W2 - Comparative Advantage - Ricardo
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
when does a country have comparative advantage
lower OC than competitors
unit labour requirement (2)
number of hours to produce one unit
high = low productivity
unit labour symbol
a
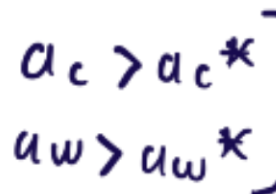
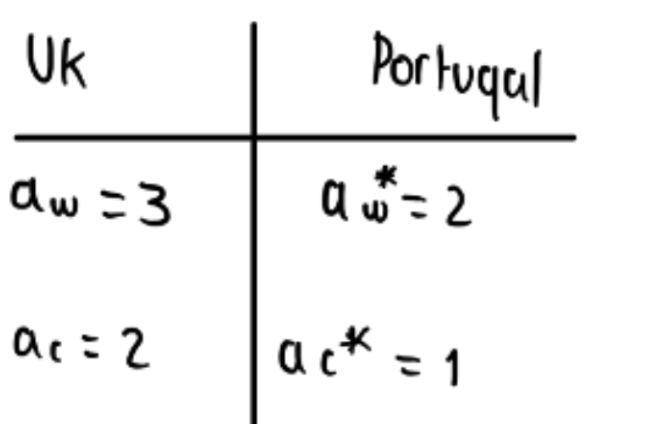
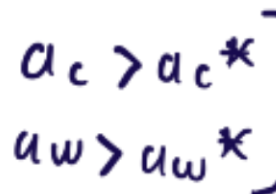
who has ABSOLOUTE advantage
portugal
what does Ricardian model seek to prove?
There are gains from specilaisation and trade liberalisation leads to price convergence
what determines how much a country can produce
labour endowment and technology
slope of PPF is equal to (3)
opportunity cost of producing one good relative to another good
ratio of unit labour requirements
how much of x you must sacrifice for y
Formula for production possibility of a good (Q)
Q = L/ax
labour hours formula
awQw + acQc
opportunity cost of x formula
ax/ay
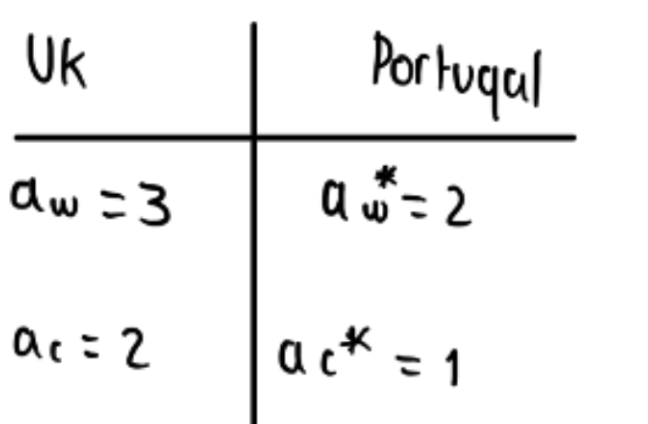
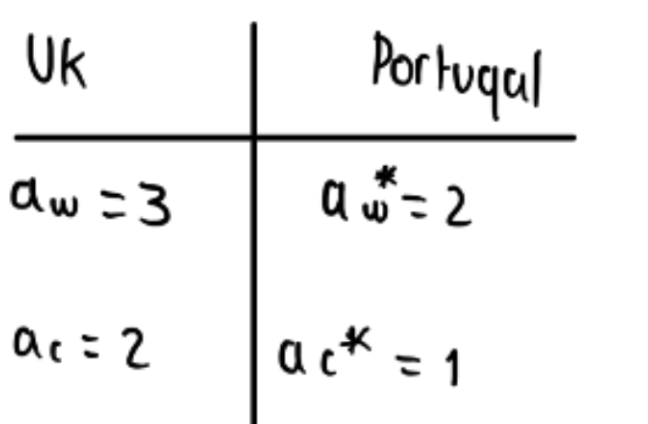
Who has comparative advantage in each good
ax/ay
ac/aw
2/3
1/2
for every sweater produced UK gives up 2/3 wine bottles
for every sweater produced Portugal gives up ½ a bottle of wine
Portugal has comparative advantage in sweaters
how do you tell who has comparitive advantage in producing a good
whoever has lower opportunity cost
if the opportunity cost for cloth relative to wine is ac/aw = 2/3, to produce one sweater, how much wine must they sacrifice
2/3 of a bottle
if a firm wants to produce +50x, how much of y must they sacrifice
50(x/y)
50 (2/3)
50 × 0.66
when will a country be happy to produce and export a good
explain then give formula
if the price at which they sell it is lower than the price at which they sell
pc/pw > ac/aw
what is the relative price of cloth in terms of wine
