Hereditary Principles: Mendel, Crosses, and Probability in Genetics
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Who is considered the father of modern genetics?
Gregor Mendel
Gene
An inherited factor that helps determine a characteristic
Allele
One of two or more alternative forms of a gene
Genotype
An organism's inherited genetic makeup, or allele combinations
Phenotype
Appearance or manifestation of a characteristic
Not inherited
What is a monohybrid cross?
A genetic cross that follows one character with two possible traits.
What is the expected phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation of a monohybrid cross?
3:1 ratio of dominant to recessive phenotypes.
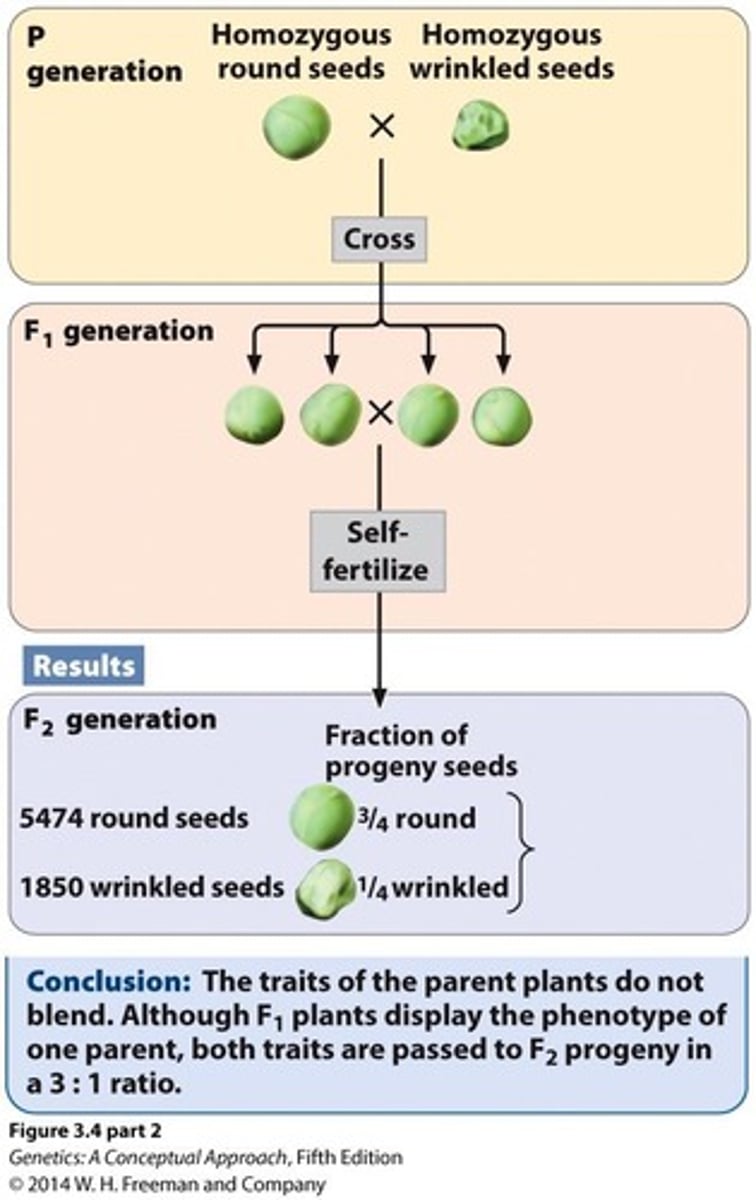
Segregation (Mendel's First Law)
1. Each individual organism possesses two alleles encoding a trait (before meiosis)
2. Alleles separate when gametes are formed (anaphase I)
3. Alleles separate in equal proportions (anaphase I)
Independent Assortment
Alleles at different loci separate independently
True Breeder or Pure Breeder
Homozygous for the trait
Backcross
Cross of F1 genotype with either P genotypes
What is a test cross?
