International Finance - Purchasing Power Parity and Real Exchange Rate
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
what is the Purchasing Power Parity
links exchange rates to the prices of goods in different countries
It provides a benchmark for determination of exchange rates
what is the formula of inflation/deflation
pi = Pt-Pt-1 / Pt-1
what is the law of one price
Two products or services should have the same price in two different markets if
They are identical
There are no transaction costs
There are no trade restrictions
A primary principle of competitive markets is that prices will equalize across markets if frictions (transportation costs) do not exist.
ex.: is it really good to go to Greece for cheaper haircut (transportation costs)
So in reality this law does not hold due to tarrifs, transaction costs, non-competitive markets, borders etc...
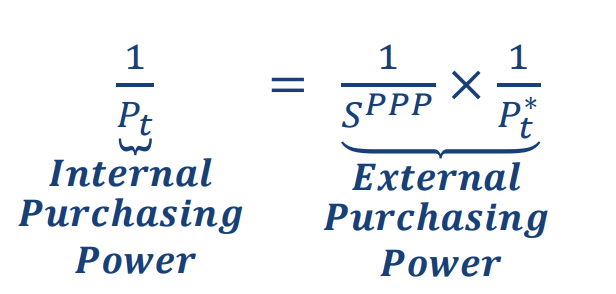
