Organic chemistry exam 1
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Alkyl halides
are organic compounds containing a carbon atom bonded to a halogen atom (F, Cl, Br, I). They are derived from alkanes by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms with halogen atoms.
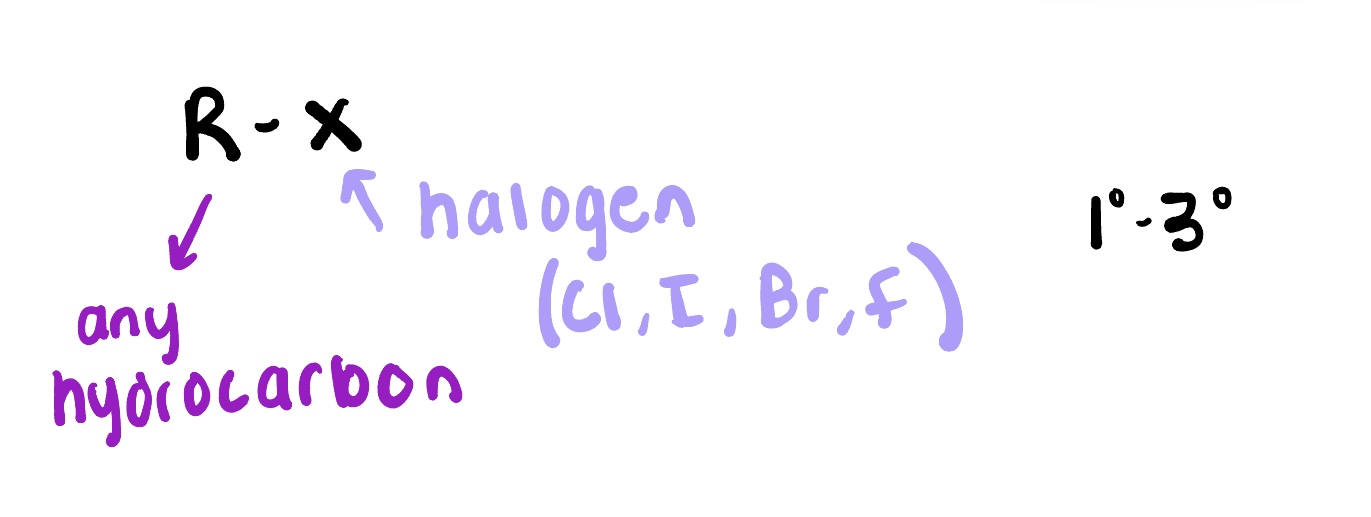
Alcohol
are organic compounds that contain one or more hydroxyl (-OH) functional groups. They are derived from alkanes by replacing a hydrogen atom with a hydroxyl group.
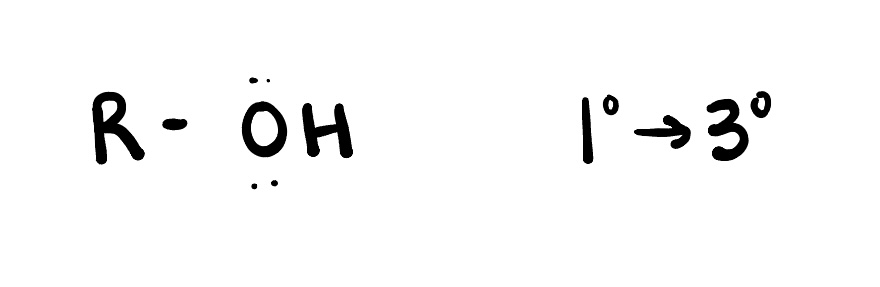
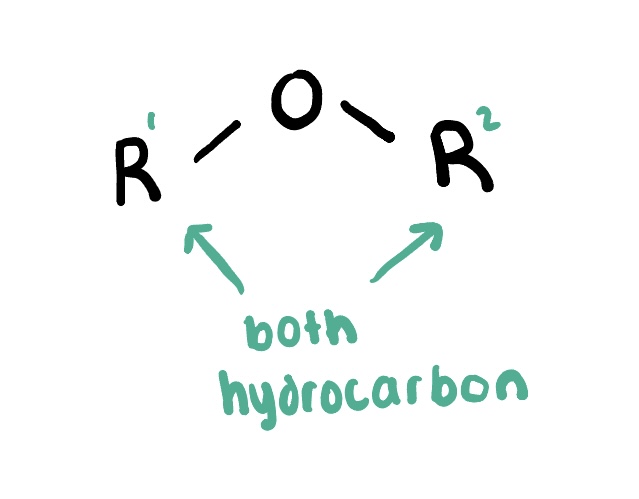
Ethers
are organic compounds that contain an ether functional group, characterized by an oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups. They are commonly formed by the reaction of alcohols with acids.
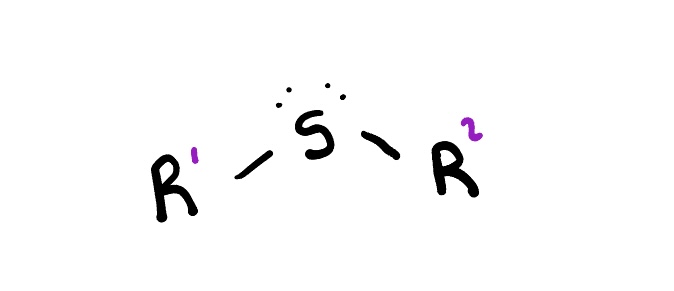
Sulfides
are organic compounds containing a sulfur atom bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups. They are analogous to ethers but with sulfur replacing the oxygen.
Thiol
