Lecture 9 - respiration/oxidative phosphorylation
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
18.1-18.3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Reduced fuels
carbohydrates, lipids, amino acids
reduce NAD+ to NADH or FAD to FADH2
Oxidative phosphorylation
energy from NADH and FADH2 used to make ATP
electrons are passed to proteins in the respiratory chain
energy of oxidation phosphorylates ADP
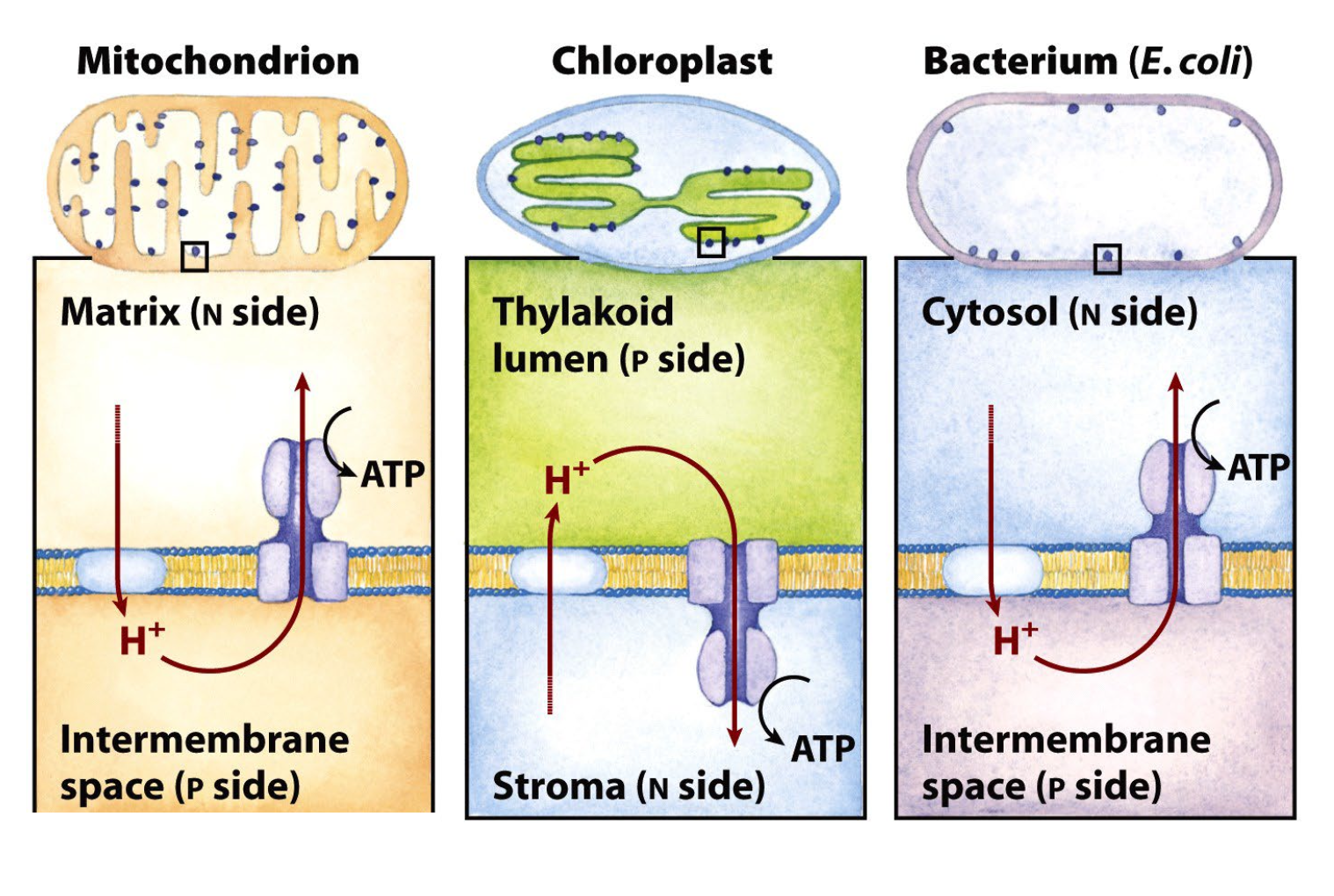
inner mitochondrial membrane
cristae in mitochondria increase surface area
outer mitochondrial membrane
freely permeable to small molecules and ions
inner mitochondrial membrane
impermeable to most small molecules and ions, including H+
contains:
respiratory electron carriers (Complexe I-IV)
ADP-ATP translocase
ATP synthase (F0F1)
Other membrane transporters
