M3 - U3 - S7 - Scanners and Cameras
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Scanner - Digital File - Flatbed Scanner - Ambient Light - Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp (CCFL) - Charged Coupled Device (CCD) Array - Pixels - Proportion - Light Intensity - Resolution - Pixels Per Inch (PPI) - Sheet-fed Scanner - Windows Image Acquisition (WIA) Software - Optical Character Recognition (OCR) Software - Digital Camera - Flash Memory Card
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Scanner
Imaging device
Creates a digital file from a page of print, photo, or another object
Typically handles flat objects
Flatbed Scanner
Sheet-fed Scanner
The 2 types of scanner in ITF+
Flatbed Scanner
Works like a photocopier
Object is placed on glass faceplate and cover is closed
Prevents ambient light affecting image
Flatbed Scanner Mechanics
Bright light usually from a Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp (CCFL), illuminates the object
The image is recorded using a Charge Coupled Device (CCD) array
Charged coupled device (CCD)
Composed of picture elements (pixels) that generate an electrical charge in proportion to the intensity of light shined on them
Records the image whilst CCFL is shining on it
This is used to create a digital image
Scanner Quality
Determined by resolution (number of pixels) in the CCD array
Measured in Pixels per Inch (PPI)
Sheet-fed Scanner
Alternative to flatbed scanner
Only handle fairly thin paper objects

TWAIN
Older
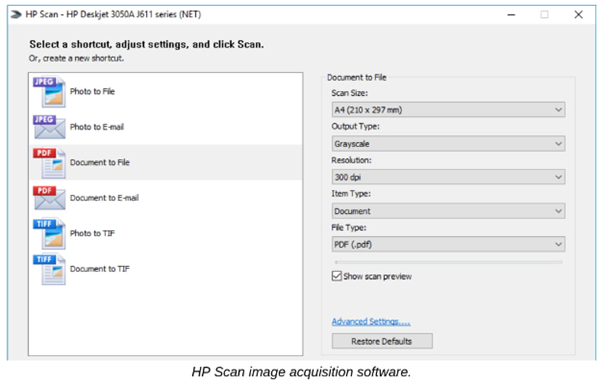
Windows Image Acquisition (WIA) Software
Presents options for image output format + tools for correcting image
The 2 types of scan acquisition software (ITF+)
Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
Software that converts text images into a computer-editable text document
Digital Camera
Stores images on flash memory based card
E.g. CompactFlash or SecureDigital
Can transfer images via:
USB | Memory Card Slot | Wi-Fi