physical science midterm
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
the steps commonly used by scientists to test hypotheses and solve problems are called
scientific method
what is the information gathered from an experiment called
data
The part of an experiment in which all conditions are kept the same is the what
control group
a scientific explanation that has never been disproved is called what
law
if you are taking measurements of the height of seedlings in an experiment, you are collecting what
quantitive data
if you are writing about colors and shapes of leaves, you are collecting what
qualtitative data
rules and patterns of nature are using which type of reasoning
inductive reasoning
what do you use to examine the world around you
your senses
what are the 3 parts of a proper hypothesis
if, then, because
name an example of scientific theory and law
theory: big bang theory
law: newtons law of motion
draw and label the proper set up for a graph. what piece of information goes on the x axis? what goes on the y axis?
x axis: independent variable
y axis : the dependent variable
which graph would you use if you are comparing the rate of change between trial subjects/objects over time?
line graph
List in order the steps of the scientific method
observation/ask a question, gather background information, form a hypothesis, design an experiment, collect and analyze data, draw conclusions, and communicate results
anything that has mass or takes up space
matter
the measure of earth gravity acting on an object
weight
a combination of 2 or more substances that are physically combined in changeable ratios
mixture
matter that can flow
fluid
a mixture that is cohesive throughout. looks as if it is one substance
Homogeneous Mixtures
what is a heterogenous mixture
a combination of substances where the composition is not uniform throughout sandwitch
what is the viscosity of liquid
its resistance to flow
What are physical properties?
Characteristics that can be observed without changing the identity of the substance
What is a physical change?
a change in look or form, but not a new substance
What are chemical properties?
how a substance interacts with other substances
What is a chemical change?
A change in matter that produces one or more new substances
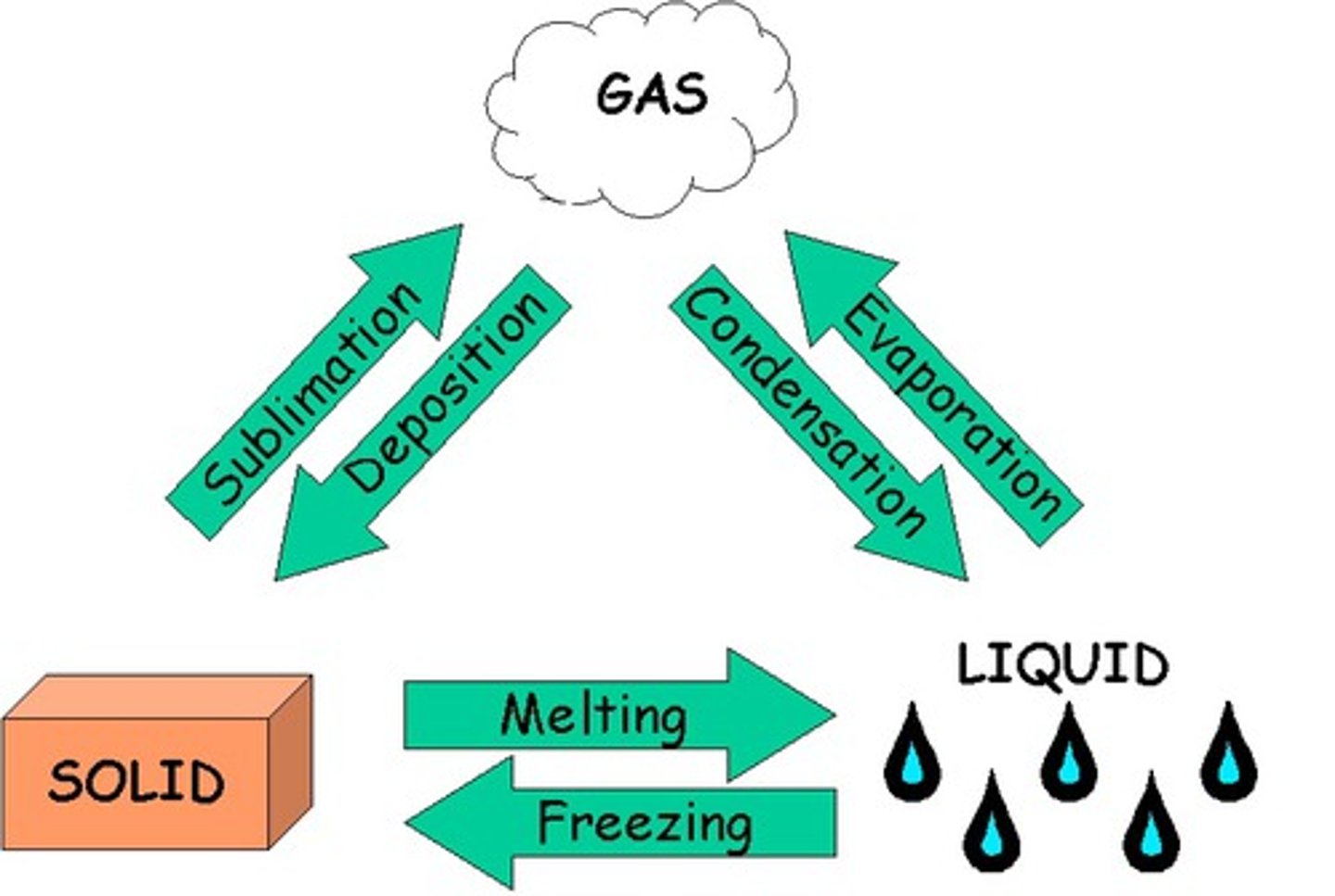
what are the states of mater and their characteristics
Solid: Has a definite shape and volume, with particles tightly packed together and vibrating in fixed positions
Liquid: Has a definite volume but takes the shape of its container, with particles able to move past each other while still being attracted
Gas: Has neither a definite shape nor volume, with particles moving rapidly and randomly with little attraction to each other
plasma: gas is so heated that some of its electrons become free from their atoms
