Topic 15- Transition Metals
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/107
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
1
New cards
Define a transition element
an element which forms at least one stable ion with a partially full d-shell of electrons
2
New cards
Where are the transition metals located in the periodic table?
in the block from Ti to Cu
3
New cards
What are some physical properties of transition metals?
- metallic
- good heat and electricity conductors
- hard
- strong
- shiny
- high m.p and b.p
- low reactivity
- good heat and electricity conductors
- hard
- strong
- shiny
- high m.p and b.p
- low reactivity
4
New cards
What are 2 uses of iron?
- vehicle bodies
- to reinforce concrete
- to reinforce concrete
5
New cards
What is a use of titanium?
jet engine parts
6
New cards
What is a use of copper?
water pipes
7
New cards
What are 4 chemical properties of transition metals?
- they have variable oxidation states
- good catalysts
- they form complex ions
- they form coloured compounds/ions in solution
- good catalysts
- they form complex ions
- they form coloured compounds/ions in solution
8
New cards
Define the term complex ion
central transition metal ion surrounded by ligands that are co-ordinated bonded to it
9
New cards
What are 3 examples of transition metal catalysts and the reactions they catalyse?
iron - the Haber process
vanadium (V) oxide - the Contact process
MnO2 - the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide
vanadium (V) oxide - the Contact process
MnO2 - the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide
10
New cards
Which electrons do transition metals lose first when forming ions?
4s
11
New cards
Define the term ligand
an ion/molecule with at least one lone pair which is donated to a transition metal ion to form a co-ordinate bond and thus a complex ion
12
New cards
Define the term mono/unidentate ligands
a ligand that forms one co-ordinate bond to the central metal ion (donates 1 lone pair)
13
New cards
Define the term bidentate ligand
a ligand that forms 2 co-ordinate bonds to the central metal ion (donates 2 lone pairs)
14
New cards
Define the term multidentate ligand
a ligang that forms 3 or more co-ordinate bonds to the central metal ion
15
New cards
What are 3 examples of common monodentate ligands?
H2O
NH3
OH-
NH3
OH-
16
New cards
How many co-ordinate bonds can ethanedioate (C2O4^2−) form to a transition metal ion?
2 co-ordinate bonds
17
New cards
How many co-ordinate bonds can benzene-1,2-diol (C6H6O2) form to a transition metal ion?
2 co-ordinate bonds
18
New cards
What is ethylenediamine shortened to when it is a ligand?
en
19
New cards
How many co-ordinate bonds can ethylenediamine (C2H8N2) form to a transition metal ion?
2 co-ordinate bonds
20
New cards
How many co-ordinate bonds does EDTA4- form?
6
21
New cards
What does it mean if a ligand can only form 2 co-ordinate bonds?
that means it is a bidentate ligand
22
New cards
Define the term coordination number
the number of co-ordinate bonds the metal ion has formed to surrounding ligands
23
New cards
What is the Chelate effect?
Chelate complexes with multidentate ligands are favoured over ligands that form fewer co-ordinate bonds per molecule
24
New cards
Explain the Chelate effect in terms of entropy and the reaction that is occuring
the no of molecules increases when multidentate ligands displace ligands that form fewer co-ordinate bonds
a significant increase in entropy → G < 0 → feasible reaction ∴ a more stable complex ion is formed
a significant increase in entropy → G < 0 → feasible reaction ∴ a more stable complex ion is formed
25
New cards
What ion is usually formed when a transition metal compound is dissolved in water? What shape is it?
an aqua ion
there are 6 H2O ligands around the central metal ion, so an octahedral complex ion forms
there are 6 H2O ligands around the central metal ion, so an octahedral complex ion forms
26
New cards
If a transition metal ion has 2 ligands, what is the usual shape?
linear
27
New cards
What is a co-ordinate bond also known as?
a dative covalent bond
28
New cards
If a transition metal ion has 4 ligands, what is its usual shape?
tetrahedral
29
New cards
What is the exception to the general rule that ions with 4 ligands is generally tetrahedral? What shape is it?
platin (which forms cisplatin)
it is square planar
it is square planar
30
New cards
What shape is a complex ion if it has 6 ligands?
octahedral
31
New cards
How can complex ions display E-Z or cis-trans isomerism and what shapes does this apply to?
