Microbiology Lab Tests: Motility, Hemolysis, Selective Media, and Antibiotic Sensitivity
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Purpose of the motility test?
To see if the bacteria can move using flagella.
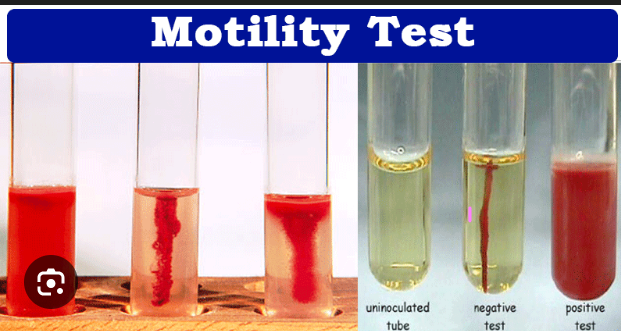
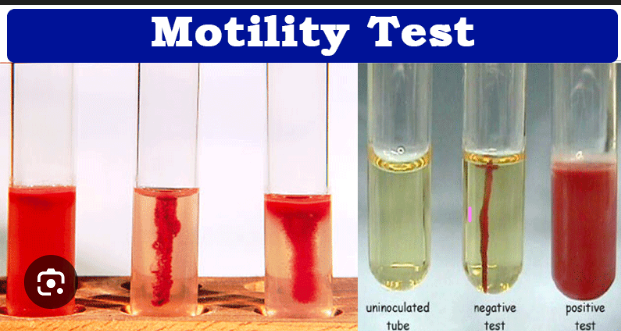
What does spreading/cloudy growth away from the stab line mean?
Motile.
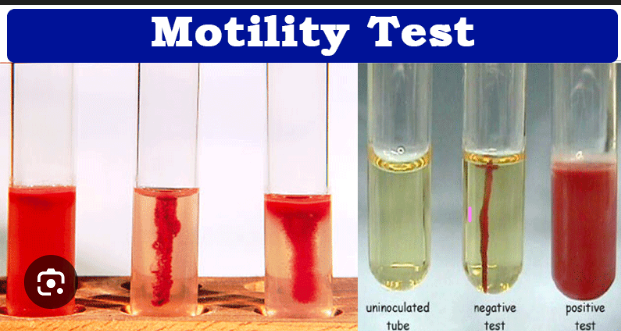
What does growth only on the stab line mean?
Non-motile.
Why might a motile organism look non-motile?
Old culture, wrong temp, stabbed too deep, or sloppy technique.

Why do we use a streak plate?
To isolate single colonies from a mixed sample.

What does separated colony growth mean?
Successful isolation.

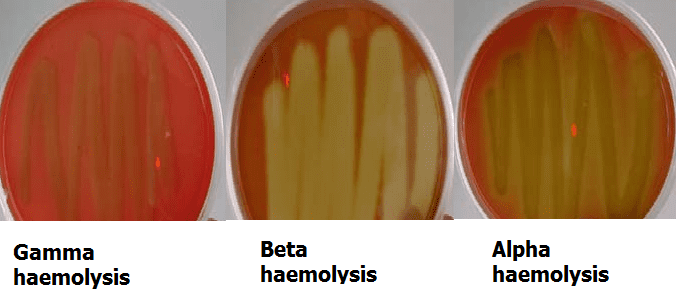
Purpose of blood agar?
To see if bacteria break down red blood cells.
What is beta hemolysis?
Complete RBC breakdown → clear zone.
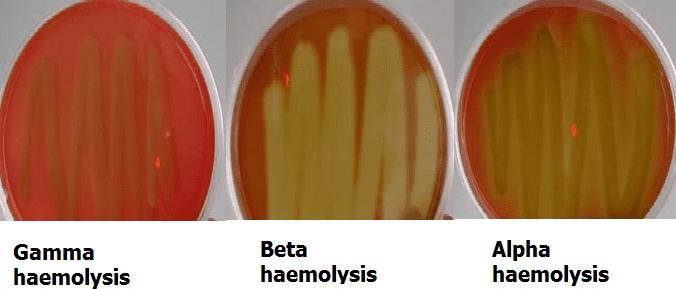
What is alpha hemolysis?
Partial breakdown → greenish zone.
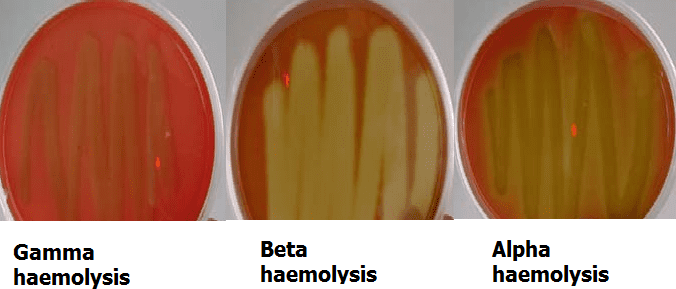
What is gamma hemolysis?
No breakdown → no color change.
Why might hemolysis look weak on old plates?
RBCs naturally deteriorate.

