Digestion
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Define digestion
The breaking down of food from large insoluble molecules, to small soluble molecules
What are the 2 methods of mechanical digestion?
Chewing in the mouth
Churning in the stomach
In what order, does food pass through our body?
Mouth
Oesophagus
Stomach
Small intestine
Large intestine
Rectum
Anus
What happens to digested food?
Absorbed back into the bloodstream in the small intestine
What happens to excess water?
Absorbed back into the body in the large intestine
What happens to undigested food?
Passes out of the anus as faeces
What does the liver produce? What does it do?
Bile- helps the digestion of lipids by breaking them up into tiny droplets (emulsifies them).
It is also alkaline to neutralise the hydrochloric acid in our stomach
What are enzymes?
Biological catalysts
Where are digestive enzymes produced? What are they?
Mouth- Amylase
Stomach- pepsin
Pancreas- carbohydrasees, proteases, lipases
Small intestine- carbohydrases, proteases, lipases
What does amylase do
Breaks down starch into simple sugars
What does protease do?
Break down priteins into amino acids
What does lipase do?
Breaks down fats into glycerol and fatty acids
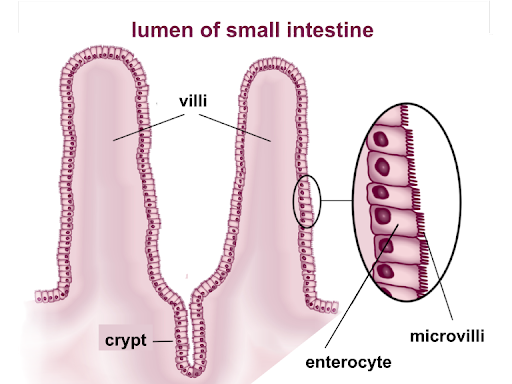
How is the small intestine adapted for digestion?
Thin cell wall → shorter diffusion pathway
Long → Increases surface area
Lots of villi → increase surface area
Good blood supply → maintain concentration gradient
Permeable → molecules can pass through easily
How do you test for starch?
Iodine solution
↳ Yellow → blue/black
What is the test for sugar?
Benedict's solution
↳ Blue → brick red
What is the test for proteins?
Biuret's solution
↳ Blue → lilac
Explain the lock and key theory
That substrates are complimentary to an enzyme. If they are denatured, they can no longer fit into the active site.
What can cause an enzyme to denature?
Temperature
pH