A cross between an unknown dominant genotype and a homozygous recessive genotype to determine the unknown genotype.
What is the purpose of a Punnett square?
To predict the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring from genetic crosses.
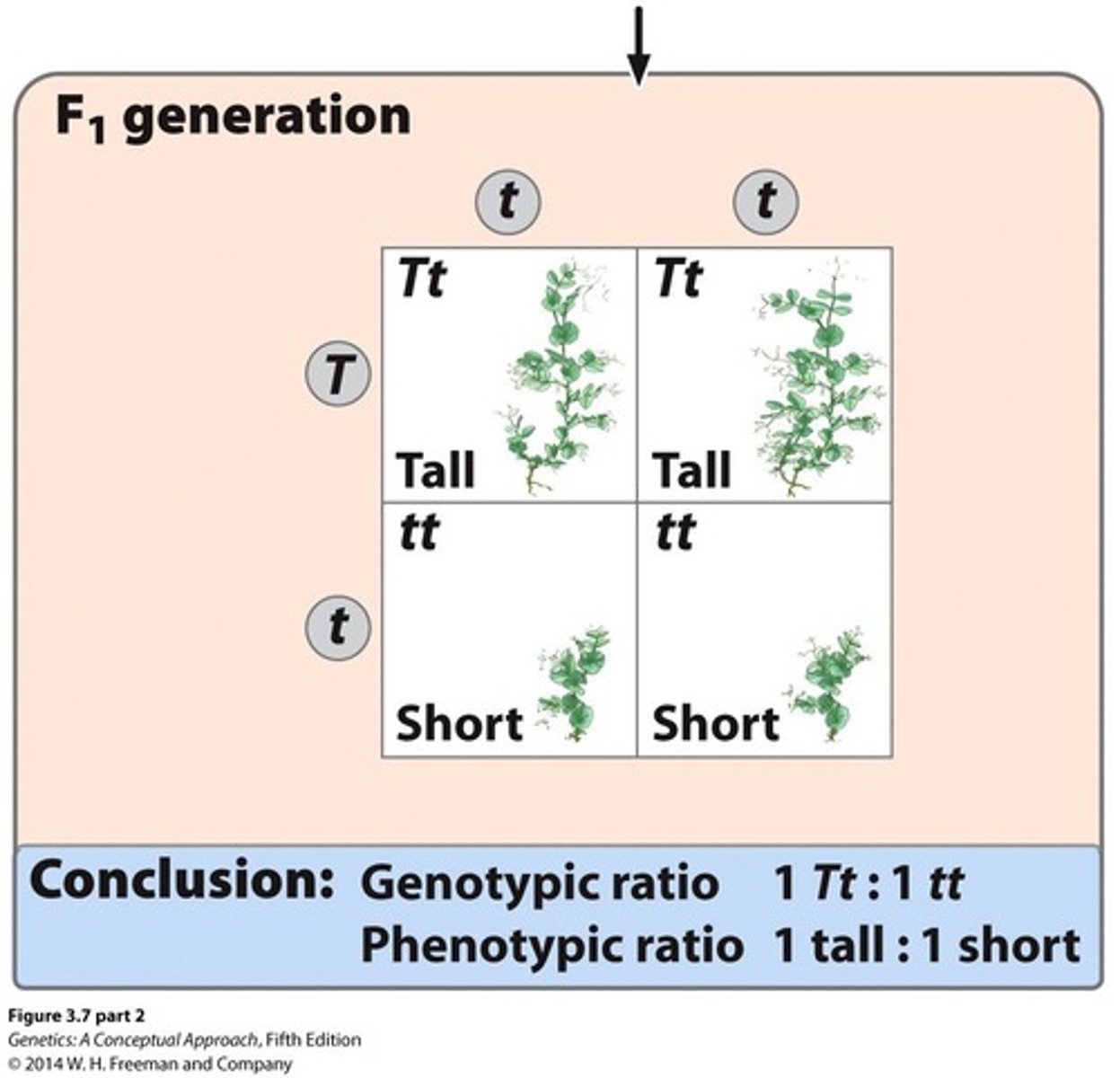
What is Mendel's second law of heredity?
