GYN-Unit 2 Vaginal/Cervix Pathology
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What is the most common congenital abnormality of the female genital tract?
Imperforate hymen resulting in obstruction
What may an obstruction of the vagina and/or uterus result in?
Accumulation of fluid(hydro) blood (hemato) or pus (pyo)
What is a Gartner’s Cyst?
Most common cystic lesion of the vagina
What does a Gartner’s Cyst occasionally cause?
Obstruction
What is the US appearance of a Gartner’s Cyst
Small cystic lesions
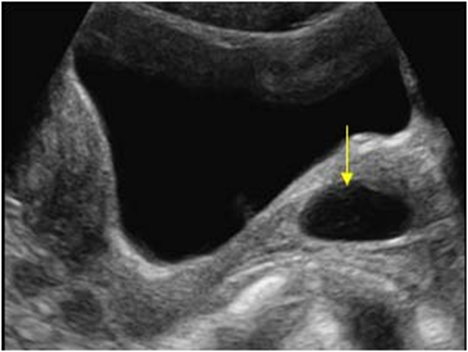
What is this image showing?
Gartner’s Cyst
What is a Rhabdomyosarcoma?
A malignant cancer of the vagina
What is the US appearance of a Rhabdomyosarcoma?
Grape like cluster protruding from vagina
What is vaginal Adenocarcinoma?
A rare type of vaginal cancer formed from the DES pregnancy exposure
What is the US appearance of Vaginal Adenocarcinoma?
Solid appearance
With an S/P hysterectomy, what is the normal measurement of the vaginal cuff?
<2.1 cm
There may be a suspicion for recurrence from a hysterectomy if the vaginal cuff is:
>2.1 cm
Defined mass seen with increased echogenicity
Why might the vaginal cuff be nodular?
Due to post radiation fibrosis
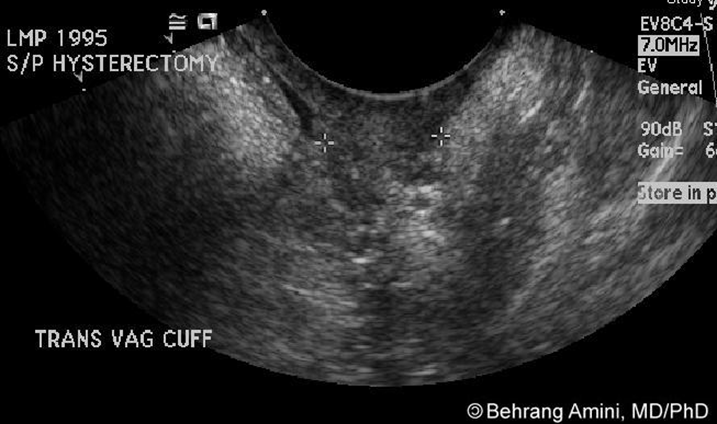
What is this image showing?
Vaginal Cuff
What is the posterior cul-de-sac?
Most posterior and inferior reflection of peritoneal cavity
What is a frequent site for intraperitoneal fluid collections and how much can be detected transvaginally?
Posterior cul de sac and as little as 5mL
True or false: Fluid in cul-de-sac can be a normal finding throughout the menstrual cycle
True
What are common pathologic fluid collections?
Ascites
Blood resulting from:
Pelvic abscesses
Hematomas
What are Nabothian cysts?
Common benign inclusion cysts within the cervix
Nabothian cysts are common in middle aged women and can be caused by what?
chronic cervicitis
Obstructed or dilated transcervical gland
What is the US appearance of a Nabothian cyst?
Discrete cyst
< 2 cm
What are Cervical Polyps?
Hyperplastic protrusion of endocervix or ectocervix
Pedunculated
Broad based
What are the causes of cervical polyps?
Chronic inflammation
Who is most affected by cervical polyps?