mitochondrial matrix
contains:
pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
citric acid cycle enzymes
fatty acid β-oxidation enzymes
amino acid oxidation enzymes
DNA, ribosomes
many other enzymes
ATP, ADP, Pi, Mg2+, Ca2+, K+
many soluble metabolic intermediates
mitochondria structure
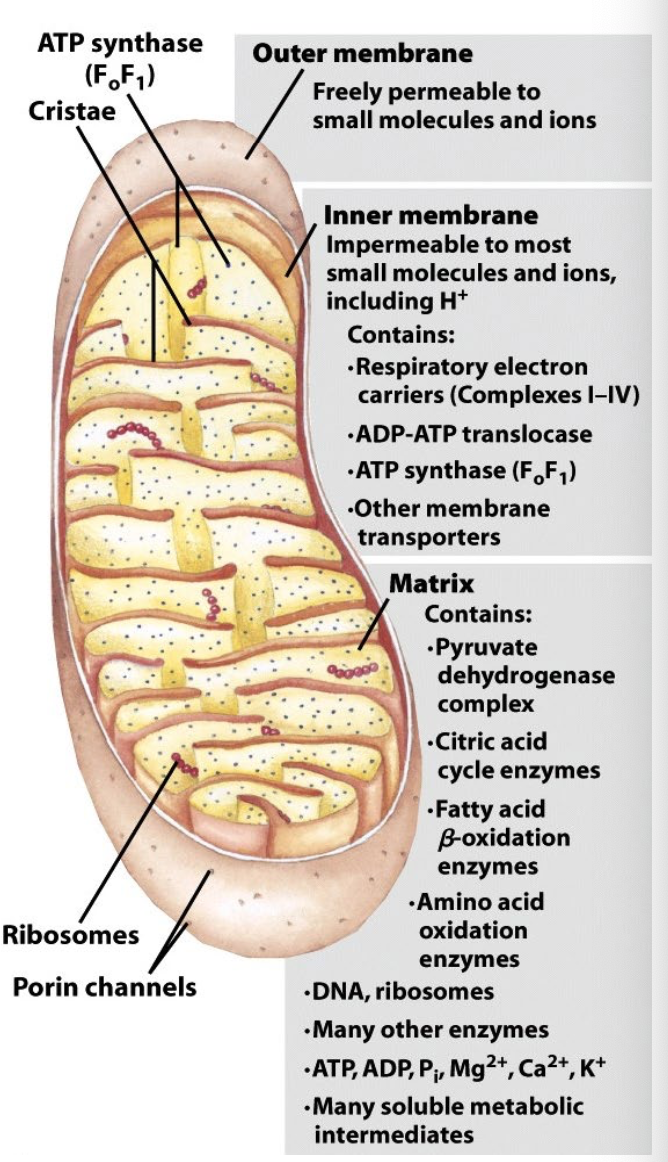
proton-motive force
protons transported uphill against electrochemical gradient during electron transport
each NADH oxidized drives 10 H+ which yields ~3 ATP molecules
Redox potentials
Δ𝜺 = Δ𝜺 (acceptor ½ rxn) - Δ𝜺 (donor ½ rxn)
ΔGredox = -nFΔ𝜺
Half reactions
An+ox + ne- ⇆ Ared
Δ𝜺(A rxn) = Δ𝜺° - RT/nF(ln [Ared/Aox])
positive: reduction favorable; strong oxidant