Purpose of MSA?
Selects for salt-tolerant bacteria and shows mannitol fermentation.
Growth + yellow media?
Mannitol fermentation → acid produced.
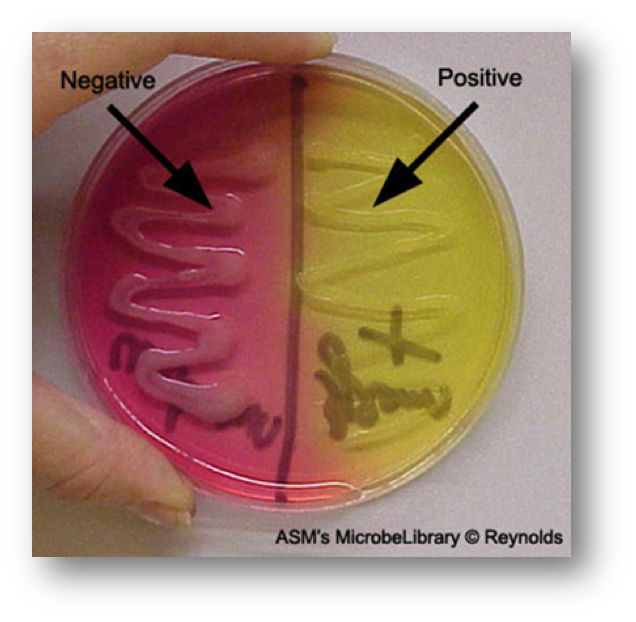
Growth + pink/red media?
No mannitol fermentation.
No growth?
Not salt-tolerant.
Why does the media turn yellow when mannitol is fermented?
Acid lowers pH → phenol red changes color.
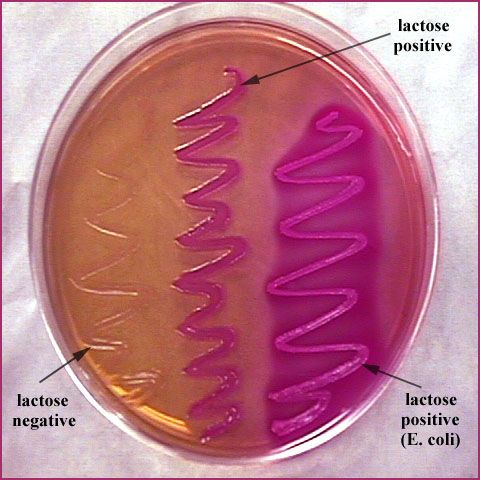
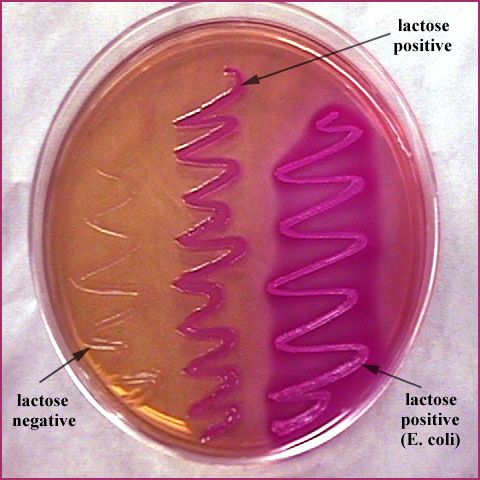
