Lab 10 (Ester Synthesis and Hydrolysis)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
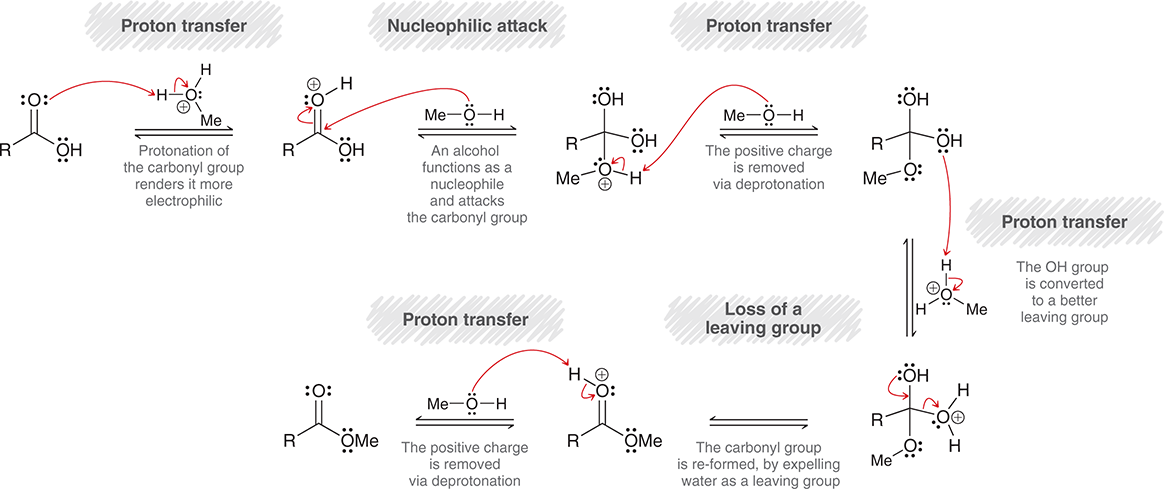
What is the mechanism of Fischer esterification of acetic acid with benzyl alcohol?
Carbonyl from acetic acid takes a proton from protonated alcohol (forms another OH)
Then the Oxygen from benzyl alcohol attacks carbonyl carbon
Then the alcohol deprotonates itself
OH from either esterification or acid takes proton from protonated alcohol to be a better leaving group
Leaving group leaves, forming a C=O bond
Then the C=OH group gets deprotonated
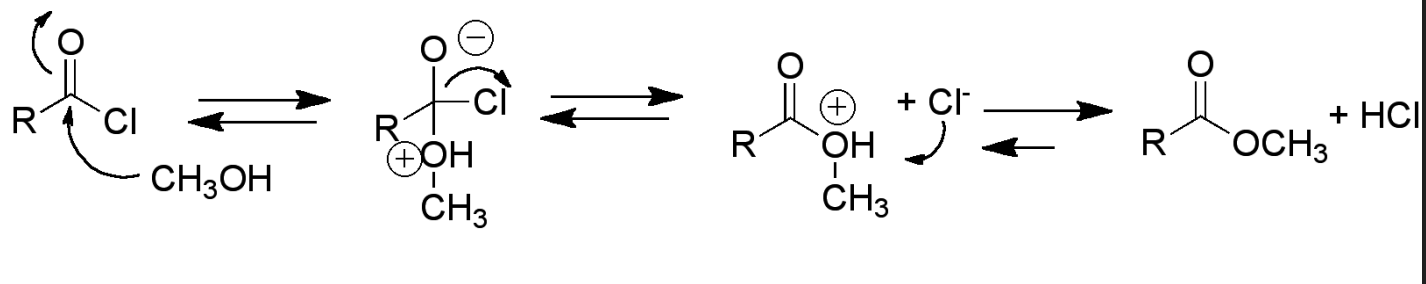
What is the mechanism of the reaction between acetyl chloride and benzyl alcohol?