are organic compounds that contain a sulfur-containing functional group, characterized by a thiol (-SH) group attached to an alkyl or aryl group. They are known for their strong odors and are often found in biological systems.
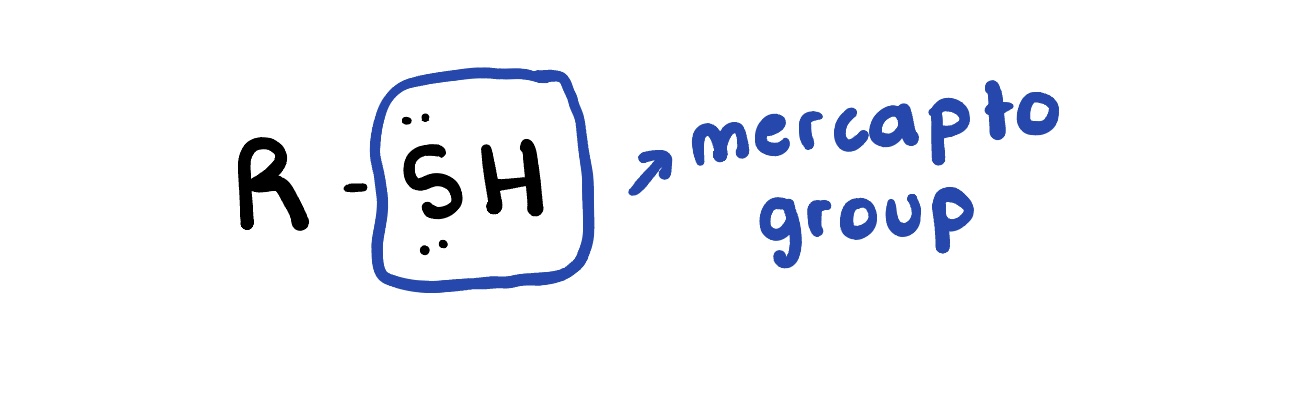
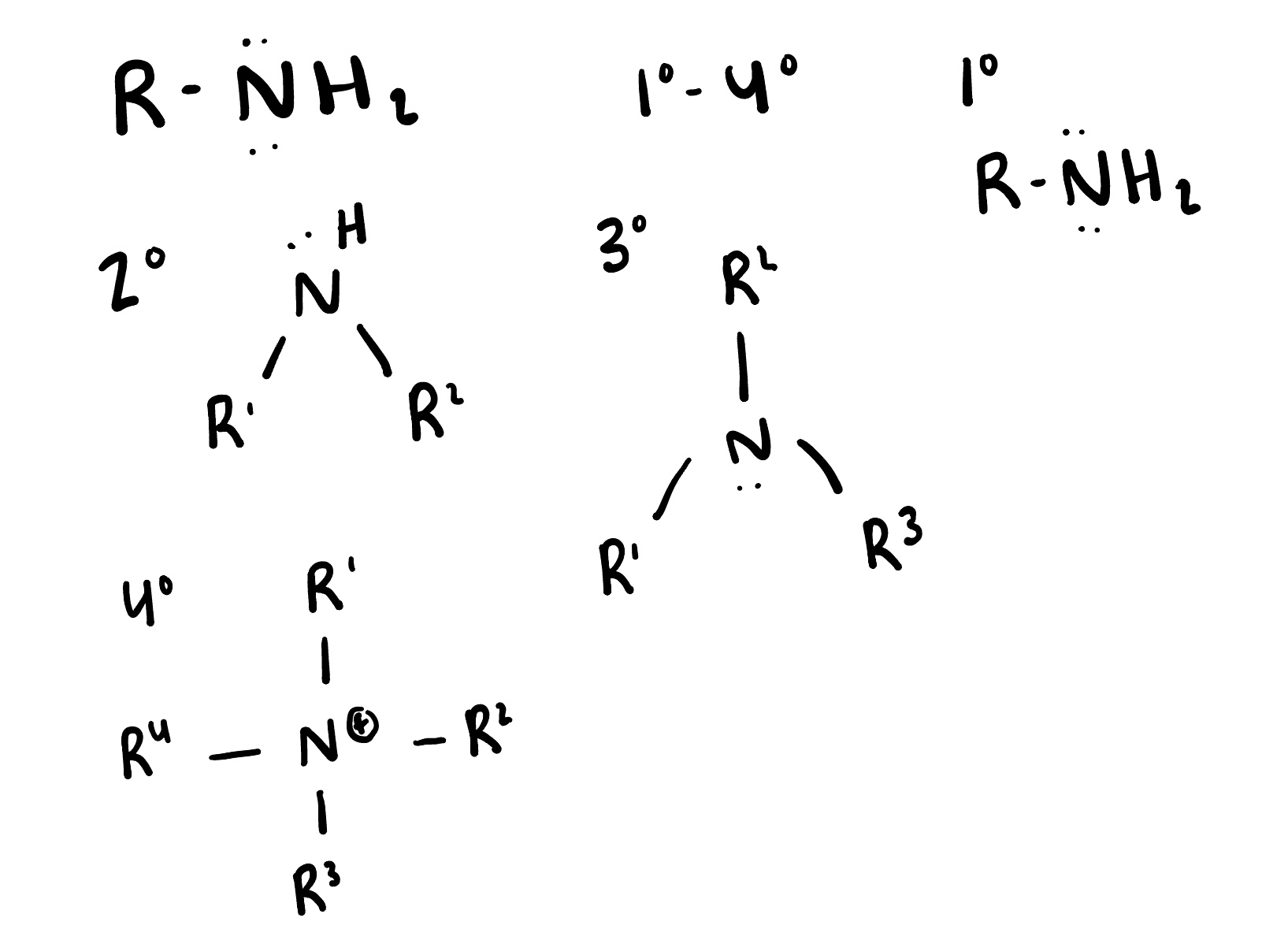
Amines
are organic compounds that contain a nitrogen atom bonded to one or more alkyl or aryl groups. They can act as bases and are commonly derived from ammonia.
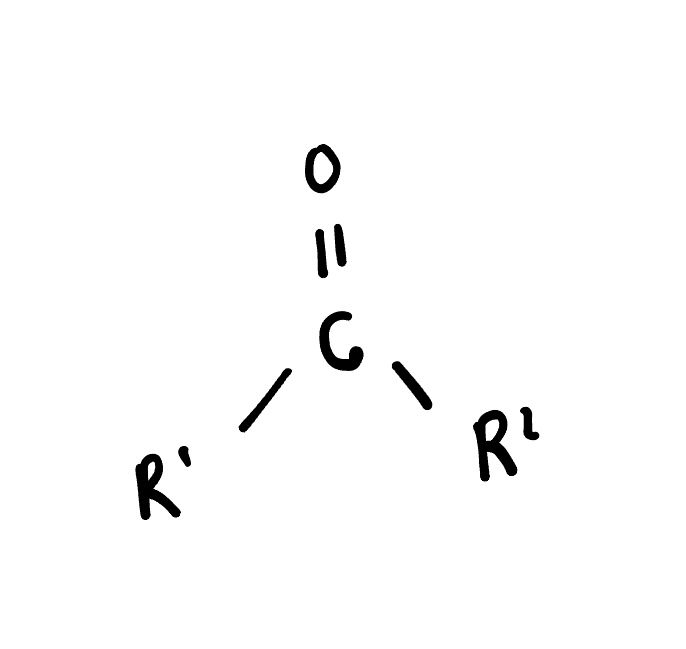
Ketone
is an organic compound containing a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups. Ketones are commonly used as solvents and in the production of various chemicals.
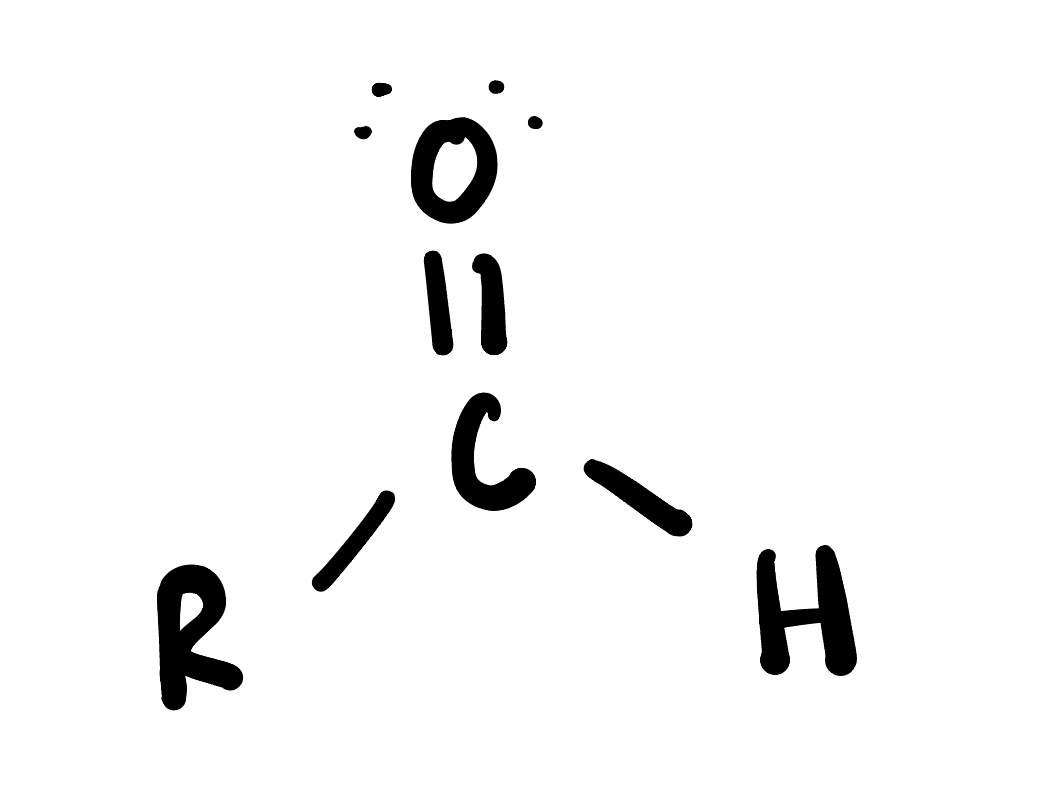
Aldehyde
is an organic compound containing a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to at least one hydrogen atom and one alkyl or aryl group. Aldehydes are often used in the synthesis of other organic compounds and have distinctive odors.
Carboxylic acid
is an organic compound that contains a carboxyl group (-COOH), which consists of a carbonyl and a hydroxyl group. Carboxylic acids are known for their acidic properties and are commonly found in nature, such as in fatty acids and amino acids.
