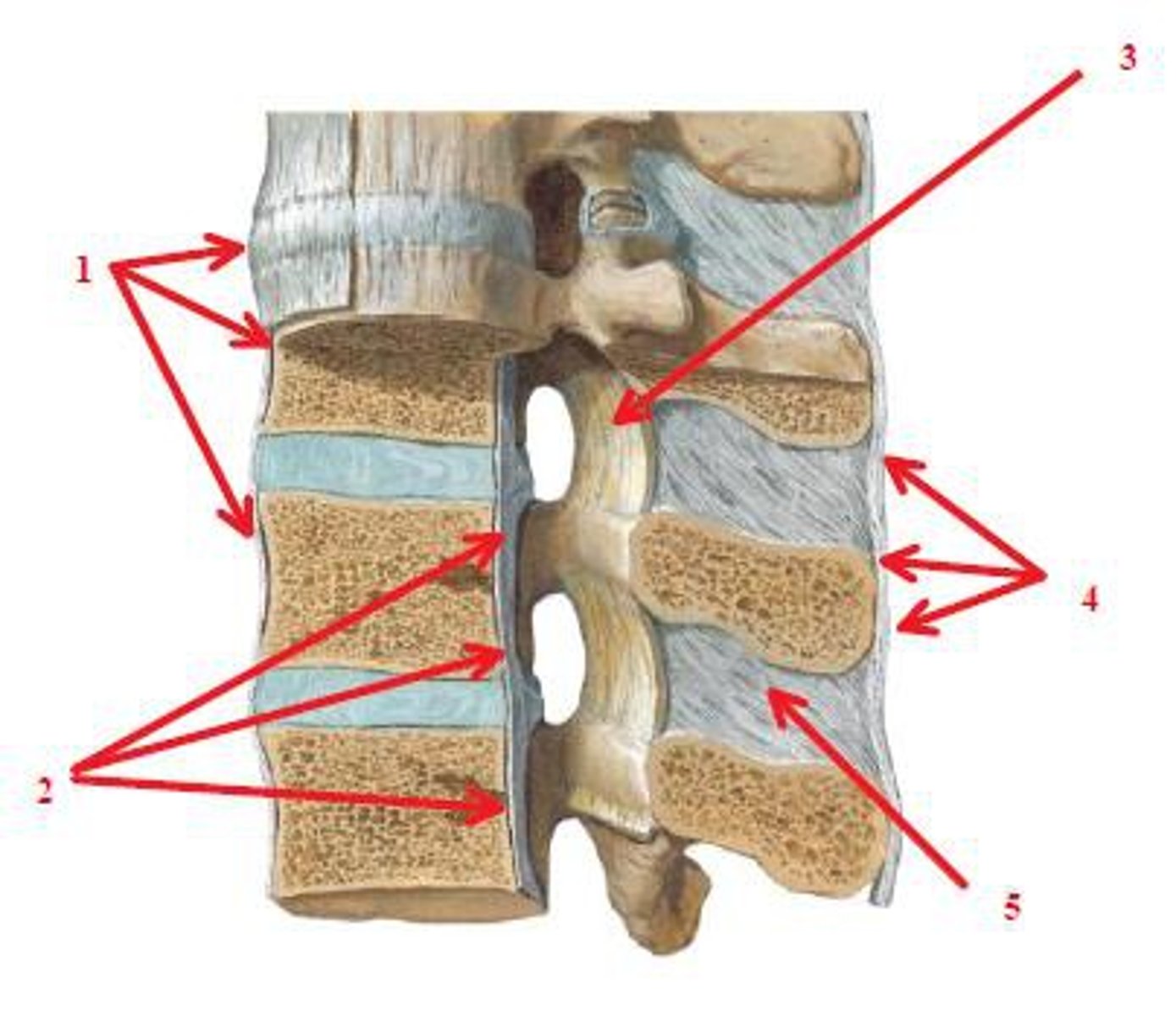
intervertebral joint
formed by adjoining vertebral bodies
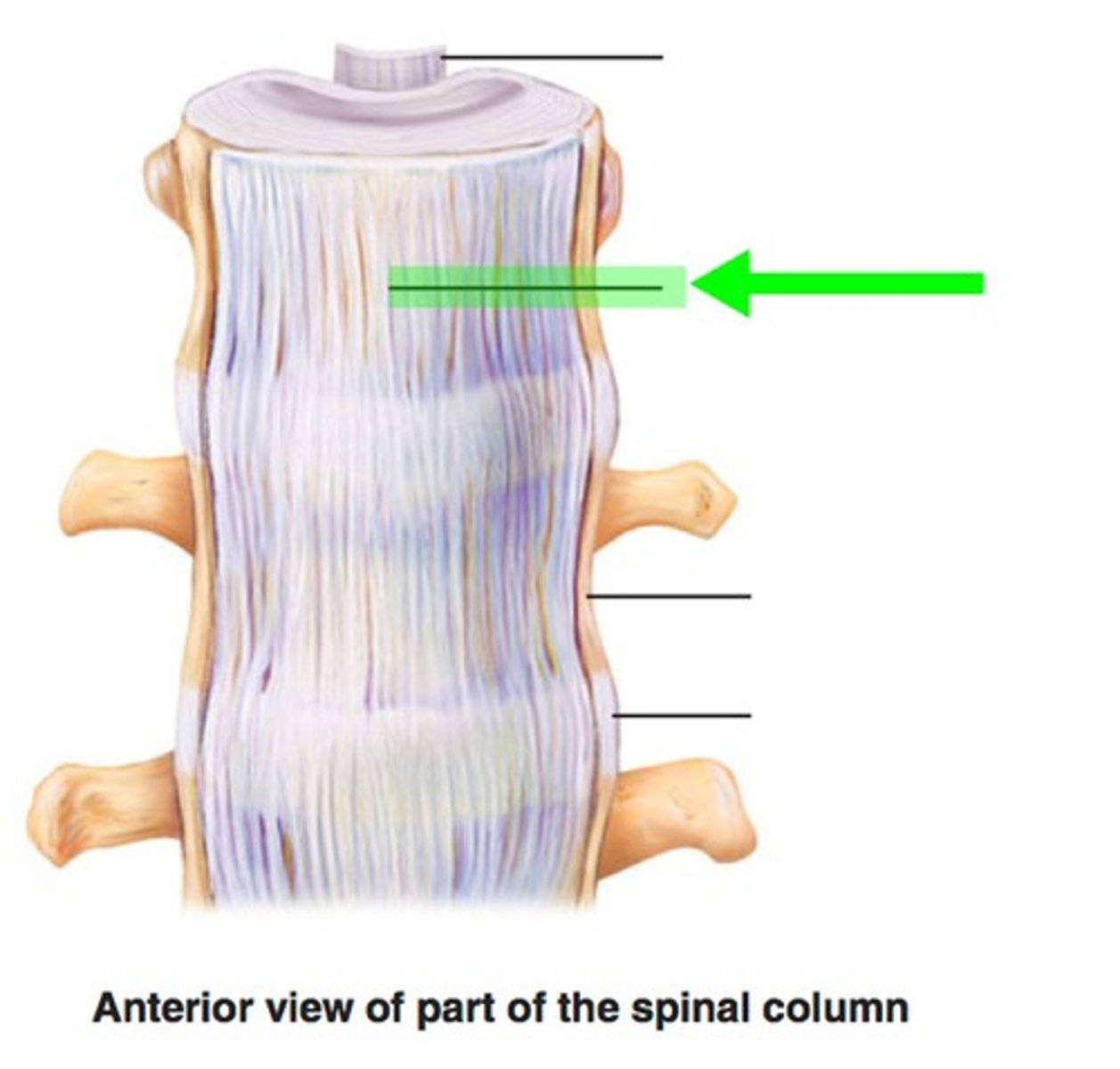
anterior longitudinal ligament
-attached to anterior surface of vertebral bodies and IVDs
-limits extension of vertebral column
-upward extension of anterior atlantooccipital membrane
posterior longitudinal ligament
-attached to posterior surface of vertebral bodies and IVDs
-limits flexion of vertebral column
-upward extension of tectorial membrane
anterior atlantooccipital membrane
upward extension of the anterior longitudinal ligament
tectorial membrane
upward extension of the posterior longitudinal ligament
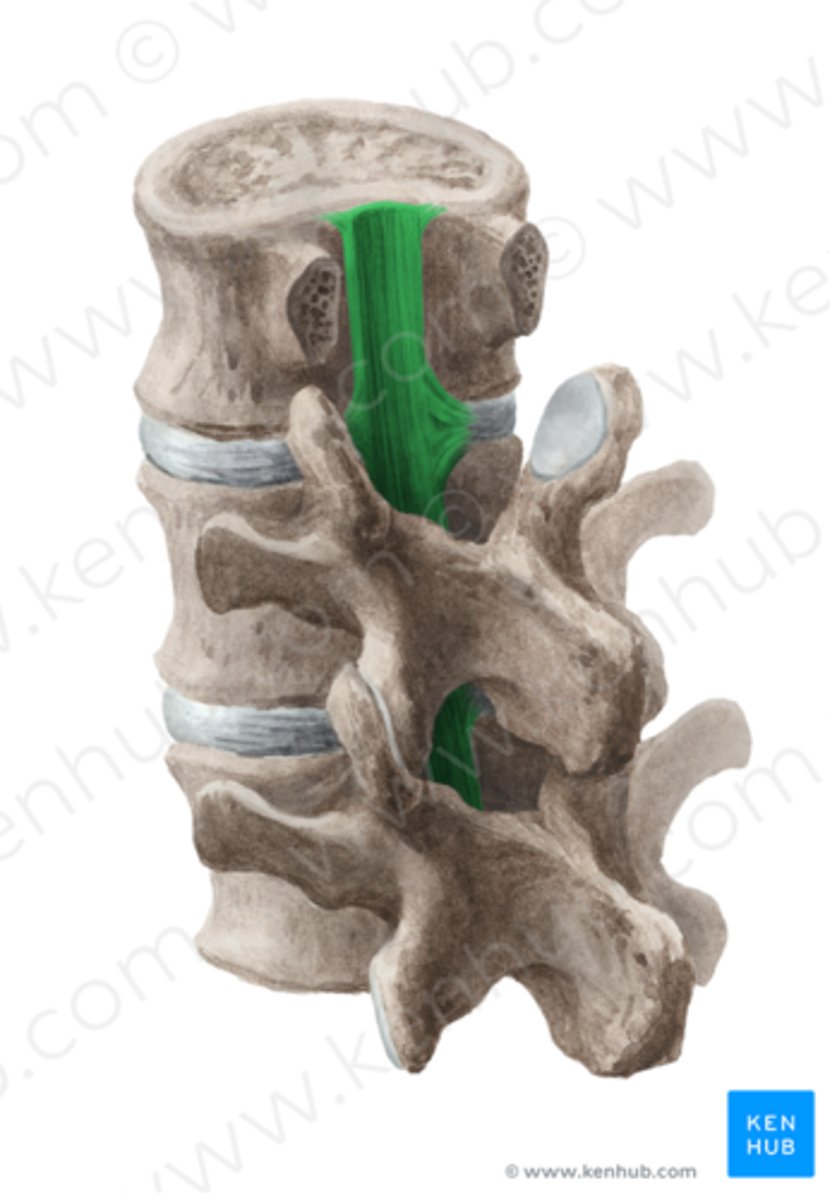
ligamentum flava
-#3
-connects the adjacent laminae of the vertebrae
