Lecture Test 1
1/134
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
Geology
study of the planet earth and the materials of which it is made, and processes that act on these materials, the products formed, and history of the planet
Uniformitarinism
fundamental principle of modern geology
Theory of Plate Tectonics (Internal)
Lithosphere: broken into plate that move relative to each other sliding on the underlying asthenosphere
Diverging boundaries and mid-oceanic ridges
Transform boundary
converging boundary and subduction zones
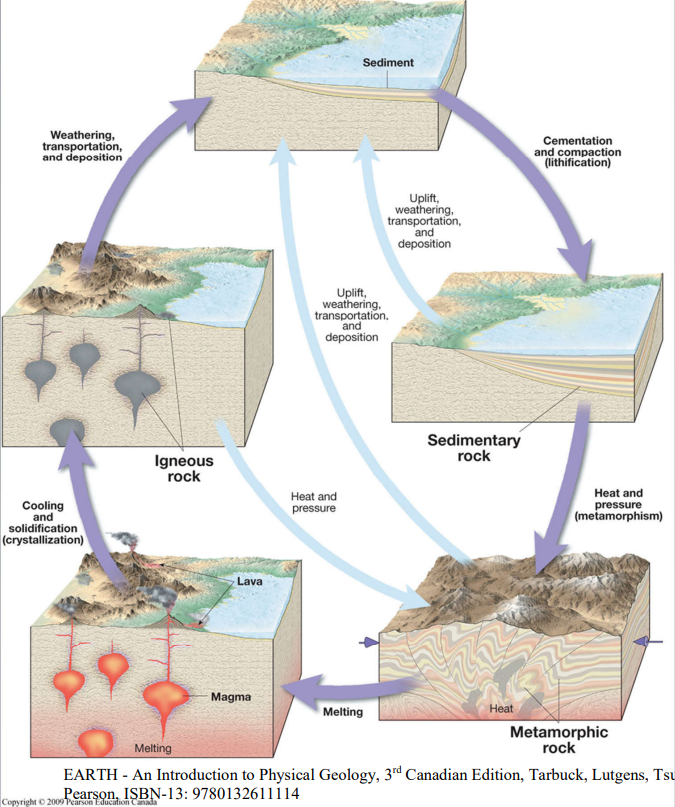
made up of igneous and metamorphic rock
Image: Rock Cycle
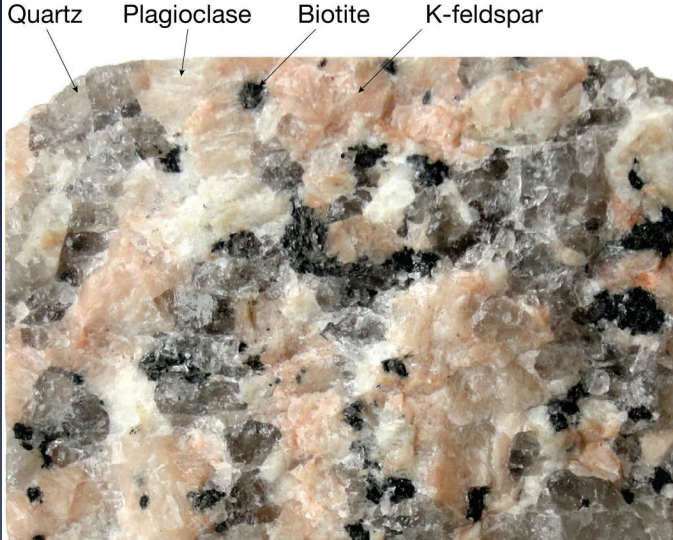
Minerals (main characteristics)
crystalline solid
occur naturally
inorganic
definite chemical composition
Crystalline substance
atoms arranged in regular repeating order
cleavage
property of mineral that allows it to break smoothly along specific internal planes when the mineral is struck
flake cleavage
fragments into very even flat flakes (perimeter of each flake is irregular)
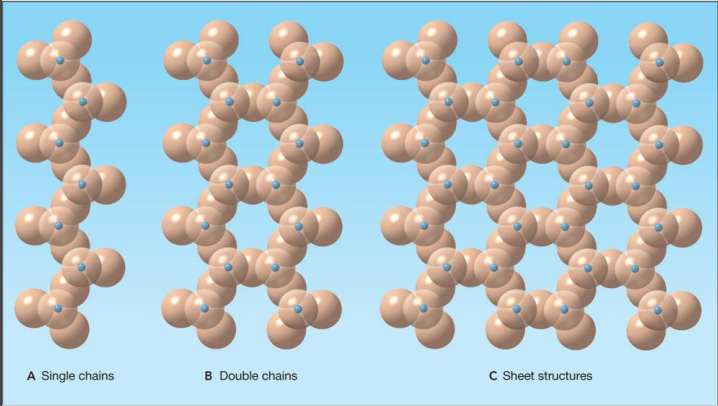
single chain… shares
single oxygen/silica
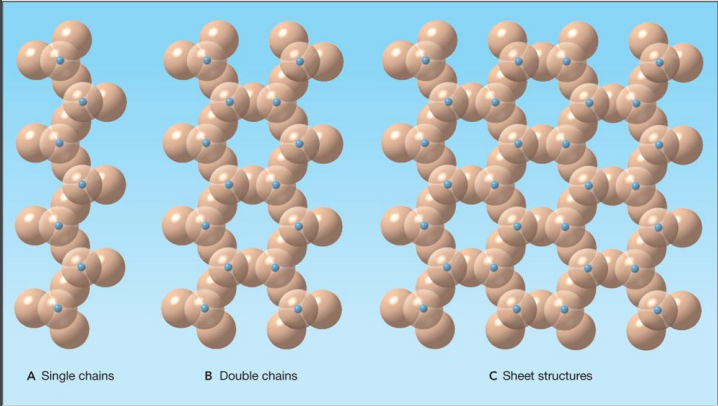
double chain… shares
two oxygen/silica
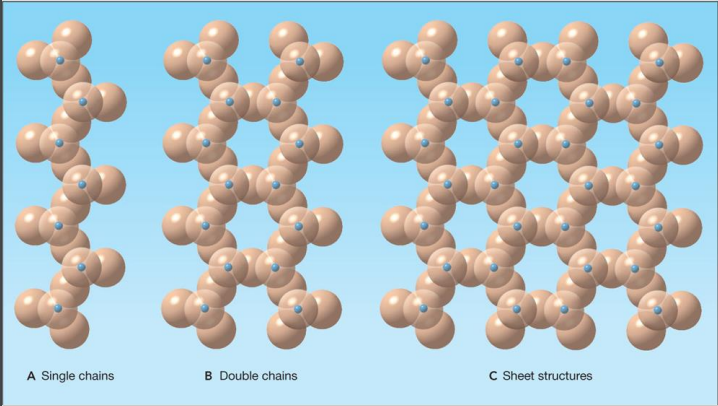
sheet structure… shares
more then two oxygen/silica
Important mineral groups:
What is in the FELDSPAR GROUP
plagioclase (Ca and Na Al silicate)
Orthoclase (K Al silicate)
Important mineral groups:
What is in the PYROXENE GROUP
Augite (Ca, Mg, Fe, Al silicate)
Important mineral groups:
What is in the AMPHIBOLE GROUP
Hornblende (Ca, NA, Mg, Fe, Al silicate)
Important mineral groups:
What is in the QUARTZ
SiO2
Important mineral groups:
What is in the MICA GROUP
Muscovite (K, Al silicate)
Biotite (K, Mg, Fe, Al silicate)
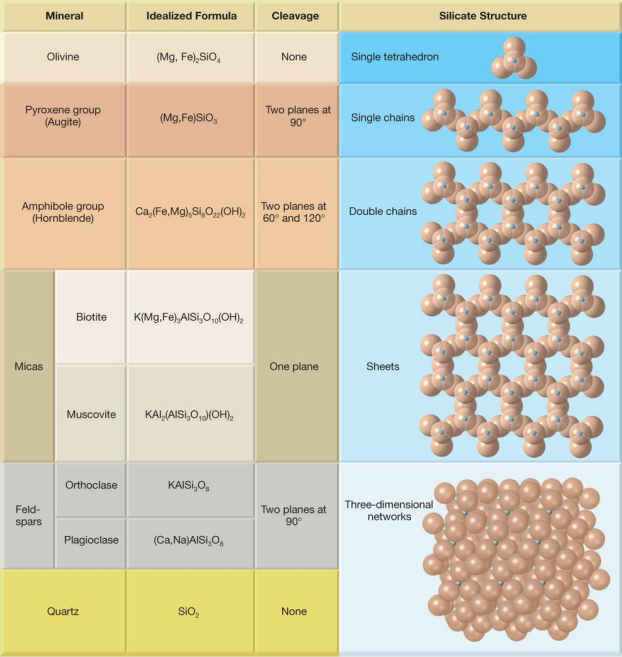
Image: Common Silicate Minerals
Minor Percentage of earths crust:
Complex Al silicate hydroxides with excess negative charge within the layer which is balanced by exchangeable cations… is what group
clay mineral group
Minor Percentage of earths crust:
ex:
calcite (CaCO3)
Dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2)
is what group:
Carbonate group
Minor Percentage of earths crust:
ex:
Gypsum CaSO4 2H2O
is what group..
Sulphate group
Minerals of Commercial Value:
Native metal group
give example…
Au
Cu
C (diamond)
Minerals of Commercial Value:
Oxide group
give example…
Chalcopyrite CuFeS2
Sphalerite ZnS
Galena Pbs
Minerals of Commercial Value:
Phosphate group
give example…
Ca F phosphate
Minerals of Commercial Value:
Halide group
give example…
NaCl
What are physical properties of minerals?
colour & streak
specific gravity
effervescence
hardness
lustre
tenacity
transparency
crystal form
odor
cleavage
magnetism
taste
What are the effects of weathering of minerals
durability issues
environmental (acid mine drainage)

