Simultaneous VS Sequential
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Simultaneous VS Sequential
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
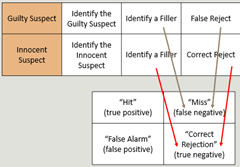
Terminology
Hit (True positive) = when a guilty person is identified as guilty
Miss (False negative) = If a guilty person is seen as innocent
False alarm (False Positive) = If a innocent person is identified as guilty
Correct rejection (True Negative) = if line up with innocent people is rejected
Diagnosticity Ratio
If a suspect is identified how likely is it that the suspect is guilty
Diagnosticity = Hit rate/False Alarm
We want more hits and fewer false alarms
Procedures with larger diagnostcity are considers the best procedures
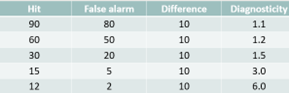
Diagnosticity - Sim vs Seq
Meta analysis of 72 test
Sim
Hits = 52
False alarms = 9
Diagnosticity = 5.8
Seq
Hits= 44
False alarms =5.6
Diagnosticity = 7.8
According to this sequential is better, studies that report diagnosticity ratio often reveal a sequential advantage
Signal detection theory
Discriminability: ability to distinguish between a signal and noise
Line up discrimination
Signal = culprit
Noise = innocent line up members
Need person to identify the signal and not be distracted by the noise
Response bias: inclination to accept that the signal is present
Lineup response bias: willingness to make an ID
Liberal = more willing to choose
Conservative = less willing to choose
Sequential is more conservative response bias
Simultaneous is more liberal response bias
Signal Detection Theory - Criticism
Doesn’t exactly measure discriminability
Dignosticity ratio is not a pure measure of discriminability
Diagnosticity increases as responding becomes more conservative
Despite being the same difference between hit and false alarms dignositicity is increasing when people are less willing to choose
Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve
Signal detection theory suggests ROC curves as a type of analysis other than dignositicity
Plotted at how many hit rates you have at each level of confidence
E.g.
O% confidence = HR = 2 FA = 5
Calculate using AUC – area under the curve
Larger area under the curve means it’s the better procedure
ROC study
All experiments by Mickes, Flowe and Wixted 2012 found that simultaneous was better
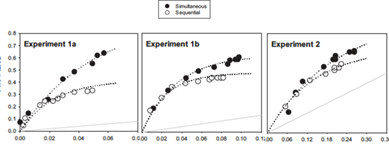
ROC findings
Studies using ROC curves tend to find that simultaneous advantage
Comparisons between faces enable witnesses to find features that distinguish the culprit from the fillers
Criticisms of ROC
1 ROC does not measure underlying (psychological) discrimination
Discriminability: Ability to distinguish a signal from noise
Signal: Culprit
Noise: Innocent Lineup Members
For lineups with innocent suspects, ROC analysis treats a filler identification as if it were a lineup rejection
ID Filler = Incorrect Decision
Reject Lineup = Correct Decision
Eyewitness identification have six possible outcomes
But ROC curves are designed for decisions that have four possible outcomes
2 ROC does not control for response bias
Response bias: Willingness to accept that a signal is present
ID = Believe the signal is present
Rejection = Believe the signal is absent
ROC analysis combines filler identification and lineup rejections
Conclusion about research
Superiority of simultaneous/sequential procedures may depend on how performance is measured
§ Diagnosticity: Advantage for sequential
§ ROC Curve: Advantage for simultaneous
Consensus is that witnesses are more conservative for sequential than simultaneous
Future of Lineup ID
Immersive stimuli
VR and 360 may produce more naturalistic results
One problem is that VR environment is hard to create and requires a lot of funding
Hybrid Lineup
Combines both types of lineup
All options are presented simultaneously but movement is presented sequentially
Some initial evidence that is more diagnostic than other procedures but results still unpublished
Trying to combine the best of both ideas
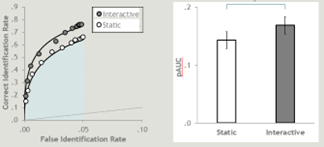
Interactive Lineup
Pose reinstatement
More likely to recognise someone if they are in the same pose they were when you saw them
o The procedure allows witnesses to the lineup to view the faces from multiple angles. The procedure also allows the user to control the images, and as such is interactive.
There is evidence that the more unique features you see, the more accurate your ID will be.
Interactive lineups improve ability to discriminated between innocent and guilty suspects
For possible false ID rate, interactive lineups increased the correct ID rate by 18%
Culture
South Korea vs UK
Sequential procedures had higher diagnosticity among UK participants, but not among SK participants.
Composites - Police Sketches
Police sketch artists were used in as many as 10% of law enforcement agencies in the mid-1980s (MacDonald, 1984)
Composites - Mechanical systems
The Identi-Kit and the Photofit Kit
use transparencies of facial features that are superimposed over each other to create facial likenesses
§ Hundreds of hairstyles and eyes, dozens of mouths, noses, and chins are available for the person to select when building the face
Composites - Computerised systems
One of the computerized systems in use in U.S. law enforcement agencies today is the FACES.
§ The person must select individual facial features and combine them for image of a face.
§ Called Feature based systems – as you select individual facial features
Composites - How Good
o Initial results were disappointing (e.g., see Davies, Ellis, & Shepherd, 1978), and modern computerized versions have not done much better (Davies & Valentine, 2006).
Participants correctly named only 22 of 800 famous faces based on composites of those faces that had been created by other individuals.
o It has been argued that there is a mismatch between the task demands that are somewhat inherent in all composite systems and the way that faces are usually perceived and remembered.
§ Faces are generally processed, stored, and retrieved at a holistic level rather than at the level of individual facial features (Tanaka & Farah, 2003).
Holistic-based systems
EvoFIT
§ A random set of faces is generated, and the witness selects the face or faces that are most similar to memory for the target face.
· Based on some descriptive factors
§ A new set of faces is then generated, based on mutations of the previous selections, and the witness again makes a choice.
§ This process is repeated until the witness cannot choose because all the faces resemble the target face equally well.
o Results of these
§ Better results with holistic approaches for matching and therefore is a better procedure
Morphing facial composites
o Some research has shown that there can be benefits to morphing multiple composite faces of the same individual created by different eyewitnesses
§ (Bruce, Ness, Hancock, Newman, & Rarity, 2002; Hasel & Wells, 2007).
Limitation - Composites
Perceptions of facial composite similarity are susceptible to bias
§ Detectives and jurors may use the perceived similarity of a suspect to a composite as evidence to determine the likelihood of a suspect’s guilt.
§ However, these similarity judgments may be biased by evaluators’ preexisting beliefs of guilt (Charman et al., 2009).
Facial composites may distort memory
§ Participants either constructed a facial composite or completed a distractor task.
· Those who created a facial composite had lower identification accuracy in a line-up identification task.
· “Creating a composite or simply viewing someone else’s composite hinders identification accuracy and one’s memory for the target face”