-forms posterior wall of vertebral canal between vertebrae
ligamentum flavum
what is pierced during lumbar puncture?
posterior atlantooccipital membrane
upward extension of the ligamentum flava is
IV Disc
-composed of a tough outer annulus fibrosus & squishy inner nucleus pulposus
-good shock absorbers
supraspinous and interspinous ligaments
-resist hyperflexion
-between spinous and transverse processes (Respectfully)
ligamentum nuchae
formed by thickened supraspinous ligaments that extend from C7 to external occipital protuberance
trapezius, latissimus dorsi, levator scapulae, rhomboids
superficial extrinsic back muscles
Extrinsic back muscles
this group of muscles is attached to either ribs, scapula, or humerus
Intrinsic back muscles
this group of muscles attaches only to vertebrae or the skull
ventral rami of spinal nerves
what are the extrinsic back muscles supplied by?
dorsal rami of spinal nerves
what are the intrinsic back muscles supplied by?
extend spine and/or head (bilateral contraction)
what do all intrinsic back muscles do?
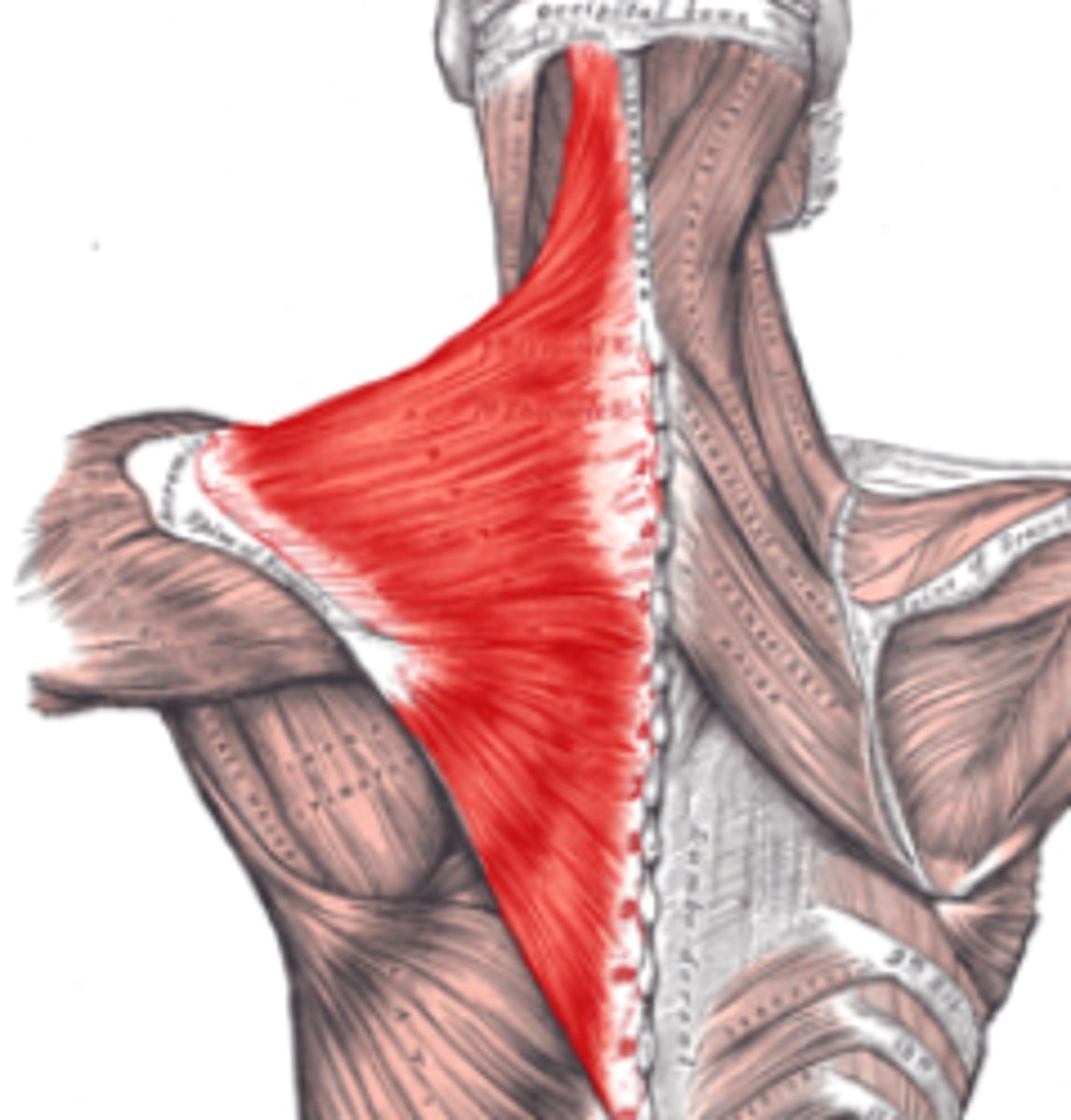
Trapezius
innervated by CN 11 (accessory nerve)
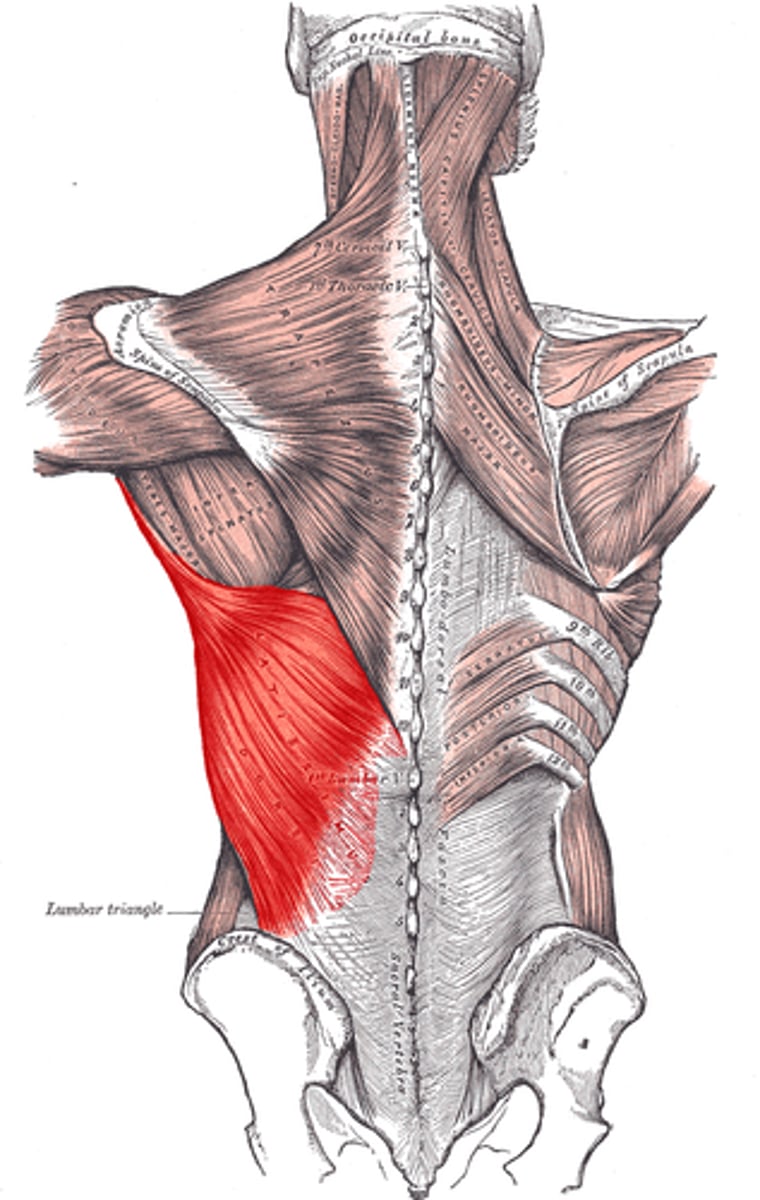
latissimus dorsi
Name the muscle
Elevates & depresses scapula, retracts, and rotates scapula & arm
action of trapezius
2 multiple choice options
thoracodorsal nerve (C6-C8)
Latissimus Dorsi Innervation
-extension, adduction, and medial rotation of the arm
-raises body toward arms when climbing
Latissimus Dorsi action
accessory nerve
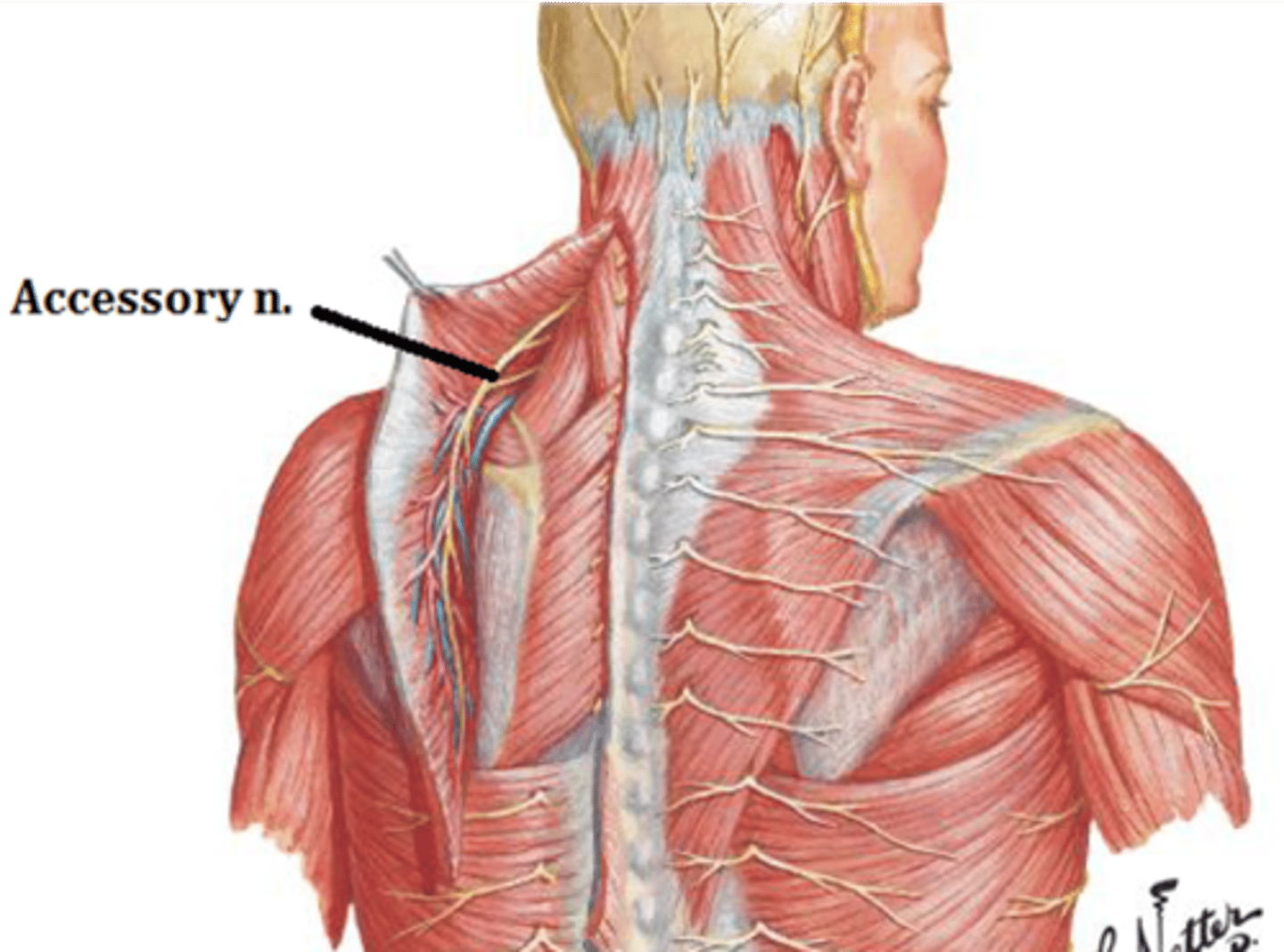
shrugging shoulders
how is the accessory nerve evaulated?