![<p>A<sup>n+</sup><sub>ox</sub> + ne<sup>-</sup> ⇆ A<sub>red</sub></p><p>Δ𝜺<sub>(A rxn)</sub> = Δ𝜺° - RT/nF(ln [A<sub>red</sub>/A<sub>ox</sub>])</p><ul><li><p>positive: reduction favorable; strong oxidant</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/af6472c5-b18a-4d19-8846-74128f048b37.png)
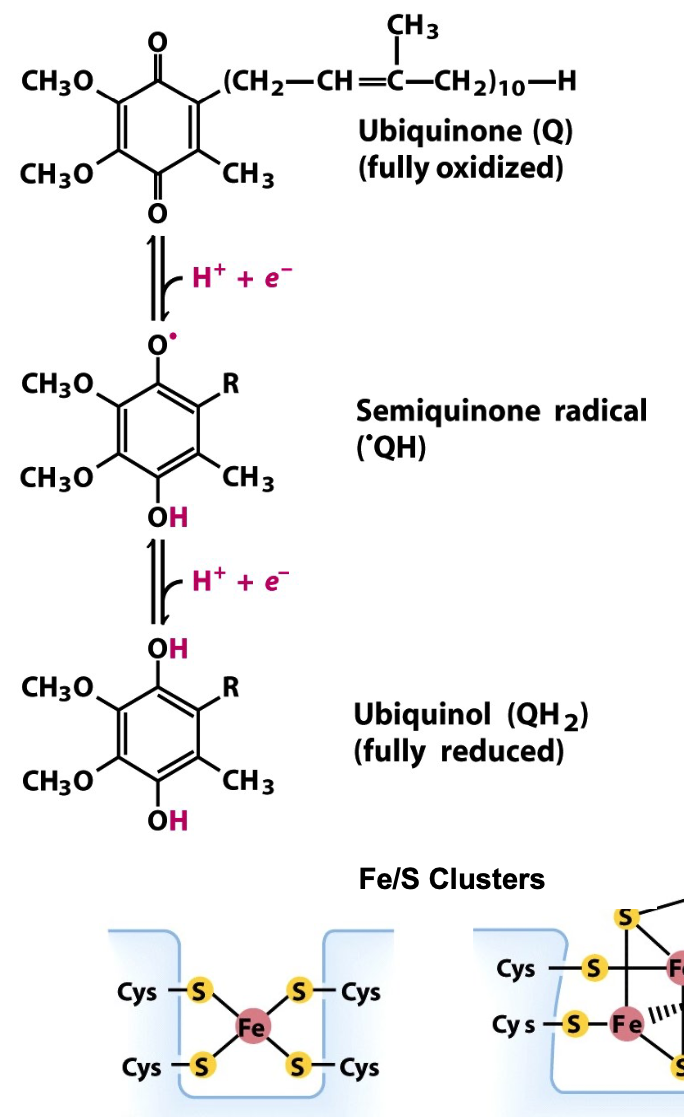
Electron transfer cofactors
quinone ⇆ ubiquinol
quinone accepts 2 e-, 2 H+ to give ubiquinol
ubiquinol: freely diffuses in membrane, carrying e- with H+ across membrane
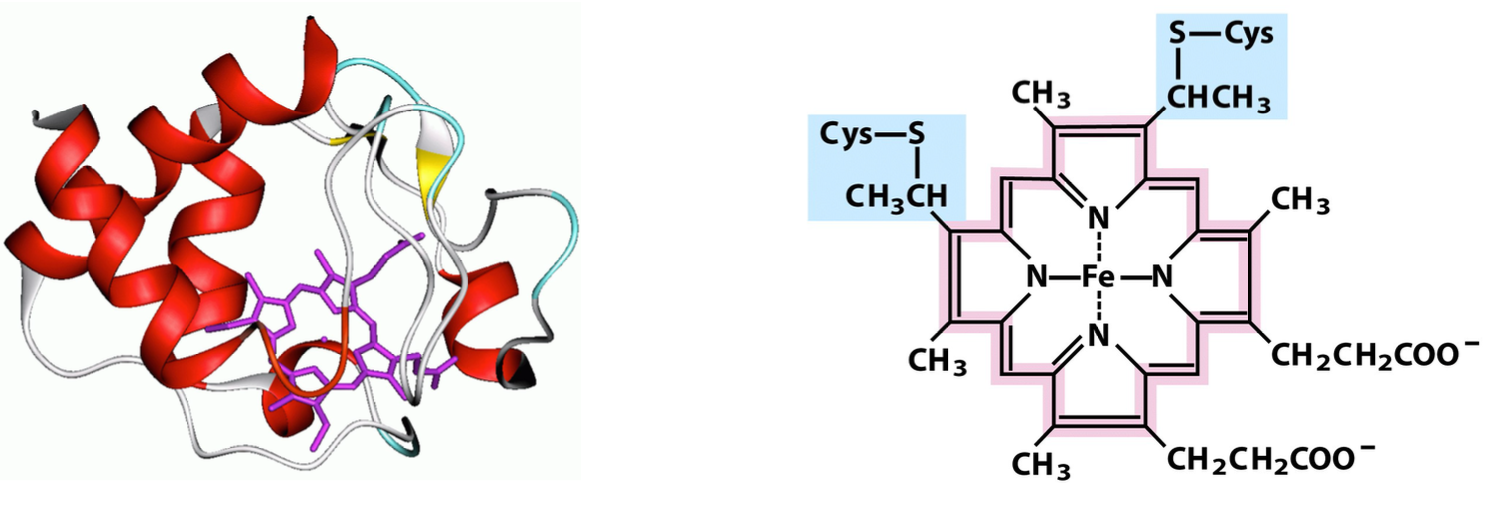
Heme
can be either ferric (Fe3+, oxidized) or ferrous (Fe2+, reduced)
Fe/S clusters
transfer 1 e- at a time
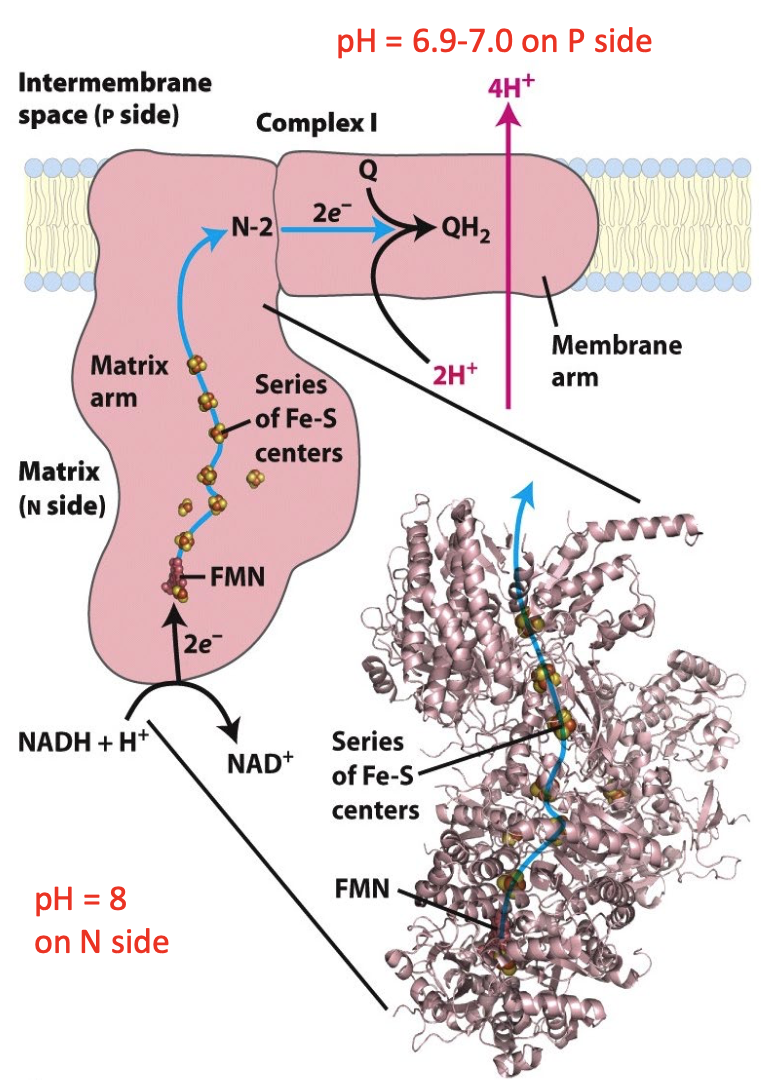
Complex I: NADH: Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase
40 subunits
complete assembly seen in EM
soluble part of bacterial protein crystallized
NADH binding site: matrix side
