Microbio Unit 2 Exam
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
what is the structure of DNA?
Double helix composed of nitrogenous bases (A,T,C,G) and a sugar-phosphate backbone
what is the structure of RNA?
a single strand composed of nitrogenic bases (A,U,C,G)
what is the genetic material of bacteria?
DNA
what is the genetic material of archaea?
DNA
what is the genetic material of fungi?
DNA
what is the genetic material of viruses?
RNA or DNA; can be double-stranded RNA, single-stranded RNA, Single-stranded DNA, or double-stranded DNA
what are the 3 processes of DNA replication?
1. initiation
2. elongation
3. termination
what happens during the first step of DNA replication?
initiation; helicase unzips the DNA strands (by breaking down hydrogen bonds). forms 2 different strands (leading and lagging strands) and makes the replication fork.
What happens during the second step of DNA replication?
elongation; DNA polymerase adds DNA nucleotides to the 3′ end of the newly synthesized template strand
What happens during the third step of DNA Replication?
In the third step of DNA replication, DNA ligase seals the gaps between DNA fragments on the lagging strand. These Okazaki fragments are joined to make one continuous strand. This finishes the new DNA molecule.
What enzymes are involved with each step of DNA replication?
inititiation- helicase
elongation- DNA polymerase and primase
termination- ligase (sometimes topoisomerase for relieving DNA twisting).
what is the structure of a codon?
three nucleotides
What 3 codons represent STOP?
UGA
UAA
UAG
which codon represents START?
AUG (to remember- school starts in august)
what base pair bonds with A (in DNA)
T
what base pair bonds with T (in DNA)
A
what base pair bonds with G (in DNA)
C
what base pair bonds with C (in DNA)
G
what base pair bonds with A (in RNA)
U
what base pair bonds with U (in RNA)
A
what base pair bonds with C (in RNA)
G
what base pair bonds with G (in RNA)
C
What types of RNAs are involved in Transcription?
dna → mRNA
What types of RNAs are involved in translation?
ribosome reads mRNA and tRNA transfers it to the right amino acid
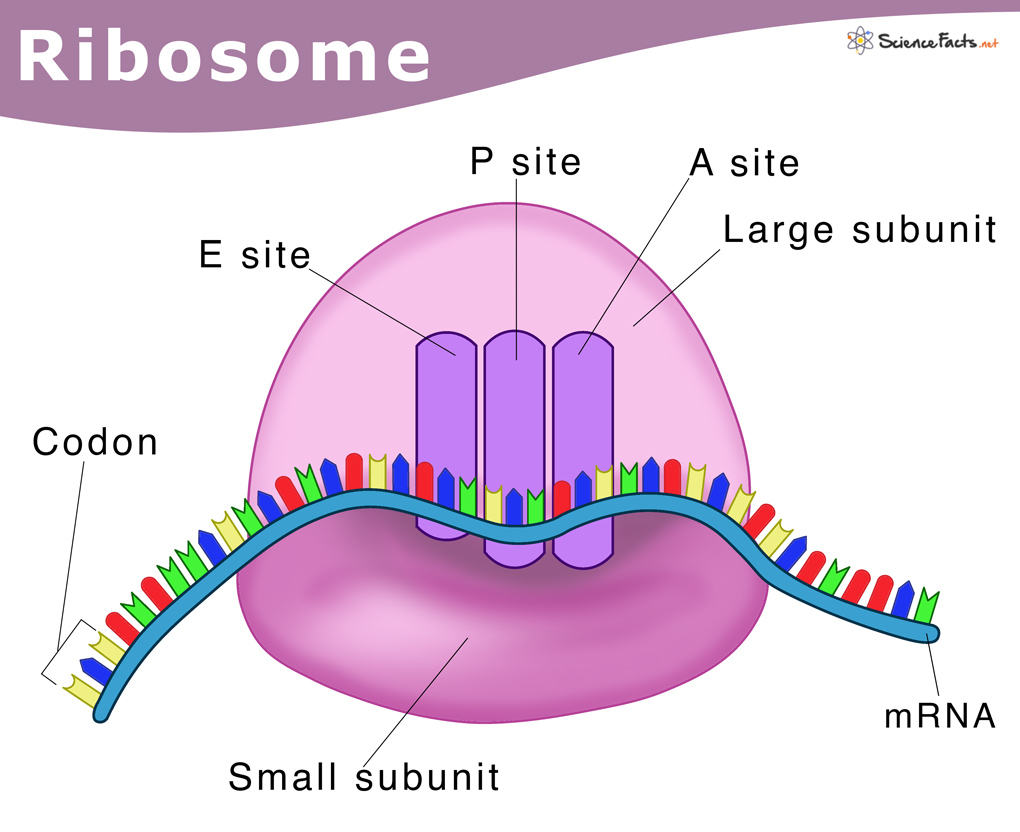
what is the structure of the ribosome?
