pda 4.1: serotonin receptors and migraine
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
what is serotonin derived from?
tryptophan
what are the effects of serotonin in the periphery?
- induced blood platelets aggregation
- stimulates GI smooth muscle movement
- stimulates pain and itch sensory nerve endings
- induce contraction of vascular smooth muscle, except in skeletal muscle and the heart
what can serotonin be converted into?
melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine)
where are cell bodies serotonin neurons found in the brain?
midbrain raphe nucleus
what is serotonin important for in the CNS?
- sleep/arousal
- mood, emotion
- appetite
- body temperature
what are the serotonin drugs are used to treat migraines?
- sumatriptan and related triptans
- lasmiditan
what are the signaling effects of serotonin drugs that treat migraine?
Gi/o and dec cAMP
what site do serotonin drugs that treat migraine act on?
the 5HT 1B/1D receptors on the nerve terminals in the brain
how do the serotonin drugs that treat migraines work?
they are agonists at the 5HT 1B/1D receptors and inhibit the synthesis and release of serotonin
migraine
recurrent headache (usually unilateral, pulsatile) often associated with nausea and sensitivity to light or sound
what is the ratio of migraines affecting men vs women?
15% of women
5% of men
when do migraines start and when do they peak?
start in teens, peak in 35-39 years
what are the duration of migraines?
4-72 hours (typically all day)
what are the potential triggers of migraines?
- stress, emotional upset
- hormonal changes
- sleep disturbances
- foods
- alcohol, smoke, allergens
- weather
- bright lights
- odors
- temperature changes
what are the two versions of migraines?
- common (w/o aura)
- classic (aura)
what are symptoms of migraines?
- confusion
- irritability
- phonophobia (sound sensitivity)
- photophobia (light sensitivity)
- vomiting, nausea
- speaks soft
- severe throbbing headache (unilateral at first, may spread to the opposite side)
what causes migraine aura?
cortical spreading depression (CSD)
what is CSD?
neuronal and glial activation followed by the depression of neuronal firing
what is CSD associated with?
commensurate changes in blood flow
what is migraine pain caused by?
activation of trigeminal system
what are trigeminovascular system modulated by?
input from dorsal raphe and locus coeruleus
what does activation of cells in the trigeminal nucleus result in?
release of vasoactive neuropeptides, particularly calcitonin gene-related peptide (likely accounts for throbbing pain)
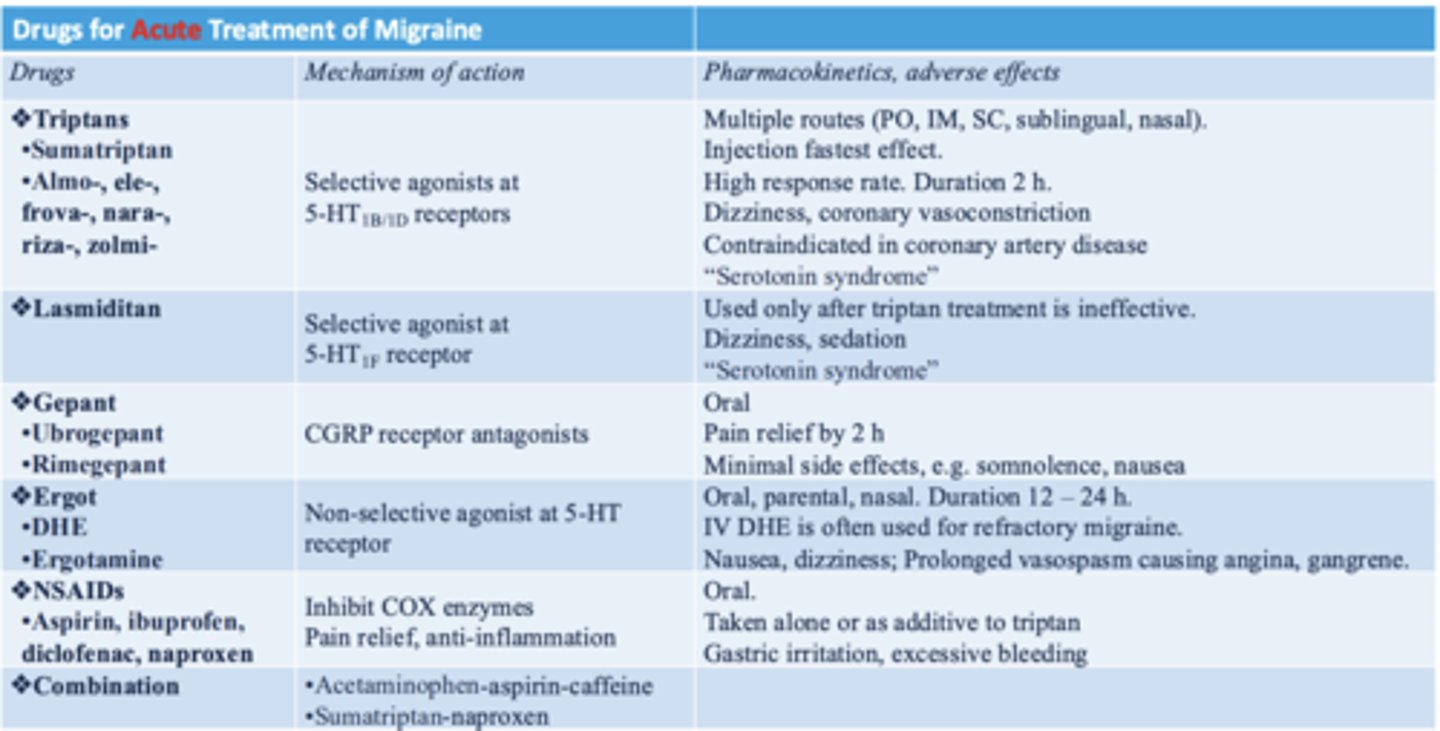
what are the drugs for acute treatment of mild to moderate migraine?