which state of matter has vapor pressure
gas
the building block of all matter
an atom
the most widely accepted workable model of matter is called what
the particle model
which state of matter has fast moving particles? so fast they can create electrical charges
plasma
what causes different liquids to vary in viscosity
the strength of intermolecular forces between their molecules
give two examples of non matter
light and sound
list 3 pieces of evidence that led to the acceptance of the particle model of matter
brown, changes in motion, law of definite proportion
give one example for the following:
element
compound
pure substance
heterogenous mixture
homogenous mixture
element: hydrogen
compound: H2O/water
pure substance: gold
hetero: oil and water
homo: air
draw and label the 4 states of matter and how they interact with one another
plasma off to the side
what is the formula for density
Density = mass/volume
know how to find density, mass, and volume
d=m/v (g/cm3)
m=dxv (g)
v=m/d (cm3)
How do Aristotle's model of matter and the particle model of matter represent matter?
Aristotle- continuously devisible
particle model- tiny indivisible particles
which scientists is associated with the discovery of electrons
Thompson
which scientist created the first modern atomic model
dalton
which scientist is credited with the discovery of the nucleus
rutherford
which model of the atom says that atoms are made of dense, positively charged central nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons
bohr model
this model of the atom says that atoms are made of a dense, positively charged central nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons
nuclear model
the observation that opposite charges repel each other
law of electrostatic charges
unequal numbers of protons and electrons giving that atom a charge is known as a(n)
ion
what is an anion
A negatively charged ion
what is a cation
A positively charged ion
why is the Bohr model still used, even though it is not completely accurate in its description of the atoms structure
it provides a simple, visual representation of atomic structure
List all subatomic particles and where their corresponding charges
Proton: Positive charge (+1)
Neutron: Neutral charge (0)
Electron: Negative charge (-1)
atoms of the same element with differing numbers of neutrons are called what
isotopes
what are the 3 types of naturally occurring carbon atoms? which is radioactive
carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14, with carbon-14 being radioactive
the smallest unit of matter is what
an atom
which scientist demonstrated fire could not be an element
laosier
How did the idea of triads influence the development of the periodic table, even though more than three elements share similar properties?