transverse cervical vessels (branch of thyrocervical trunk)
runs posteriorly and then inferiorly deep to the trapezius
dorsal scapular nerve (C4 and C5)
innervation for levator scapulae and rhomboid muscles
elevates scapula
action of levator scapula
retracts scapula
(major does most of the work)
action of rhomboids
elevates ribs
action of serratus posterior superior
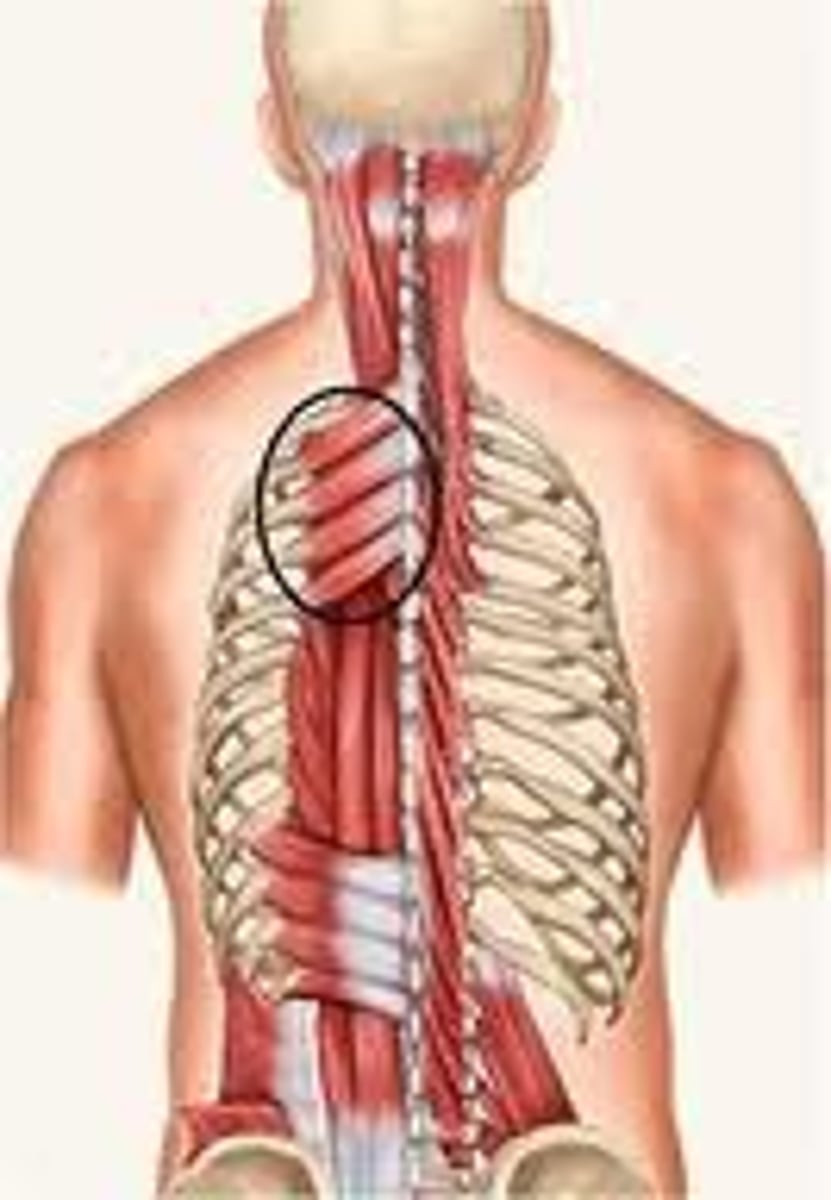
depresses ribs
action of serratus posterior inferior
proprioceptive, motor