- naproxen/APAP
- caffeine
- metoclopramide
what are the effects of naproxen and acetaminophen?
analgesic and anti inflammatory affect
what are naproxen and APAP used to prevent?
avoid rebound headaches
what are the benefits of caffeine in migraines?
- cerebral vasoconstriction
- potentiate analgesics
- adjuvant with other anti migraine drugs
what are the effects of metoclopramide?
adjunctive therapy that is an antagonist at the D2 receptors in the CNS and periphery
what is metoclopramide used for in migraines?
used as antiemetic and enhances gastric emptying due to effects of vomiting center and GI tract
what are the drugs used for the acute treatment of severe migraines?
- triptans
- ergots
- lasmiditan
- CGRP receptor blocker
what drug that is used to treat severe migraines is controlled?
lasmiditan (has euphoric effects)
egots
non selective 5HT recpetor agonists
what are examples of ergots?
- ergotamine
- dihydroergotamine (DHE)
lasmiditan
5HT 1F receptor agonist indicated for acute treatment of migraine with or without aura (not prevention)
what are the CGRP receptor blockers?
- ubrogepant
- rimegepant
how do CGRP receptor blockers work?
COME BACK
what is the first line of treatment for migraines?
triptans
what are the routes of triptans?
- PO
- IM
- subq
- sublingual
- nasal
what is the onset of action of triptans?
- 5 mins with injection
- 10-15 mins with nasal/sublingual
- 20-40 mins with oral
which form of triptans have the fastest acting response rate?
injectable sumatriptan
what triptan dosage form is effective in children?
sprays
what is the best form of combo therapy that is more effective than either drug alone?
sumatriptan + naproxen
what are the adverse effects of triptans?
minimal adverse effects but major issue is coronary artery vasoconstriction
who should avoid use of triptans?
patients with coronary artery disease
what could use of triptans induce?
serotonin syndrome
what puts a patient at the greatest risk for developing serotonin syndrome when using triptan drugs?
- MAOIs
- SSRIs/SNRIs
- herbal supplements (st. john's wort)
- other agents that increase serotonin neurotransmission
what are the symptoms of serotonin syndrome?
- agitation, hallucination coma
- autonomic instability (tachycardia, labile blood pressure, hyperthermia)
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
- muscle hyperreflexia, incoordination
what are side effects of lasmiditan?
- dizziness, fatigue
- paresthesia (skin tingling, itching, burning)
- sedation
- driving impairment
- serotonin syndrome
- euphoria and hallucination (1% of patients)
what is the mechanism of ergots for treating migraine?
- cerebral vasoconstrictors
- non-selective 5HT receptor agonist working at trigeminal nerves
what is the new formulation of ergots?
a nasal spray formulation of DHE
what are the side effects of ergots?
- nausea
- dizziness
- cramps
- vertigo
- prolonged vasospasm causing angina, gangrene
when can ergotamine dependence be seen in patients?
use >3/week
what are the contraindications for ergot usage?
- pregnancy
- sepsis
- vascular diseases
what are the drug interactions with ergots?
