Orthodontics CH. 60
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Orthodontics
Specialty concerned with the prevention, interception, and correction of growing and mature dentofacial structures. It is the oldest specialty. Started in 1900.
Esthetics, health, function, and stability.
what are the orthodontic objectives?
Normal (ideal) occlusion.
describes the contact relationship of the mandibular arch with the maxillary arch.
Malocclusion
any deviation from normal occlusion; includes misalignment of a single tooth, a group of teeth, or an entire arch.
factors associated with Malocclusion
Development Causes
-Congenitally missing
-Malformed teeth
-Supernumerary teeth
-Interference with eruption
-Ectopic eruption
Genetic Causes
Environmental Causes
-Birth injuries or injuries
Habits
-Tongue thrusting
-tongue when swallowing
-Thumb and finger sucking
-Bruxism
-Mouth breathing- kids need to do this because their palate is growing.
Crowding
-The most common contributor to malocclusion; one or many teeth can be involved in misplacement
Overjet
-An excessive protrusion of the maxillary incisors causes space or distance between the facial surface of the mandibular incisors with the lingual surface of the maxillary incisors.
Overbite
An increased vertical overlap of the maxillary incisors occurs.
Openbite
A lack of vertical overlap of the maxillary incisors creates an opening of the anterior teeth when occluded.
Crossbite
A tooth is not properly aligned with its opposing tooth.
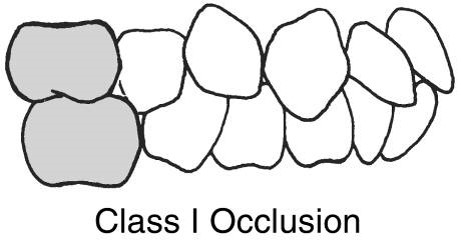
Class I Occlusion
Maxillary mesial buccal cusp is in line mandibular buccal groove of 1st molar.
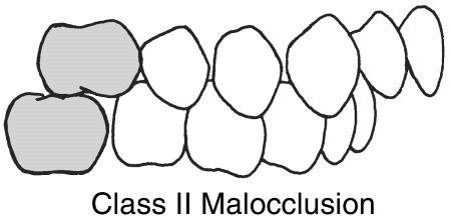
Class II Malocclusion
-Also called disocclusion
-The body of the mandible is in abnormal distal relationship to the maxilla.
-Gives the appearance of the maxillary anterior teeth protruding over the mand anterior arch.
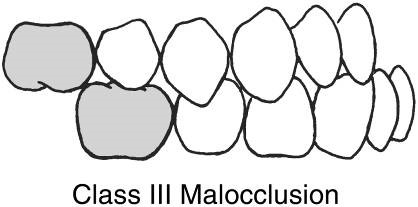
Class III malocclusion
-also called mesiocclusion
-The body of the mandible is in an abnormal mesial rel of the maxilla.
Benefits of Ortho Treatment
-Psychosocial
-Oral Function
a. proper occlusion
b. swallowing
c. speech
d. TMJ
-Dental Disease
a. crowding
b. malocclusion>excessive forces> periodontal dz
Preventive Ortho
-To prevent or eliminate irregularities and malposition in the developing dentofacial region
a. Space
b. Removing habits.
c. Restoration of caries.
Interceptive Ortho
-Intercede or correct problems as they are developing.
a. serial extractions
b. correction of crossbite (palate expander)
c. Headgear
d. extraction of primary or permanent teeth to correct crowding
corrective ortho
-condition that require the movement of teeth and the correction of malocclusion and malformations.
a. removable of Invisalign,expander, or braces
b. orthognathic (jaw surgery)
records and treatment planning
-Medical and Dental History
-Physical Growth Evaluation
-Social and Behavioral Evaluation
a. home care and nutrition
b. able to place lingual brackets. or have clear brackets. or they can have invisaligns
Clinical Examination
-Facial aspects
-Oral health
-Jaw and occlusal relationship
A. Facial Evaluation
Lateral
Frontal
Oral Health
a. Plaque control (OHI or home care)
b. Periodontal condition
-Evaluation of Jaw and Occlusion
-Functional Characteristics of the Jaw
Diagnostic Records
-Impressions
-Extra/intraoral photos
-Radiographs
Panoramic radiograph
General overview
cephalometric radiograph
-extraoral radiograph makes it possible to evaluate the anatomic bases for malocclusion, skull, bones, and soft tissue
Cephalometric Analysis
-Tracing or computerized drawing using a series of points to compute a means of mathematical descriptions and measurement of the status of the skull.