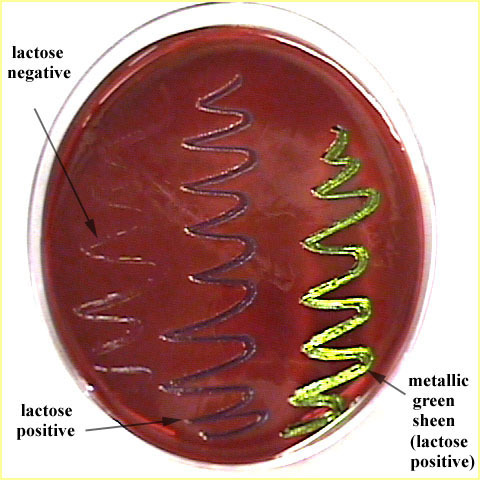
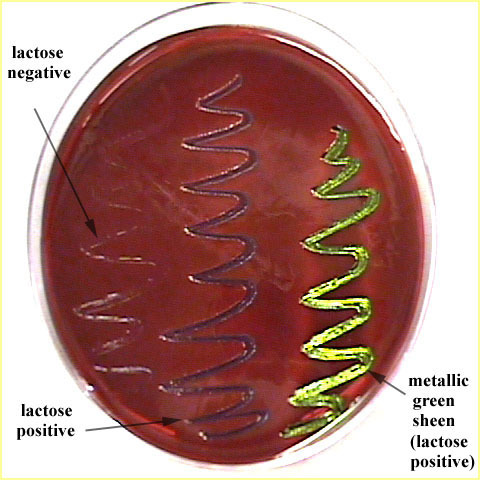
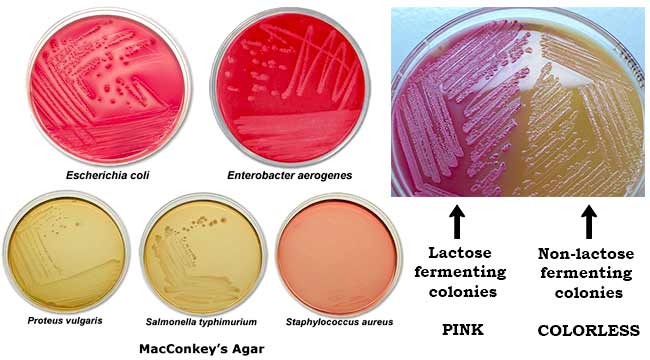
Purpose of EMB?
Selects for Gram-negatives coliforms (can live in the intestines) and shows lactose fermentation.
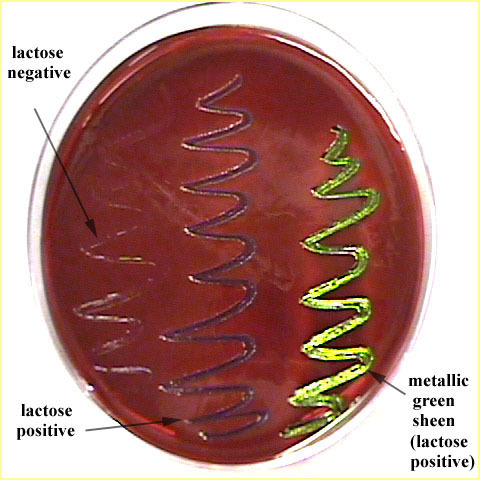
Metallic green colonies?
Strong lactose fermenter.
Pink colonies?
Weak lactose fermenter.
Colorless colonies?
Non-lactose fermenter.