Benzyl alcohol attacks carbonyl group (rate determining)
Benzyl alcohol has a positive charge and oxygen has a negative charge
Chloride leaves and then C=O bond reforms
Chloride then deprotonates the benzyl alcohol, removing the positive charge
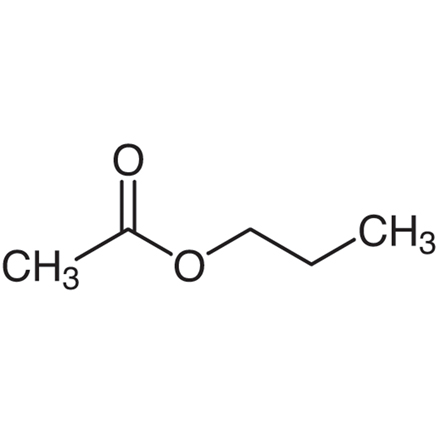
What is the structure of propyl acetate?
3 carbon chain
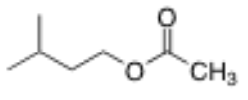
What is the structure of 3-methylbutyl acetate?
4 carbon chain with a methyl group on C3
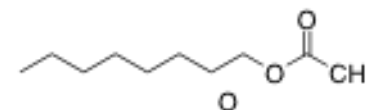
What is the structure of octyl acetate?
8 carbon chain
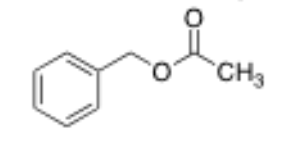
What is the structure of benzyl acetate?
1 carbon and then a benzene ring
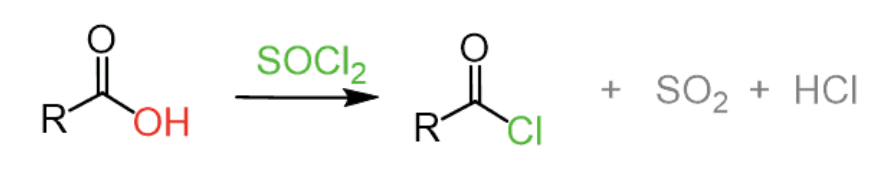
How do you synthesize acetyl chloride from acetic acid and any inorganic reagent? Show the balanced equation.
CH3COOH + SOCl2 → CH3COCl + SO2 + HCl
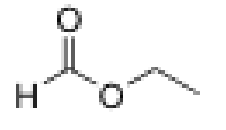
What is the structure of ethyl formate?
Aldehyde with 2C ether
What is the structure of Ethyl Acetate?
2C Ketone with 2C ether
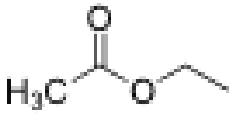
What is the structure of ethyl propionate?
Ketone with 3 carbons and 2C ether group
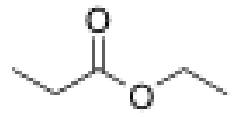
What is the structure of ethyl benzoate?
Ketone with benzene ring and then 2C ester
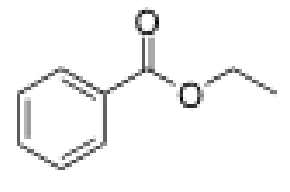
What is the mechanism of the base catalyzed ester hydrolysis?