Diagnostic Models
-Diagnosis
-Case presentation
-Financial Arrangements
Basically their evaluation appointment!!!!
Orthodontic Scaler
-Bracket placement, removal of elastomeric rings, and removal of excess cement or bonding material
Ligature Director
-Guides the elastic or wire ligature tie around the bracket; tucks the twisted and cut ligature tie under the arch wire.
Band plugger
-Help seat a molar band for a fixed appliance
Bite Stick
-Used to aid in seating a molar band for a fixed appliance
Bracket placement tweezers
-Used to carry and place the bonded bracket on the tooth
Bird beak pliers
-Forming and bending wires
Weingart utility pliers
-used in placing arch wires
Three-prong pliers
-Closing and adjustment of clasps
Posterior band remover pliers
-removes bands
Distal end “cutting pliers”
-Cuts the ligature wire for removal after seated in posterior band
Ligature/Wire Cutters
-Curs ligature after tied to arch wire
Contouring pliers
-crimping wires
Howe (110) pliers (Universal)
-allows placement and removal, and the making of adjeustment bends in the arch wire.
Arch bending pliers
-Holding, bending, and adjusting arch wires to create movement.
Bracket remover (green handler)
-removes bracket
Ligature-tying pliers (Coon)
-Allow for ease in ligature tying
Orthodontic Hemostat
-Hold, place, tie ligature to arch wire
Fixed Appliances
Sequence of Application
-Placement of Application
-Cementation of Molar bands
-Bonding of Brackets
-Insertion of arch wire, and tying in with ligature ties or elastomeric ties
-Adjustment checks
-removal of appliance
-retention of teeth
Separators
-Teeth are separated before fitting and the placement of the molars bands
-brass wire separators
-steel separating springs
-elastomeric separators
Orthodontic Bands
-Performed stainless steel bands fitted and cemented to molar teeth.
-Buttons, tubes, and cleats are attached for the arch wire and power products.
Bonded Brackets
-designed so the arch wire is placed horizontally through the wings of the bracket and then ligated.
-This stabilization initiates tooth movement by allowing the forces from the arch wire to be transmitted to the tooth.
Headgear tubes
-Round tubes places routinely on maxillary first molar bands. Used for the insertion of the inner bow of a facebow appliance.
Edgewise Tubes
-Rectangular tubes placed on the buccal surfaces of the upper and lower first molar bands to receive the arch wire.
Labial Hooks
-Located on the facial surfaces of the first and second molars bands for both arches. These hooks hold the interarch elastics.
Lingual Arch Attachment
-Button or bracket located on the lingual portion of the bands to stabilize the arch and to reinforce anchorage and tooth movement.
Nickel Titanium or “Niti” Arch Wires
-For movement because of its flexibility
Stainless Steel Wire “SS”
-Stiffer and stronger
Beta Titanium (TMA)
-Provides a combination of strength, flexibility, and memory
Optiflex
-Used for light force and its esthetics.
Thermoactive wire
-engages when warmed.
Round wires
Used in the initial and intermediate stages of treatment. To correct crowding, level the arch, opening the bite, and closing the spaces.
Square or rectangular wires
are used during the final stages of treatment to position the crown and root in the correct maxillary and mandibular relationship
Stainless steel Ligature ties
A .010-guage stainless steel wire ligature is used to “tie” in arch wires.
Elastic Chain Ties
-Continuous “O’s” that form a chain. Used to close space between teeth or to correct rotated teeth.
Elastics
-Commonly referred to as rubber bands.
-Helps in closing space between teeth and correct occlusal relationships
Headgear
-an orthopedic device used to control growth and tooth movement
facebow headgear
-used to stabilize or move the maxillary first molar distally and create more room in the arch.
traction device
-applies the extraoral force used to achieve the desired treatment results.
Herbst appliance
used in situations when the growth of the lower jaw is not keeping up with the growth of the upper jaw. Reasons for this can be both genetic and developmental
Expanders
-Function of the palatal separating appliances is to spread the mid-palatal suture.
-Used to correct posterior crossbites
-Activated daily with a key
homecare for orthodontics
a. Brushing (charter method)
b. Flossing
c. brush 2 times a day
d. Swish water
e. Inspect
f. fluoride rinse or gels
Ortho Positioner
-Retain the teeth in their desired position
-Permits the alveolus to rebuild support around the teeth before the patient wears a retainer
-Massages the gingiva
Hawley Retainer
a removable retainer worn to passively retain the teeth in their new position
Lingual Retainer
a fixed lingual wire bonded canine to canine on the lingual surfaces to provide lower incisor position during late growth.