Economics
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Role of Government
Maintaining law and order, ensuring the needs of the people, and fostering positive growth for the future.
Fiscal Policy
The use of government spending and taxation to influence the economy.
Monetary Policy
Rules followed by central banks to monitor the money supply for sustainable economic growth.
Social Safety Nets
Programs like welfare, unemployment benefits, and social security to support the poor, elderly, and disabled.
Circular Economy
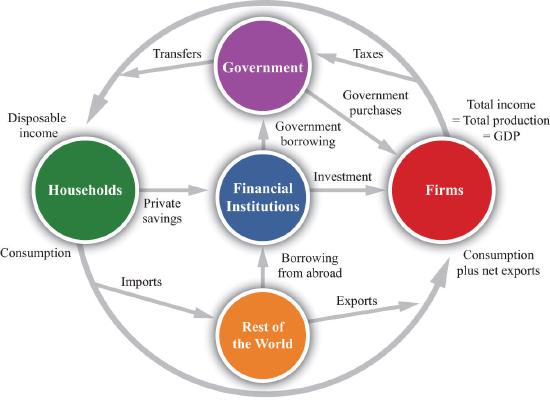
Leakages
Money that exits the economy through savings, taxes, and imports.
Injections
Money that enters the economy through government spending, investments, and exports.
Resource Market
The market where households provide labor, land, capital, and enterprise to businesses.
Product Market
The market where businesses sell goods and services to households.
GDP (Gross Domestic Product)
The market value of all finished goods and services produced within a country in a year.
Intermediate Goods
Goods used to produce other goods that will be sold again.
Finished Goods
Goods that will not be sold again as part of another product.
Capital Goods
Goods used to create more goods, such as machinery or equipment.
National Spending Approach
A method of calculating GDP by summing consumption, investments, government purchases, and net exports.
GDI (Gross Domestic Income)
The factor income approach that includes income, capital interest, rent, and profit.
Economic Growth
The increase in the market value of goods and services produced by an economy over time, typically measured in real GDP.
Open Economy
An economy that engages in trade and has leakages such as financial markets and imports.
Closed Economy
An economy where households only spend money on firms, with no leakages.
Consumer Spending
Money spent by households on goods and services.
GDP Formula
Consumption + Investment + Government Spending + Net Exports
Economics
a social science that studies how human beings use their limited resources to satisfy their infinite needs and wants and how they improve their economic well-being. People cannot have everything they desire, and that is where economics comes in
Opportunity cost
the value of the next-highest-valued alternative use of that resource. If, for example, you spend time and money going to a movie, you cannot spend that time at home reading a book, and you cannot spend the money on something else. If your next-best alternative to seeing the movie is reading the book, then the opportunity cost of seeing the movie is the money spent plus the pleasure you forgo by not reading the book
Scarcity
People's needs and wants are unlimited, but it is not possible to produce all the goods and services to fulfil them, because the resources available are limited. Therefore, societies are forced to choose what it is they need or desire most
Production
The process of combining various inputs, both material (such as metal, wood, glass, or plastics) and immaterial (such as plans, or knowledge) in order to create output. Ideally this output will be a good or service which has value and contributes to the utility of individual
Consumption
the use of goods and services by households. Different from consumption expenditure which includes services and goods that have multiple uses like a car.
Sustainability
the ability of the present generation to meet its needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Equity
does not mean equal, but instead implies fairness. Everyone gets what they need
Equality
This means everyone uses the same resources and the same chances
Planned economy
Communism, where everyone gets everything from the government
(Bonus! What are the pros and cons of this variation)
Mixed economy
When a country where it is partly run by government and partly by businesses
(Bonus! What are the pros and cons of this variation)
Pure market economy
Everything is sold by businesses and there is no government intervention
(Bonus! What are the pros and cons of this variation)
How can an economy grow?
increase in household spending, employment rate, wages and exports