Blood Bank Test 1
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
ABO antibodies are mainly
IgM
20% ABO antibodies can also be
IgA
Most clinically significant antibodies in blood bank (besides ABO) are
IgG
Which antibodies are best at binding complement
IgM
Which antibodies react best at body temperature
IgG
Which antibodies are usually naturally occurring?
IgM
All antigens are immunogens.
False
A and B genes are dominant over O
False
Which of these is a secretor?
SeSe
Sese
A person with these genes has what antigens in their secretions:
SeSe, AA
A and H
A person with these genes has what antigens in their secretions:
sese, AA
Nothing, sese is a nonsecretor
People who are group O have what immunodominant enzyme?
L-fucosyltransferase
People who are group B have what immunodominant enzyme?
D-galactosyltransferase
Who has the most H?
O
Who has the least H?
A1B
Which immunoglobulin is best noted for its ability to cross the placenta?
IgG
Which gene in the ABO blood group is an amorph?
O
What is the immunodominant sugar of the A antigen?
N-acetyl-D-galactosamine
What is the frequency of blood type AB in the general population?
4%
In reverse typing, you are testing for the patient's
Antibodies in serum
In forward typing you are testing for the patient's
antigens on RBCs
As long as the forward type looks fine, the reverse typing doesn't have to match
False
What do you add first to tubes for testing?
Serum
You can use serum or plasma for testing
True
Which of these subgroups gives a mixed field agglutination?
A3
Bombay individuals will phenotype as group
O
All Bombay individuals have the O genotype
False
Many will have the B genotype
Individuals that are A2 are more likely to have an anti-H antibody than individuals that are A1
False
What percentage of the population of Group A is A2?
20%
Anti-H is always a potent and clinically significant antibody
False
Will only be significant in a Bombay blood group because even though it is IgM it will react at body temperature
The reagent Anti-A,B is good for
Testing donor units as they come into the blood bank
Bombay individuals can only be transfused with blood from another Bombay individual
True
Diseases like leukemia can weaken the expression of A and B antigens on RBCs
True
B subgroups are much more common than A subgroups
False
Almost all A2 individuals will make Anti-A1
False
The most often used practice is to transfuse A2 individuals with group
O
Which of the following is not involved in the acquired (adaptive) immune response?
Phagocytosis
Which cells are involved in the production of antibodies?
B lymphocytes
Which of the following immunoglobulins is produced in the primary immune response?
IgM
Which of the following immunoglobulins is produced in the secondary immune response?
IgG
Which of the following immunoglobulins is most efficient at binding complement?
IgM
Which portion of the immunoglobulin molecules contains complement binding sites
Heavy chain constant region
Which complement pathway is activated by the formation of antigen antibody complexes?
Classical
Which of the following is known as the recognition unit in the classical complement pathways
C1q
Which of the following immunoglobulin classes is capable of crossing the placenta and causing hemolytic disease of the newborn?
IgG
What term describes the unique confirmation of the antigen that allows recognition by a corresponding antibody?
Epitope
What percentage of the type A population is A1?
80%
Which cells agglutinate most strongly with ulex europaeus?
O and A1B
The phenomenon of an Rh positive person whose serum contains anti-D is best explained by:
Partial D
An ABO discrepancy between forward and reverse grouping owing to weak reacting or missing antibodies could be best explained by which of the following?
Acquired B phenomenon
Which antigen represents Rh4 in Rosenfield terminology?
little c
Reverse grouping showed positive reactions to A1 and B cells. Forward grouping showed negative reactions with A and B antisera. What blood type is consistent with these results?
O
If there is a mutation in the RHAG gene, the individual may be Rhnull. This means that:
They will type as Rh negative but may still have the RHD gene
A blood donor has the genotype hh, AB. What is his red blood cell phenotype?
O
Which of the following antigens has the highest frequency?
little e
98%
In an emergency Rh negative RBC's are transfused to an Rh positive person of the genotype R2R2 (DcE/DcE). They may make an antibody to:
Anti-e
What three genes are responsible for the production of Rh antigens?
RHAG, RHD and RHCE
Which blood group is most likely to make an Anti-H?
A1B
Several genotypes are possible for an individual that has this Rh phenotype: D+ C+ E+ c+ e. Which of the following is not possible?
a. R1R2=DCe/DcE
b. R0r"=Dce/dce
c. R2r'=DcE/dCe
d. R1r"=DCe/dcE
What immunogenic sugar is responsible for the B antigen?
D-galactose
All of the following may depress antigen expression except:
Coronary artery disease
Mixed field reaction is commonly seen in the forward ABO test if a group _____ patient has received several transfusions with group ______.
A,O
The ABO group antibodies are primarily:
Naturally occurring
A sample gives the following results:
Forward type:
Anti-A: 4+
Anti-B: 4+
Reverse type:
A1 cells: 1+
B cells: 0
Which lectin should be used first to resolve this discrepancy?
Dolichos biflorus
Most Rh antibodies are of what immunoglobulin class?
IgG
Which of the following genotypes would demonstrate the strongest expression of the D antigen?