ligands differ in the way they are arranged in space
2 ligands of the same type can be on the same side of the metal ion and form the E/cis isomer and they can be on opposite sides and form the Z or trans isomer
- it applies to square planar and octahedral complex ions
2 ligands of the same type can be on the same side of the metal ion and form the E/cis isomer and they can be on opposite sides and form the Z or trans isomer
- it applies to square planar and octahedral complex ions
32
New cards
What conditions are needed for a complex ion to display optical isomerism?
it usually applies to octahedral molecules with 2 or more bidentate ligands, so the mirror images are non-superimposable
33
New cards
What happens to Co2+, Cu2+, Fe3+'s coordination numbers when Cl- ligands replace NH3 or H2O ligands
they decrease from 4 to 6 as Cl- is a mucher bigger ligand than NH3 and H2O
34
New cards
What is haem, its metal ion, coordination number and ligands?
haem is a component of haemoglobin is made up of protein chains
it has Fe2+ central metal ion
6 coordinate bonds
4 of the bonds form a porphyrin (ring system)
1 is bonded to the N of a globin molecule
1 is bonded is to an oxygen
it has Fe2+ central metal ion
6 coordinate bonds
4 of the bonds form a porphyrin (ring system)
1 is bonded to the N of a globin molecule
1 is bonded is to an oxygen
35
New cards
How does haemoglobin transport oxygen?
O2 forms a weak coordinate bond to the metail ion which is transported around the body
when haemoglobin reaches cells, the bond breaks and oxygen is released
when haemoglobin reaches cells, the bond breaks and oxygen is released
36
New cards
Why is carbon monoxide toxic?
CO is a better ligand and coordinately bonds stronger to Fe2+ than O2
this stops O2 from bonding to haemoglobin so O2 can't be transported
this stops O2 from bonding to haemoglobin so O2 can't be transported
37
New cards
Why are transition metal compounds coloured?
they have partially filled d-orbitals and electrongs are able to move between the d-orbitals
in compounds, the d-oritals split into different energy levels
in compounds, the d-oritals split into different energy levels
38
New cards
How is energy of photon related to light frequency?
E \= hf
39
New cards
How is the colour of transition metal compounds determined?
the colour corresponding to the frequency of the energy change is missing from the spectrum, so we see a combination of all the colours that aren't absorbed
40
New cards
How is the colour of transition metal compounds emitted?
electrons can absorb energy in the form of photons to become excited and move to a higher energy level (excited state)
41
New cards
What affects the colour of a transition metal compound?
ΔE (enthalpy) affects the frequency of asborbed photons (which determines colour)
42
New cards
What affects enthalpy/energy (which determines colour)? [4]
- the oxidation state of the metal
- the number and type of ligands
- shape
- coordination number
- the number and type of ligands
- shape
- coordination number
43
New cards
Why is there a lack of colour in some aqueous ions and other complex ions?
ions that have completely filled 3d energy levels (e.g. Zn2+) and ions that have no electrons in their 3d energy levels (e.g. Sc3+) are not coloured
44
New cards
What is the oxidation number and colour of VO2^+?
+5
yellow
yellow
45
New cards
What is the oxidation number and colour of VO^2+?
+4
blue
blue
46
New cards
What is the oxidation number and colour of V^3+?
+3
green
green
47
New cards
What is the oxidation number and colour of V^2+?
+2
violet
violet
48
New cards
What can you use to reduce vanadium?
zinc
49
New cards
What is the colour change when zinc reduces V^3+?
it goes green to violet
50
New cards
What colour is Fe^2+'s aqua ion?
green
51
New cards
What colour is Fe^3+'s aqua ion?
pale brown
52
New cards
What colour is Cr^2+'s aqua ion?
blue
53
New cards
What colour is Cr^3+'s aqua ion?
red-violet
54
New cards
What colour is Co^2+'s aqua ion?
brown
55
New cards
What colour is Co^3+'s aqua ion?
yellow
56
New cards
What does a colorimeter do?
it measures the absorbance of a particular wavelength of light by a solution
57
New cards
How would you use colorimetry experimentally?
use solutions of known concentration to create a calibration graph; find the unknown conc
58
New cards
What information can a colorimeter give you?
the concentration of a certain ion in the solution
59
New cards
Why can transition metals have variable oxidation states?
they have partially filled d-orbitals, so they can lose 4s and 3d electrons
60
New cards
What oxidation state do all transition metals (other than Scandium) have and why?