The Principle of Independent Assortment, which states that alleles at different loci separate independently of one another.
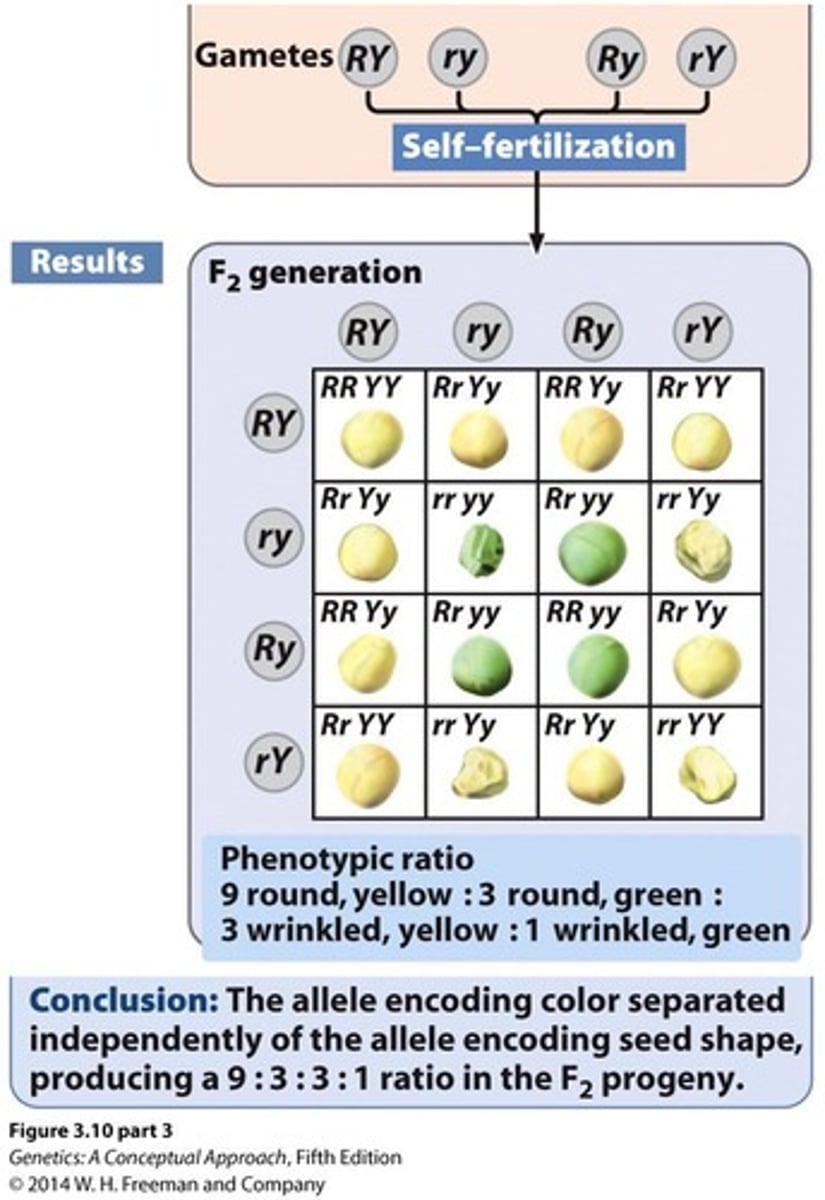
What is the phenotypic ratio resulting from a dihybrid cross?
9:3:3:1 ratio in the F2 generation.
