Business Ownership Types: Sole Proprietorships, Partnerships, and Corporations
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
What are the three major forms of business ownership?
Sole proprietorship, partnership, and corporation.

What is a sole proprietorship?
A business owned, and usually managed, by one person.
What is a partnership?
A legal form of business with two or more owners.
What is a corporation?
A legal entity with authority to act and have liability separate from its owners.
What is a general partnership?
A partnership in which all owners share in operating the business and in assuming liability for the business's debts.
What is a limited partnership?
A partnership with one or more general partners and one or more limited partners.
What is the advantage of being a sole proprietor?
Ease of starting and ending the business.
What is a major disadvantage of sole proprietorships?
Unlimited liability — the responsibility of business owners for all debts of the business.
What are the advantages of partnerships?
More financial resources, shared management, pooled skills, longer survival, and no special taxes.
What is a general partner?
An owner who has unlimited liability and is active in managing the firm.
What is a limited partner?
An owner who invests money in the business but does not have management responsibility or liability for losses beyond the investment.
What is limited liability?
The responsibility of a business's owners for losses only up to the amount they invest.
What is a master limited partnership (MLP)?
A partnership that acts like a corporation but is taxed like a partnership.
What is a limited liability partnership (LLP)?
A partnership that limits partners' risk of losing their personal assets to only their own acts and omissions.
What percentage of businesses are sole proprietorships?
72 percent.
What percentage of total business receipts do corporations earn?
81 percent.
What is the pride of ownership in a sole proprietorship?
The satisfaction derived from owning and managing one's own business.
What challenges do sole proprietors face?
Management difficulties, overwhelming time commitment, and limited growth.
What is the legacy aspect of sole proprietorships?
The ability to leave a legacy through the business one has built.
What are the disadvantages of partnerships?
Unlimited liability and division of profits.
How does a limited liability partnership protect partners?
It limits their risk of losing personal assets to only their own acts and omissions.
What is the role of a limited partner in a limited partnership?
To invest money in the business without management responsibilities.
What is the significance of Peter Cancro in the context of business ownership?
He is the founder of Jersey Mike's Subs, illustrating the journey from employee to successful business owner.
What is a franchise?
A business model that allows individuals to operate a business under the brand and business model of an established company.
What are the opportunities for diversity in franchising?
Franchising can provide pathways for diverse entrepreneurs to enter the business world.
What challenges does global franchising present?
Cultural differences, legal variations, and market entry strategies.
What is a major disadvantage of partnerships?
Unlimited liability.
What is the difference between a limited partner and a general partner?
A general partner has unlimited liability and is involved in management, while a limited partner has limited liability and typically does not manage the business.
What is a conventional (C) corporation?
A state-chartered legal entity with authority to act and have liability separate from its owners (stockholders).
What are alien corporations?
Corporations that do business in the U.S. but are chartered in another country.
What are domestic corporations?
Corporations that do business in the state in which they are chartered.
What are the advantages of corporations?
Limited liability, ability to raise more money for investment, size, perpetual life, ease of ownership change, ease of attracting talented employees, and separation of ownership from management.
What are the disadvantages of corporations?
Initial cost, extensive paperwork, double taxation, two tax returns, size, difficulty of termination, and possible conflict with stockholders and board of directors.
What is a B Corp?
A benefit corporation that aims to do good as well as earn profits, certified by B Lab.
What is an S corporation?
A unique government creation that looks like a corporation but is taxed like sole proprietorships and partnerships.
What are the qualifications for S corporations?
No more than 100 shareholders, shareholders must be individuals or estates who are U.S. citizens or permanent residents, only one class of stock, and no more than 25% of income from passive sources.
What are limited liability companies (LLCs)?
Business structures similar to S corporations but without special eligibility requirements.
What are the advantages of LLCs?
Limited liability, choice of taxation, flexible ownership rules, and flexible distribution of profits and losses.
What are the disadvantages of LLCs?
No stock; ownership is nontransferable, fewer incentives, and more paperwork.
What is the purpose of the board of directors in a corporation?
To elect top officers, set their pay, and oversee management.
What is the significance of Delaware for corporations?
About one-third of all corporations are chartered in Delaware due to its attractive rules for incorporation.
What is a closed (private) corporation?
A corporation with stock held by a few people and not available to the general public.
What is an open (public) corporation?
A corporation that sells stock to the general public.
What is a quasi-public corporation?
A corporation chartered by the government as an approved monopoly to perform services for the general public.
What are professional corporations?
Corporations owned by those who offer professional services.
What are nonprofit corporations?
Corporations that do not seek personal profit for their owners.
What is the role of individuals in incorporating?
Anyone can incorporate, and stock is usually not issued to outsiders, limiting shared advantages and disadvantages.
What are some of America's oldest companies?
Casswell-Massey (1752), The Hartford Courant (1764), Baker's Chocolate (1765), Ames (1774), King Arthur Baking Co (1790).
What is the primary goal of benefit corporations?
To balance profit-making with social and environmental goals.
What are the major advantages of incorporating a business?
Limited liability, easier access to capital, and perpetual existence.
What are the major disadvantages of incorporating a business?
Double taxation, more regulations, and increased administrative costs.
What is the role of stockholders in a corporation?
Stockholders own shares of the company and have voting rights on corporate matters.
Can stockholders be sued if someone is injured by a corporation's product?
Generally, no; stockholders have limited liability and are not personally responsible for corporate debts.
Why are many new businesses choosing a Limited Liability Company (LLC) form of ownership?