- triptans
- beta blockers
- nicotine
ergotism (st. anthtony's fire)
when grains are contaminated with ergot fungus and experience hallucination, vasospasm, and stimulation of uterine smooth muscle
what is the main reason ergots are contraindicated in pregnancy?
ergots induce smooth muscle contraction in the uterus and could induce abortion
what are the CGRP's used for acute treatment of migraines?
- ubrogepant
- rimegepant
- zavegepant
what are the CGRP's used to prevent migraines?
- atogepant
- erenumab
- galcanezumab
- fremanezumab
- eptinezumab
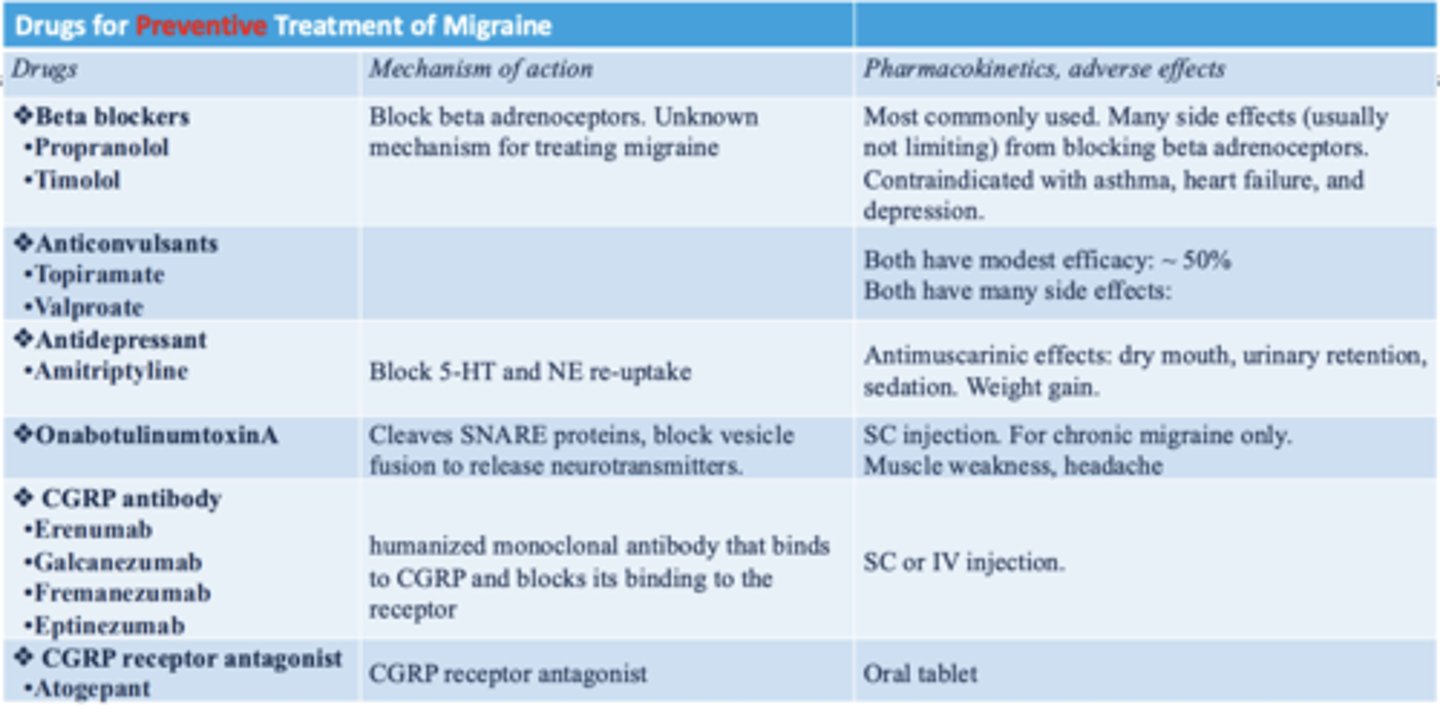
prophylactic migraine therapy
preventative migraine therapy
what does prophylactic migraine therapy work best with?
mild to moderate especially when predictable in classic migraine
what is the MOA of prophylactic migraine therapy?
elevate CSD threshold and suppress CSD
what are the primary prophylactic migraine therapies?
- beta blockers
- anticonvulsants
what are examples of beta blockers used to prevent migraines?
- propranolol
- timolol
what are examples of anticonvulsants used to prevent migraine?
- valproate
- topiramate
what are other preventative migraine therapies that is not a beta blocker or anticonvulsant?
- monoclonal antibodies targeting CGRP
- atogepant (CGRP receptor antagonist)
- antidepressant
- onabotulinumtoxinA (botox)
summary of acute treatment of migraine
know her well
summary of preventative treatment of migraine
know her well too