bound flavin mononucleotide (FMN) accepts 2 e- from NADH
series of Fe/S centers pass e- from FMN to ubiquinone binding site
per NADH, 4 H+ transferred from matrix (N) to inter-membrane space (P)
NADH + Q + 5 H+N → NAD+ + QH2 + 4 H+P
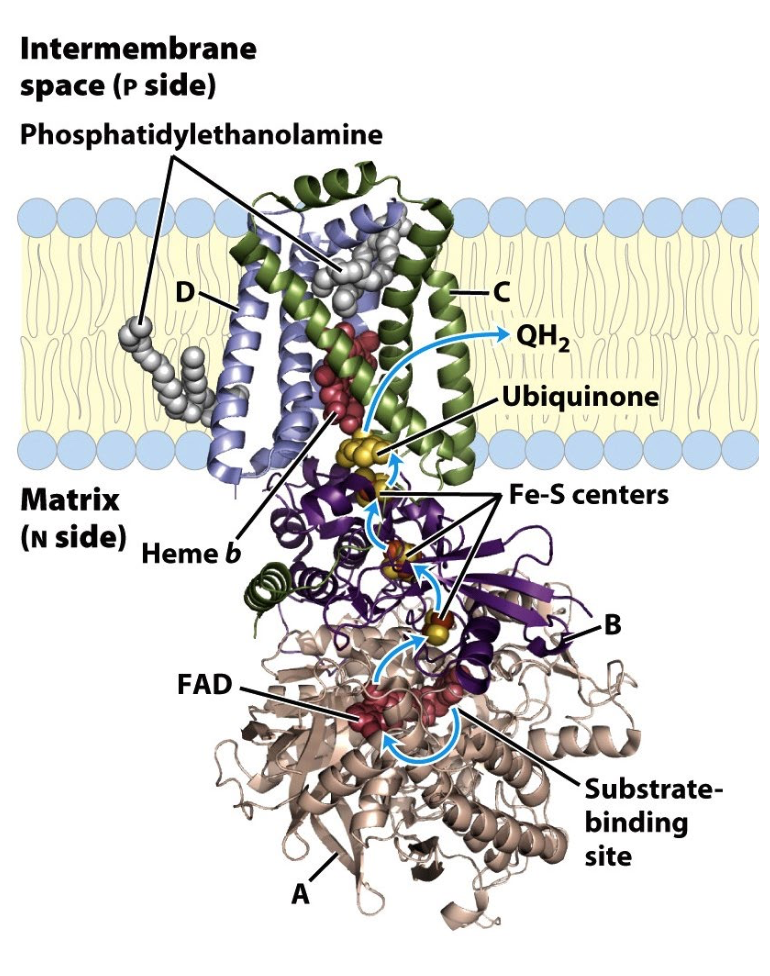
Complex II: Succinate Dehydrogenase
FAD accepts two e- from succinate
FADH2 e- passed via Fe/S centers → ubiquinone, becomes reduced QH2
Succinate + FAD + Q → Fumarate + FAD + QH2
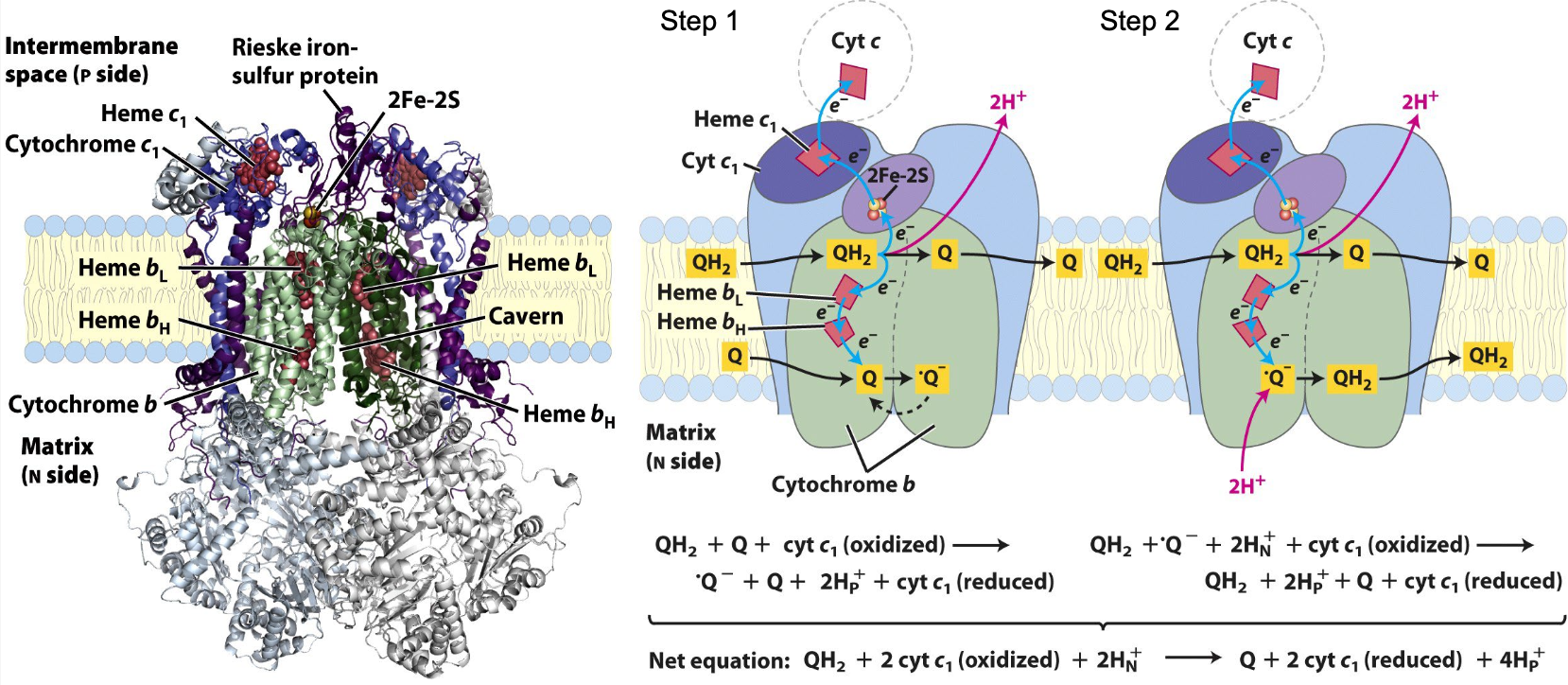
Complex III: Cytochrome bc1
uses 2 e- from QH2 to reduce two molecules of cyt c via 2 step cycle
4 H+ transported across membrane per 2 e- that reach cyt c
step 1: QH2 give 2 out of 4 H+
step 2: regeneration of QH2 gives 2 H+ from matrix
cytochrome c
soluble heme-containing protein in intermembrane space
carries a single e- from the cytochrome bc1 complex to cytochrome oxidase