Late middle age
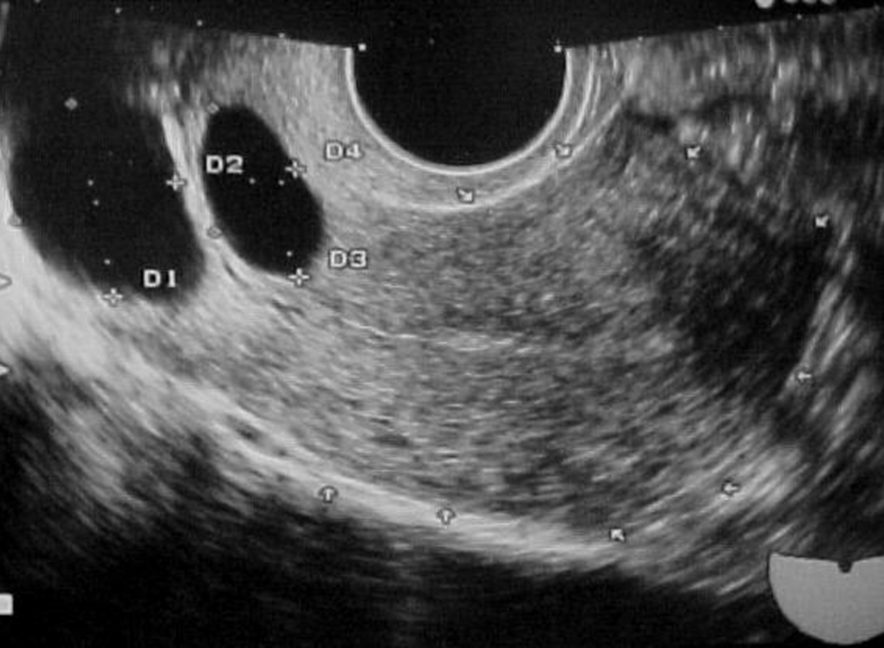
What are these images showing?
Nabothian Cysts
What are leiomyomas?
Also called fibroids
Most common benign condition
Small % originates at cervix
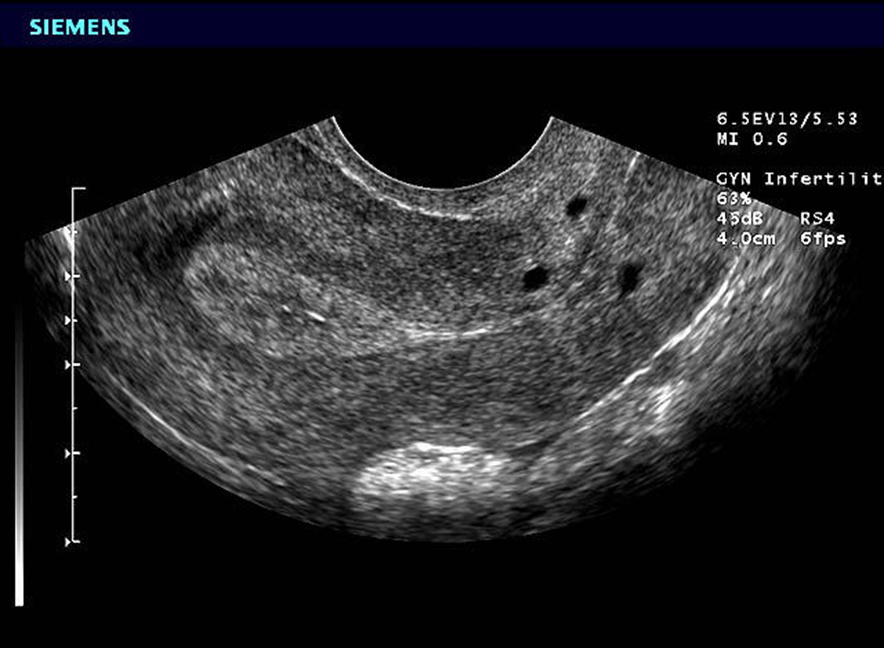
What is the US appearance of a leiomyoma?
Varying echotexture
Within cervical tissue
Pedunculated
Internal protrusion
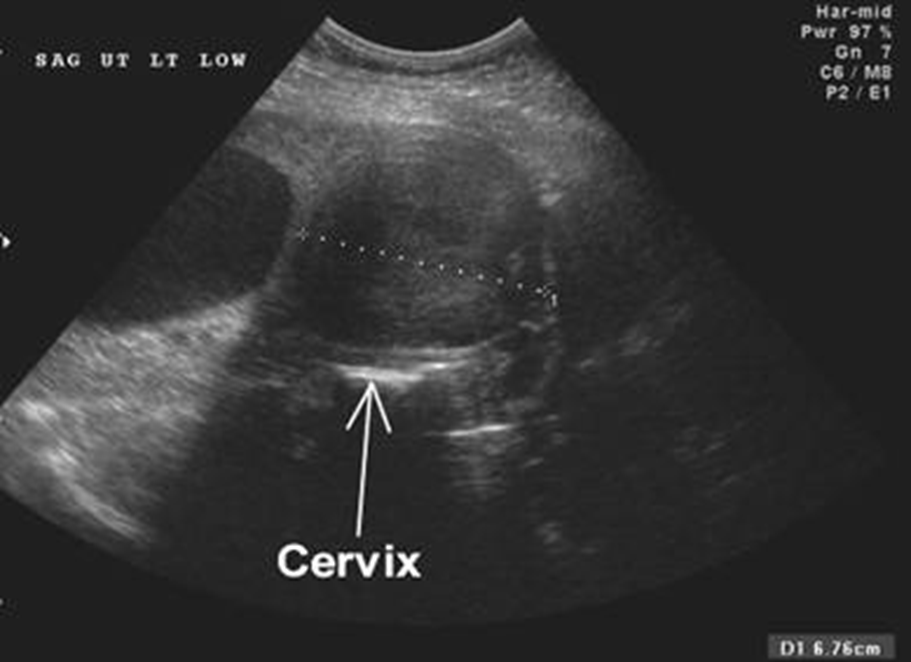
What is this image showing?