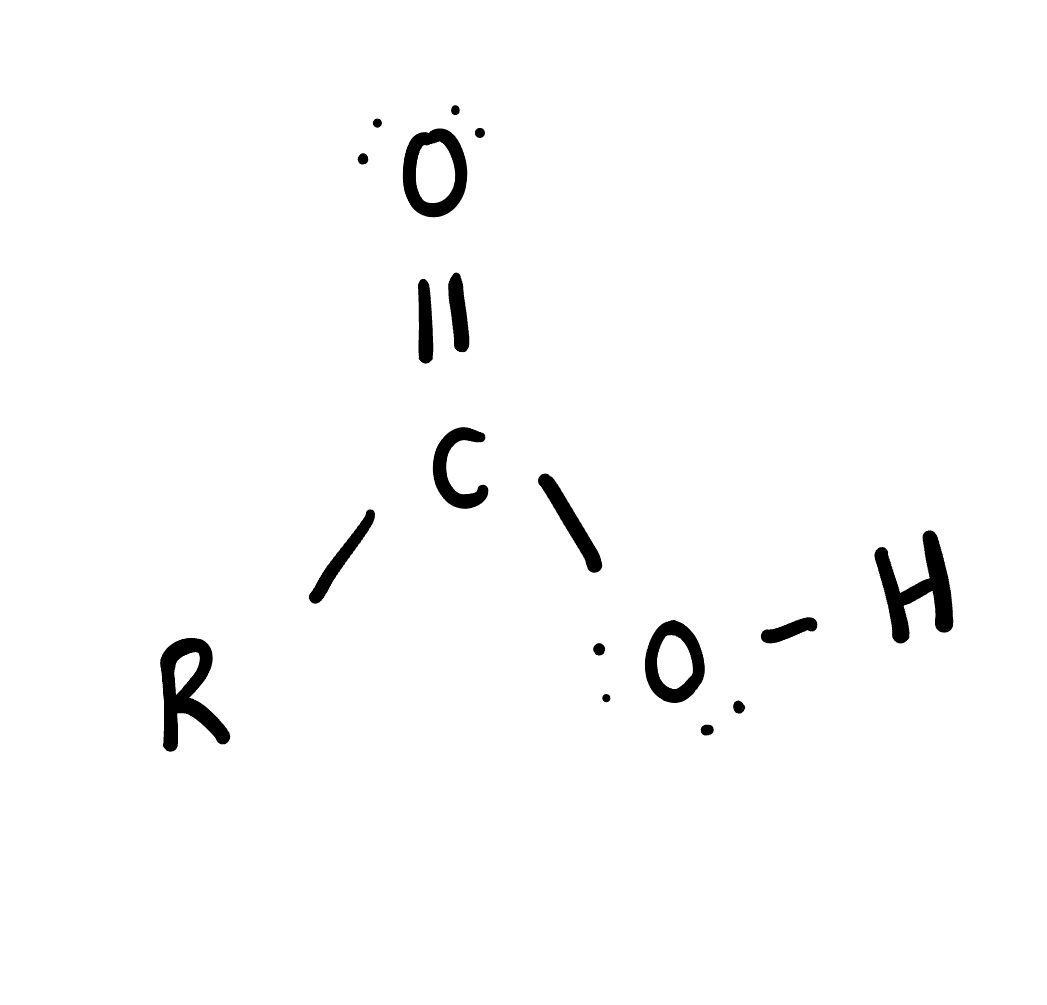
Ester
is an organic compound formed from the reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol, characterized by the functional group -COO-. Esters are often used in fragrances and flavorings due to their pleasant aromas.
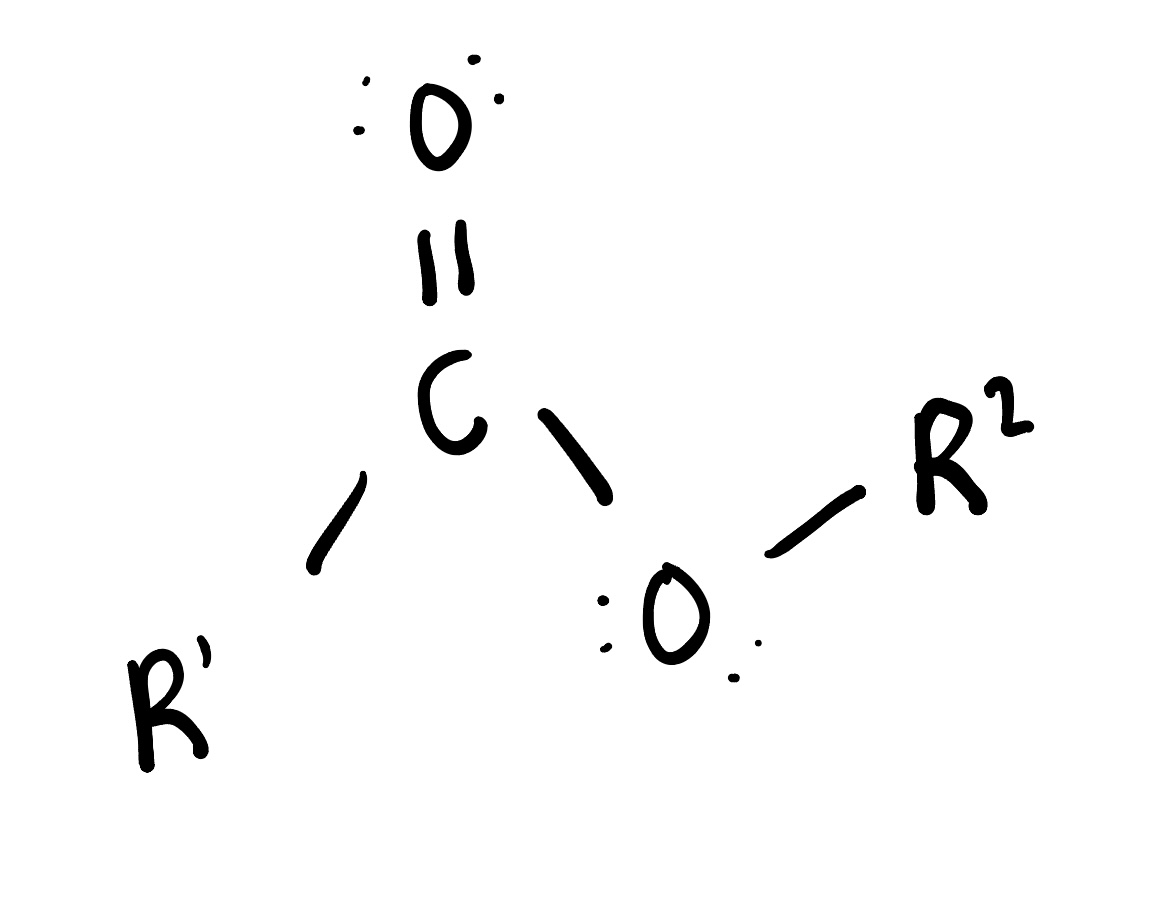
Amides
are organic compounds that contain a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to a nitrogen atom. They are derived from carboxylic acids and are commonly found in proteins and pharmaceuticals.