small (12 kD), binds/unbinds quickly from Complexes III and IV
can exit the mitochondrion as part of the apoptotic cell death pathway
Complex IV: Cytochrome c Oxidase
4 cyt c oxidized
O2= ultimate e- sink
4e- and 4 H+ from matrix used to reduce O2 molecule into H2O
4 more H+ pumped to inter-membrane space
4 cyt c + O2 +*H+N → 4 cyt c(ox) + 2 H2O + 4 H+P
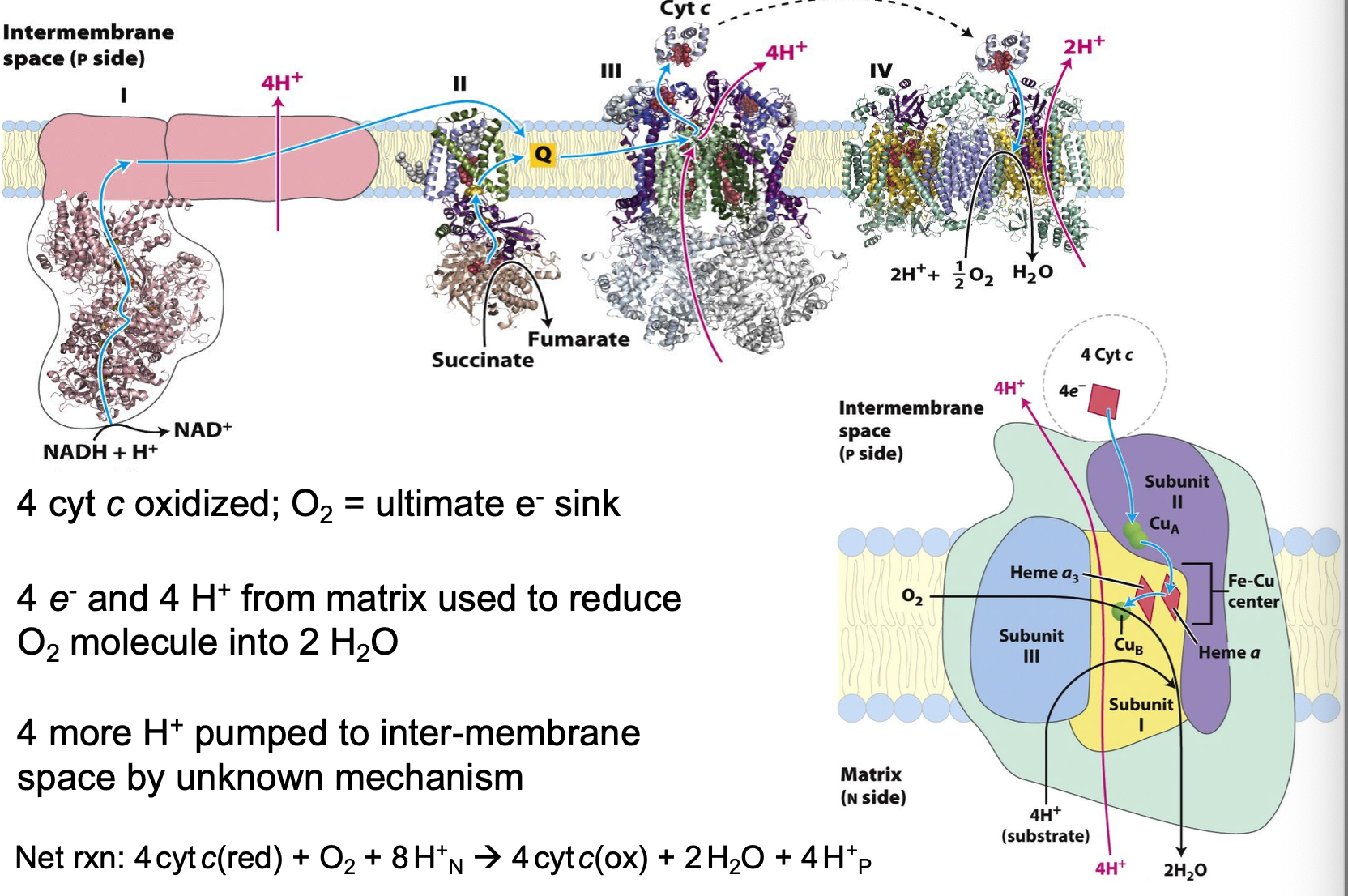
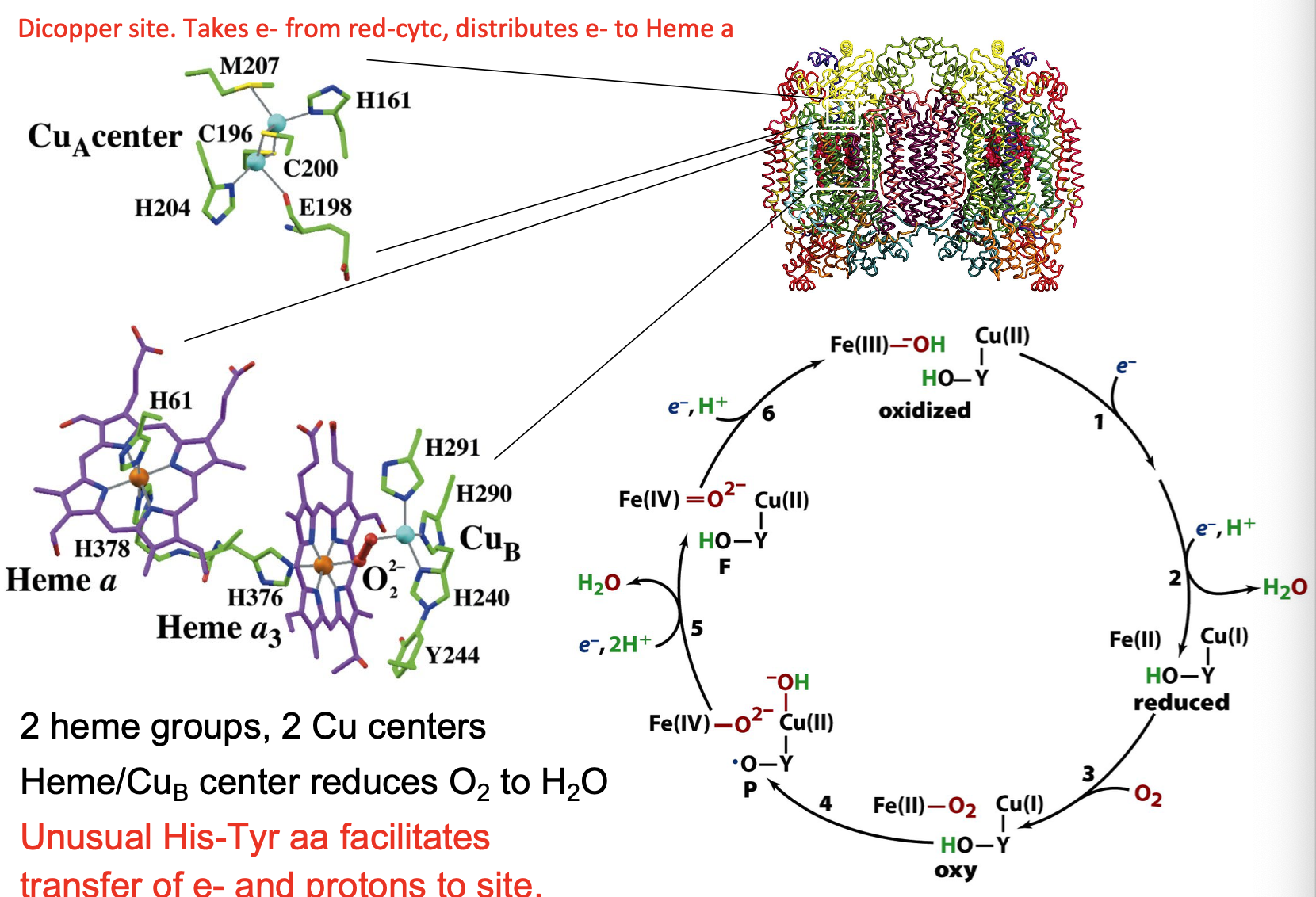
Cytochrome c Oxidase mechanism
2 heme groups, 2 Cu centers
Heme/CuB center reduces O2 to H2O
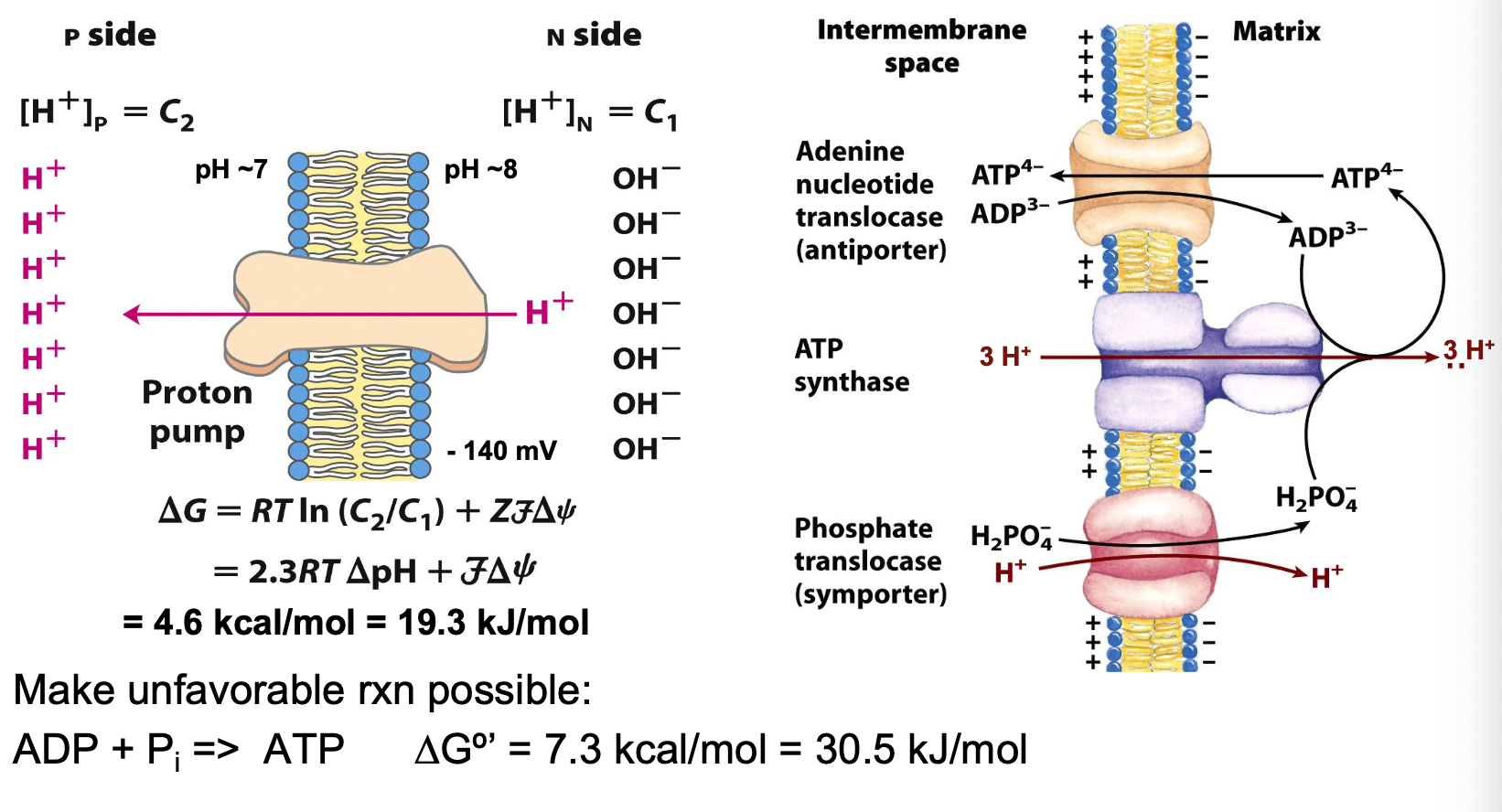
ATP synthesis energy
energy needed to phosphorylate ADP provided by flow of protons down electrochemical gradient (PMF)
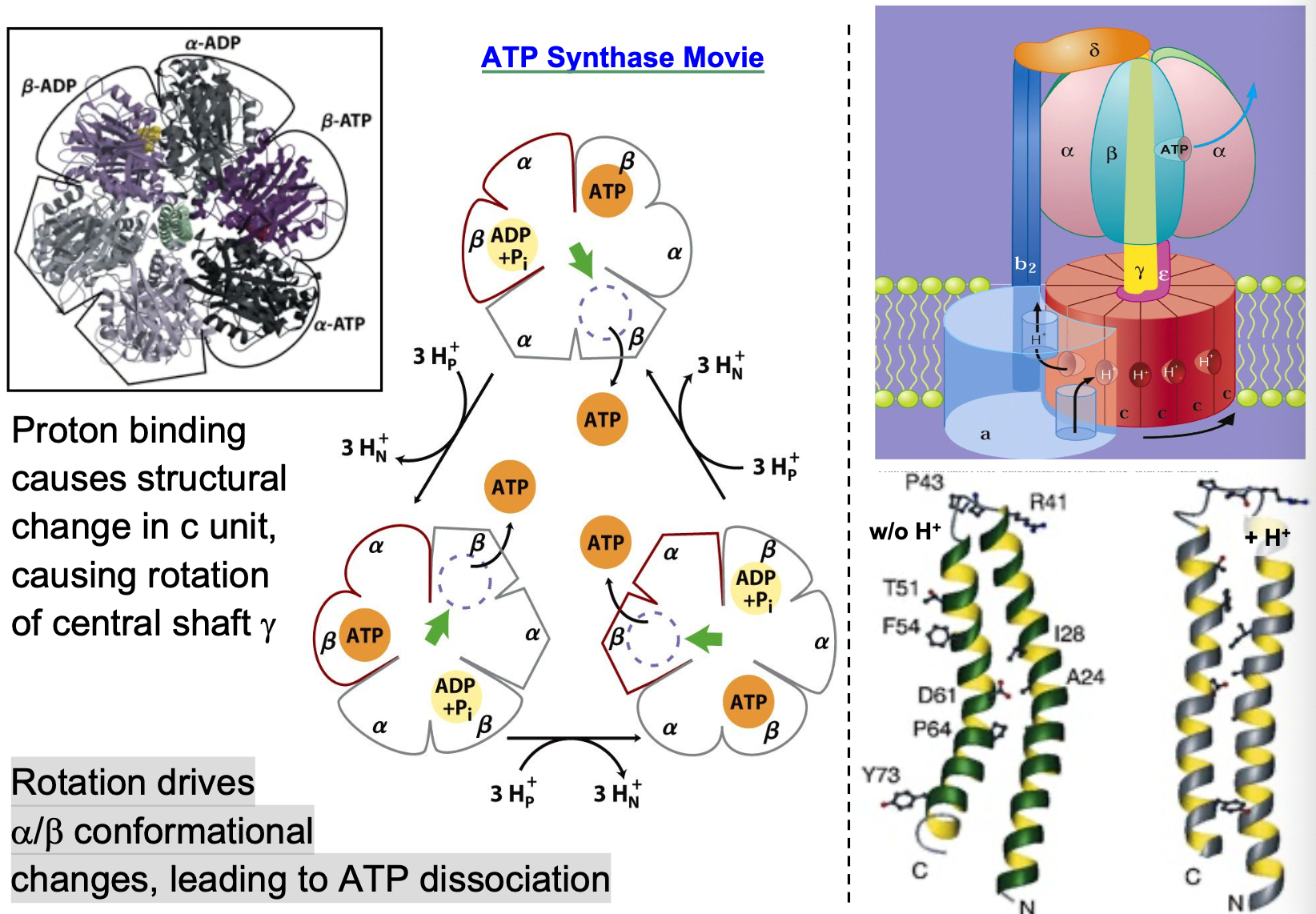
ATP synthase structure
two separable domains