explain then formula
the amount of wine that can be exchanged for cloth
pc/pw
relative cost (same as opportunity cost)
ac/aw
if pc/pw > ac/aw who exports what
everyone will produce cloth and no one will produce wine due to no profits
assumption of relative price model
price of good is equal to its unit labour requirement
if the price of cloth increases relative to its cost (unit labour requriement) what happens to the quantity produced
supply more cloth instead of wine
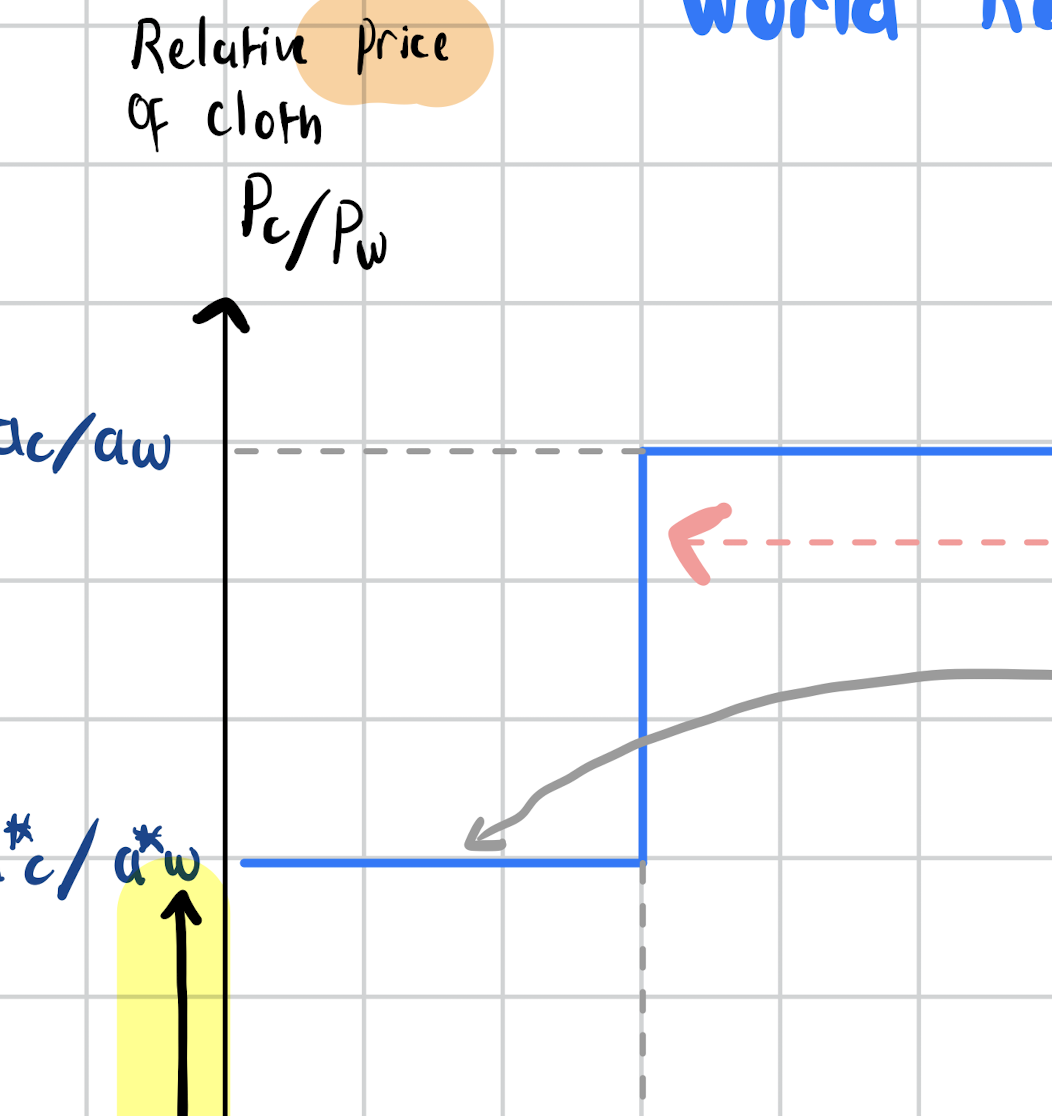

why does world supply of cloth relative to wine jump
world supply jumps when prices exceed the opportunity cost, so Q increases
jump is where UK enters the market as they have a higher opportunity cost
maximum cloth production possibility formula
L/ac

why is RS curve initially flat
because portugal can produce at any Q it likes until it reaches maximum quantity based on labour endowement
what happens at equilibrium between world supply, demand and price
price is between different auturky prices so as specialisation takes place prices converge
why do prices converge in case of portugal
because world supply expands beyond portugal and other countries enter market and demand forces prices to converge

why would relative demand curve be low at RD’
UK’s relative price of cloth is below cost so they only produce wine and Portugal has monopoly in cloth
what happens to consumption when countries specialialise and engage in global trade?
consumption possibilites expand beyond production possibility frontier as countries can engage with cheaper world price of cloth Q = L/ax
EVAL of comparative advantage model (2)
Hausmann: developing countries should, and do, diversify rather than specialise
Does not model inequality or protectionism
Labour is only input