Weathering and soil section
Pyrite oxidation produces sulfuric acid, limonite (yellow/brown). Acids react with calcium carbonates to produce gypsum whose crystallization will cause backfill to swell, stone/concrete to crack/burst.
SLOW PROCESS (10yrs)
MINING - ONTARIO’S ‘RING OF FIRE’
Key points:
2002 DaBeers went into Hudson’s Bay looking for precious stones
discovered copper and zinc instead
2008 they found what was a first time commercial quantity of chromite in North America
Rock
a consolidated aggregate of one or more minerals
Igneous Rocks
crystallized from an entirely or largely molten material (magma)
Sedimentary Rocks (describe three ways they could be formed)
Rock formed from
lithification of any type of sediment
precipitation from solution
consolidation of the remains of plants or animals
Metamorphic Rocks (describe how they form)
Formed from pre-existing rocks into a texturally or mineralogically distinct new rock as a result of high temperature, high pressure, or both, but without significant melting
No melting
Igneous Rocks:
what did they originate from
molten material mainly in the upper mantle
magma if below the earth’s surface
lava if extruded above earth’s surface
What are igneous rocks classified based on
Composition and
texture:
grain size is the most important textural characteristic

Igneous Rocks:
Texture:
explain fine grained (aphanitic)
Mineral grains <1mm
Volcanic or extrusive rocks (cool quickly); intrusive rocks that cooled quickly
Glassy texture (obsidian)

Igneous Rocks:
Texture:
explain coarse grained (phaneritic)
Mineral grains >1mm
Plutonic Rocks (intrusive, cooled slowly)
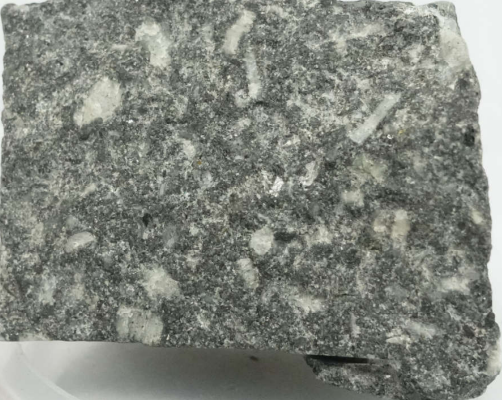

Igneous Rocks:
Texture:
explain Porphyritic
extrusive rock in which large crystals are enclosed in a matrix of fine grained minerals or obsidian
two episodes of crystallization
large crystals are called phenocrysts

Igneous Rocks:
Texture:
explain Pegmatitic
crystals are very large (cm-m)
form during the last stages of granitic magma solidification

Igneous Rocks:
Texture:
explain Pyroclastic
welded fragments from eruption
tuff (fine grained)
volcanic breccia (larger pieces of volcanic rock)

