physical science unit test
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Group
Going vertical (up and down)
Periods
Horizontal (left and right), the atoms always gain 1 proton and the # of electrons shells stays the same
Alkali metals
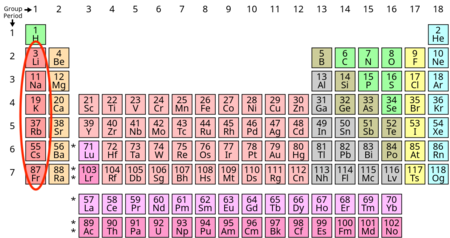
Alkaline earth metals
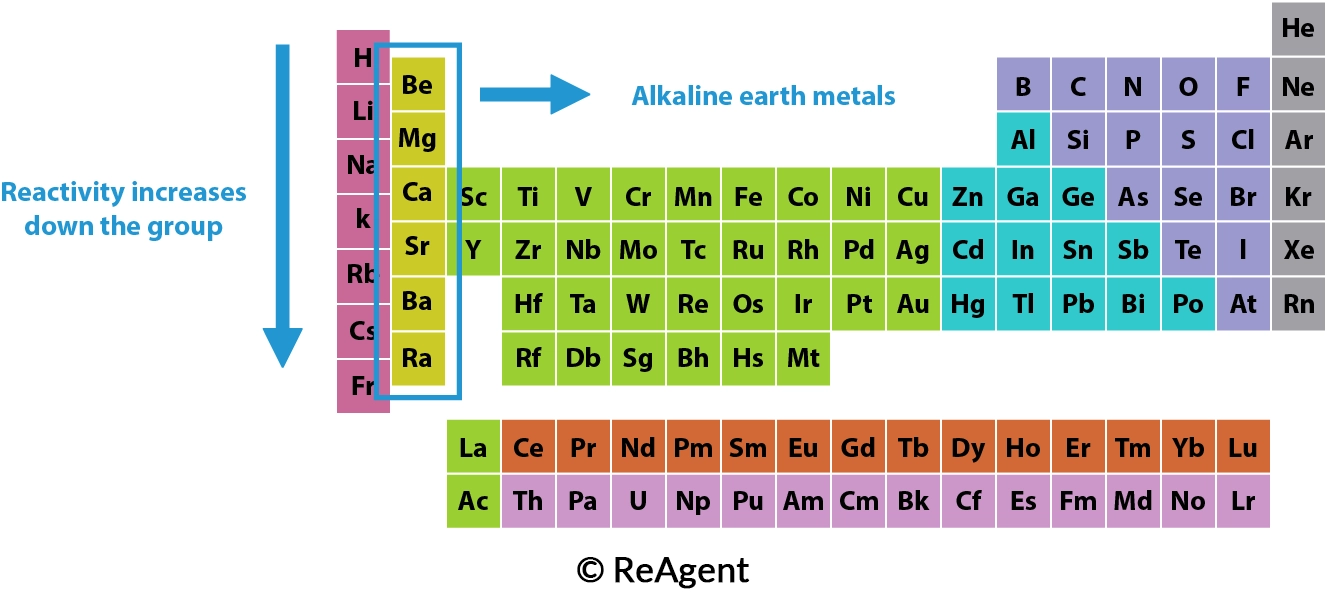
Halogens
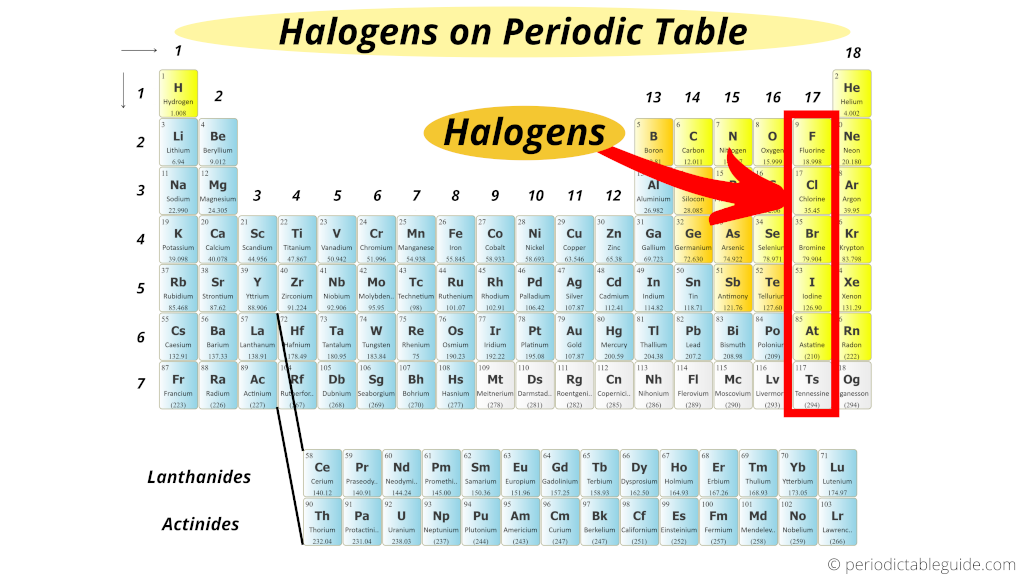
Noble gases
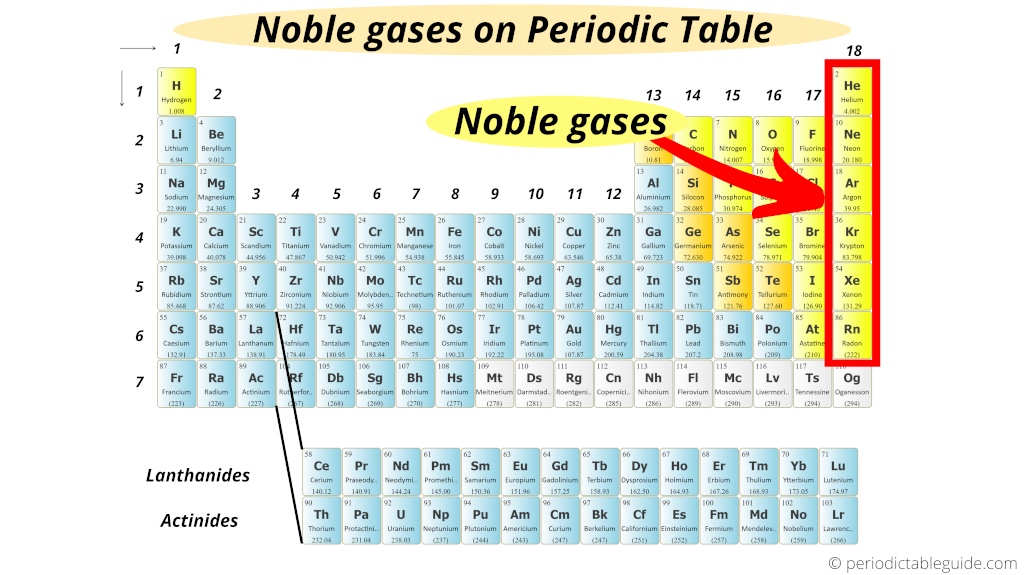
A particle found in the nucleus of an atom with a mass of 1 and a charge of 0
Neutron
Dense positive center of an atom
Nucleus
Basic unit of a chemical consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons
Atom
A particle found in the nucleus of an atom with a mass of 1 and a charge of +1
Proton
Has 0 mass and a -1 charge, surrounding the nucleus
Electron
Elements found in top right corner of periodic table
Nonmetals
The elements that touch the staircase line of the periodic table
Metalloids
Elements on the left and center of periodic table
Metals
Atoms with unequal number of protons and electrons
Ion
An area around the nucleus that can hold a specific number of electrons
Electron shell
Atoms of the same element with different number of neutrons
Isotope
An atom that has gained electrons and has a negative charge
Anion
Electrons found on the outermost shell