F1 (ATP synthase)pocket binds ADP and stabilizes ATP formation
F0 (transmembrane proton channel) uses H+ translocation to force ATP out of binding pocket, bind new ADP + Pi
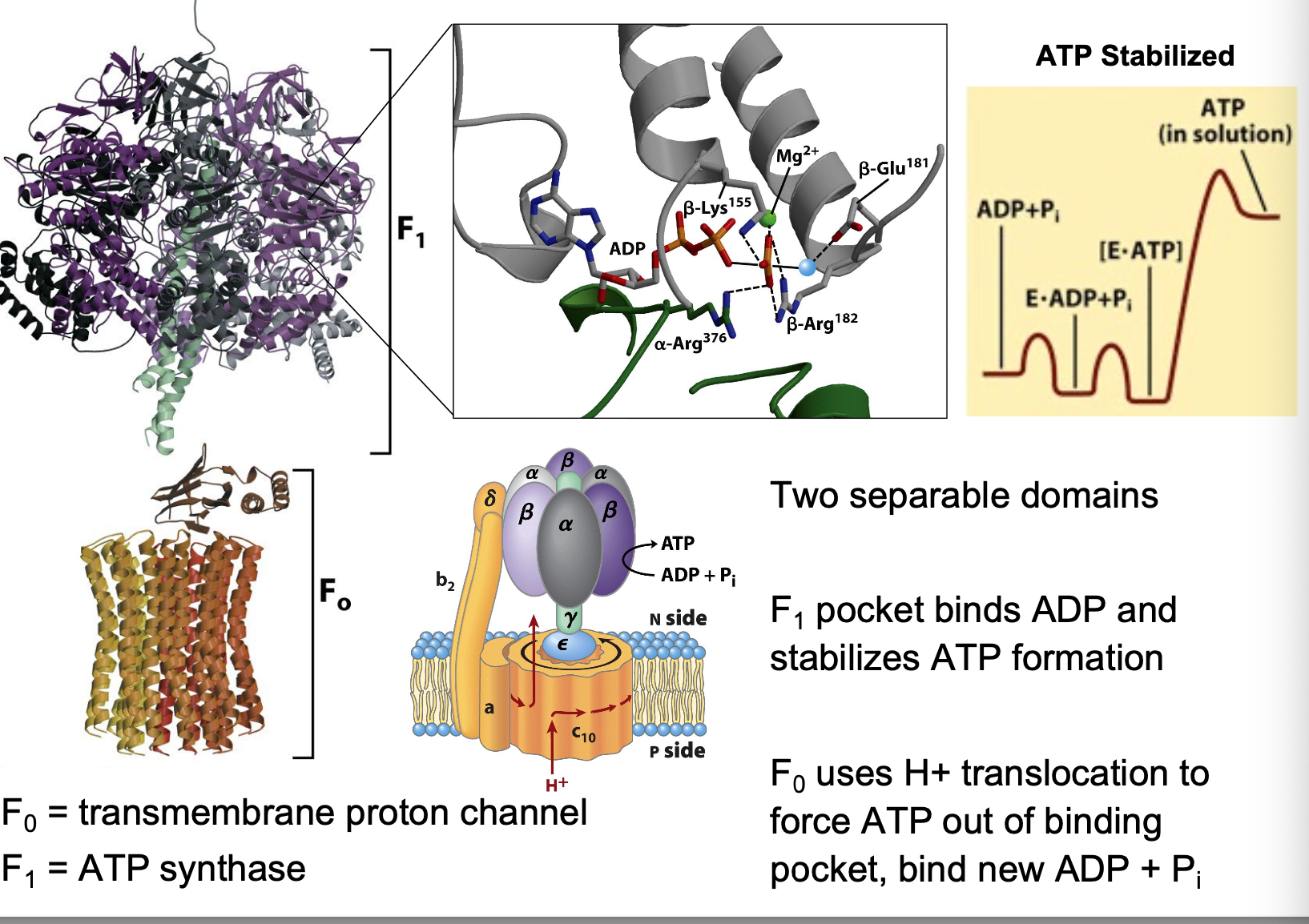
ATP synthase conformational change
proton binding causes structural change in c unit, causing rotation of central shaft γ
Rotation drives α/β conformational changes, leading to ATP dissociation
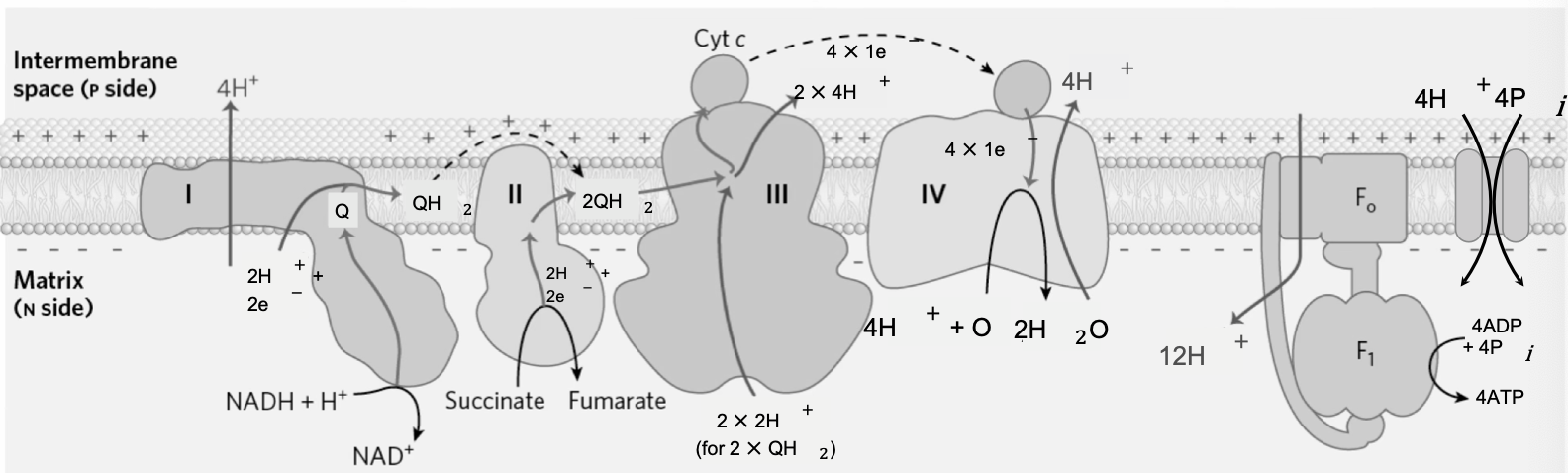
Oxidative Phosphorylation with Succinate (FADH2)
Complex I: NADH + Q + 5 H+N → NAD+ + QH2 + 4 H+P
Complex II (FADH2): Succinate + Q → Fumarate + QH2
Complex III: 4 cyt c(ox) + 2 QH2 + 4H+N → 4 cyt c(red) + 2 Q + 8H+P
Complex IV: 4 cyt c(red) + O2 + 8H+N → 4 cyt c(ox) + 2H2O + 4H+P
ATP Synthase + Pi Translocase: 4 ADP + 16H+P + 4Pi(p) → 4ATP + 16H+N