MARS ROVER IMAGE
bomb sag preserved in layered rocks on the lower slopes of Home Plate
Bomb sags form in volcanic explosions on Earth when rocks ejected skyward by the explosion fall into soft deposits, deforming them as they land
Igneous Rocks:
Composition:
explain Felsic
give examples
igneous rock having abundant light coloured minerals
ex:
quartz
k-feldspar
muscovite
plagioclase (sodium)
Igneous Rocks:
Composition:
explain Mafic
give example
igneous rock having abundant dark coloured of ferromagnesium minerals
ex:
biotite
amphibole
pyroxene
olivine
plagioclase (calcium)
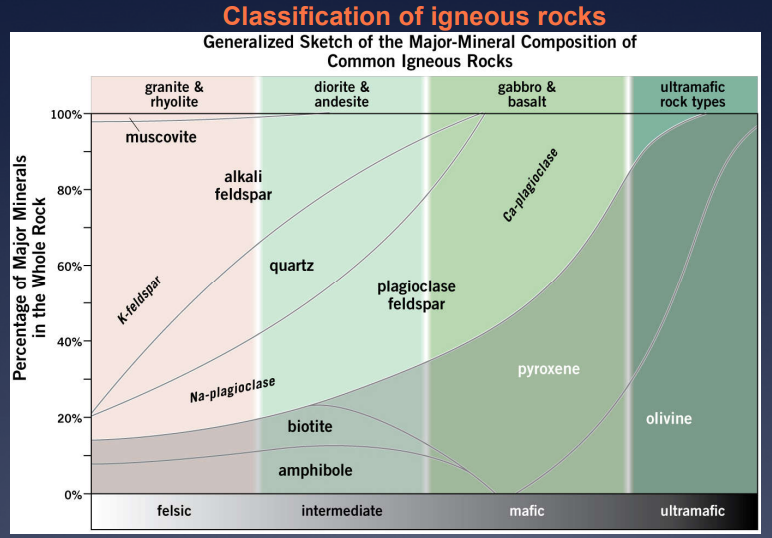
Image: Classification of igneous rocks (textbook)
Image: Classification of igneous rocks (lab manual)
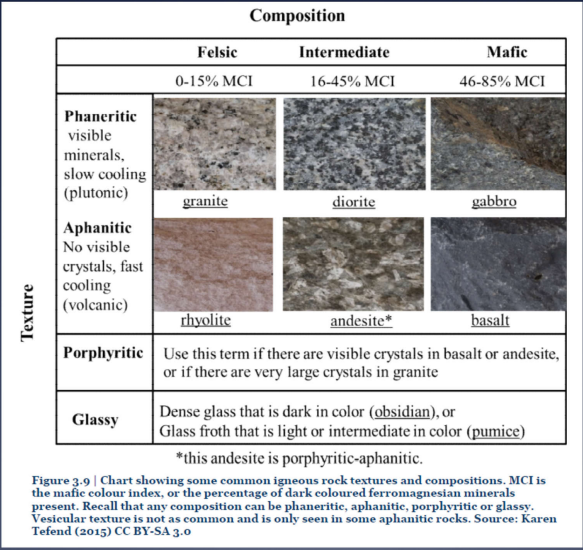
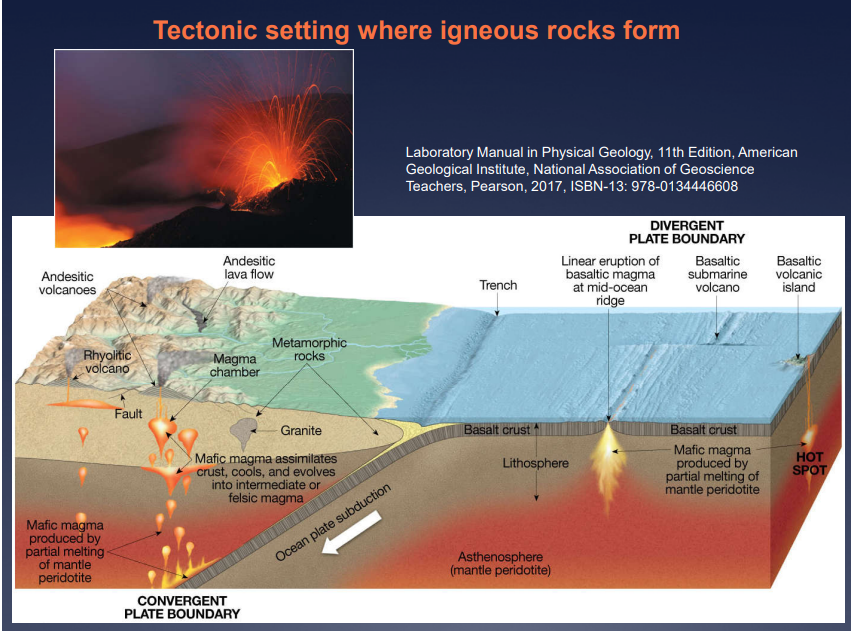
Image: How igneous rock form
Name one of the largest valcanoes extending from B.C. to N. Calif
Mount St. Helenes
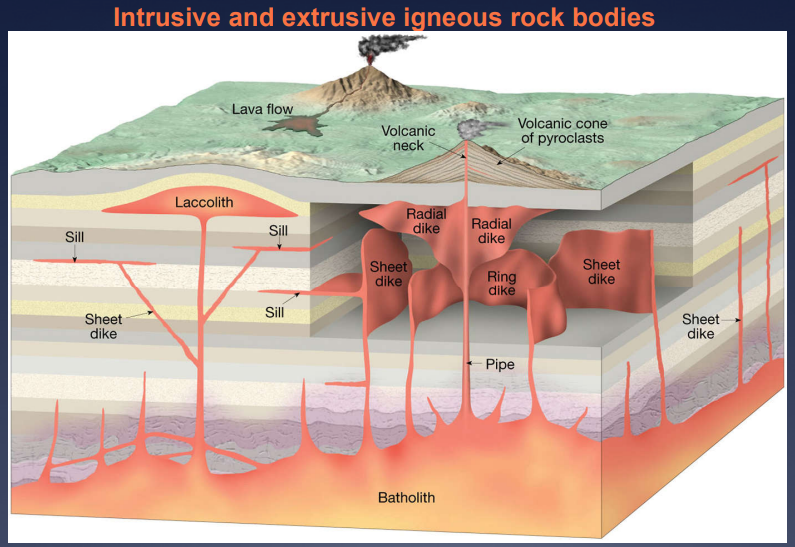
Image: Intrusive and extrusive igneous rock bodies
Image: Tectonic setting where igneous rocks form

INDONESIAN VOLCANO ERUPTS, LEAVING AT LEAST 13 DEAD
mount semeru on the indonesian island of Java erupted
many people had burns, dozen dead, hundreads displaced
flow of hot gas clouds had stopped amid rain on sunday, by urged caution
breathing in polluted air is dangerous
authorities asked citizens to put off returning to several areas
127 active volvanoes in indonesia
indonesia is on the the ring of fire where a series of tectonic fault lines around the pacific that produce frequent earthquakes and eruptions
eruptions at mount semeru have been recorded since 1818 with a spike in activity in 2000s
Deadliest erruptions three were in indonesia
krakatau in 1883 (caused a tsunami and killed 26 000)
tambora in 1815 (killed 92 000)
kelut in 1586 (killing 10 000)
what are the two factors that determine the degree of violence or explosiveness of an eruption
amount of gas in the lava or magma
the viscosity of the lava that determines the ease with which the gas escapes to the atmosphere
Acidic Magma (felsic)
very viscous and explosive
Basaltic Magma
low viscosity and less explosive
What is the composition of volcanic gas
water vapour + SO2, H2O, CO2, HCl
Volcanic Hazards
lava and pyroclastic flows, mudflows, ash eruptions
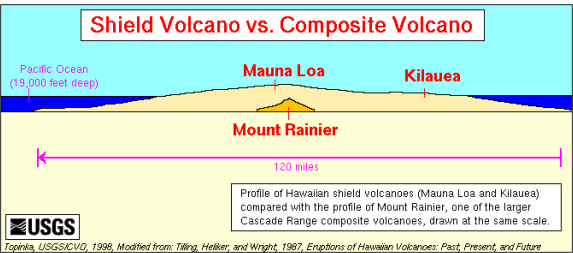
Types of Volcanoes
describe a Shield volcanoe
give an example of where it is found
broad, gently sloping cones (2-10) constructed of solidified lava flows
lava of low viscosity (basaltic)
found in hawaii islands

