Chapter 3 and 4: Prokaryotic Diversity
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Eukaryotic Cells
Animals, plants, fungi, and protist
Membrane-bound organelles; compartmentalize the cytoplasm and perform specific functions.
Nucleus with DNA chromosomes.
Prokaryotic Cells
Monera
No Nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles
Cytoplasm
Fluid that fills the cell
70-80% water
3 major parts
Cytosol, organelles (ribosomes), inclusions.
The “Factory area” of the cells
Prokaryotic Ribosomes
60% Ribosomal RNA and 40% protein
Size 70S (S=Svedberg Unit)
Two subunits
Large and small
Site of protein synthesis
Found in all cells
Vary in size and number
Inclusions and Granules
Intracellular storage bodies
Vary in size, number, and content.
Used when environmental sources are depleted.
Gas vesicles. (Buoyancy)
Magnetosomes (Direction)
Cytoskeleton
An internal network of protein polymers that is closely associated with the cell wall.
Chromosome
Single, circular, double-stranded DNA molecule that contains all the genetic information required by a cell.
Plasmids
Free small circular, double-stranded DNA.
Not essential for bacterial growth and metabolism
Used in genetic engineering.
Readily manipulated and transferred from cell to cell.
Endospore
Inert, resting structures produced by some Gram-positive genera.
Clostridium, Bacillus, and Sporosarcina.
Have a 2-phase life cycle:
Vegetative cell
Endospore
Sporulation
Formation of endospores.
Hardiest of all life forms.
Withstands extreme conditions.
Not a means or reproduction.
Germination
Return to vegetative growth
Vegetative Cells
Sensitive to extreme temperatures and radiation
Gram-positive
Normal water content and enzymatic activity
Capable of active growth and metabolism
Endospores
Resistant to extreme temperatures and radiation
Do not absorb gram stain, only special endospore stains.
Dehydrated; no metabolic activity
Dormant; no growth or metabolic activity.
Cell Evelope
External covering outside the cytoplasm
Composed of two basic layers:
Cell wall
Cell membrane
Maintains cell integrity
Two different groups of bacteria demonstrated by Gram stain.
Gram-positive bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria
Gram-Positive Bacteria
Cell Membrane
Cell Wall with a thick peptidoglycan layer.
Gram-______
Gram-Negative Bacteria
Cell Membrane
Cell wall with a thin peptidoglycan layer
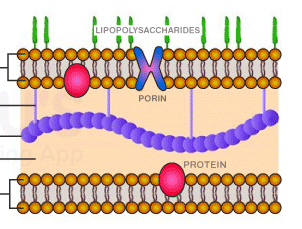
Outer membrane
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
A toxin composed of Lipid A embedded in the outer membrane, a core polysaccharide, and the O side chain.
Outer membrane of a gram-negative bacterial cell
Structure of Cell Walls
Determines cell shape, and prevents lysis due to changing osmotic pressures.
Peptidoglycan (aka Murein)
Peptidoglycan
Aka Murein
Unique macromolecule composed of a framework of long glycan (NAG and NAM) chains cross-linked by short peptide fragments.
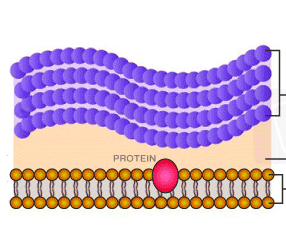
Gram-Positive Cell Wall
NAG
N-acetylglucosamine
NAM
N-acetylmuramic acid
Pentapeptide
tetrapeptide
Gram-negative Cell Wall
NAG
N-acetylglucosamine
NAM
N-acetylmuramic acid
Direct link
Cell Membrane
aka Cytoplasmic membrane, Plasma membrane.
Phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins.
Fluid mosaic model
Cell Membrane Functions
Protection
Selective Permeability
Compartmentalization
Transport of molecules
Cell Recognition & communication.
Providing a site for energy reactions, nutrient processing, and synthesis.
Cell Membrane Structure
Phospholipid bilayer
Glycoprotein
Carbohydrate Protein
Glycolipid
Carbohydrate lipid
Glycocalyx
Coating of molecules external to the cell wall
Made of sugars and/or proteins
Two types
Slime layer
Capsule
Glycocalyx Function
Protection
Prevent Phagocytosis
Attachment
Dehydration
Slime Layer
Loosely organized and attached
Hard to phagocytosize
Capsule
Highly organized, tightly attached
Phagocytosis
a type of endocytosis in which large particles are engulfed by membrane invagination, after which the particles are enclosed in a pocket, which is pinched off from the membrane to form a vacuole.
Biofilms
NEEDS TO BE WET
Microbes non resilient to stressors
Collect nutrients from flowing liquids
Nutrient exchange
Resistant to penetration from toxic molecules.
Genetic Exchange
Filamentous Appendages
Two Major groups of appendages
Motility
Flagella
Axial filaments (periplasmic flagella)
Attachment or channels
Fimbriae
Pili
Flagella
Motility - 360 rotation
Mechanism of rotation: “Run & Tumble”
Move toward or away from stimuli (taxis)
attraction
Chemotaxis
Phototaxis
Magnetotaxis
Phototaxis
directional movement using flagella in response to light
Chemotaxis
When a chemical gradient of an attractant exists, the length of runs is extended, while the length of tumbles decreased.
Magnetotaxis
directional movement of bacterial cells using flagella in response to a magnetic field.