Valence electron
An atom that has lost electrons and has a positive charge
Cation
Cations
Have more protons than electrons
-positive charge
-ex: beryllium (Be) cation with +2 charge
Anions
Have more electrons than protons
-negative charge
-ex: oxygen anion with a -2 charge
Atom with labels
Valence electrons are on the outermost shell
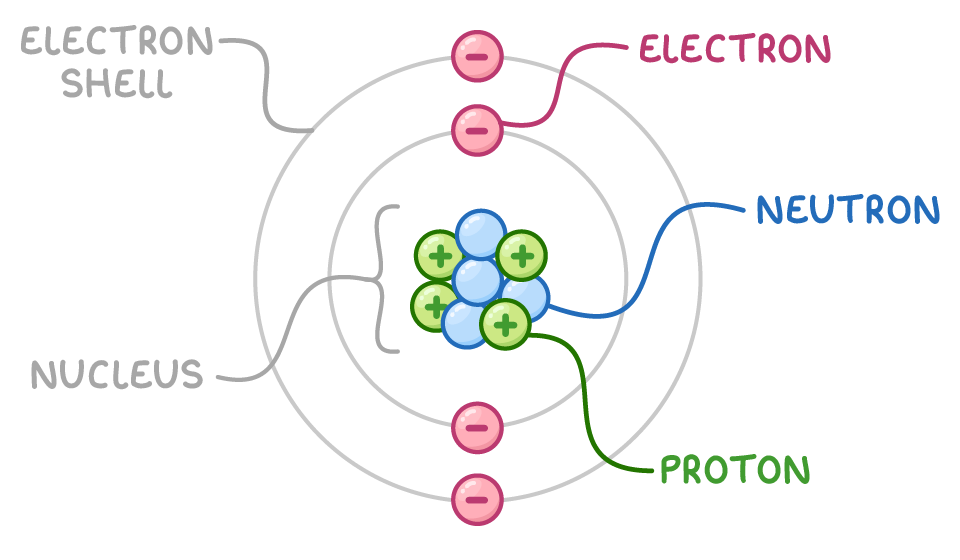
Isotopes
Atoms with the same # of protons but a different # of neutrons
Ions
Have a different # of electrons
-two types: cations & anions
How to get protons
They’re the same # as the atomic #
How to get electrons
For a neutral atom the # of electrons is the same as the # of protons
How to get neutrons
Round the atomic mass to the whole and subtract the atomic # (proton #)
If electrons are NOT neutral…
The atom becomes an ion
-if it has more electrons than protons it’s a anion (negatively charged)
-if it has more protons than electrons it’s a cation (positively charged)
Metals
Shiny, malleable (can be bent or hammered into shape, great at conducting heat and electricity
Nonmetals
Dull, brittle (break easily), conductors of heat and electricity
Metalloids
Mix of both metals and nonmetals, shiny yet brittle, semiconductors, conduct electricity in certain conditions
Equations to know
# of protons + # of neutrons = mass
Mass - # of protons = # of neutrons