Types of Volcanoes
describe a Cinder Cones
constructed of pyroclastic ejected from a central vent
slopes of approx. 30
much smaller than shield volcanoes
Types of Volcanoes
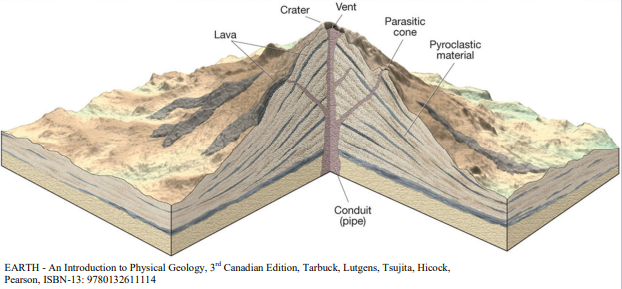
describe a Composite Volcano
give example
constructed of alternating layers of pyroclastic and rock solidification from lava flows
intermediate slopes, built over long periods of time and becomes very large
mainly andesite
ex: mount st helens

ST HELENS
in spring of 1980 a series of ash emissions blackened the peak and the north slope had developed a prominent bulge
the current summit is a point along the crater rim
crater is 2000 ft deep and mile wide
may 18 1980 was the eruptions.
Igneous Intrusions:
define Discordant Intrusion
not parallel to any layering in the country rock
Igneous Intrusions:
define Concordant Intrusion
parallel to any layering in the country rock
Igneous Intrusions:
define Volcanic Neck
magma solidified within the throat of volcano
Igneous Intrusions:
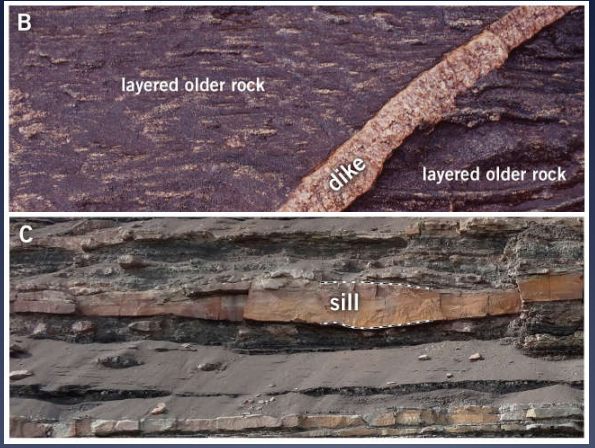
define Dike
tabular discordant intrusive structure
Igneous Intrusions:
define Sill
tabular concordant intrusive structure
Igneous Intrusions:
define Stock
small discordant pluton (body of igneous rock that crystallized at considerable depth) with outcrop area of <100km²
Igneous Intrusions:
define Batholith
a large discordant pluton (>100km²); formed of numerous, coalesced plutons called diapirs
DARK AND LIGHT COLOURED SILLS
A: the dark coloured rock layer in this photo is a sill made of gabbro
in upper Brock River Canyon

DARK AND LIGHT COLOURED SILLS
B: dark mafic sill in mountains made of lighter coloured sedimentary rock
dry valleys area of antarctica

LIGHT AND DARK - COLOURED DYKES
A: dykes of felsic composition cut through dark-coloured mafic volcanic rocks
near Lakelse, BC

LIGHT AND DARK - COLOURED DYKES
B: Dark-coloured dyke of mafic composition cuts through ligh-coloured granitic rocks
north of sudbury