it is an organelle made up of rRNA and proteins. It has 2 parts: a large subunit and small subunit
what is a genome?
a complete set of genetic information
whats more stable: DNA or RNA?
DNA
what is considered a “fairly large polypeptide”?
a protein
what are the 2 steps of gene expression?
transcription and translation
what are the 2 tasks a cell must accomplish to multiply?
DNA replication
Gene Expression
is replication conservative, semi-conservative or nonconservative?
semi-conservative
what is DNA polymerase responsible for?
building new templates of DNA
what is primase (primers) responsible for?
telling DNA polymerase where to start
what is ligase responsible for?
forms covalent bonds between 2 nucleotides
which end can DNA polymerase add nucleotides to?
the 3’ end
what seals okazaki fragments?
DNA ligase
do bacteria perform mitosis?
no; binary fission
what is also known as the “positive strand”?
the non-template strand
why can DNA initiate without primer?
bc RNA is less stable
what are removed: introns or extrons?
introns
what remain: introns or extrons?
extrons
how many codons are there total?
64
what are the 2 different “branches” of mutations?
spontaneous mutations and induced mutations
what are the different types of mutations?
point mutations (changes 1 base pair)
frameshift mutations (removal or addition of base)
what are the subtypes of mutations within point mutations?
missense mutations
silent mutations
nonsense mutations
what are the subtypes of mutations within frameshift mutations?
insertion (adding extra bases)
deletion (removing base/s)
These shift the reading frame, which changes every amino acid after it.
what are silent mutations?
DNA is mutated but amino acid does not change
what are missense mutations?
the DNA is mutated and the amino acid is changed (but may not change anything in the end)
what are nonsense mutations?
causes a stop codon in the wrong place in the protein
what are the different types of horizontal gene transfer?
transformation, transduction and conjugation
what is the difference between horizontal versus vertical gene transfer?
vertical gene transfer: parent cell → offspring
horizontal gene transfer: genes from environment or neighbors → offspring
what are the different types of viruses?
DNA viruses (can be single stranded or double stranded. e.g. dsDNA is herpesvirus)
RNA viruses (ssRNA or dsRNA. e.g. ssRNA influenza virus)
retroviruses (use reverse transcriptase to turn RNA into DNA. e.g. HIV).
what is the “dogma of molecular biology”?
genetic information flows only in one direction, from DNA → RNA → protein; or RNA directly → protein.
what is the function of reverse transcriptase?
making a strandDNA from an RNA template
who is the discoverer of reverse transcriptase?
Howard M. Temin and David Baltimore
What is the function of PCR?
PCR is used to amplify a specific segment of DNA, making millions of copies quickly.
What is the function of gel electrophoresis?
It separates DNA, RNA, or proteins based on size and charge, allowing scientists to visualize and compare fragments.
What is the function of blotting techniques?
Southern blot detects specific DNA sequences.
Northern blot detects specific RNA sequences.
Western blot detects specific proteins using antibodies.
What is the function of CRISPR-Cas9?
CRISPR-Cas9 is a gene-editing tool that can cut and modify DNA at specific locations.
What is the function of DNA cloning?
used to make identical copies of a DNA segment by inserting it into a plasmid and growing it in bacteria.