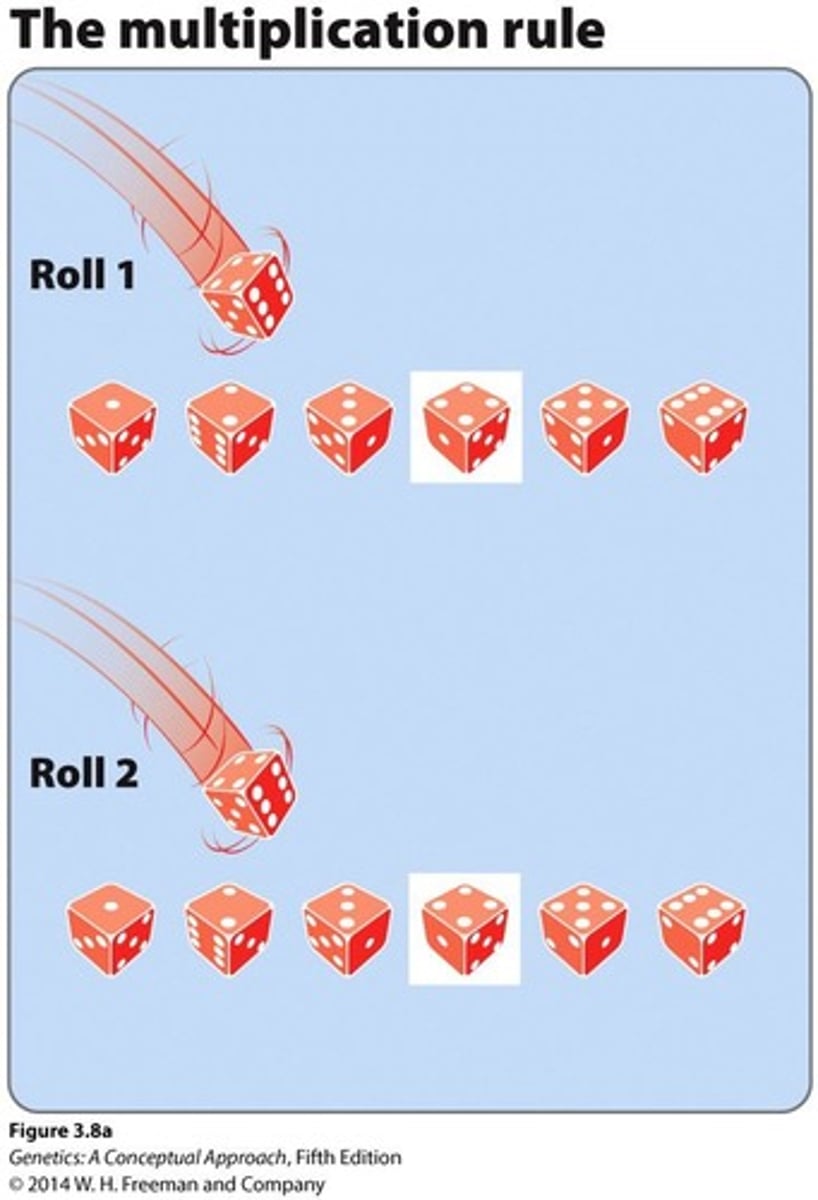
What is the Rule of Multiplication in probability?
The probability of two independent events occurring in sequence is the product of their individual probabilities
What is the Rule of Addition in probability?
The probability that either (OR) 1 of 2 mutually exclusive events will occur is the sum of their individual probabilities
What is the expected outcome of a cross between two heterozygous individuals (Aa x Aa)?
The offspring genotypes will be ¼ AA, ½ Aa, and ¼ aa.
What is the expected genotype ratio from a test cross of Aa with aa?
1:1 genotype ratio of Aa to aa.