Igneous Activity and Plate Tectonics
what is Mid-oceanic ridge
diverging plate boundary
basaltic magma erupts and forms pillow basalts and oceanic crust
Igneous Activity and Plate Tectonics
what is Intraplate Activity
give example
plate overrides a hot mantle plume
where the plates move and are most likely to cause earthquakes and erruptions
ex: hawaiian volcanism (oceanic plate)
Igneous Activity and Plate Tectonics
what is Converging boundaries
intermediate and felsic magma
an area on Earth where two or more lithospheric plates collide
Metamorphism
the solid state (without melting) transformation of pre-existing rock into texturally or mineralogically distinct new rock as a result of high temperature, high pressure
Name the two main types of metamorphism
Regional and Contact
List the main factors controlling the characteristics of metamorphic rocks
composition of parent rock
temperature and pressure during metamorphism
tectonic forces
effects of fluids (ex. water)
METAMORPHIC EVIRONMENT
illustration showing geothermal gradient and its role in metamorphism
geothermal gradient is lowered by the subduction of comparatively cool oceanic lithosphere
thermal heating is evident where magma intrudes the upper crust
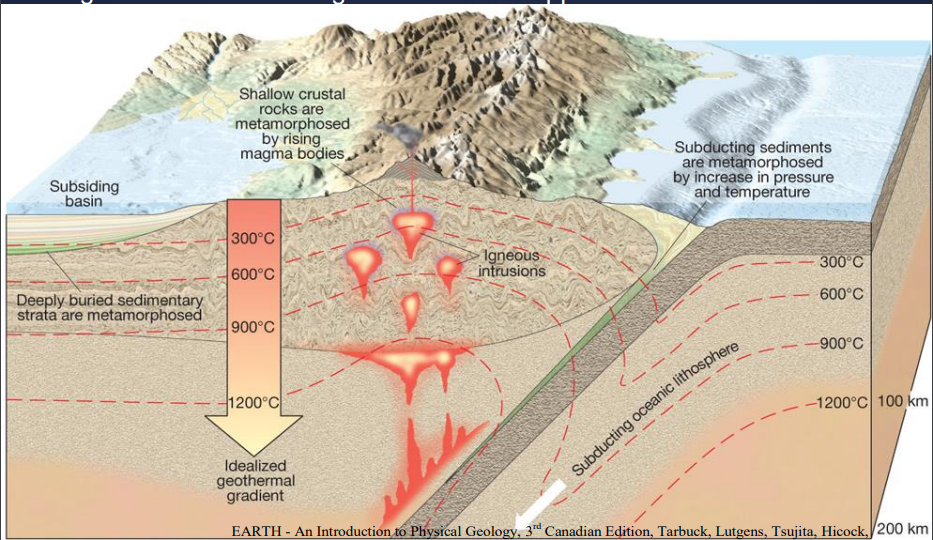
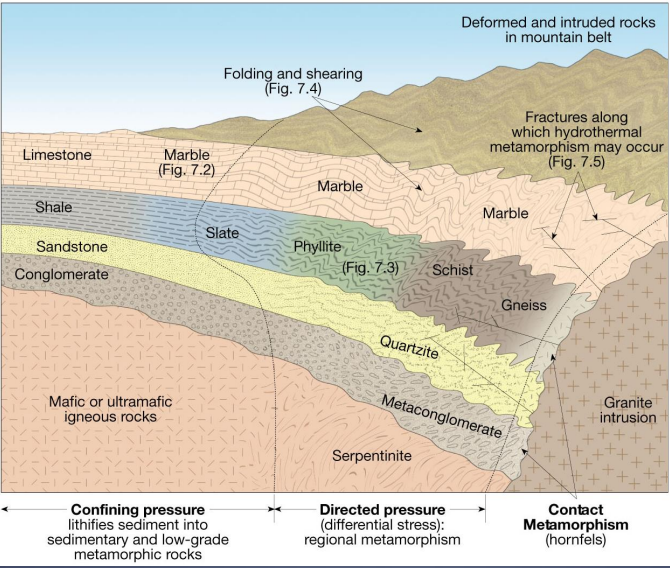
Image: Metamorphism by heat, pressure, and hydrothermal fluids
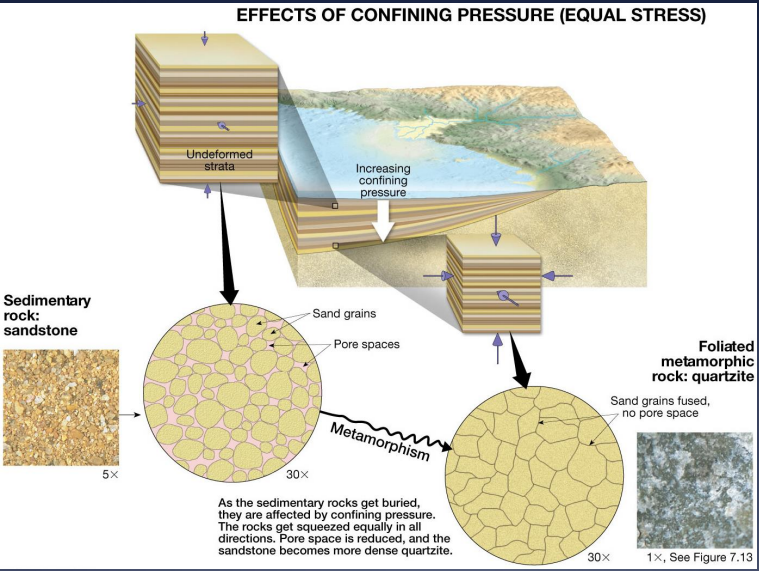
Image: When rocks get buried they experience confining pressure that is equal in all direction
rock becomes more dense and remain non foliated
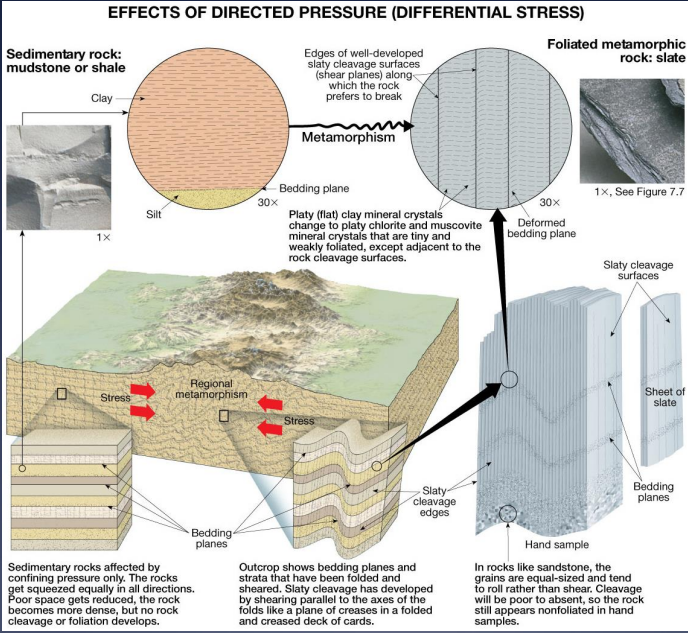
Regional Metamorphism
what is the result of high temperatures and pressure
list four reasons
foliation (parallel alignment of the textural and structural features of a rock)
new compact minerals
recrystallization
plastic flow contorts layers and other constituents (pebbles)
Image: in places like convergent plate boundaries rocks experience differential stress
