Chem 1A: Balancing Reactions and Stoichiometry
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Stoichiometry
Quantitative relationships in chemical reactions.
Limiting Reagent
Reactant producing the least amount of product.
Molar Mass
Mass of one mole of a substance in g/mol.
Balancing Equations
Adjusting coefficients to equalize reactants and products.
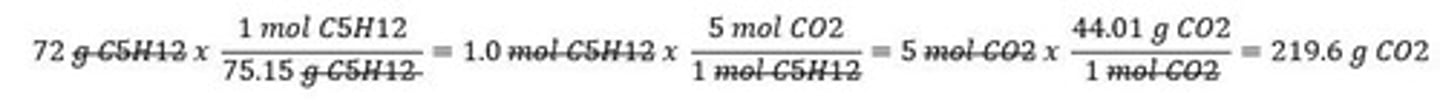
Law of Conservation of Mass
Mass is neither created nor destroyed in reactions.
Mole
Quantity equivalent to 6.022 x 10²³ particles.
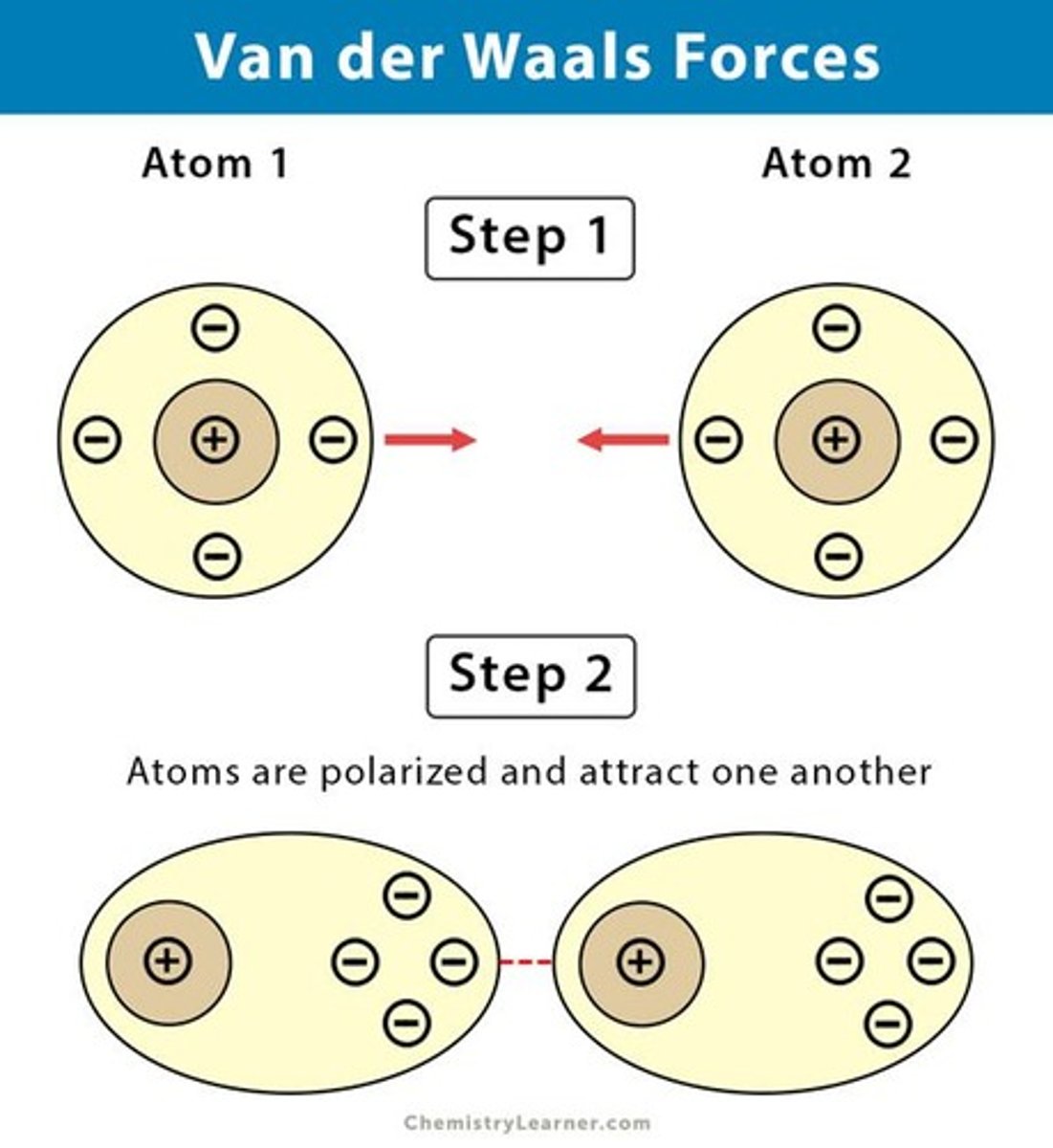
London Dispersion Forces
Weak forces from temporary dipoles in molecules.