Net: 4 ADP + 4Pi(p) + NADH + H+N + Succinate + O2 → 4 ATP + NAD+ + Fumarate + 2 H2O
Oxidative Phosphorylation per Matrix NADH
Complex I: NADH + Q + 5 H+N → NAD+ + QH2 + 4 H+P
Complex III: 2 cyt c(ox) + QH2 + 2H+N → 2 cyt c(red) + Q + 4H+P
Complex IV: 2 cyt c(red) + 0.5 O2 + 4H+N → 2 cyt c(ox) + H2O + 2H+P
ATP Synthase + Pi Translocase: 2.5 ADP + 10H+P + 2.5Pi(p) → 2.5ATP + 10H+N
Net: 2.5 ADP + 2.5Pi(p) + NADH + H+N + 0.5 O2 → 2.5 ATP + NAD+ + H2O
Oxidative Phosphorylation per Cytosolic NADH
Complex NAHDH: NADH + H+ + Q → NAD+ + QH2
Complex III: 2 cyt c(ox) + QH2 + 2H+N → 2 cyt c(red) + Q + 4H+P
Complex IV: 2 cyt c(red) + 0.5 O2 + 4H+N → 2 cyt c(ox) + H2O + 2H+P
ATP Synthase + Pi Translocase: 1.5 ADP + 6H+P + 1.5Pi(p) → 1.5ATP + 6H+N
Net: 1.5 ADP + 1.5Pi(p) + NADH + H+N + 0.5 O2 → 1.5 ATP + NAD+ + H2O