the actions of the serratus posterior muscles are more _______ than ________
splenius muscle
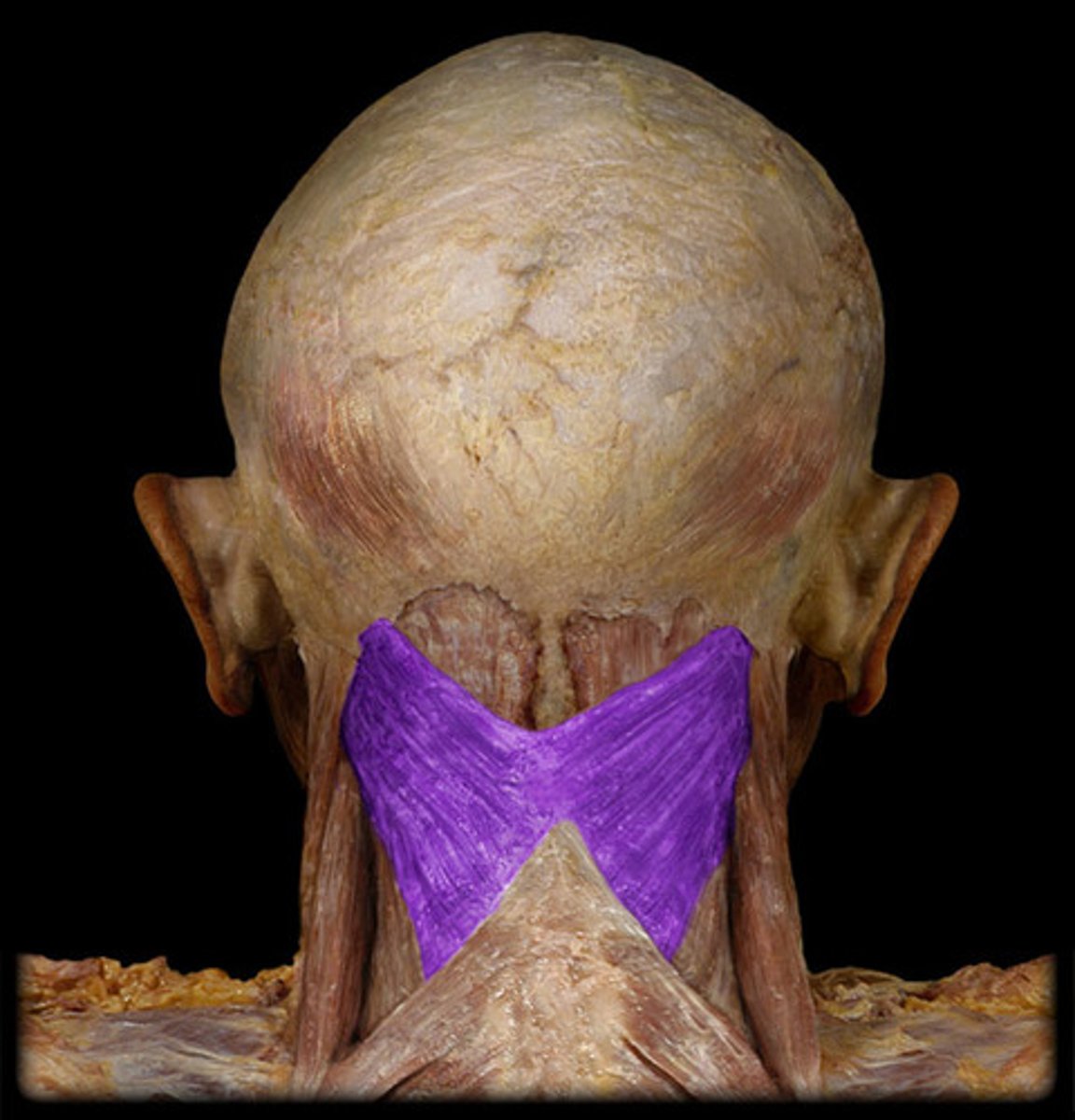
bilateral: extends cervical spine and head
unilateral: flexes and rotates head to the same side
bilateral and unilateral actions of the splenius
splenius innervation
1st muscles not supplied by a named nerve
dorsal rami of cervical spinal nerves
splenius innervation
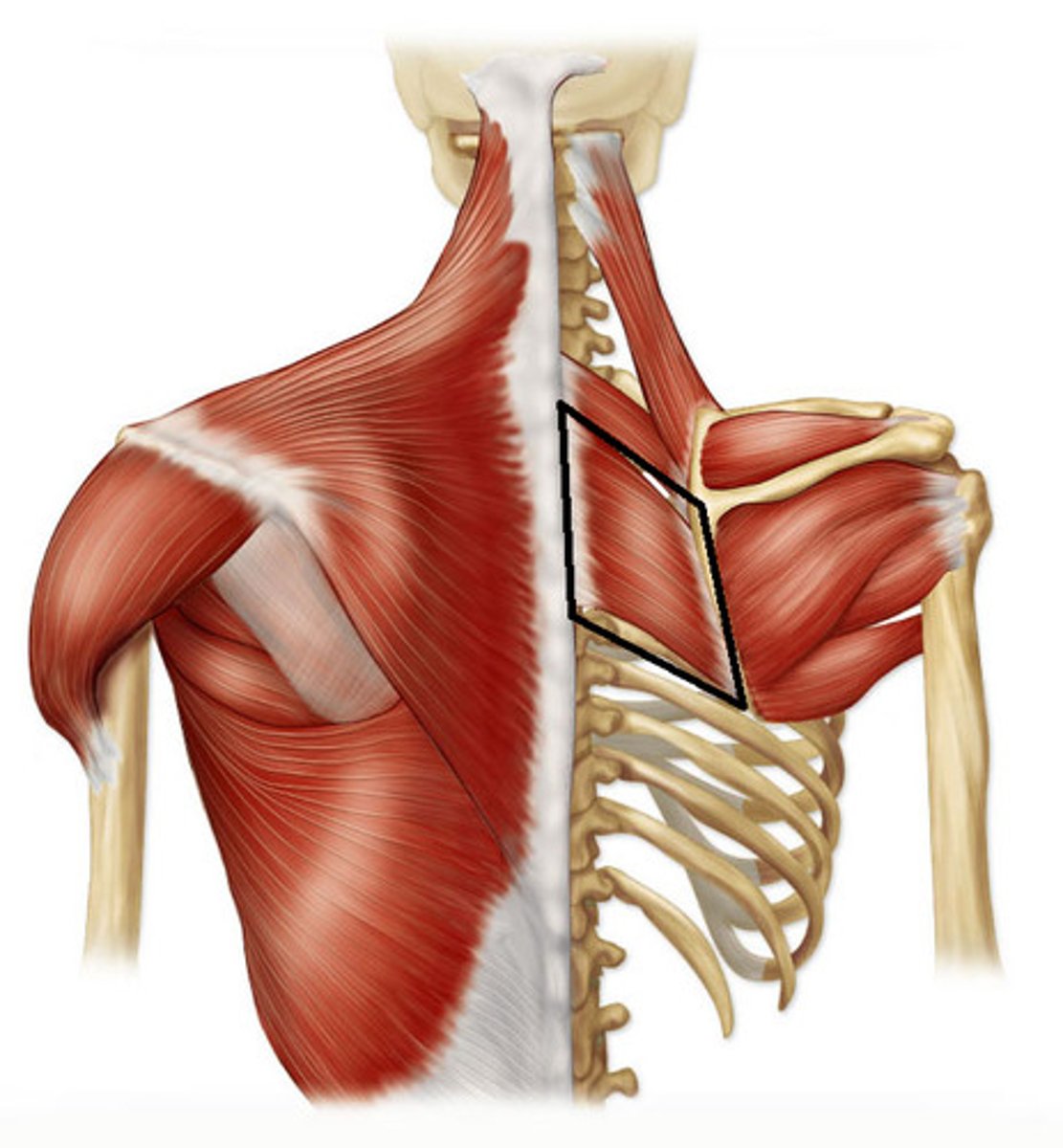
Triangle of Auscultation
good location for listening to heart sounds
A- erector spinae