How are prokaryotes identified through chemical tests?
using biochemical tests that detect metabolic activities. For example, the catalase test checks if bacteria produce the enzyme catalase. Many tests use pH indicators and are organized in a dichotomous key.
what is phylogeny
the evolutionary history and relationships between groups of organisms
How is phylogeny between prokaryotes determined?
16S rRNA sequence analysis, DNA hybridization, and DNA base ratios (like G+C content).
What basic information should you know about coronaviruses?
are enveloped, single-stranded (+) RNA viruses from the Coronaviridae family. They have spike proteins that look like a crown. their receptor is ACE-2
How do you culture viruses and what happens on a petri plate?
Viruses are grown in living host cells, like bacteria. When viruses lyse bacteria in a soft agar layer, they form clear zones called plaques on the bacterial lawn.
What is the structure of a fungal cell wall and plasma membrane?
The cell wall contains chitin and glucan, and the membrane contains ergosterol instead of cholesterol (like in humans).
What are the groups of fungi and their features?
Ascomycota: Sac fungi; make ascospores, includes yeasts, molds, truffles.
Basidiomycota: Club fungi; make basidiospores, include mushrooms, rusts, and smuts.
Mucromycota: Produce zygospores; includes Rhizopus (bread mold).
What are the groups of protozoa and their features?
Amoebae: form and move with pseudopods; form cysts.
Apicomplexans: Use apical complex to enter host; cause diseases like malaria.
Dinoflagellates: single celled Marine organisms; sometimes photosynthetic, may make toxins like brevetoxin.
What are helminths?
Helminths are parasitic worms. Two main types are:
Roundworms (nematodes)
Flatworms (platyhelminths
what are the different types of flatworms
Tapeworms (cestodes)
Flukes (trematodes)
What is elephantiasis and what causes it?
caused by roundworms that block lymph vessels, leading to swelling in the limbs. The worms come from the Filarioidea family.
What are oomycetes?
not true fungi. They are protists that lack chloroplasts and are not photosynthetic. DNA shows they are closer to brown algae and diatoms.
what are the different types of algae?
diatoms
brown algae
red algae
green algae
What is green algae?
Algae closely related to plants; contain chlorophyll a and b. Some are single-celled, others form colonies like Volvox.
What are red algae?
Can be single or multicellular; contain red pigments like phycoerythrin. Nori, used in sushi, is red algae.
What are brown algae?
Large, multicellular algae like kelp; grow in cold oceans and contain the pigment fucoxanthin.
What are diatoms?
Single-celled algae with silica shells called frustules; common in water and used in diatomaceous earth.
What’s the difference between lytic and lysogenic viruses?
Lytic viruses immediately destroy the host cell to release new viruses.
Lysogenic viruses insert their DNA into the host’s DNA and can stay dormant, later entering the lytic cycle.
What is binomial nomenclature?
the scientific naming system that uses two names: the genus and the species (e.g., Escherichia coli).
What important viral disease has been eradicated globally?
Smallpox is the only viral disease that has been eradicated worldwide through vaccination.
what do topelasiametases do?
relieve tension in growing double helix
true or false:
most mutations are harmless
false
what is the opposite of a mutant?
a wild type
what is the human genome project?
The Human Genome Project was a big science project that mapped all the DNA bases in human cells.
what is transformation of horizontal gene transfer?
DNA taken from the environment
what is transduction of horizontal gene transfer?
DNA moved by a virus
what is conjugation of horizontal gene transfer?
DNA shared through direct contact
What’s the difference between viruses and bacteria?
Viruses can’t live on their own—they need a host. Bacteria are living cells that can survive and grow on their own.
What are the two main types of viral infections?
Acute: Fast and short
Persistent: Long-lasting (chronic or latent)
what kind of microscope do you need to see a virus?