they may have fracture or fold and develop rock cleavage and foliation of platy minerals
Contact Metamorphism
what is the dominant factor with relatively low confining pressures (<10 km burial depth)
High temperatures
Metasomatism
change in the composition of a rock as a result of the introduction or removal of chemical constituents.
Hydrothermal rocks
rocks formed by precipitation of ions derived from hydrothermal solutions
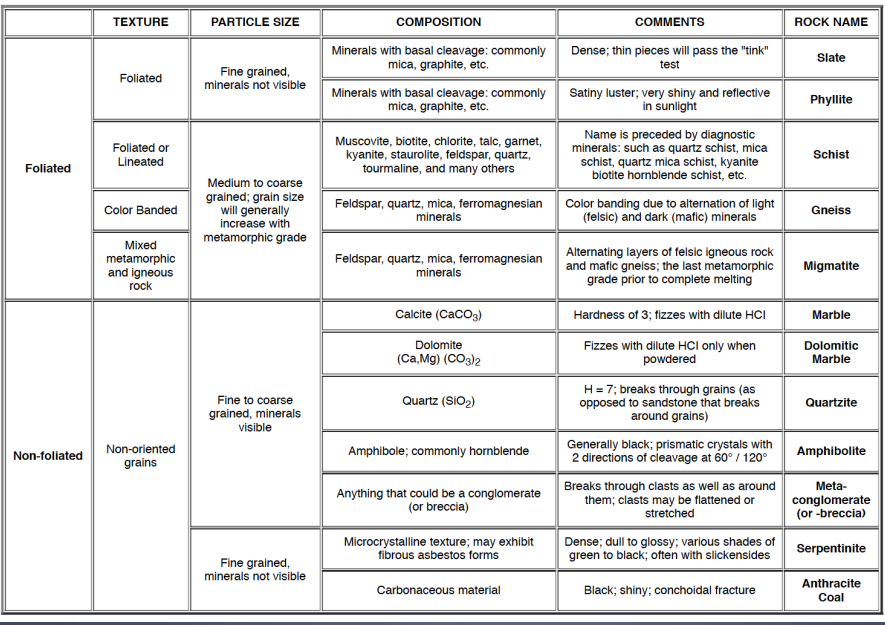
Image: metamorphic rock identification (based on the degree of foliation and grain size
TUNNELLING AND ROCK DRILING UNDER HIGH STRESS CONDITIONS AT THE NATHPA-JHAKRI HYDRO PROJECT
Main sliding and creeping surfaces coincide with this foliation which is encountered in a series of quartz-mica-schists, schistose quartzites and amphibolites
define sediment
loose solid particles that originate from
weathering and erosion of pre-existing rocks
chemical precipitation from solution
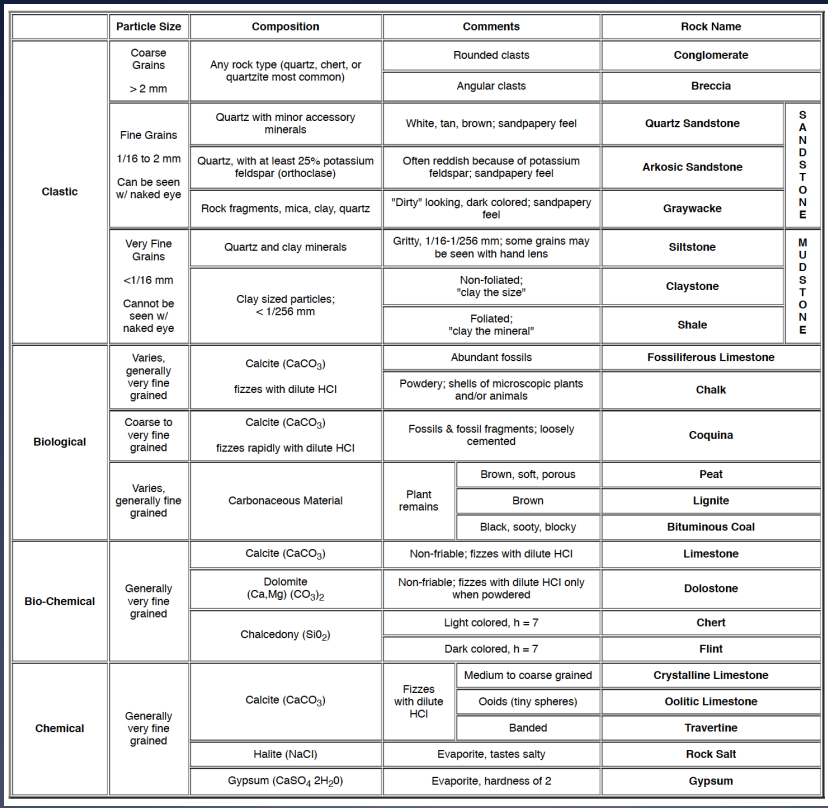
how are sedimentary rocks classified
size
rounding
composition
transportation (rivers, currents, wind, glaciers, rounding and sorting of sediment)
Preservation (need to ‘protect’ sediments from re-erosion
Lithification (transformation of sediments into rock
compaction - water forced out
cementation - precipitation of cements around grains
Deposition (sedimentation)
velocity is too low to carry clasts
solution becomes saturated
Image: material is often deposited in beds (layers or strata)
Law of super position: within a sequence of undisturbed sedimentary rocks, the oldest layers are on the bottom, youngest are on the top
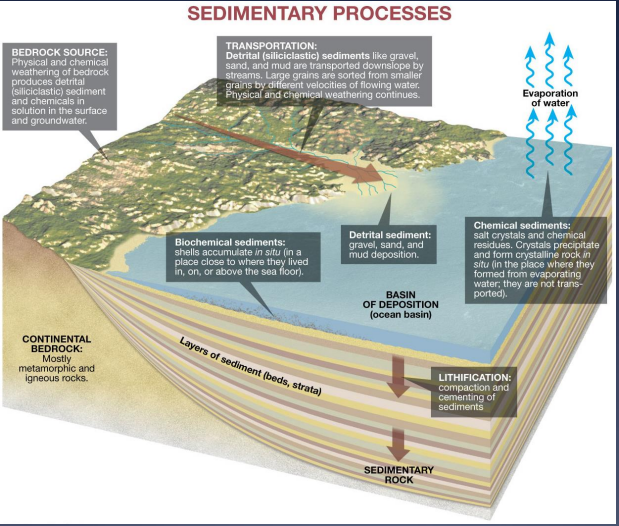
Sedimentary Rocks form from:
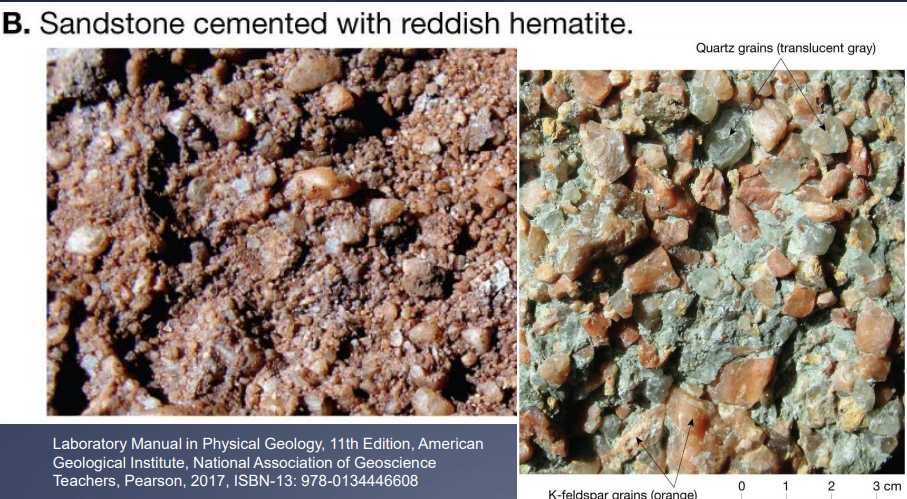
Lithification of sediment (clastic rocks)… give other examples
quartz
sandstone
greywacke
arkose
Sedimentary Rocks form from:
Precipitation from solution (chemical)… give other examples
limestone
dolomite