Leiomyoma
What is a Cervical Stenosis?
A benign acquired condition
An obstruction at either the internal or external os
What are the causes of cervical stenosis?
Prior instrumentation
Childbirth
Surgery
Cancer
Irradiation (post radiation)
US appearance of cervical stenosis postmenopausal?
Fluid-filled uterus
Asymptomatic
US appearance of cervical stenosis premenopausal?
Oligomenorrhea/Amenorrhea
Dysmenorrhea
What is the most common type of cervical cancer?
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
What type of infections are precursors to cervical cancer?
HPV infections
What are the risk factors of cervical carcinoma?
Early sexual partners
Multiple sexual partners
STI’s
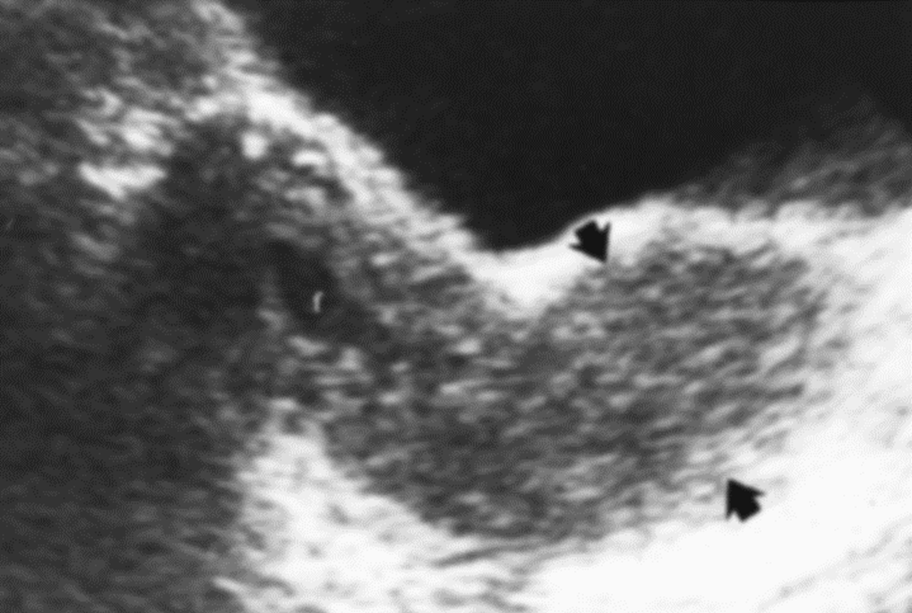
What is this image showing?
Squamous cell carcinoma
Cervical cancer is most prevalent in what age and how can it be detected early?
Menstrual age
PAP smear can be an early detection
What are the clinical symptoms of Cervical Carcinoma?
Asymptomatic- early
Vaginal discharge- bleeding
Malodorous
Palpable mass
US appearance of Cervical Carcinoma?
Hypoechoic mass
Enlarged cervix
Invasion of surrounding structures- spread
Cervical stenosis can cause hematometra
What imaging modality is best for cervical carcinomas?
CT/MRI
Staging of lymph nodes
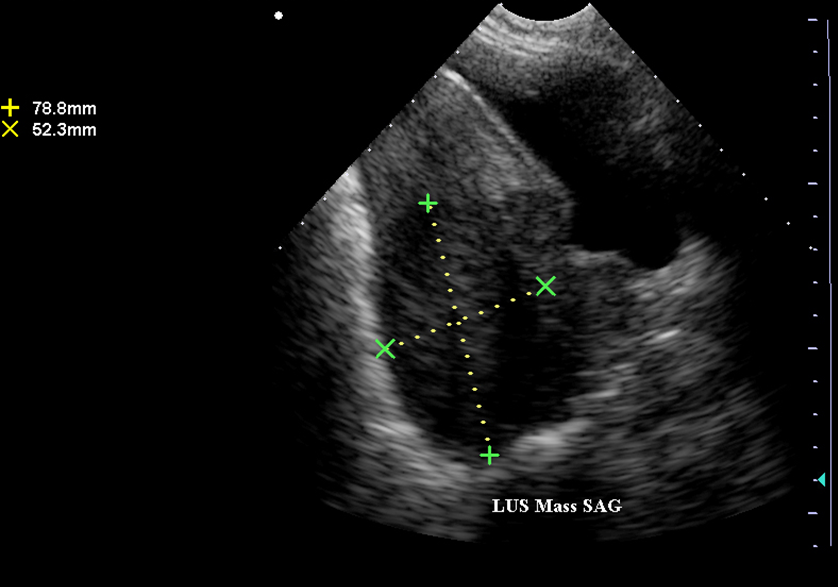
What is this image showing?