what is the internal purchasing power
The amount of goods and services that can be purchased with USD 1 in the U.S.
1/Pt
what is the external purchasing power
The amount of goods and services that can be purchased with USD 1 outside the U.S
1/St x 1/Pt*
what is the absolute purchasing power parity
external = internal
→Arbitrage is possible only if the exchange rate does not adjust
When its external purchasing power exceeds its internal purchasing power
Overvalued
→Currency must weaken (depreciate)
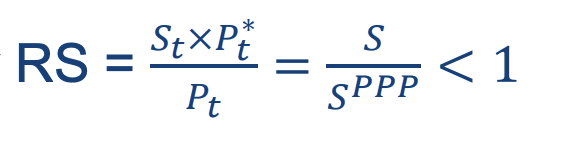
When its external purchasing power is less than its internal purchasing power (RS formula)
Undervalued
→Currency must strengthen (appreciate)
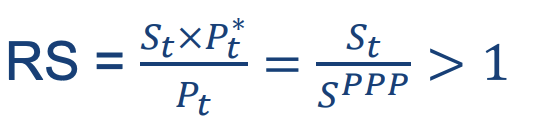
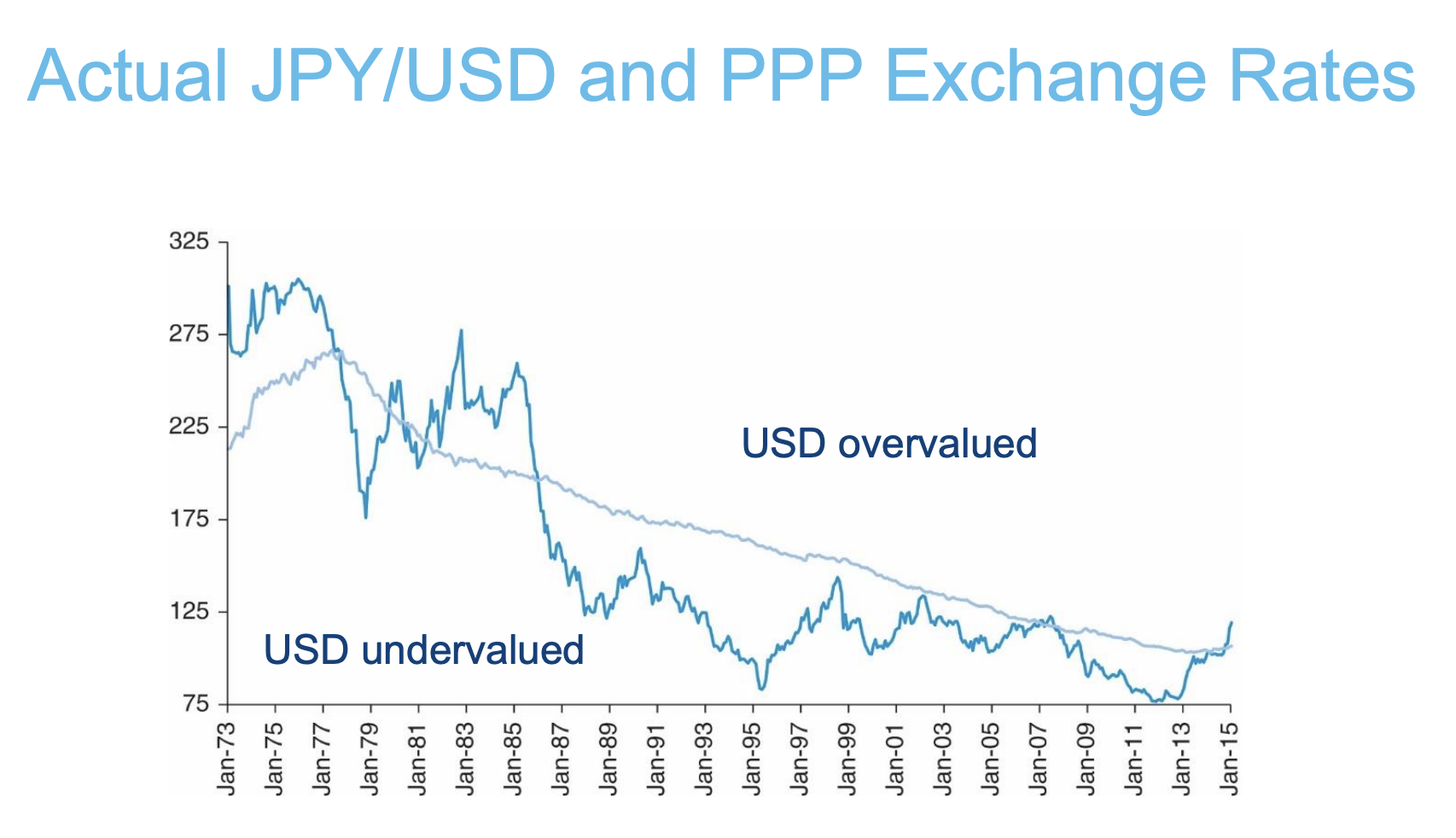
overvalued or undervalued above/below PPP line JPY/USD
overvalued or undervalued above/below PPP line USD/GBP