Monotrichous
Having a single flagellum at one end of cell, usually a bacterial cell

Amphitrichous
having two flagella or tufts of multiple flagella, with one flagellum or tuft located at each end of the bacterial cell

Lophotrichous
having a single tuft of flagella located at one end of a bacterial cell
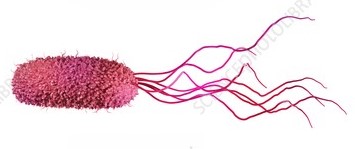
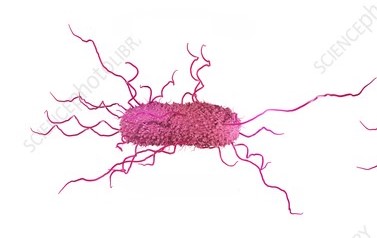
Peritrichous
having numerous flagella covering the entire surface of a bacterial cell
Periplasmic Flagella
aka axial filaments, endoflagella or axial fibrils.
Found in spirochetes
A type of internal flagellum
Fimbriae
Fine, hair-like bristles
More numerous
Function:
Adhesion/stick to surfaces and other cells
Pili
Rigid, long, tubular structures
Less numerous
Sex pili:
Transfer of genetic material
Prokaryote Habitats and Functions
_______ are ubiquitous
Extremely resilient and adaptable
Metabolically flexible
Functions:
Capturing (“fixing”) and recycling elements.
Cleaning up the environment.
Cause diseases.
Food production
Food spoilage.
Mutualism
type of symbiosis in which two populations benefit from, and depend on, each other.
Bacteria in human colon
Commensalism
type of symbiosis in which one population benefits and the other is not affected.
Staphylococcus on skin
Parasitism
type of symbiosis in which one population benefits while harming the other.
Tuberculosis bacteria in human lung.
The Gram Stain
Developed by Hans Christian Gram
Differential Stain
Gram-positive stain
Gram-negative stain
Atypical Stain
Important basis of bacterial classification and identification.
Practical aid in diagnosing infection and guiding drug treatment.
Differential Stain
Using more than one dye
Gram-Positive Stain
Retain crystal violet and stain purple
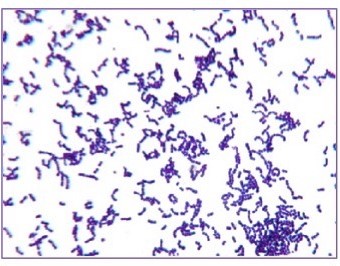
Gram-Negative Stain
Lose crystal violet and stain red from safranin counterstain.
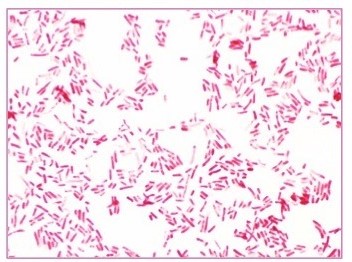
Atypical Stain
Neither Gram-Positive nor Gram-Negative stains
Nontypical Cell Walls
Some bacterial groups lack typical cell wall structure
Mycobacterium and Nocardia
Gram-Positive cell wall structure with lipid mycolic acid (cord factor)
Pathogenicity and high degree of resistance to certain chemicals and dyes
Basis for acid-fast stain
Some bacteria have no cell wall
E.g Mycoplasma
Cell membrane is stabilized by sterols (to resist lysis)
Pleomorphic
Cyanobacteria
Oxygenic Photosynthesis
Gram-Negative
Contain photosynthetic chlorophyll-A pigments and gas vesicles.
Give off oxygen (use H2O as an e-donor)
Free-Living nonpathogenic bacteria
Oxygenic Photosynthesis
type of photosynthesis found in plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, and in which H2O is used as the electron donor to replace an electron lost by a reaction center pigment, resulting in oxygen as a byproduct
Green and Purple sulfur bacteria
Use sulfides for oxidation
Contain photosynthetic bacteriochlorophyll pigment
Do not give off oxygen
Anoxygenic photosynthesis
Free-living nonpathogenic bacteria
Green and purple non-sulfur bacteria
Anoxygenic Photosynthesis
Use substrates other than sulfides for oxidation
Contain photosynthetic bacteriochlorophyll pigment
Free-Living nonpathogenic bacteria
Anoxygenic Photosynthesis
type of photosynthesis found in many photosynthetic bacteria, including the purple and green bacteria, where an electron donor other than H2O is used to replace an electron lost by a reaction center pigment, resulting no oxygen production
Rickettsia
Tiny, gram-negative bacteria
Most are pathogens
transmitted by arthropods
E.g. Rickettsia rickettsii
Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
Obligate intracellular parasites
Chylamdias
Tiny, gram-negative coccobacillus
Not transmitted by arthropods
Chlamydia trachomatis
Severe eye infection (trachoma) and one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases
Chlamydia Pneumoniae
Lung infections
Archaea
Some are extremophiles.
Adapted to heat, salt, acid pH, pressure, and atmosphere.
Includes: methane producers, hyperthermophiles, extreme halophiles, and sulfur reducers.
Constitute third Domain ______
Contain unique genetic sequences in there rRNA
Have unique membrane lipids and cell walls
Extremophiles
Live in the most extreme habitats in nature
Bacteria cell wall
Peptidoglycan, or none.
Archaea cell wall
Pseudopeptidoglycan, or
glycopeptide, or
Protein (s-layer), or
none
Bacteria motility structure
Rigid spiral flagella composed of flagellin
Archaea motility structure
Rigid spiral flagella composed of archaeal flagellins
Bacteria Ribosomes
70S
Archaea Ribosomes
70S
Structure similar to 80S