In basic conditions alcohol attacks carbonyl carbon, shifting electrons to oxygen on carbonyl
Then electrons on carbonyl carbon shift back, kicking off ether group
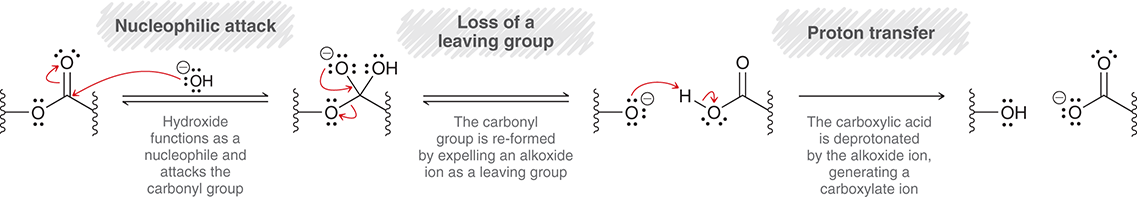
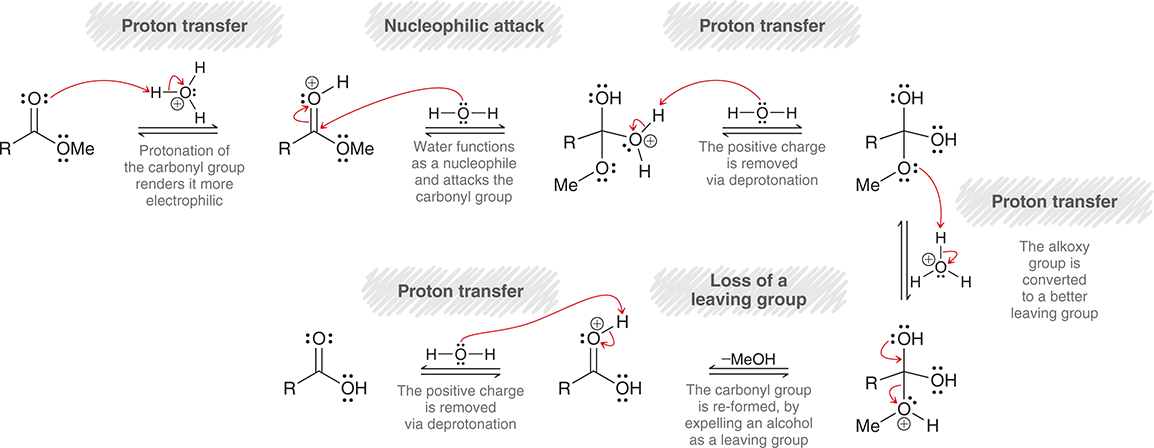
What is the mechanism of the acid catalyzed ester hydrolysis
First, the O in carbonyl takes proton from hydronium ion
Then the H2O attacks carbonyl carbon
H2O then gets deprotonated
Ether group gets protonated
OH shifts electrons to make double bond, and then ether group leaves
Finally water deprotonates OH on carbonyl
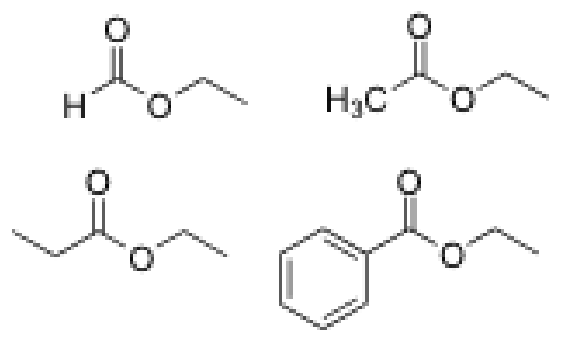
Rank these ester slowest to fastest for reactivity in hydrolysis
Benzyl Group
2 chain
1 Chain
Formic acid
More electron donating means slower hydrolysis
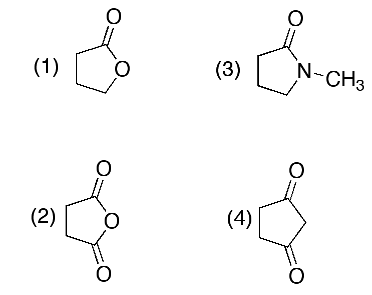
Which of the following is not a derivative of carboxylic acids?
4

Acid chloride is more reactive than ester in reaction with alcohol, because;
4
Better leaving group
Makes carbonyl carbon more prone to nucleophilic attack (more electron withdrawing)
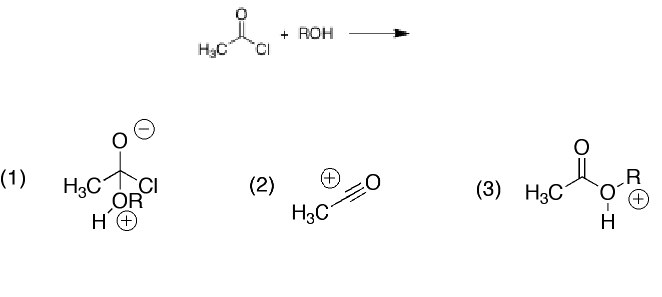
Which of the following species is not an intermediate in the reaction of acid chloride with alcohol?
2
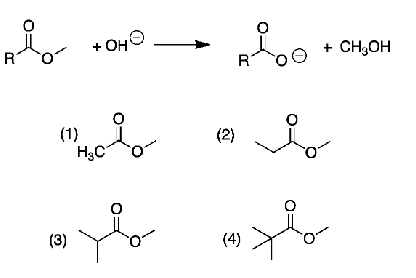
Which ester should be the least reactive in base-catalyzed hydrolysis?
4 because it is the most sterically hindered of all the esters