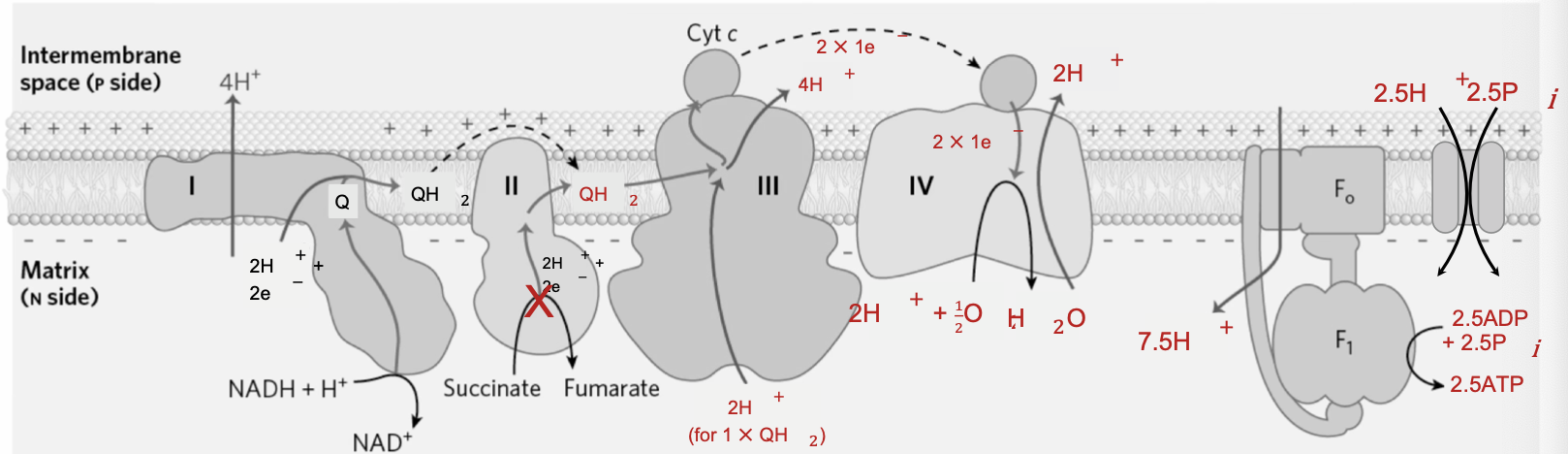
Oxidative Phosphorylation per FADH2
Complex II (FADH2): Succinate + Q → Fumarate + QH2
Complex III: 2 cyt c(ox) + QH2 + 2H+N → 2 cyt c(red) + Q + 4H+P
Complex IV: 2 cyt c(red) + 0.5 O2 + 4H+N → 2 cyt c(ox) + H2O + 2H+P
ATP Synthase + Pi Translocase: 1.5 ADP + 6H+P + 1.5Pi(p) → 1.5 ATP + 6H+N
Net: 1.5 ADP + 1.5Pi(p) + 2H+N + 0.5 O2 → 1.5 ATP + H2O
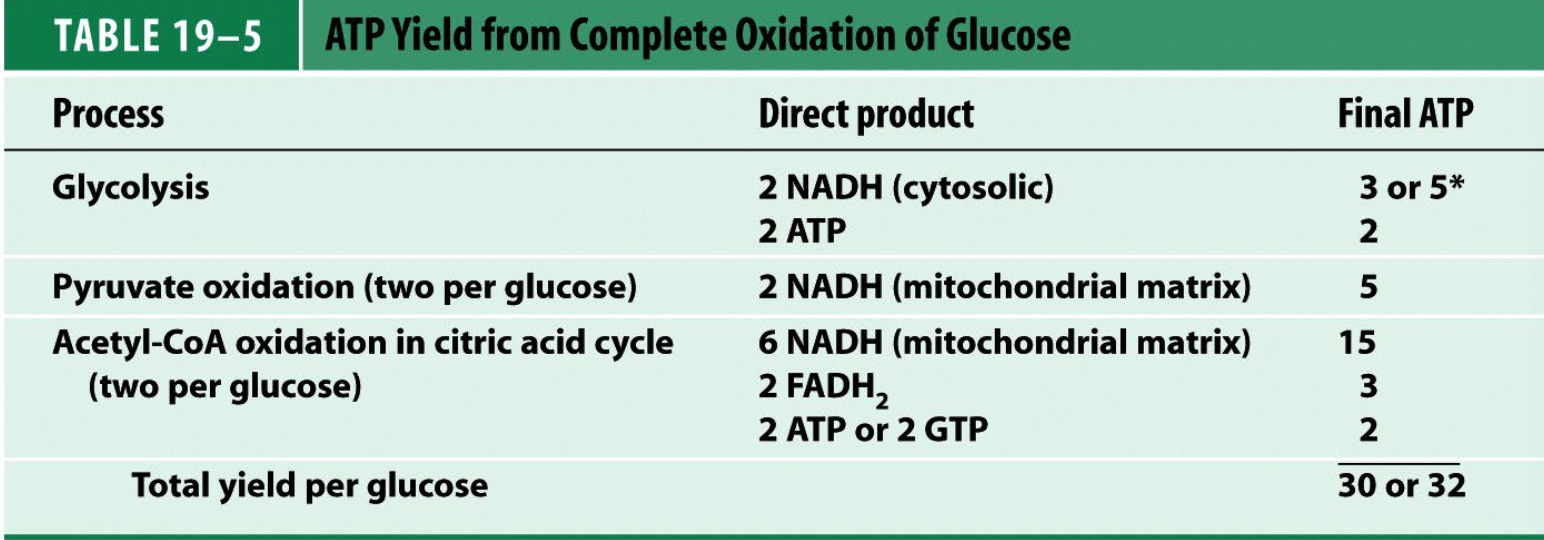
ATP yield
4 H+ per ATP synthesized, 3 per turn of ATP synthase, 1 per PO4 import
10 H+ per NADH when e- donated to complex I, so 2.5 ATP per matrix NADH.
6 H+ per NADH when e- donated to quinone (4 H+ pumped by complex III, 2 H+ by complex IV), 1.5 ATP per cytosolic NADH.
6 H+ per FADH2 when e- donated to quinone (Succinate Dehydrogenase), 1.5
ATP per FADH2
PMF-Driven energy systems: Common origin