Dipole-Dipole Forces
Attractions between permanent dipoles in polar molecules.
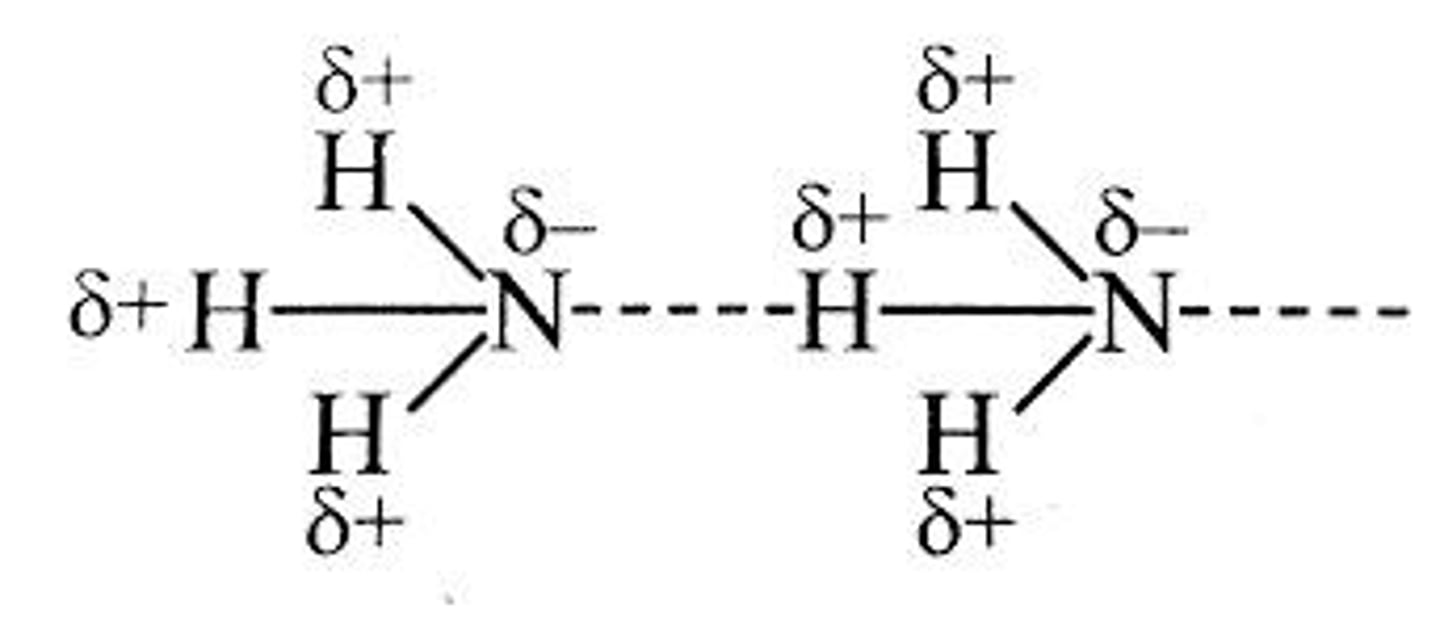
Hydrogen Bonds
Strong dipole-dipole interactions involving H, N, O, or F.