LLCs provide limited liability protection and pass-through taxation.
What is a merger?
The result of two firms forming one company.
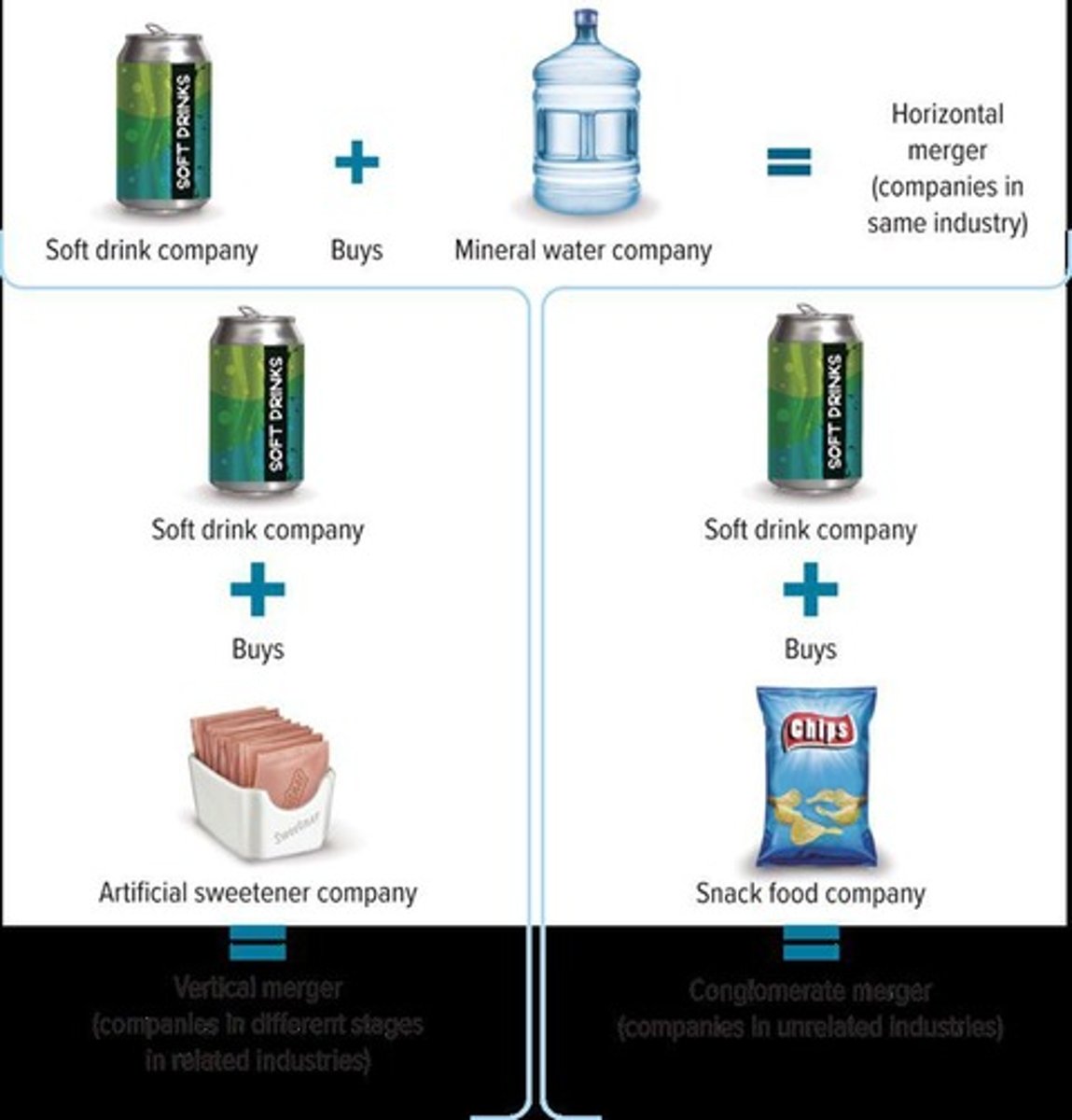
What is an acquisition?
One company's purchase of the property and obligations of another company.
What is a vertical merger?
The joining of two companies in different stages of related businesses.
What is a horizontal merger?
The joining of two firms in the same industry.
What must mergers between competitors prove to the FTC?
That the new combined company does not limit competition unfairly.
What is a conglomerate merger?
The joining of firms in completely unrelated industries.
What is a leveraged buyout (LBO)?
An attempt by employees, management, or private investors to buy out the stockholders in a company.
What is a franchise agreement?
An arrangement where a franchisor sells the rights to use a business name and sell a product or service to franchisees.
What are some advantages of franchising?
Management assistance, nationally recognized name, and lower failure rates.
What are some disadvantages of franchising?
Large start-up costs, shared profits, and management regulation.
What is the significance of diversity in franchising?
Women and minorities are increasingly becoming franchisors and franchise owners.
What is the impact of e-commerce on franchising?
Many brick-and-mortar franchises have expanded online, but conflicts can arise with franchisee-sponsored sites.
What challenges do franchises face when going global?
Adapting products and brand names to different countries while maintaining quality and service.
What is a cooperative (Co-Op)?
A business owned and controlled by the people who use it for mutual gain.
How do cooperatives provide economic power to their members?
By pooling resources and democratically controlling the business.
What are some factors to consider before buying a franchise?
Start-up costs, support from the franchisor, and market demand.
What opportunities exist for starting a global franchise?
Expanding into markets like Canada, China, and the Middle East.