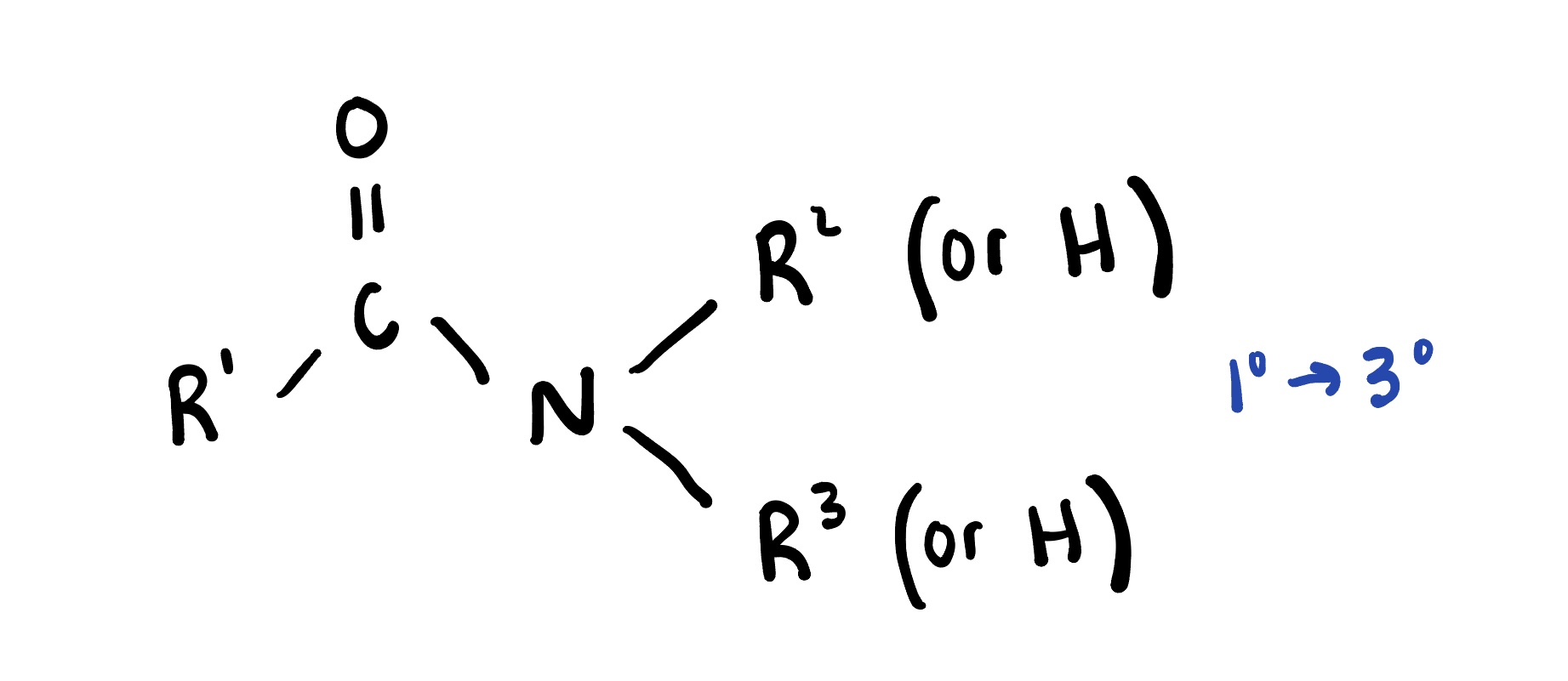
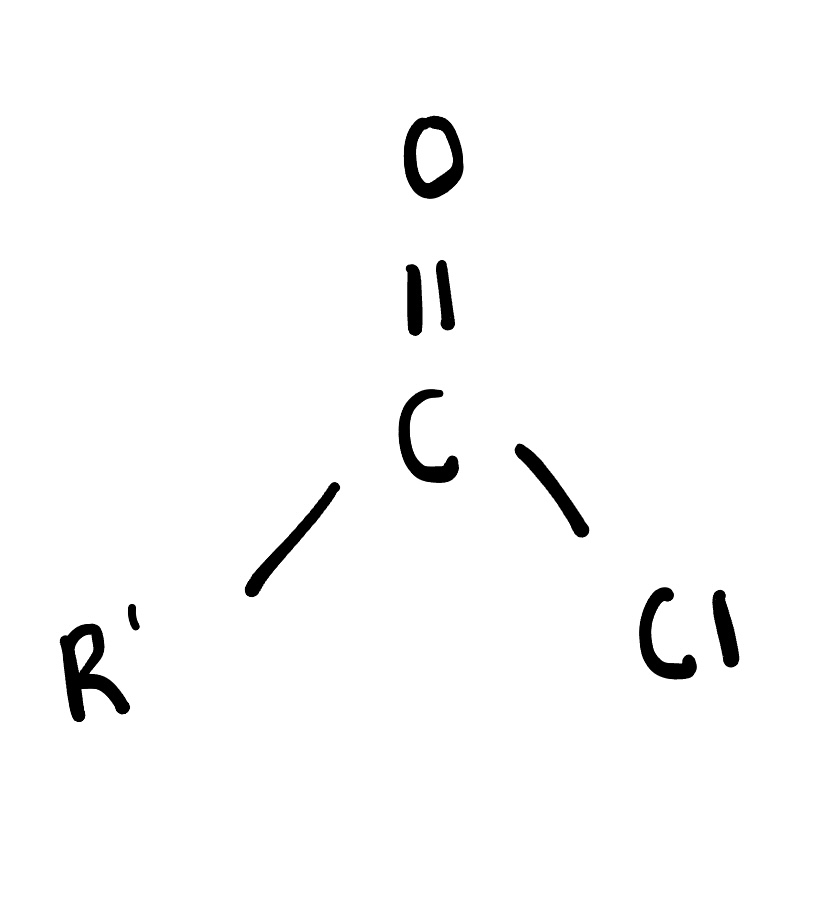
Acid chlorides
are reactive organic compounds derived from carboxylic acids, characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to a chlorine atom. They are commonly used in the synthesis of esters and amides.
Nitrile
is an organic compound containing a cyano group (-C≡N) attached to a carbon atom. Nitriles are used in the production of plastics, pharmaceuticals, and as solvents.
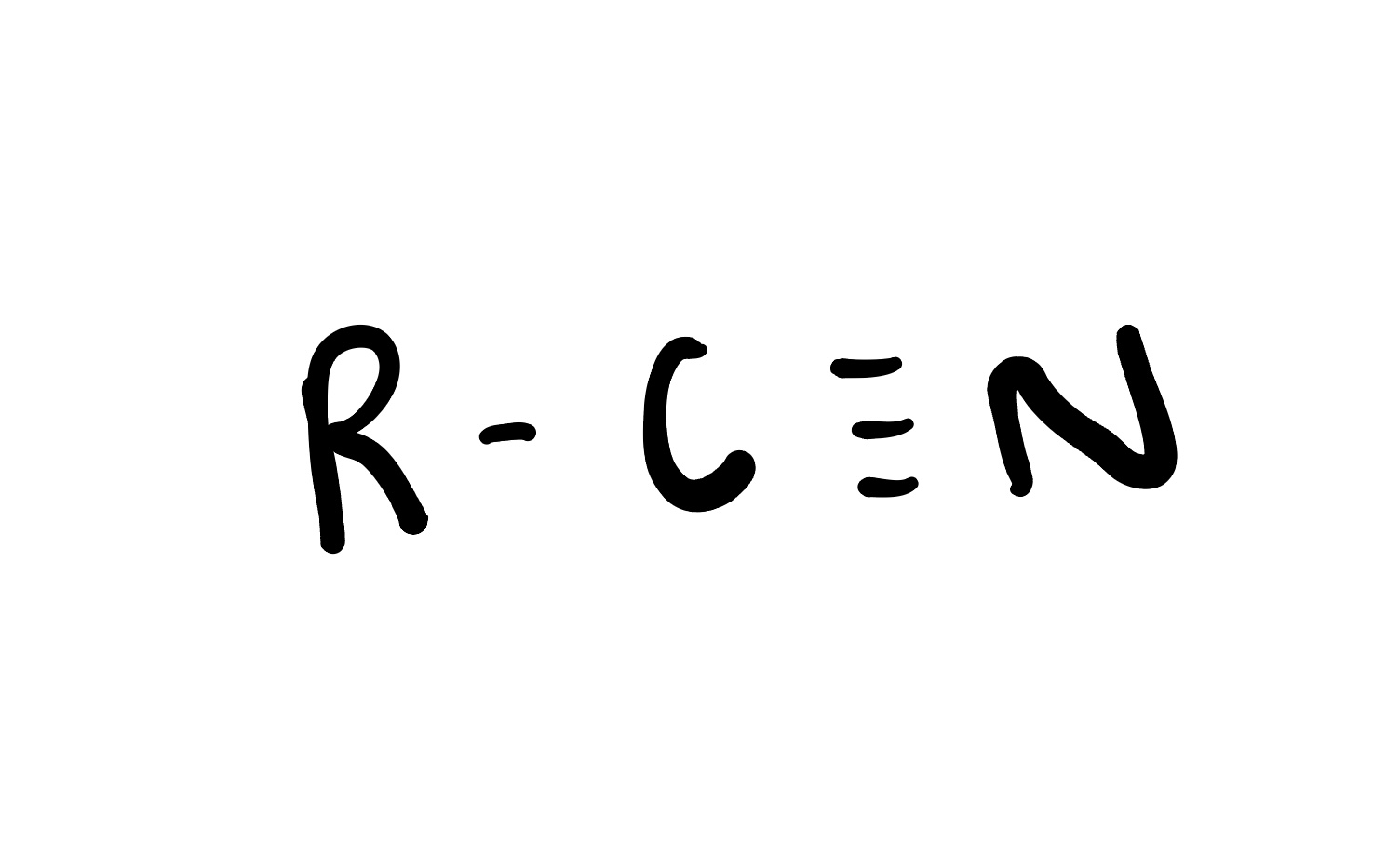
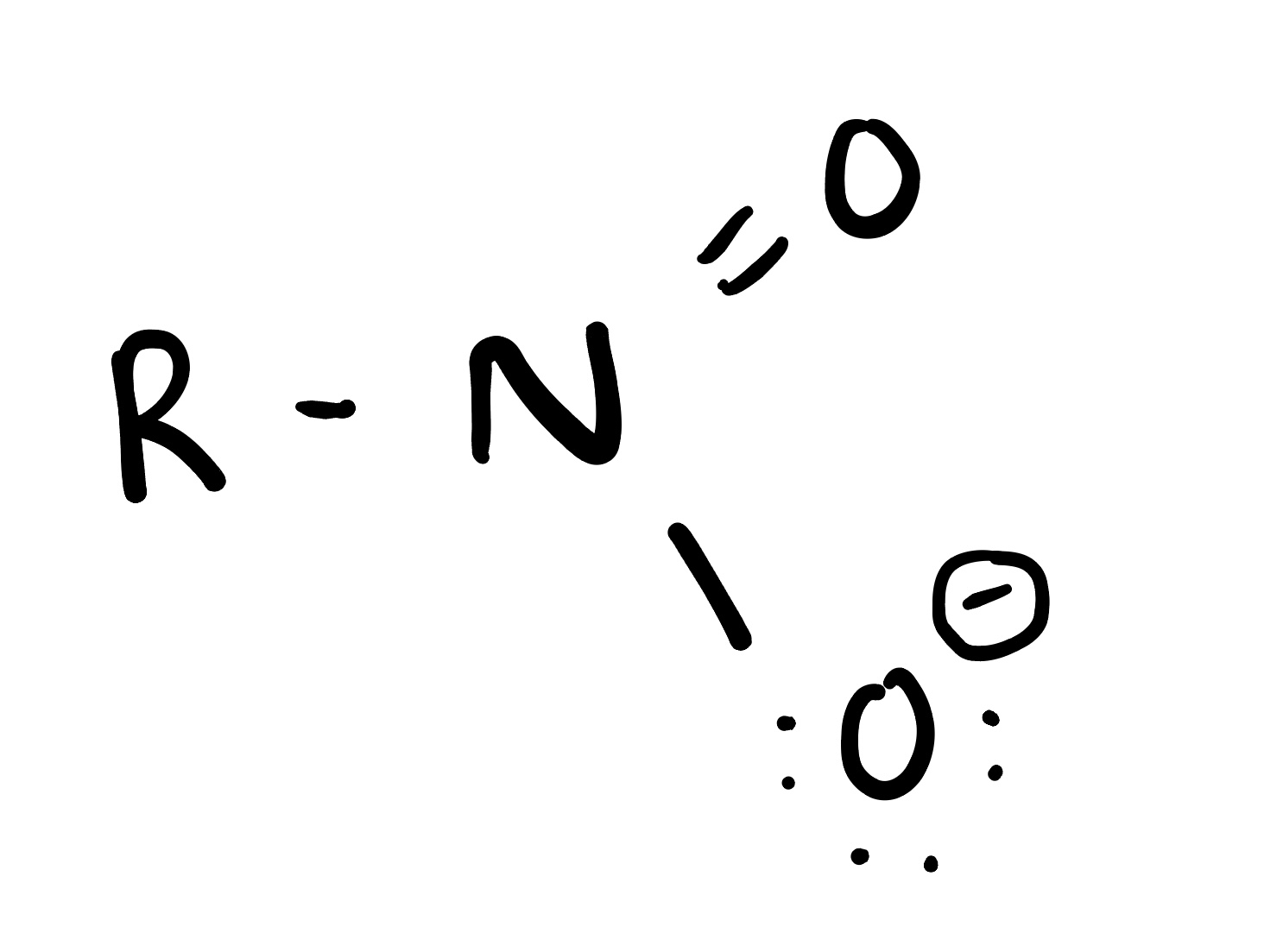
Nitro
compounds are organic molecules that contain one or more nitro groups (-NO2) attached to a carbon atom. They are often used in explosives, dyes, and pharmaceuticals.