DCe/dce
A patient is typed with the following results:
Forward type:
Anti-A: 0
Anti-B: 0
Anti-A,B: 2+
Reverse type:
A1 Cells: 1+
B-Cells: 4+
The most probable reason for these findings is that the patient is group:
Ax; with Anti-A1
The following reactions were obtained:
Forward type:
Anti-A: 4+
Anti-B: 2+
Anti-D: 4+
Reverse type:
A1 Cells: 2+
B Cells: 4+
The technologist washed the patients RBC's with saline and repeated the forward typing. A saline replacement technique was used with the reverse typing. The following results were obtained:
Forward type:
Anti-A: 4+
Anti-B: 0
Anti-D: 4+
Reverse type:
A1 Cells: 0
B cells: 4+
These results are consistent with:
Acquired B antigen
A patient's red blood cells type as follows:
Anti-D: 4+
Anti-C: 0
Anti-E: 0
Dce/Dce
Which of the following genotypes would be consistent with these results?
a. R0R0=Dce/Dce
b: R1r: DCe/dce
c: R1R2: DCe/DcE
d. R0r': Dce/dCe
Which of the following are produced after exposure to genetically different non self antigens of the same species?
Alloantibodies
Which of the following statements is false?
A.Anti-D usually stimulates complement.
B.Anti-D is mostly IgG.
C.Anti-D can cause hemolytic disease of the newborn.
D.None of the above
Remember: Anti-D is IgG and cannot stimulate complement
At which temperature to IgM antibodies optimally react?
22 degree celsius
What immunodominant sugar is responsible for B specificity?
D-galactose
The Rh (D) antibody agglutinates what percentage of the population's red cells.
85%
The Rh testing on a blood donor was negative at immediate spin. The tube was incubated at 37°C for 15 minutes. The tube was centrifuged and read macroscopically. The test was negative at 37°C. The tube was washed three times with saline and two drops of AHG were added. After centrifugation, the tube yielded a 2+ reaction. How is this Rh type reported on the donor unit?
Rh positive
A patient who was recently diagnosed with an obstructed bowel became septic from Escherichia coli. Prior to surgery, a routine type and screen was performed. Though this person typed as an A two years ago, his forward type is consistent with an AB individual, albeit weaker in strength with anti-B. What is the reason for this discrepancy?
Acquired B antigen
Remember: Acquired B is most likely due to Colon cancer
At what age do infants begin to produce their own antibodies?
4 months
When one or more D epitopes within the entire D protein is missing it is termed__________.
Partial D
In an immune response, __________ antibodies are formed before _______ antibodies.
IgM, IgG
A group B patient with multiple myeloma exhibits rouleaux formation in both reactions of the reverse type. What procedure is recommended to distinguish true red blood cell agglutination from nonspecific agglutination?
Saline replacement
Rouleaux can also happen in the forward type, the recommendation for that is to wash the RBCs several times before you make a 3% cell suspension
What Rh type does a mother have to be to produce antibodies to Rh(D) from an Rh-positive infant?
Rh negative
What ABO group contains the least amount of H substance?
A1B
Why is reverse grouping not performed on cord blood specimens?
Antibodies are generally not present at birth
Which substance must be formed first before A or B specificity is determined?
H
Which gene combination is expressed in the greatest frequency in the black population?
Dce or R0
What class of immunoglobulin is capable of crossing the placenta?
IgG
What would be a possible genotype of an A2B individual?
A2B
G antigen is present on all of which type of red blood cells?
C-Positive
Mom is dce/dce. What antibodies can this Mom make?
Anti-D, C, E
A blood donor has the genotype: hh, AB. What is his RBC phenotype?
O
This is a Bombay, they do not make H antigens so they phenotype as group O.
Cells of the A3 subgroup will:
Mixed field reaction with anti-A,B or anti-A
A3 and B3 = mixed field agglutination- an example of how it would be graded is: 1+mf
Ax will only react with anti-A,B, and it will have at least a 1+ or 2+ reaction with anti-A, B only
The enzyme responsible for conferring H activity on the red cell membrane is:
L-fucosyl transferase
Anti-D and anti-C are identified in the serum of a woman pregnant with her second child. She is Rh negative. She received RhIG during and after the delivery of her first child, 2 years ago. Tests of the patient, the father of the child and the child revealed that all 3 were negative for the C antigen. What is the most likely explanation for the presence of anti-C?
Anti-G
The phenomenon of a Rh-positive person whose serum contains anti-D is best explained by:
Missing antigen epitopes
Frequencies of ABO
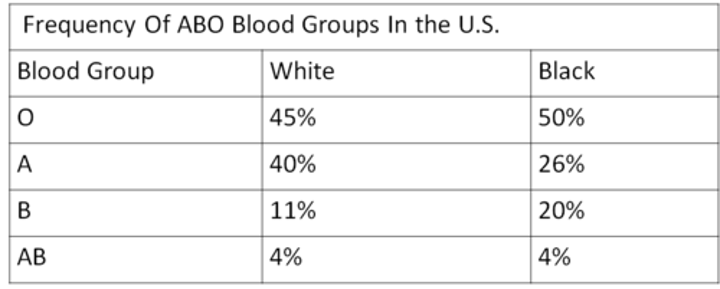
H concentration

Anti-A1 lectin reagent
agglutinates A1 (or A1B) cells but does not agglutinate A2 (or A2B cells)
Dolichos biflorus (Anti-A1)
•agglutinates A1 or A1B
•DOES NOT agglutinate A2 cells
Bandeiraea simplicifolia
agglutinates B cells
Ulex europaeus (Anti-H)
•agglutinates O cells (H specificity) and other ABO blood groups depending on the amount of H antigen available