Electron light microscope
what are the three shapes of viruses?
helical, complex, icosahedral
what are the different routes of transmission of viruses?
enteric (fecal-oral route)
respiratory
zoonotic (animal to human)
arboviruses (spread from insects)
sexually transmitted
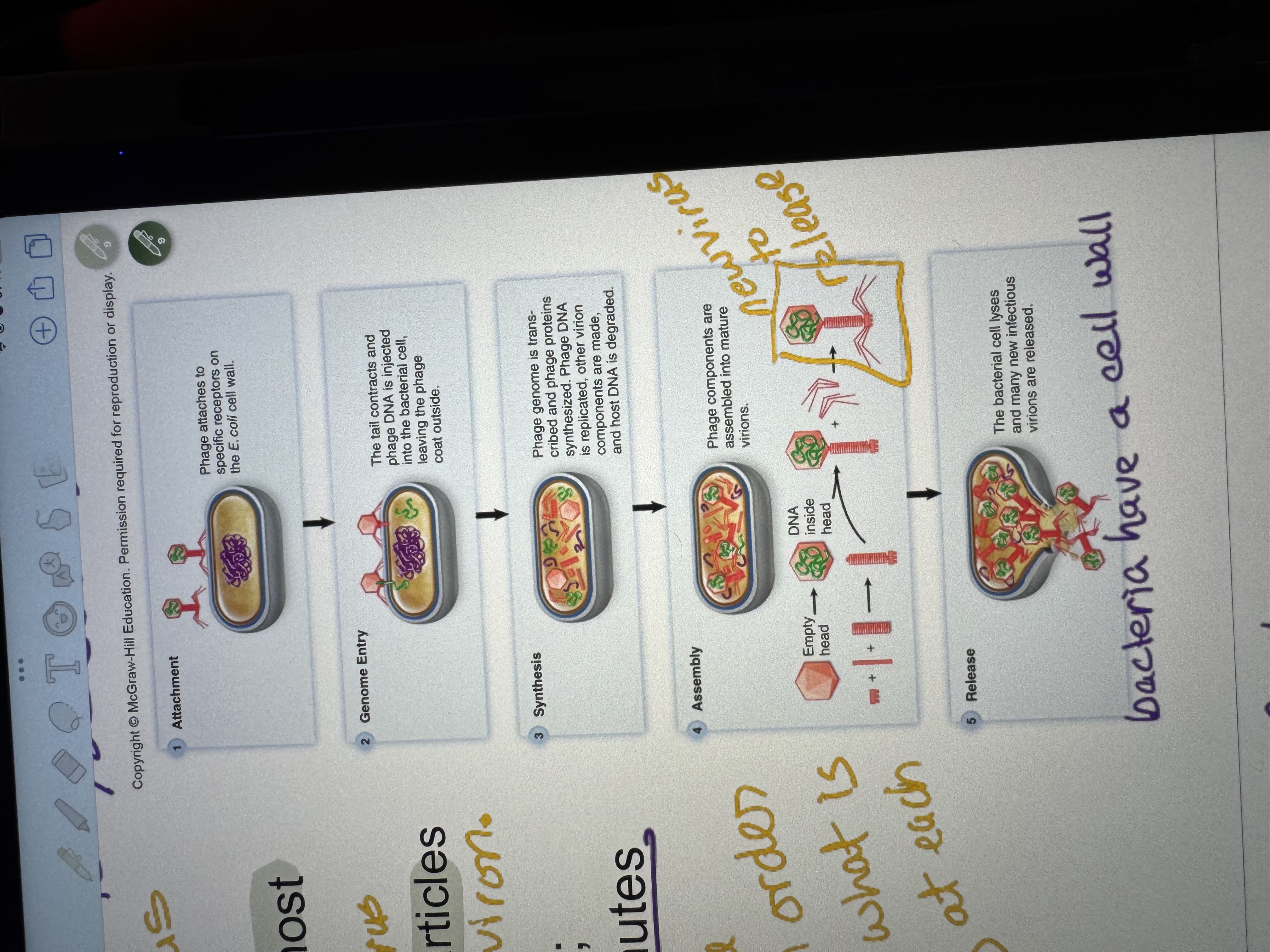
What are the five steps of bacterial infection?
attachment
Genome entry
Synthesis
Assembly
release
what is the vectors of malaria?
mosquitoes
what weapon is found in membrane of the animal cell?
call Astra
what is a visible mass of hyphae in molds called?
mycelium