Constitutional isomers
Same formula but connectivity of atoms is different
Resonance
Same atoms and same connectivity
Only move electrons, never move atoms
Only move lone pairs or multiple bonds
Covalent bond
-2 elements from the same side of the periodic table
-sharing 2 electrons between nonmetals
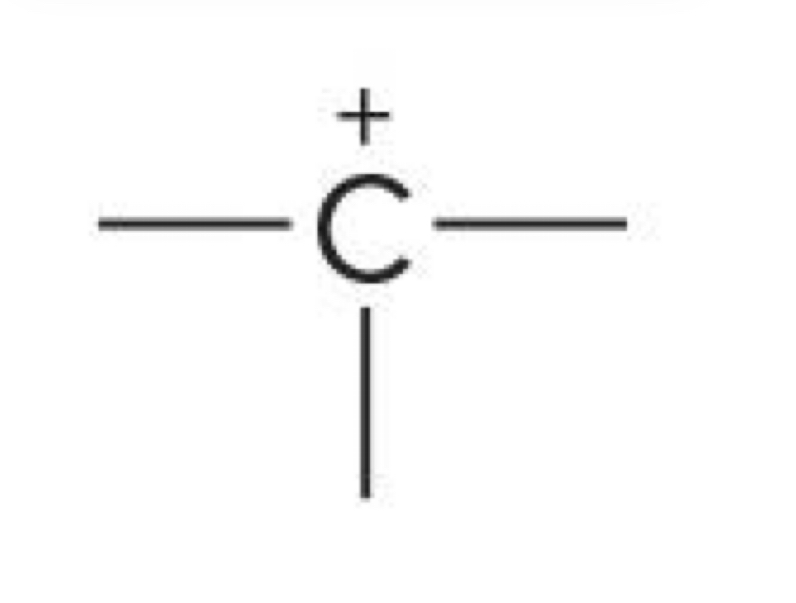
Carbon with 3 bonds
+1 charge
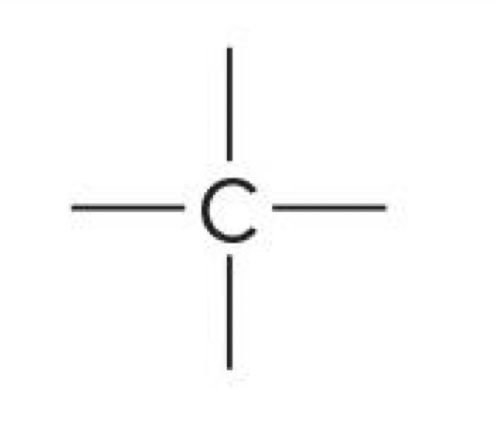
Carbon with 4 bonds
0 charge
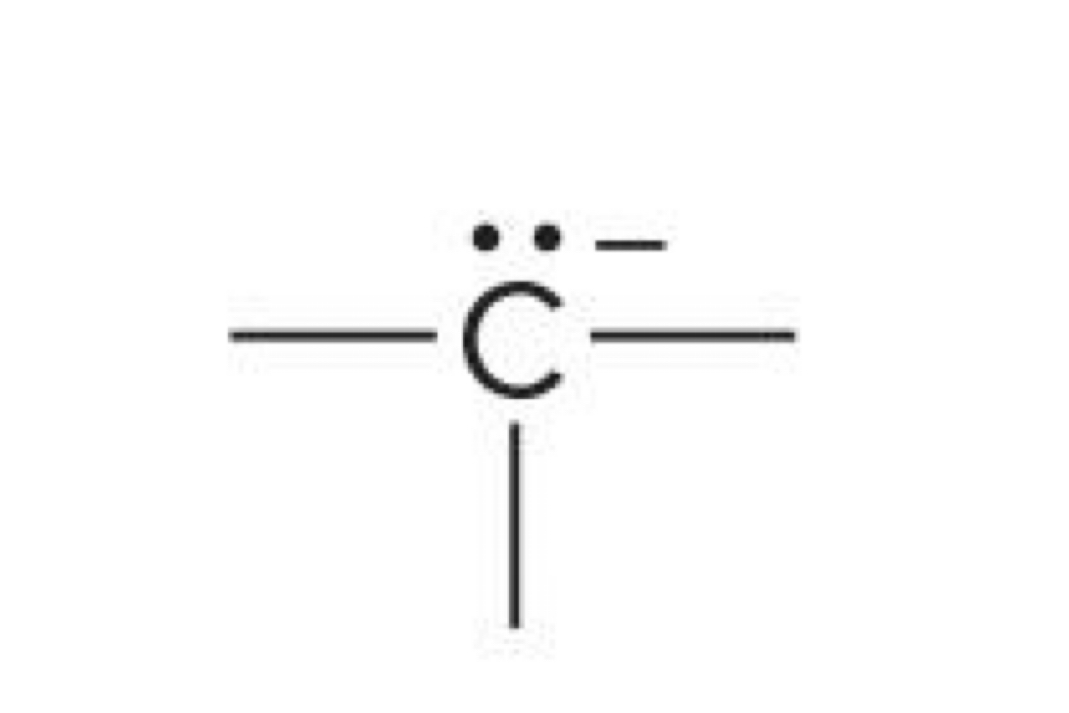
Carbon with 3 bonds and a lone pair
-1 charge
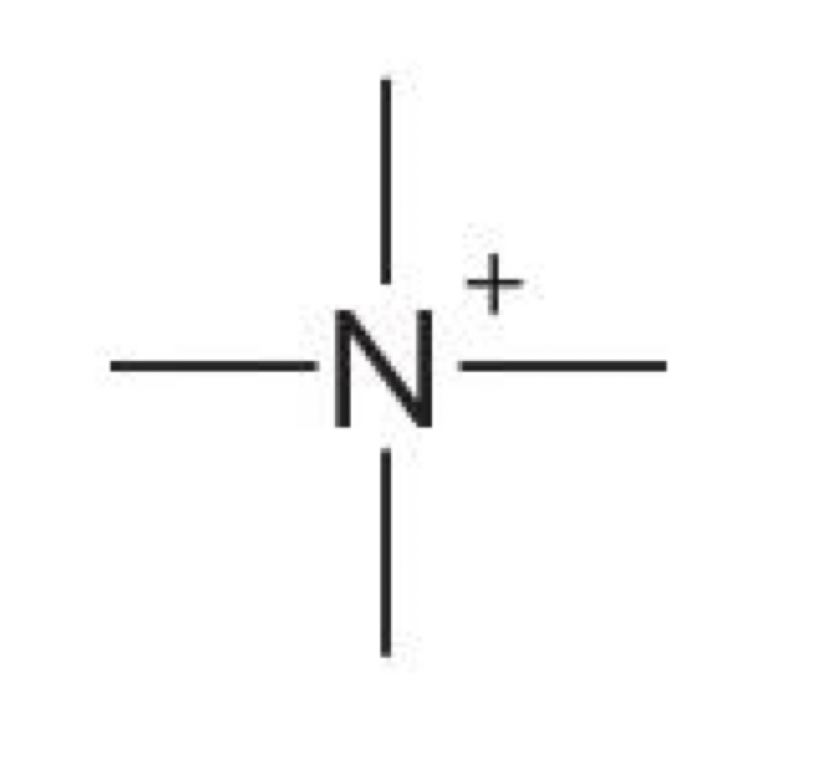
Nitrogen with 4 bonds
+1 charge
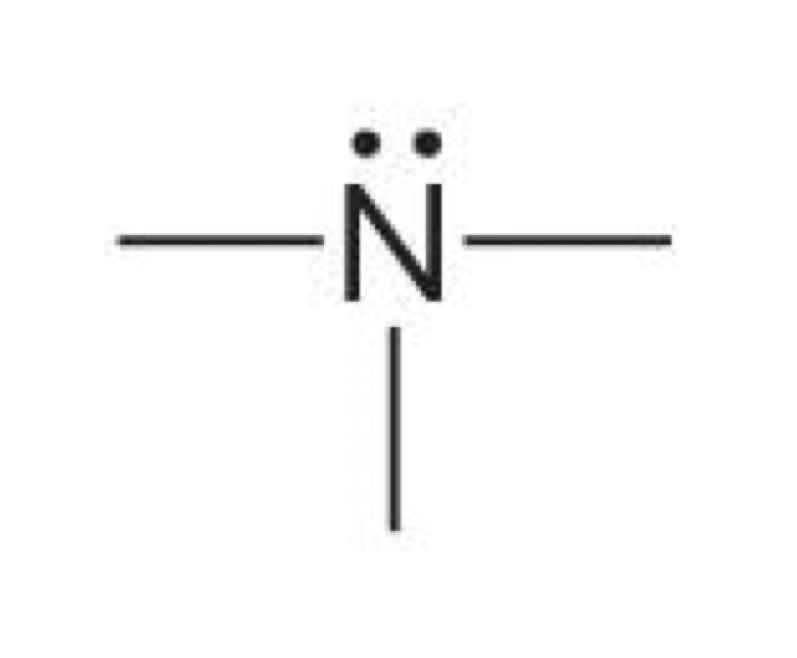
Nitrogen with 3 bonds and a lone pair
0 charge