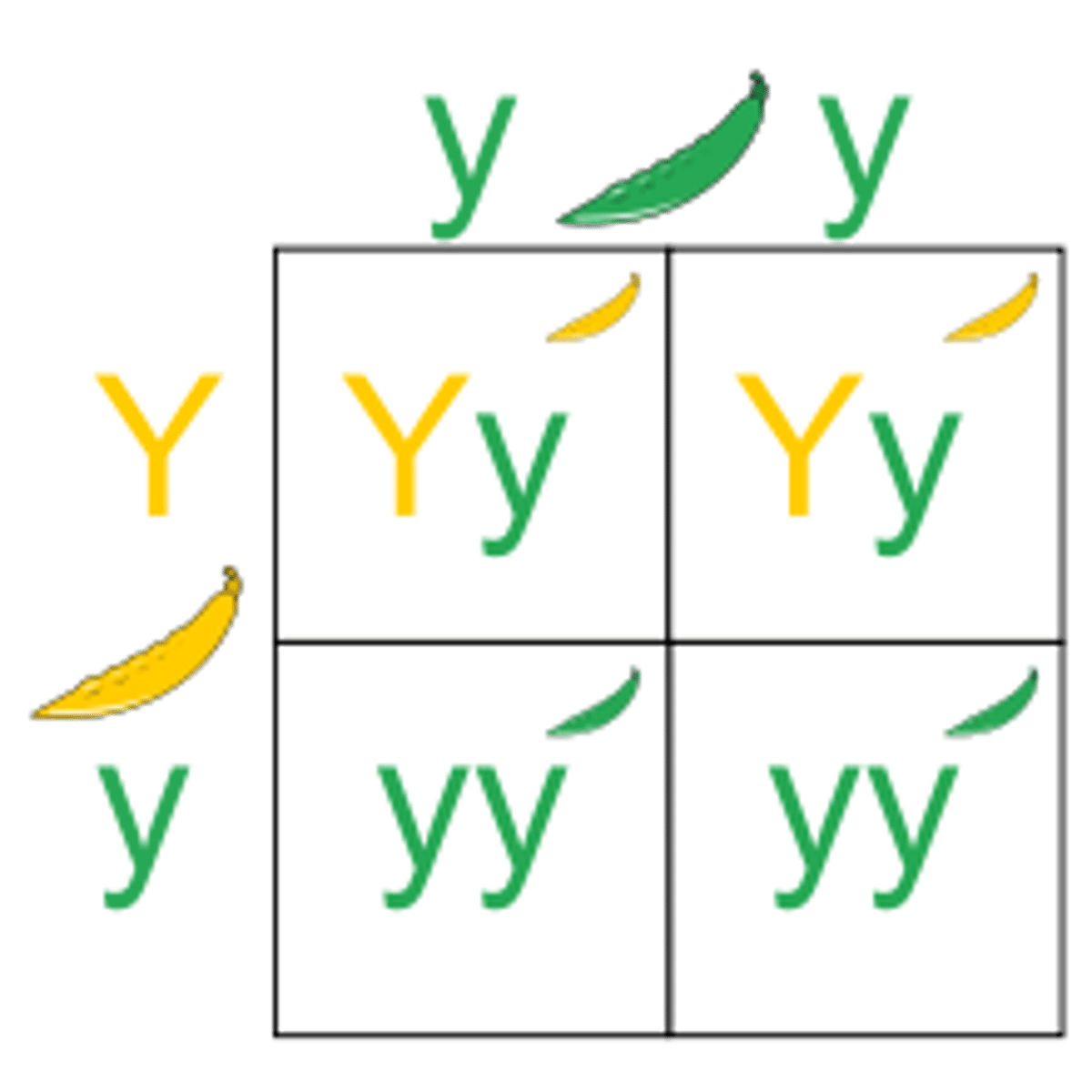
What is the significance of reciprocal crosses in Mendel's experiments?
They confirmed that the results were consistent regardless of which parent contributed which trait.
What is the expected probability of obtaining a heterozygous offspring from a cross between two homozygous recessive individuals?
0% chance, as the offspring will all be homozygous recessive.
What is the genetic symbol convention for dominant and recessive alleles in plants?
Uppercase letters for dominant alleles and lowercase letters for recessive alleles.
What does the term 'wild type' refer to in genetics?
The most common allele for a character, often designated with a plus sign.