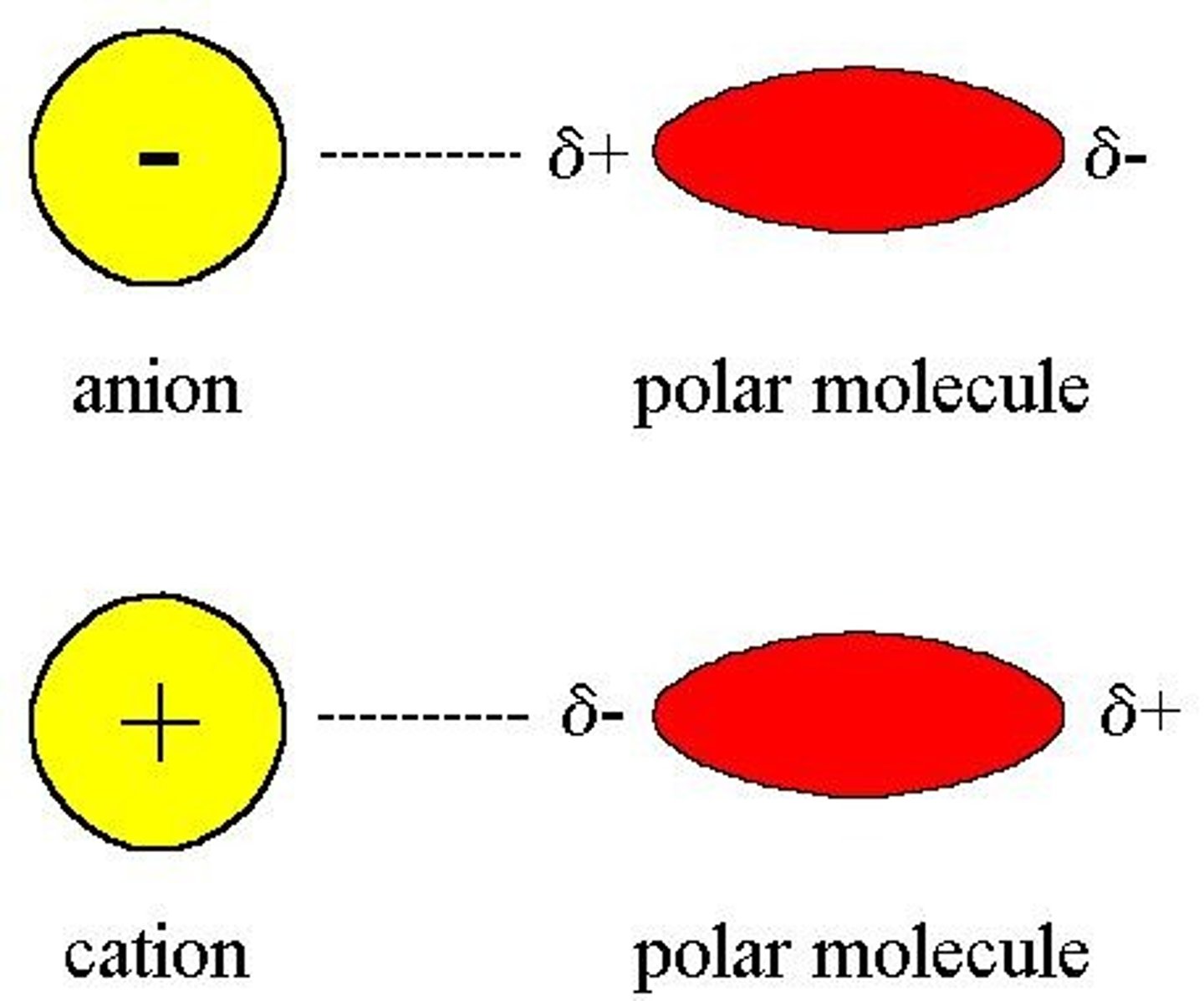
Ion-Dipole Forces
Interactions between ions and polar molecules.
Intermolecular Forces (IMFs)
Forces mediating interactions between neighboring molecules.
Hydrocarbons
Organic compounds consisting solely of hydrogen and carbon.
Isomers
Compounds with the same formula but different structures.
Bond Connectivity
Arrangement of atoms in a molecule affecting properties.
Electronegativity Difference
Measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons.
Diamagnetic
Substance with all paired electrons, no net magnetic field.
Paramagnetic
Substance with unpaired electrons, exhibits magnetism.
Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram
Visual representation of electron distribution in molecules.