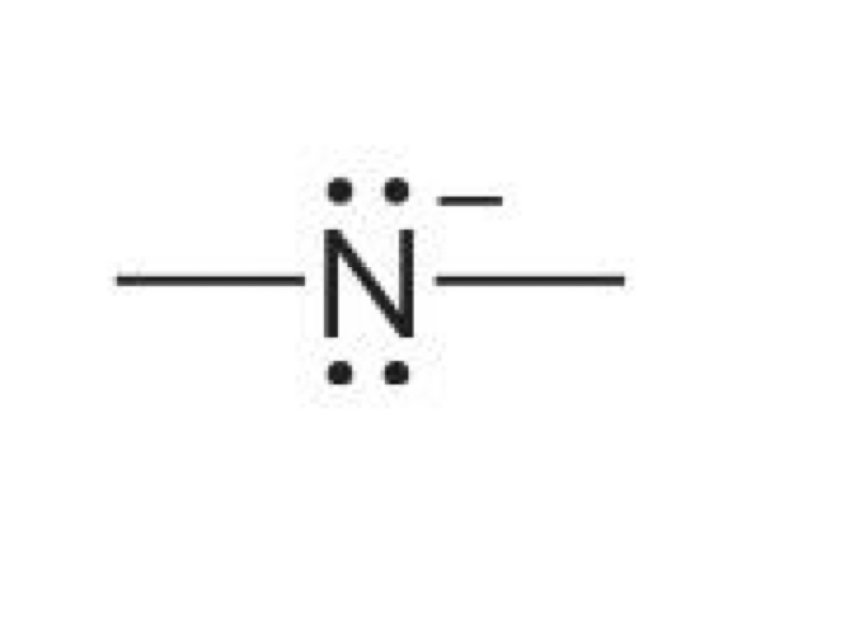
Nitrogen with two lone pairs and two bonds
-1 charge
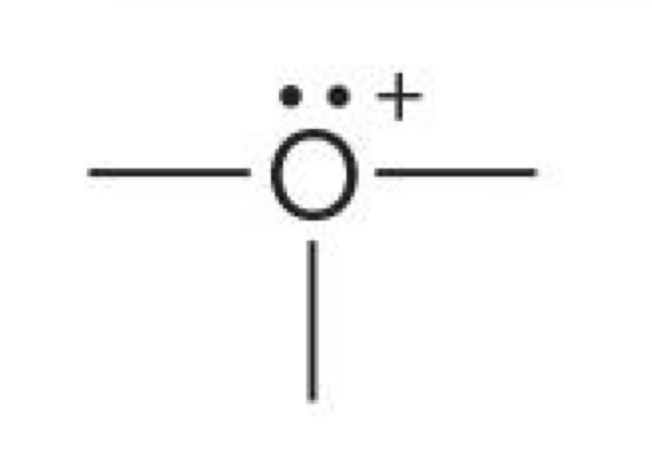
Oxygen with 3 bonds and one lone pair
+1 charge
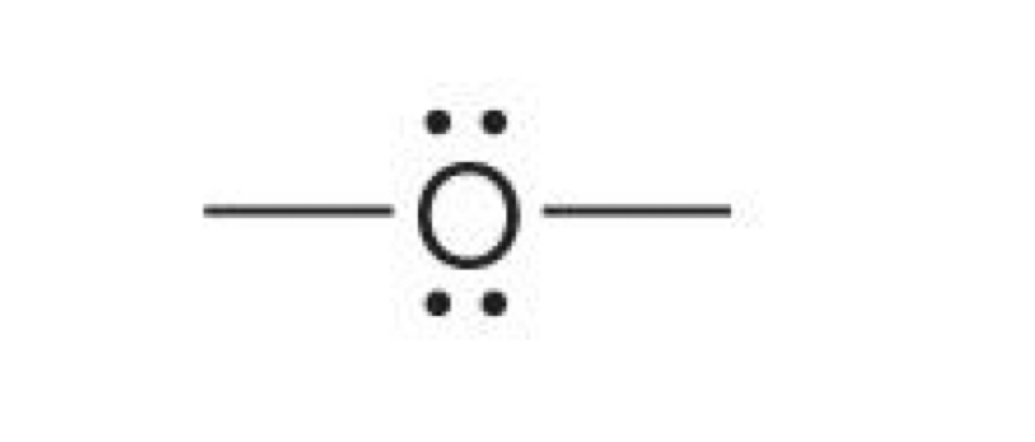
Oxygen with 2 bonds and 2 lone pairs
0 charge
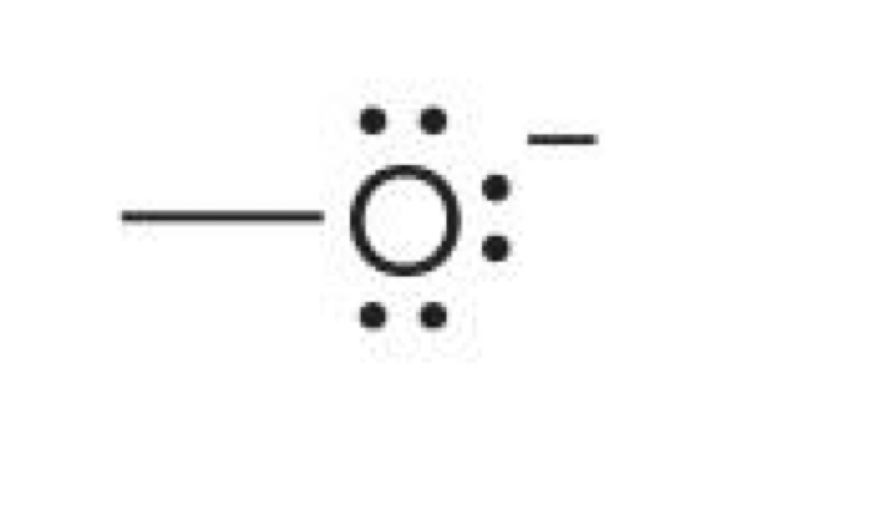
Oxygen with 3 lone pairs and one bond
-1 charge
what are the rules for picking the major resonance contributor structure
Contains more bonds and fewer charges
Better when all the atoms have octets
Negative charges are best placed on electronegative atoms
Sp hybridization
180 degrees and two groups around atom
Sp2
120 degrees and 3 groups around atom
Sp3
109.5 degrees and 4 bonds