B- iliocostalis
C- longissimus
D- spinalis
A,B,C,D
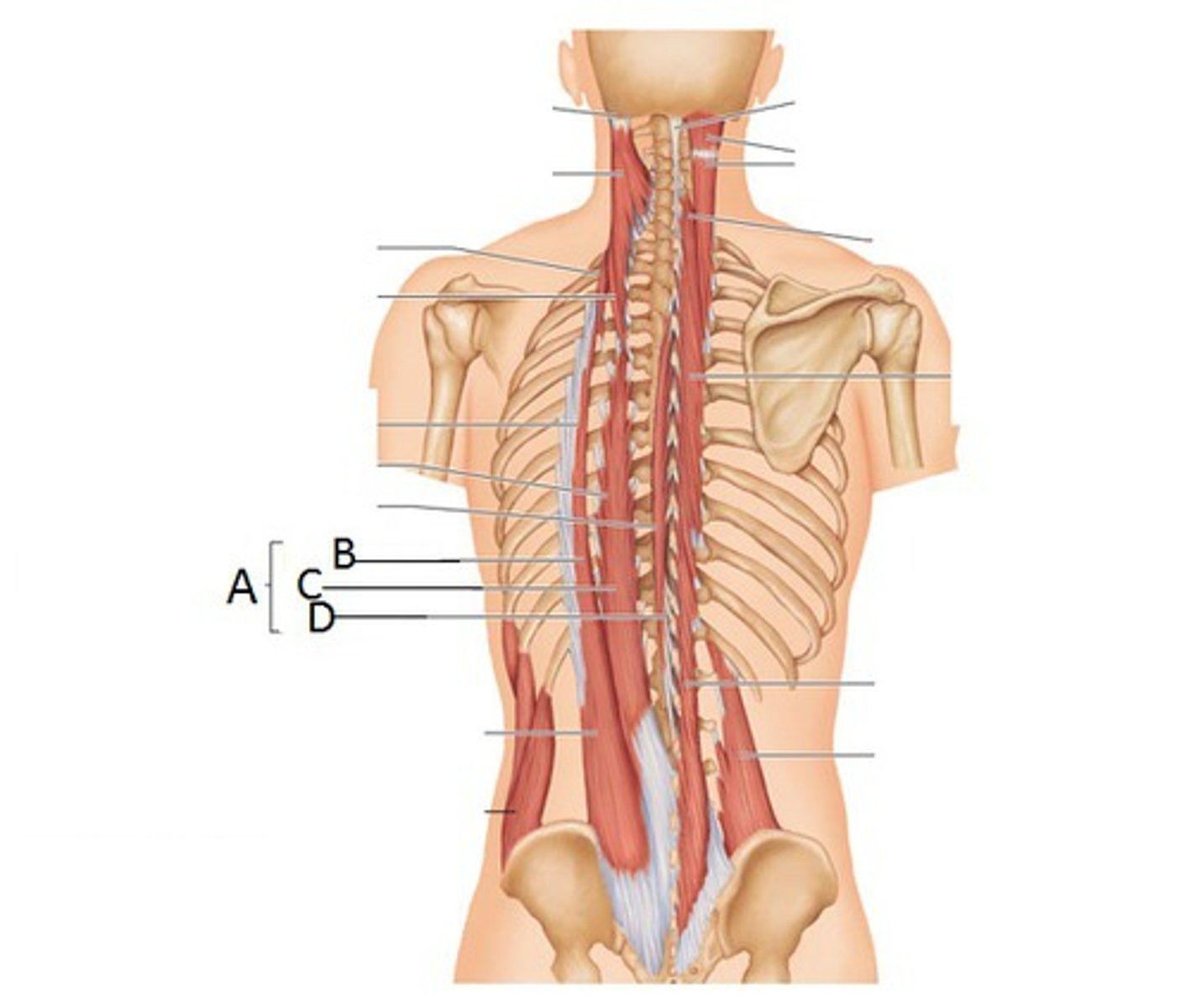
dorsal rami of spinal nerves
erector spinae innervation
bilateral: extension of spine/neck
unilateral: ipsilateral flexion of spine/head
action of erector spinae muscles
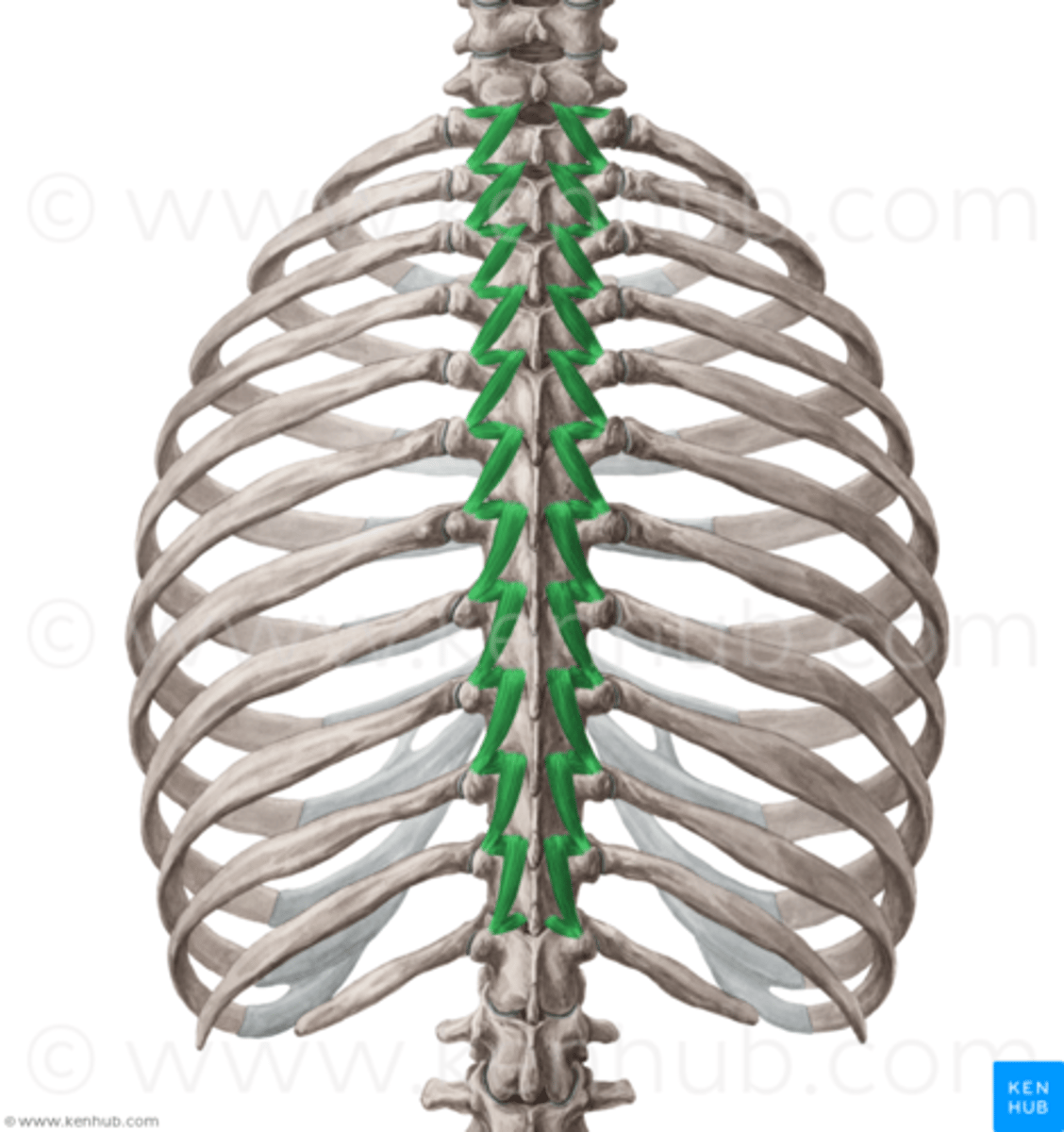
rotatores, multifidus, semispinalis
transversospinalis muscles
rotatores
-allows vertebral flexibility
-sits in between transverse process & spinous process
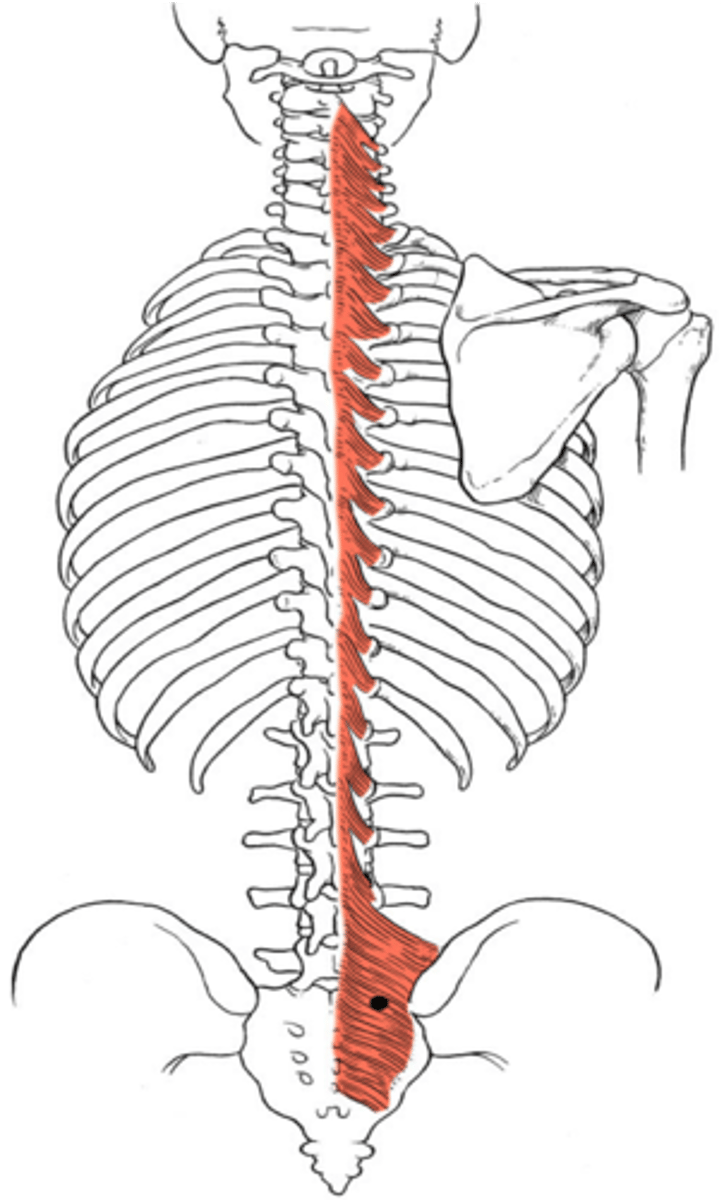
Multifidus