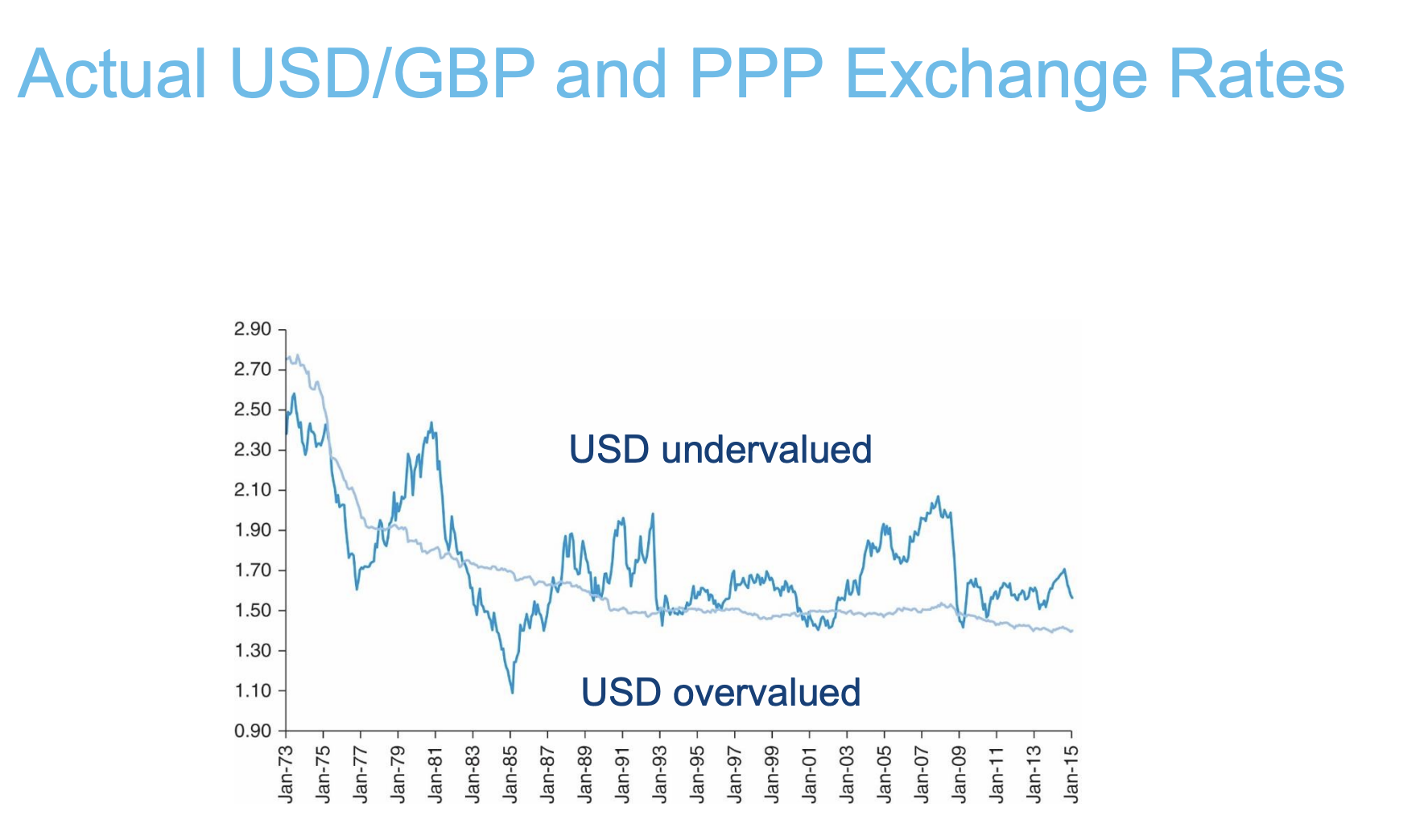
what is the relative purchasing power parity
takes market imperfections into account
says that exchange rates change over time to offset differences in inflation between two countries.
We can use the relative purchasing power parity to determine the future predicted value of the spot exchange rate (formula)
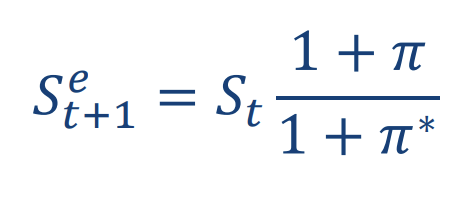
what is the percentage change in RS
If 𝒓𝒔 > 𝟎, the real exchange rate increases: we have a real appreciation of the foreign currency, and a real depreciation of the home currency
If 𝒓𝒔 < 𝟎, the real exchange rate decreases: we have a real depreciation of the foreign currency, and a real appreciation of the home currency
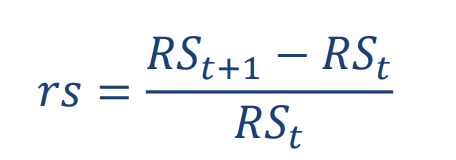
what is the real rate of interest (Fisher)
is the difference between the nominal rate of interest and the expected rate of inflation.
i(t) = re +pie