What has the most S character (sp, sp2 or sp3)
Least sp3 most is sp
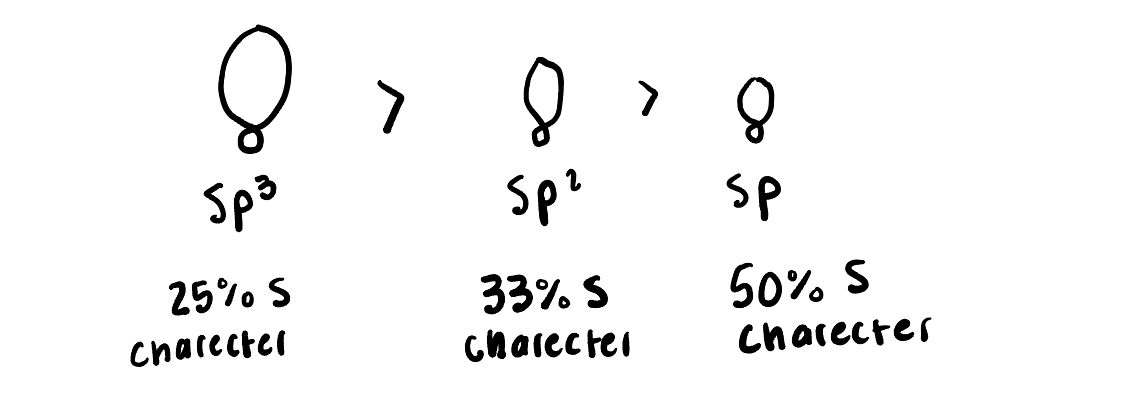
Put these in increasing bond strength (sp3, sp2, and sp)
Sp3, sp2, sp
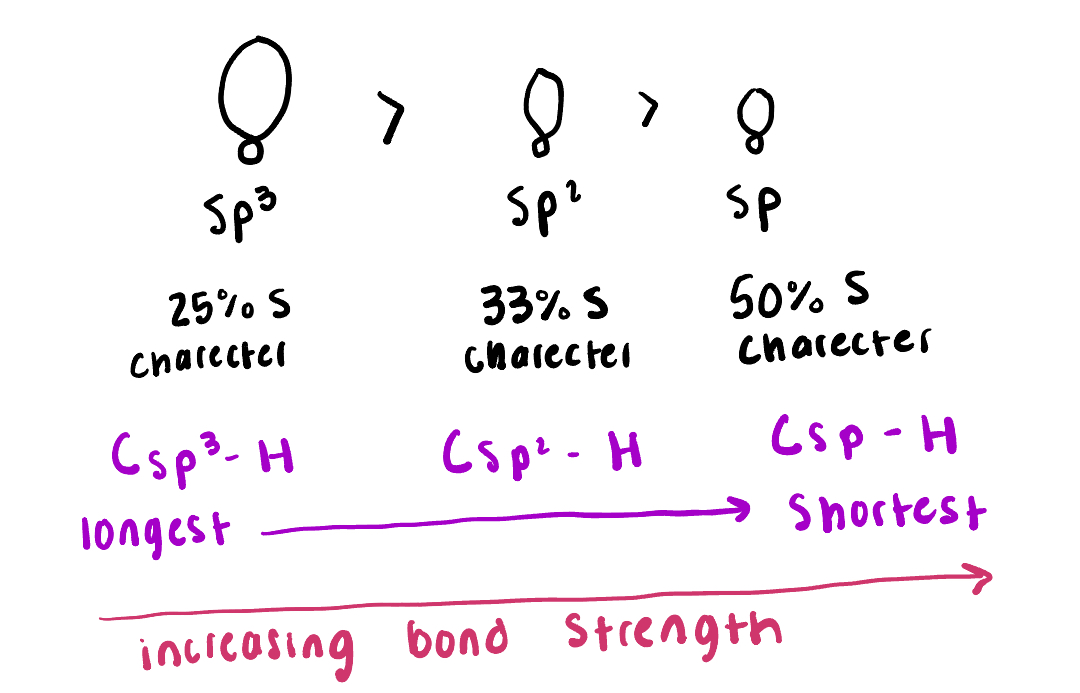
What is the longest? (Csp3, Csp2 and Csp)
Csp3 is the longest and Csp is the shortest
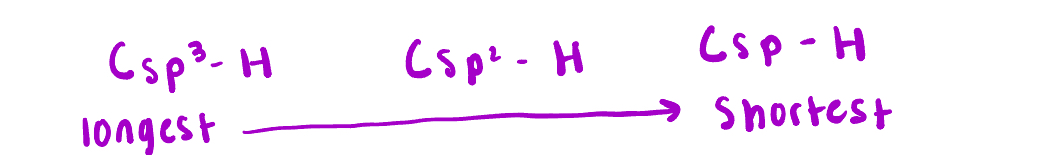
Bronsted-lowery acids
Contain a proton (the net charge may be zero (+), or (-)
Bronsted-lowery bases
Contain a lone pair of electrons or a pie bond (the net charge may be zero or (-))
Pka = ?
-logKa
The larger the Ka…
The smaller the pka
Smaller pka =>
Stronger acid
Larger pka=>
Weaker acid
A strong acid produces..
A weak (stable/less stable) CB
A weak acid produces a..