Triads showed a pattern in element properties, hinting at order, which helped develop the periodic table.
the unique feature of mandeleevs classification method was that he
left gaps in his periodic table to accommodate elements that were not yet discovered
which scientists discoveries led to organizing the periodic table using atomic number rather than atomic mass
Moseley
the modern periodic table has. how many periods and how many groups
7 periods and 18 groups
How would a highly conductive, malleable, and lustrous solid most likely be classified?
metal
which of the following correctly arranges the elements from smallest atomic radius to largest
A. barium, beryllium, magnesium, strontium
B. barium, magnesium, strontium, beryllium
C. barium, strontium, magnesium, beryllium
D. beryllium, magnesium, strontium, barium
D. beryllium, magnesium, stontium, barium
what affects the size of an elements atomic radius
the number of electron shells it has
what is electronegativity? where would you find the largest amount on the table?
a measure of an atom's ability to attract shared electrons in a chemical bond. top right corner
the development of the modern periodic table came as a result of what?
-organize the elements
- similar atributes
- structure of the atom
the modern periodic table arranges elements according to what
atomic number
elements in the same _ on the periodic table have the same number of valence electrons
group
Where are nonmetals located on the periodic table?
right of staircase
uranium, found below the main body of the periodic table, is best classified as what
an actinide
what is the family name for the group containing chlorine
halogens
which of the following has the largest atomic radius?
A. sodium
B. argon
C. cesium
D. radon
cesium
Which of the following correctly arranges the elements from greatest electronegativity to least?
A. carbon, fluorine, lithium, nitrogen
B.fluorine, nitrogen, carbon, lithium
C. lithium, carbon, nitrogen, fluorine
D. nitrogen, fluorine, carbon, lithium
B. fluorine, nitrogen, carbon, lithium
ancient greeks thought that all matter in the universe was made of only 5 elements
true
the symbols that represent each elements must always use two letters
false- only some
alkaline-earth metals are slightly more reactive than alkaline earth metals
false- they are less reactive
elements with more protons and electrons almost always have larger atomic radii then those with fewer protons and electrons
true
demonstrated that combustion requires the presence of oxygen
Lavoisier
developed the law of octaves through arranging elements by atomic mass
Newlands
first recognized groups of three elements with similar elements
Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner
led to reorganizing the period table on the basis of atomic number
Mosele
organized elements with similar characteristics in columns like the modern periodic table used letters to represent each element and superscripts to represent the number of atoms
mendeleev
how did Mendeleev use his periodic table to predict future discoveries of unknown elements
he left gaps
because groups 3-16 contain metals, non-metals, and metalloids, they are known as what
mixed groups
the measure of an elements ability to attract and hold electrons when bonded to other atoms is called what
electronegativity
would you expect fluorine or iodine to act more like a nonmetal? explain.
Fluorine would be expected to act more like a nonmetal compared to iodine because fluorine is more electronegative
what are the rules and characteristics of chemical bonding?
rules- octet rule
characteristics- strength, polarity, reactivity, and shape
the octet rule states that atoms are generally more stable when
they have eight electrons in their valence shell
the properties of water are different than hydrogen and oxygen because
when they chemically combine the create a whole new molecule
covalent bonding forms _ while ionic bonding forms _
covalent- 2 non metals
ionic- 1 metal 1 non-metal
why does diatomic nitrogen form a triple bond
each nitrogen atom has five valence electrons
what type of atom is most likely to take valence electrons in ionic bonding
a nonmetal atom
write the lewis structure for potassium fluoride
[K+] [F-]
how many atoms are represented by the chemical formula CuSO4
6
what is the chemical structure for potassium nitride
K₃N
most atoms are unstable when bonded to other atoms
false- most atoms become more stable when they form bonds with other atoms
molecules form only when different elements bond together
false- molecules can form when any elements bond together
Only one covalent bond can exist between two atoms.
false- multiple covalent bonds (double or triple) can also exist between the same two atom
electrons shared in covalent bonds are not necessarily shared
false- the sharing isn't always equal between atoms
a superscript on a chemical formula indicates the number of atoms
a superscript usually represents the charge of an ion.
metals can only have one oxidation state
most metals can have more than one oxidation state
between oppositely charged ions
ionic
between atoms with very different electronegativities
ionic
between elements such as transition metals with similar low electronegativities
metalic
most often formed between non-metals
covalent