Sedimentary Rocks form from:
Consolidation of the remains of plants or animals (organic)… give other examples
coal

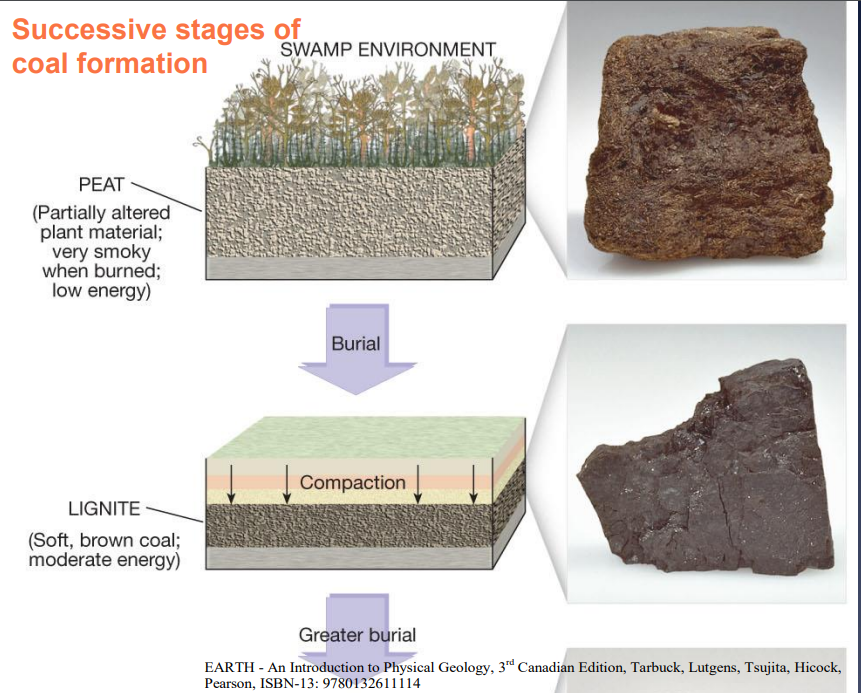
Image: successive stages of coal formation
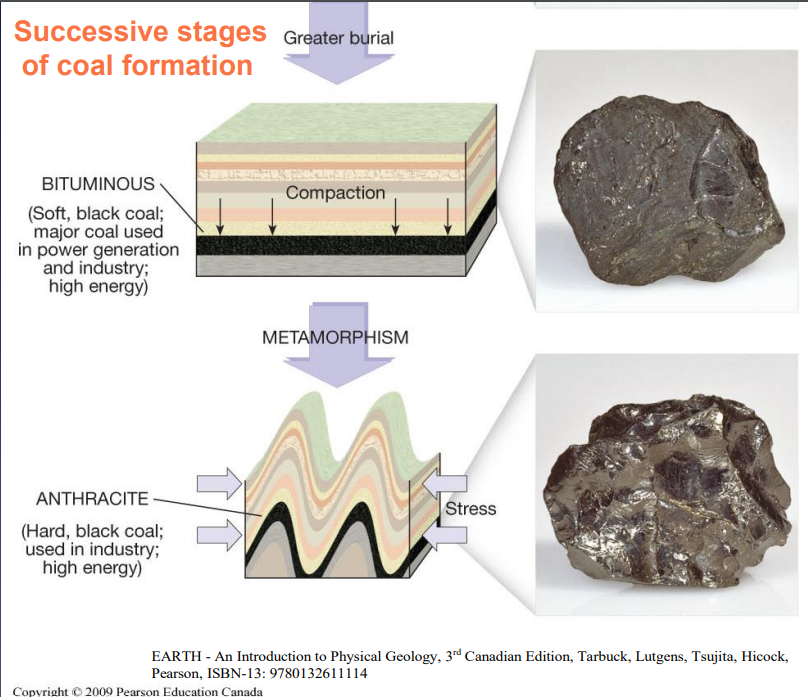

Image:
a: chert commonly forms beds and blob-shaped nodules. This chert nodule in dolostone near hamilton ON
contains fossil sponge, the silica-rich skeleton of which acted as a “seed” for dissolved silica to precipitate around
Image:
b: banded iron formation from northern ON
shows the alternating bands of magnetite/hematite (purple) and iron-bearing chert (red)

List what sedimentary structures would look like
bedding planes & original horizontality
cross-bedding
graded bed
mud cracks
ripple marks
cut & fill structures
Image:
Bedding Planes: cretaceous strata exposed near Drumheller, Alberta illustrate the characteristic layering of sedimentary rocks. These dark coloured beds are composed of organic-rich mudstone, whereas the light-coloured beds are composed of sandstone
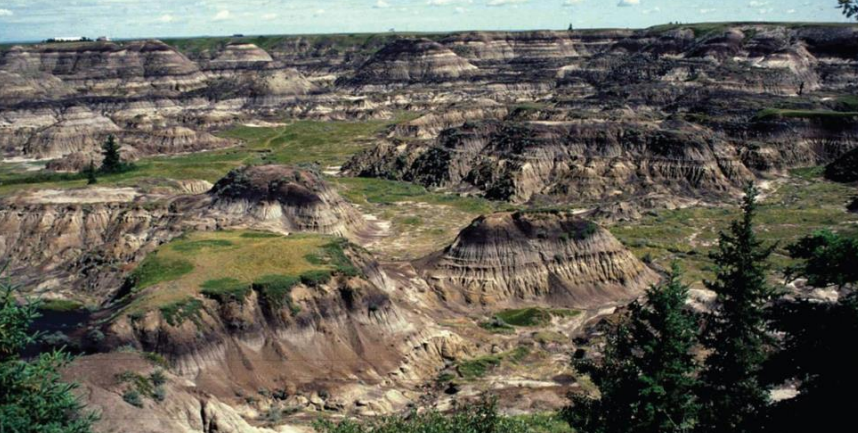