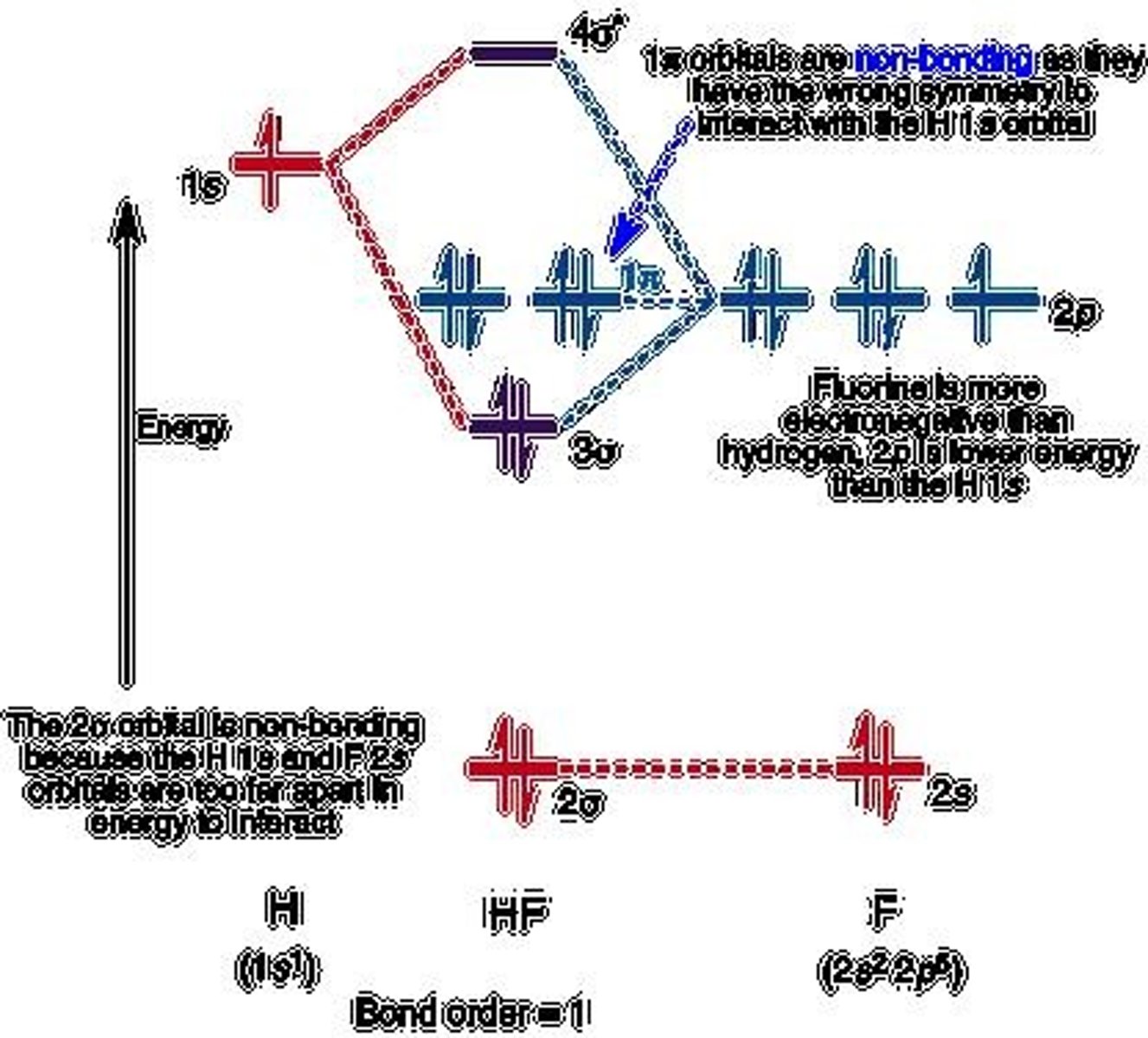
Ground State
Lowest energy state of an atom or molecule.
LUMO
Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital.
HOMO
Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital.
Viscosity
Resistance of a liquid to flow.
Boiling Point
Temperature at which a liquid turns to vapor.
Stable Molecule
Molecule with lower energy configuration.