-extends and rotates vertebral column
-Chronic lower back pain here
semispinalis
extends neck and vertebral column
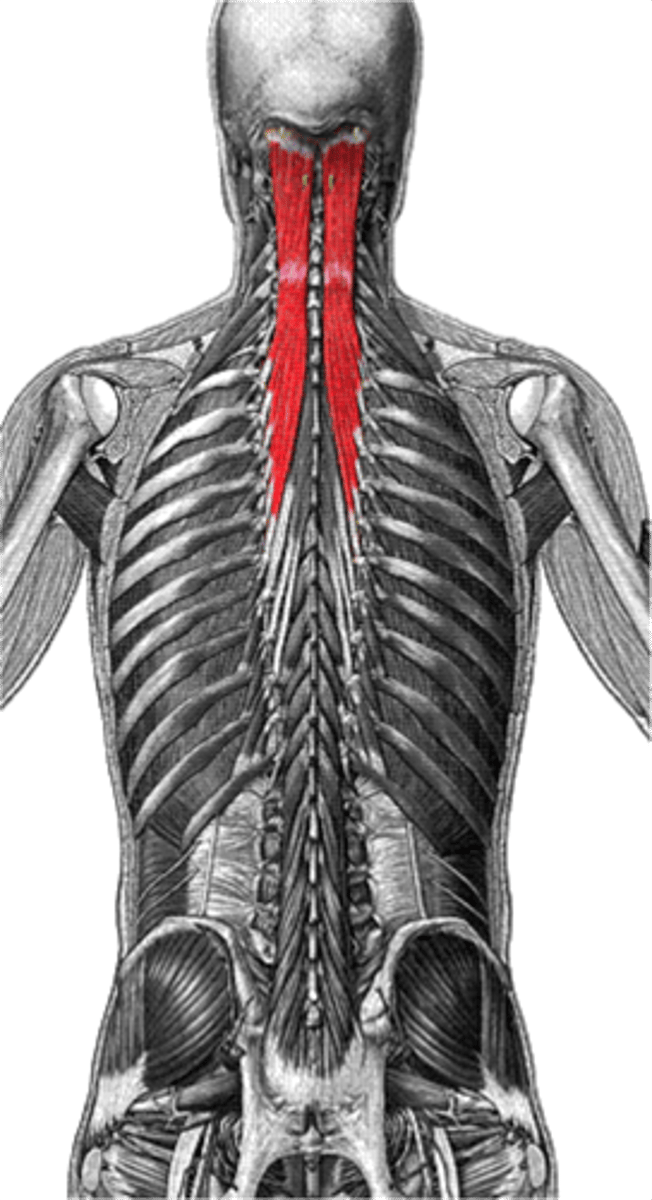
dorsal rami of spinal nerves
transversospinalis muscles innervation
Bilateral: extension of spine/neck
unilateral: contralateral spine/head rotation
actions of the transversospinalis muscles
interspinales
muscle located between spinous processes
levatores costarum
expansion of ribs during breathing
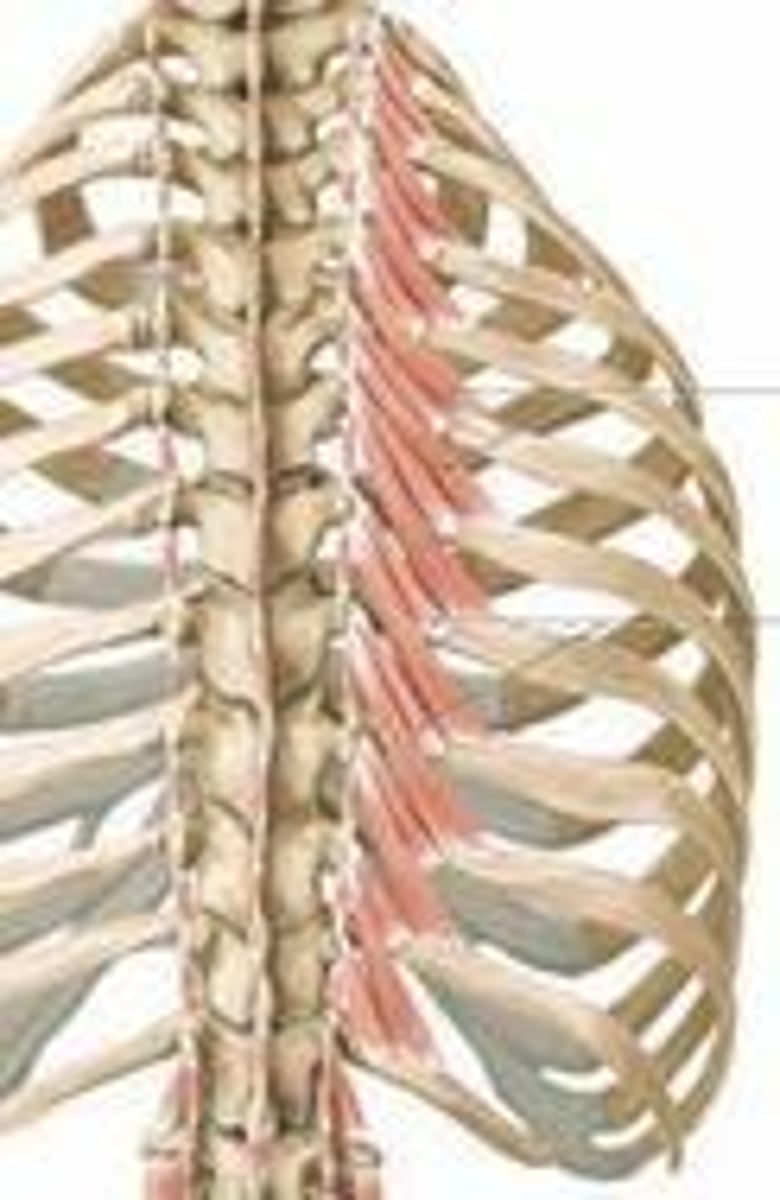