Cervical Carcinoma
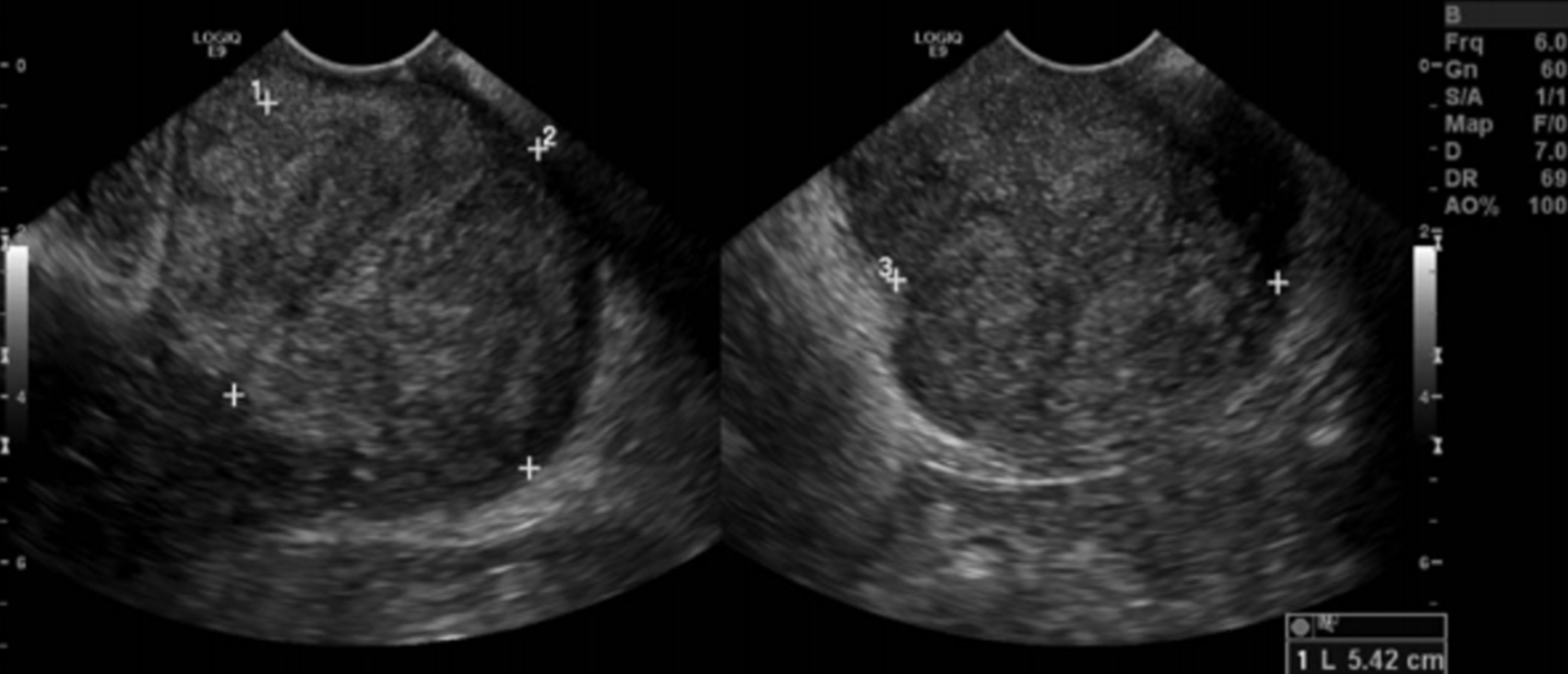
What is this image showing?
Cervical Cancer
Prognosis of cervical cancer depends on what?
The disease stage
What is stage 0 of cervical cancer and prognosis?
Early, confined to surface of cervix
What is stage 1 survival rate of cervical cancer and prognosis?
Greater than 90% and
What is stage 2 survival rate of cervical cancer and prognosis?
60-80% and spread beyond cervix into vaginal wall
What is stage 3 survival rate of cervical cancer and prognosis?
Approximately 50% and spread beyond the cervix and uterus
What is stage 4 survival rate of cervical cancer and prognosis?
Less than 30% and spread to surrounding organs (bladder and rectum)
What is this image showing?
Cervical Cuff