Strong (unstable/ reactive) CB
CB stability
Ability of the CB to deal with (stabilize) the negative charge
Charge on the larger atom
Identify of atom with charge base more stable
Charge is on the more electronegative atom
Identify of atom with charge base more stable if
Atomic size =
Larger atoms form more stable conjugate bases
Electronegativity=
More EN atoms form more stable conjugate bases
A base is more stable the closer the (-) charge (or lone pair) is to EN atoms
True
Resonance effects on CB stability
The greater the number of resonance structures you can draw the more stable the CB
Hybridization effects on CB stability
CB is more stable if lone pair is in smaller orbital (more “s” character)
Lewis acid
Electron pair accepter (electrophoile)
Lewis base
Electron pair donee (nuclcophile)
All Lewis bases have either
Lone pairs or pie bonds
All B-L acids are also Lewis acids
True
All B-L bases are also Lewis bases
True
All Lewis acids are B-L acids
False
Group 13 metals and transition metals often are Lewis acids, but not B-L acids
True
Sulfuric acid
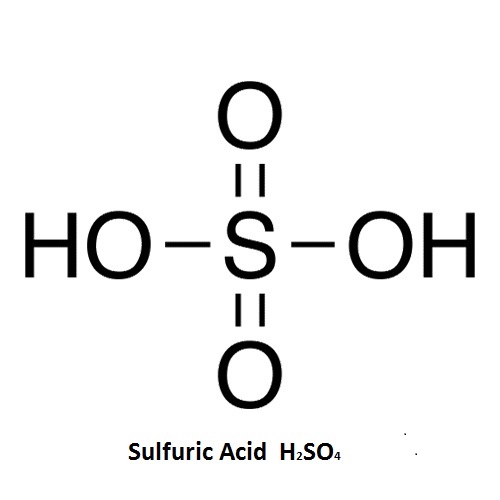
Nitric acid
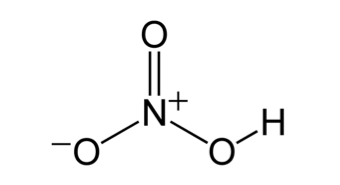
Hydrochloric acid
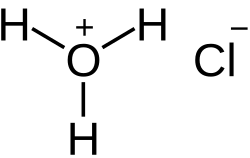
Carbonic acid
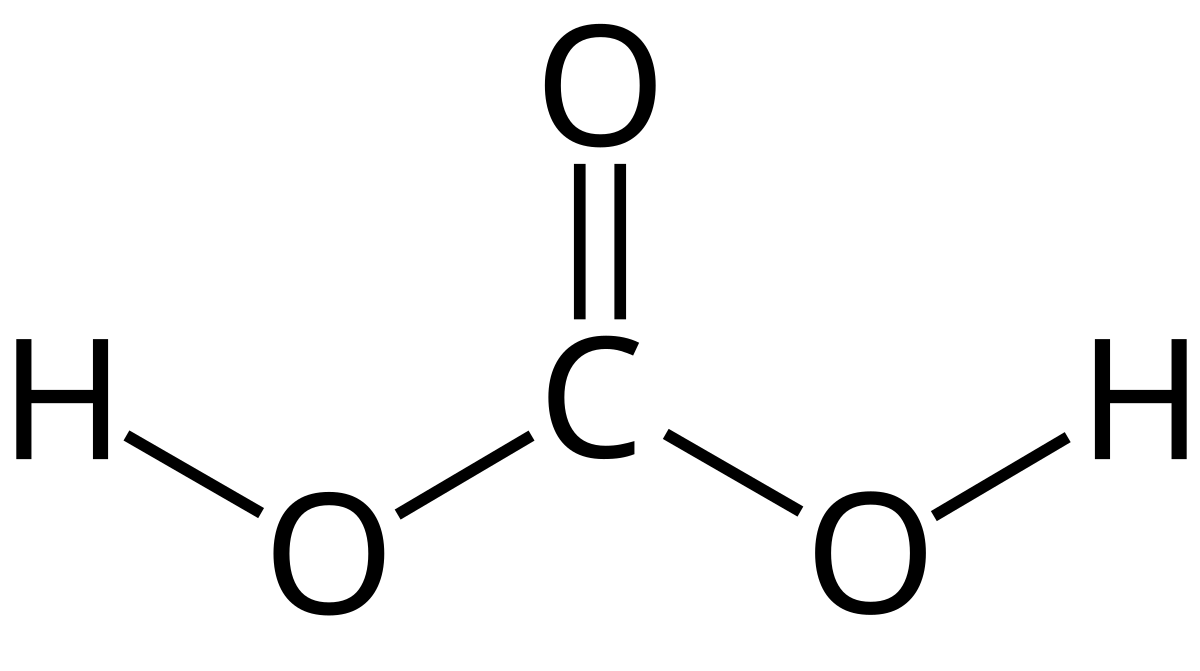
Acetic acid

Hydroxide
OH-
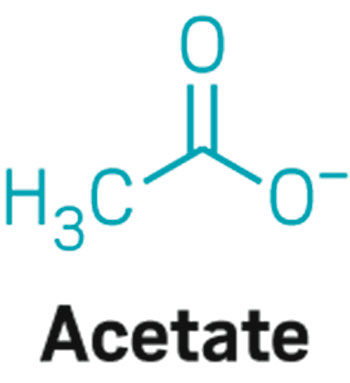
Acetate
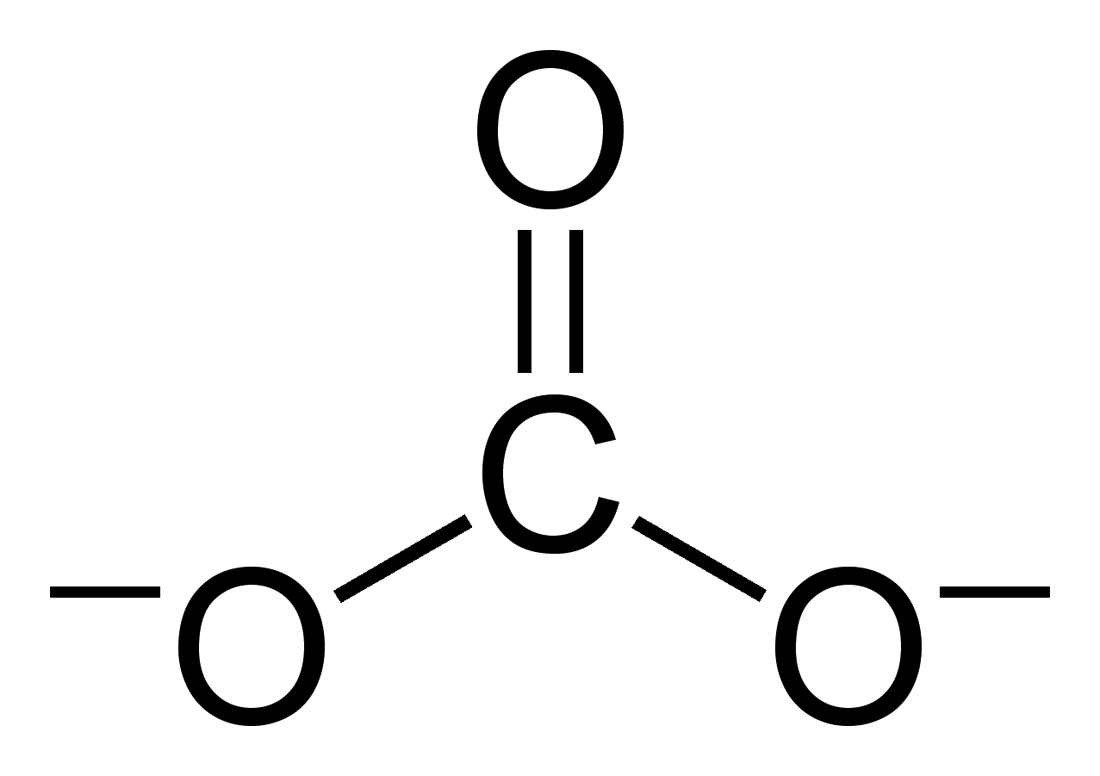
Carbonate
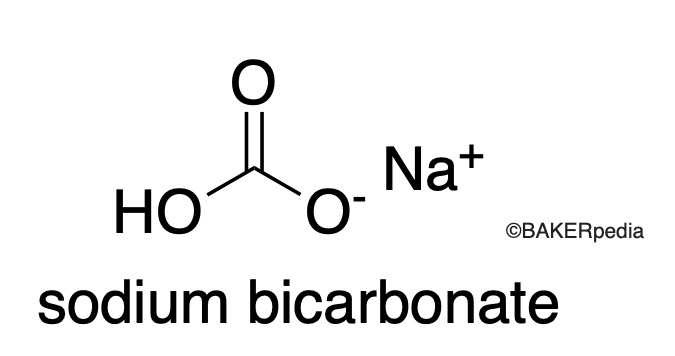
Bicarbonate
Ammonia
NH3
Hydride
H-