Why does E. coli turn metallic green?
High acid production precipitates the dyes.
Purpose of MAC?
Selects for Gram-negatives and shows lactose fermentation.
Purpose of PEA?
Selects for Gram-positive organisms.

Strong growth?
Likely Gram-positive.

Weak/no growth?
Likely Gram-negative.

Purpose of the oxidase test?
Checks for cytochrome c oxidase.
Purple color change?
Oxidase positive.

No color change?
Oxidase negative.

Why does oxidase positivity create color?
The reagent reacts with their enzyme.
Purpose of the catalase test?
Checks if bacteria break down hydrogen peroxide.

Bubbles?
Catalase positive.

No bubbles?
Catalase negative.

Why do bubbles appear?
Oxygen gas releases.
Purpose of sugar fermentation broths?
Shows if bacteria ferment specific sugars.
Yellow broth?
Fermentation → acid produced.

Gas in Durham tube?
Gas-producing fermentation.

Red/pink broth?
No fermentation.

Why might a tube turn yellow then back to red?
Alkaline reversion after sugar is used up.
Purpose of Kirby-Bauer test?
Measures how sensitive bacteria are to antibiotics.

Large zone of inhibition?
Susceptible.
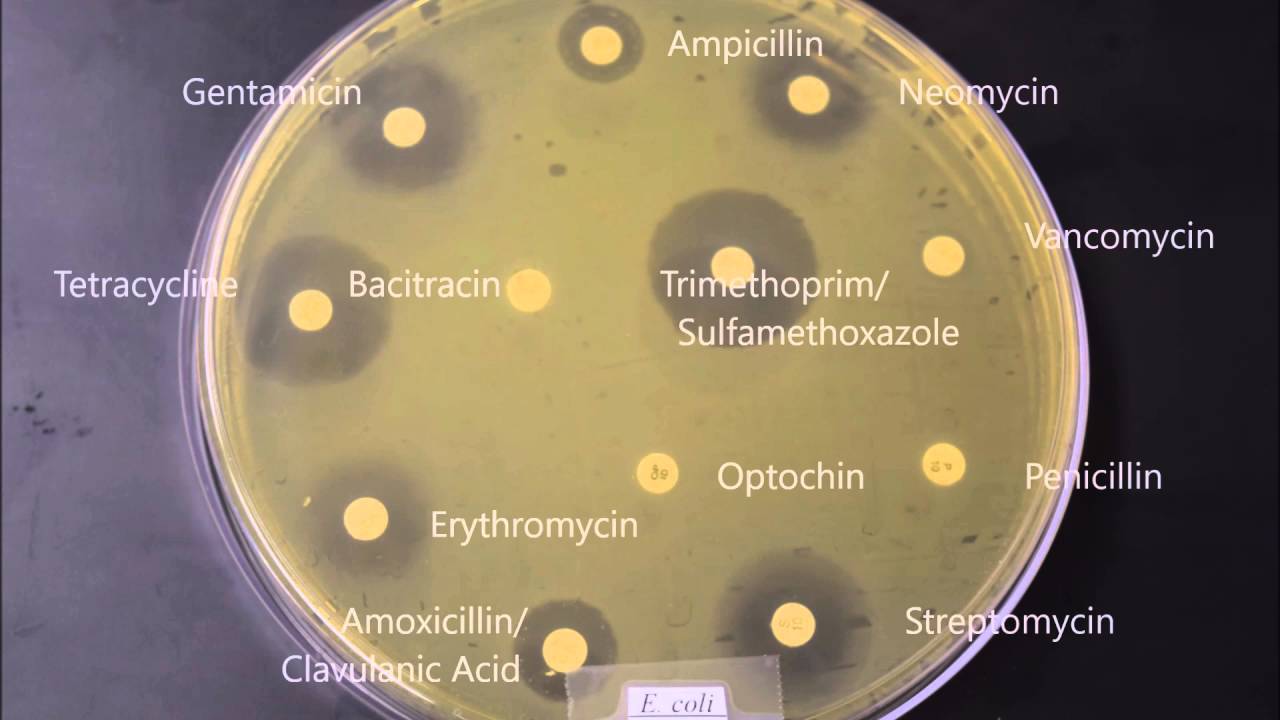
Small or no zone?
Resistant.
Can you compare two antibiotics' zones directly?
No, each has its own standards.
Why might a resistant strain still show a tiny zone?
Slight slowing of growth but still resistant.
Purpose of antiseptic/disinfectant testing?
Tests how well household chemicals inhibit bacteria.
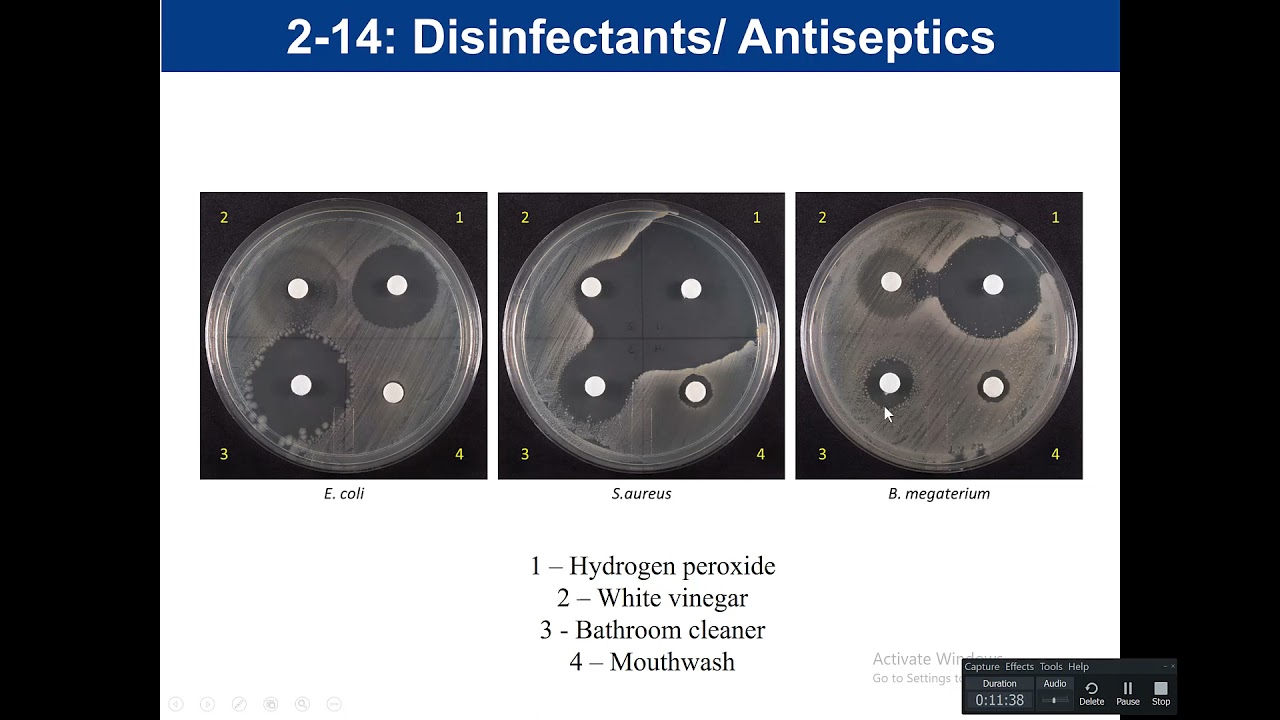
Large zone?
Chemical is effective.
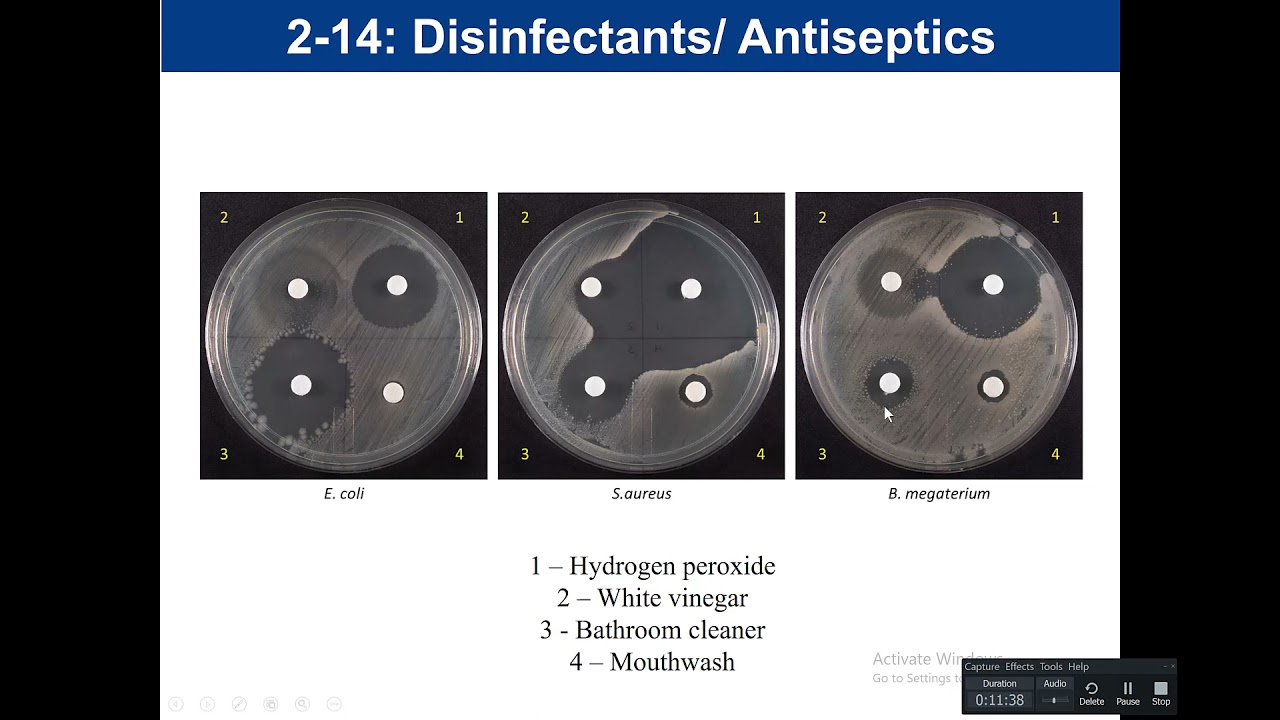
Little/no zone?
Chemical is ineffective.
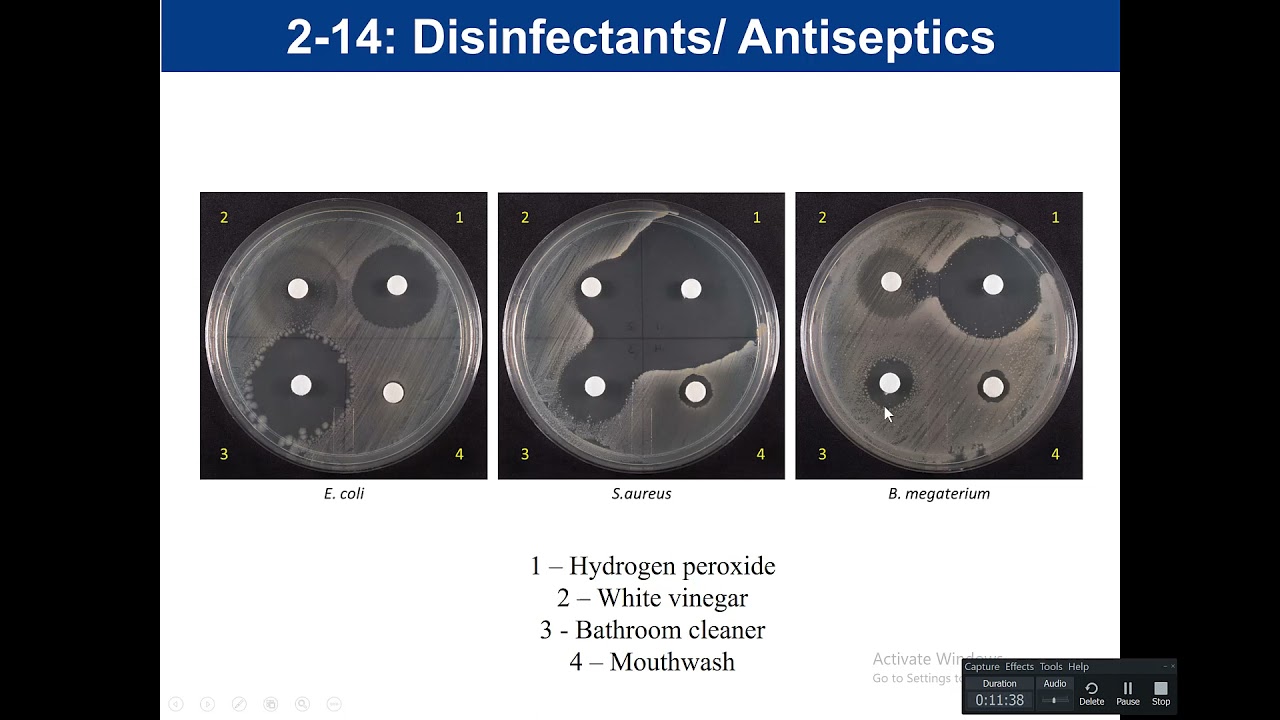
Why do disinfectants usually perform better than antiseptics?
They're stronger since they're used on surfaces, not skin.
What does the zone of inhibition actually measure?
How strongly a drug or chemical stops bacterial growth.
What is a zero zone?
Complete resistance.
Why do we measure diameter, not radius?
Standardization across labs.
Why can a big zone be misleading?
Some drugs simply diffuse (spread) faster in agar.
If something grows on MSA but doesn't ferment mannitol, what does that suggest?
Salt-tolerant, likely a coagulase-negative Staph species.
If your organism grows on EMB but not PEA, what does that mean?
Gram-negative.
Yellow glucose broth but red lactose broth — what's the conclusion?
Ferments glucose but not lactose.
Two antibiotics have the same zone size — does that mean they work equally well?
No — interpret each using its own chart.
If a disinfectant has a big zone on E. coli but none on S. aureus, why?
They have different resistance traits and cell walls.
If your motility tube is cloudy everywhere, what happened?
Messy stab or contamination.
Gram-positive + catalase positive + grows on MSA — what group is it? (optional)
Staphylococcus.
Gram-negative + lactose fermentation on EMB/MAC — what group is it? (optional)
Coliforms (like E. coli, Enterobacter, Klebsiella).