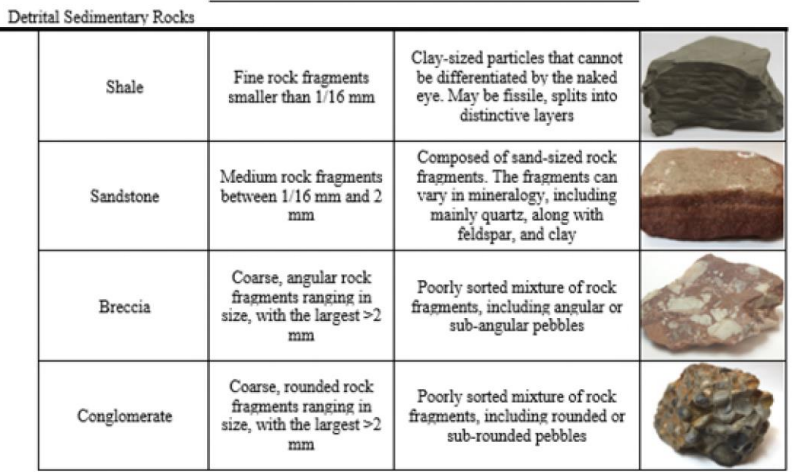
Image: Classification of Sedimentary Rocks - Detrital
Image: Classification of Sedimentary Rocks - Chemical and Biochemical
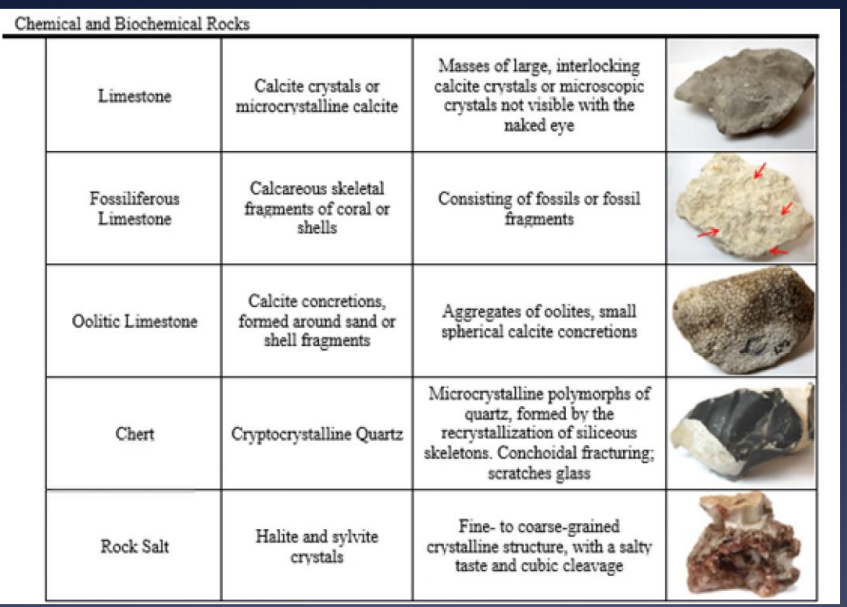
Image: How to classify sedimentary rocks
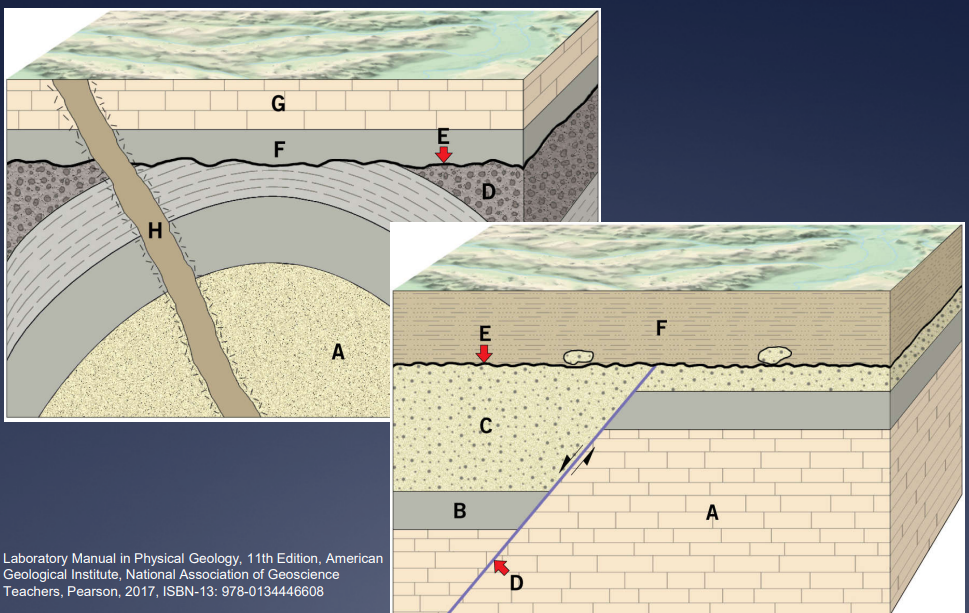
Define Relative Dating
rocks placed in their proper sequence of formation
Define absolute dating
actual time in history when something took place
Explain the Principle of Uniformitarianism
geological processes operating in the present are the same processes that have operated in the past
Explain the law of superposition
within a sequence of undisturbed sedimentary rocks, the layers get younger going from bottom to top
Explain the principle of original horizontality
beds of sediment typically deposited in horizontal layers
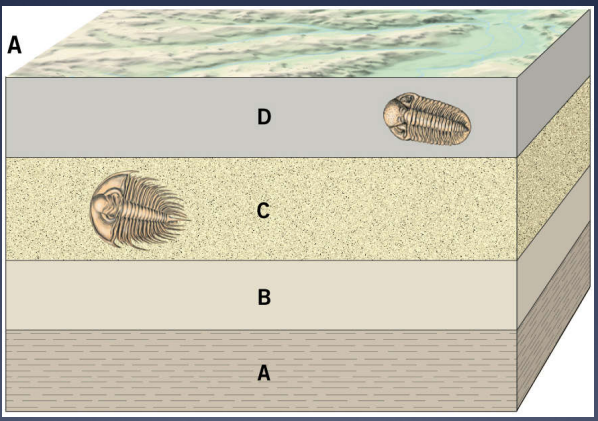
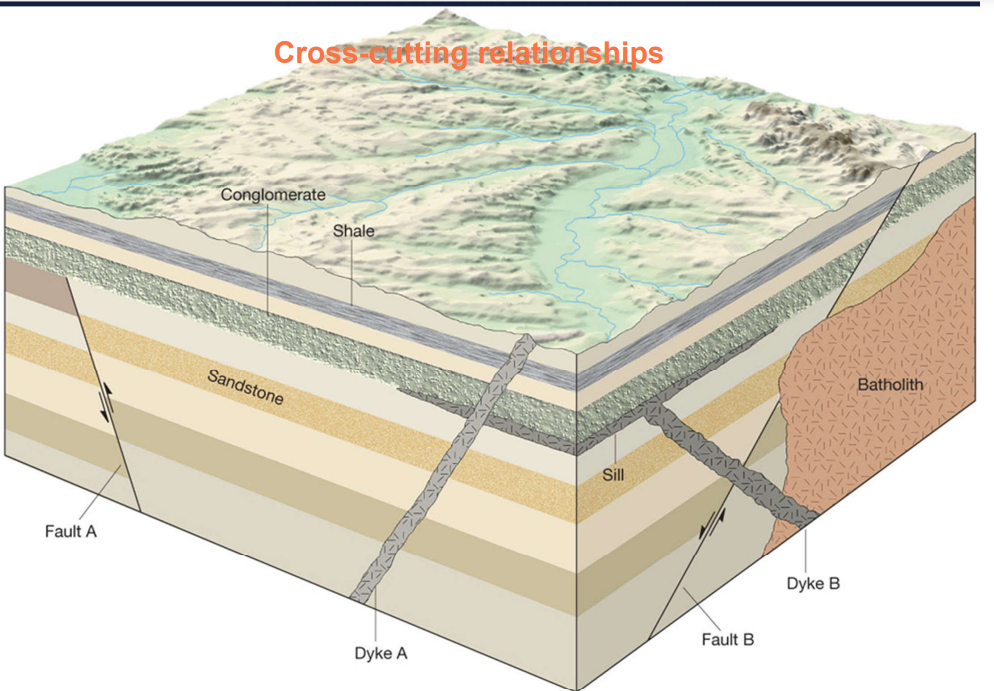
Explain the principle of cross cutting relationships
a disrupted pattern is older than the cause of the disruption