dorsal rami of spinal nerves
interspinales & levatores costarum innervation
intertransversarii
lateral flexion of vertebral column
muscle located between transverse processes
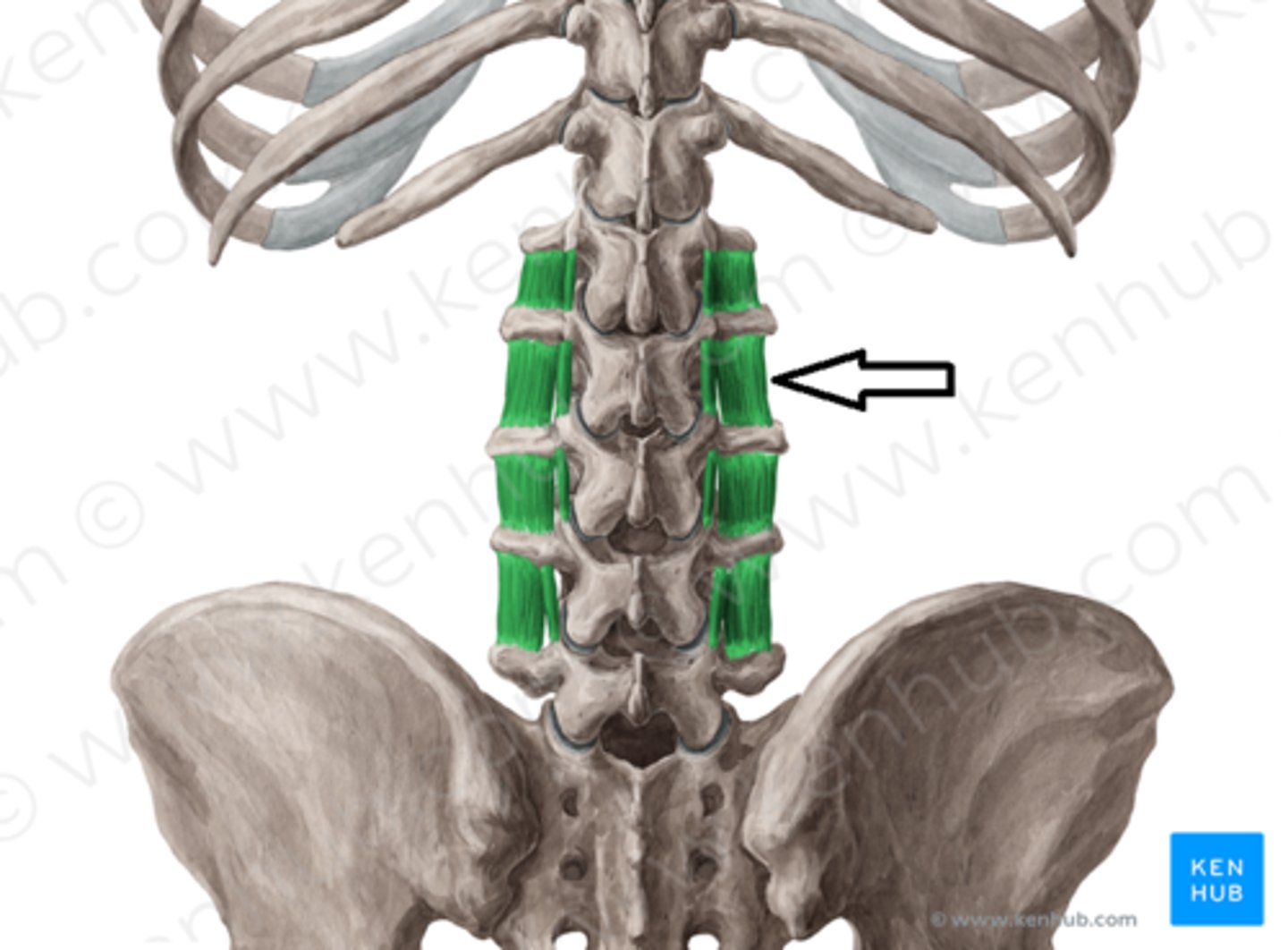
dorsal rami AND ventral rami of spinal nerves
intertransversarii innervation
Extend spine
major role of deep minor intrinsic back muscles
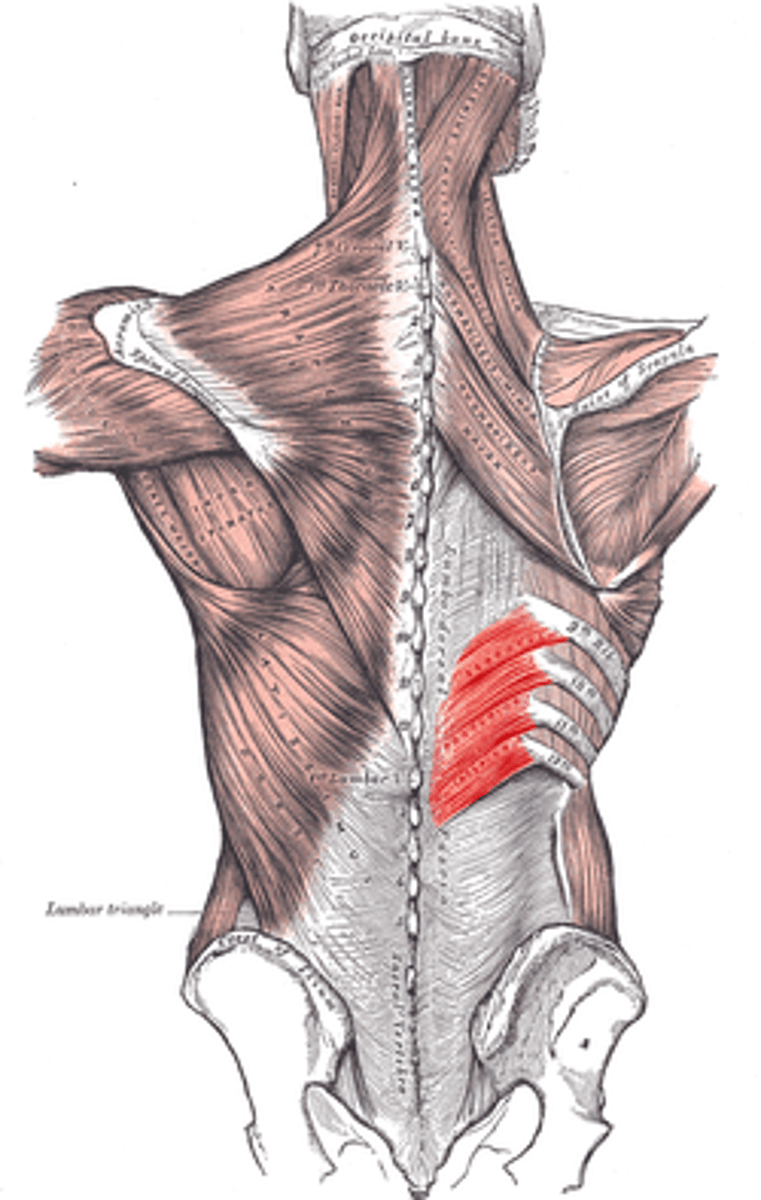
under the semispinalis
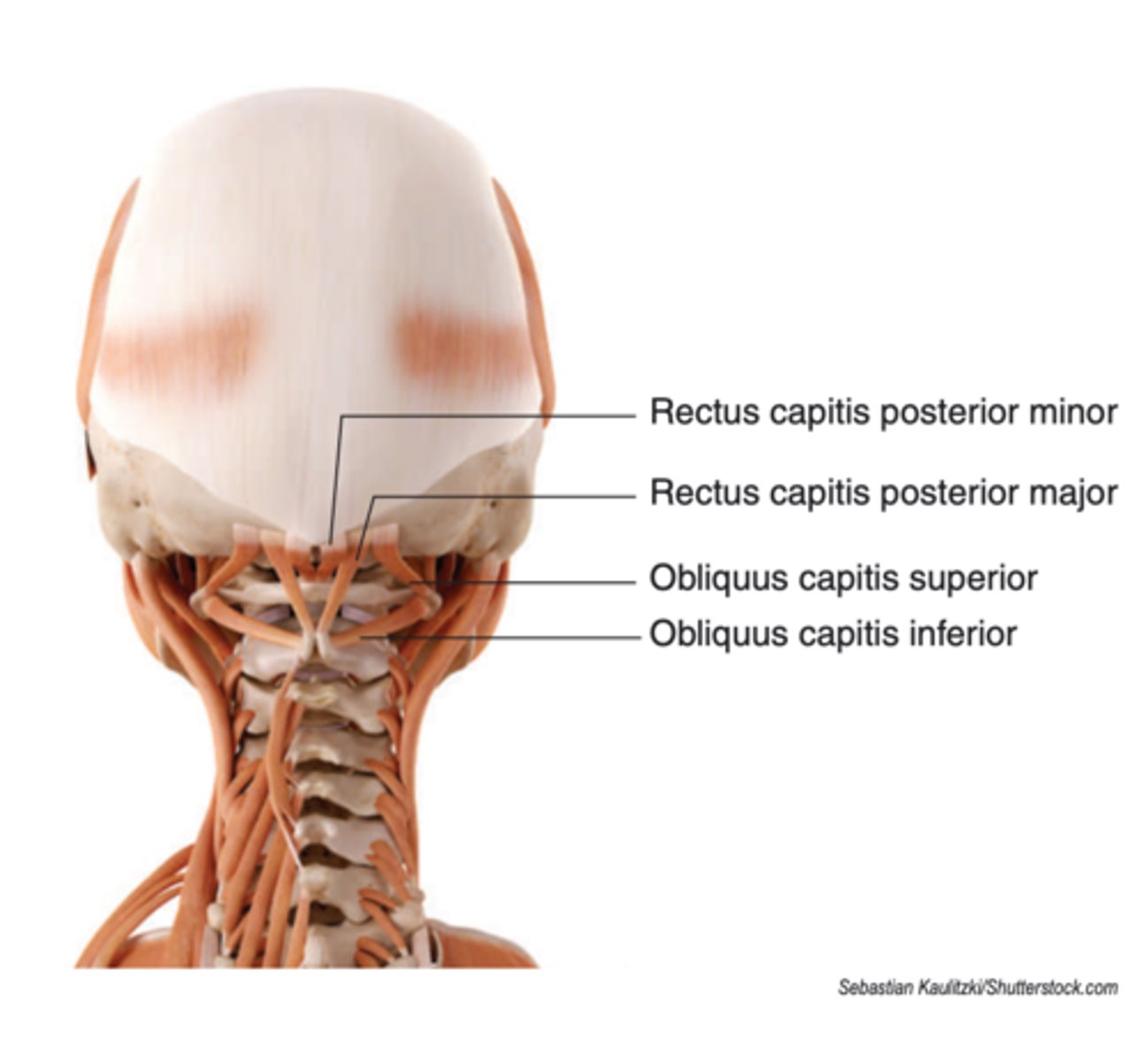
location of suboccipital triangle
suboccipital triange