+2 because of loss of electrons from the 4s orbital
61
New cards
What is scandium's most prominent oxidation state?
+3 (but it can exist in 0. +1 and +2)
62
New cards
When the oxidation state is high, do transition metals exist as simple ions?
after an oxidation state of about 3, no.
metal ions covalently bond to other species
metal ions covalently bond to other species
63
New cards
What is the use of the complex silver diammine cation [Ag(NH3)2]+?
it's the tollens' reagant - tests for aldehydes/ketones
an aldehyde forms a silver mirror
ketons have no visible change
an aldehyde forms a silver mirror
ketons have no visible change
64
New cards
What colour is MnO4^-?
deep purple
65
New cards
What colour is Mn^2+?
pink
66
New cards
Why are redox titrations with transition metal compounds said to be self-indicating?
they usually involve a colour change as the metal is changing oxidation state (an indicator is still sometimes useful/needed)
67
New cards
What colour is Cr2O7^2-?
orange
68
New cards
What colour is Cr^3+?
green
69
New cards
What happens to aqua metal ions in acidic conditions?
they get reduced
70
New cards
What is the colour change when zinc reduces Cr^3+ in acidic conditions?
solution goes from orange to blue
71
New cards
What happens to aqua metal ions in alkaline conditions?
they get oxidised
72
New cards
What is the colour change when H2O2 oxidises Cr^3+ in alkaline conditions?
solution goes from green to yellow
73
New cards
What is the colour change for the chromate → dichromate equilibrium reaction?
solution goes from yellow to orange
74
New cards
What happens to aqua metal ions in neutral conditions?
no change
75
New cards
What does oxidation/reaction and the readiness of the reaction depend on?
E° values
76
New cards
What two things can change E° values?
pH
ligands involved
ligands involved
77
New cards
Define a catalyst
a substance that increases the rate of a reaction without being chemically changed at the end of the reaction
78
New cards
How do catalysts usually work?
they provide an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy
79
New cards
Why are transition metals good catalysts?
they can exist in variable oxidations states so they can easily provide alternative pathways
80
New cards
Why are group 1, 2 & 3 metals not as good catalysts?
they only exist in one oxidation state
81
New cards
What are advantages of using a catalyst for a reaction?
they save valuable energy & resources → reactions to proceed at lower temps & pressures
82
New cards
How do catalytic converter decrease CO and NO emissions from internal combustion engines?
- CO and NO molecules are adsorped onto the catalyst surface
- they weaken the bonds and chemical reaction
- CO2 and N2 product molecules are desorbed from the catalyst surface
- they weaken the bonds and chemical reaction
- CO2 and N2 product molecules are desorbed from the catalyst surface
83
New cards
What metals are used in a catalytic converter?
platinum
palladium
rubindium
palladium
rubindium
84
New cards
Define a heterogeneous catalyst
a catalyst that is in a different phase to the reactans
\[catalytic activity occurs on the solid surface as the reactants pass over it]
\[catalytic activity occurs on the solid surface as the reactants pass over it]
85
New cards
How do heterogeneous catalysts work?
reactants adsorb to the catalyst's surface at active sites
the bond weakens within the reactants, holds reactants close together on the surface and/or in the correct orientation to react
once the reaction has occurred, products desorb from the active sites.
the bond weakens within the reactants, holds reactants close together on the surface and/or in the correct orientation to react
once the reaction has occurred, products desorb from the active sites.
86
New cards
What properties does the catalyst need to have to make it a good catalyst?
- can't absorb too strongly (otherwise the products won't desorb)
- can't absorb too weakly (as the reactant won't stay in place for lond enough and the bonds won't weaken enough)
- a good balance between desorption and adsorption is needed
- can't absorb too weakly (as the reactant won't stay in place for lond enough and the bonds won't weaken enough)
- a good balance between desorption and adsorption is needed
87
New cards
How can you increase the efficiency of heterogeneous catalysts?
- increase SA to increase the no. of active sites present
- spead onto an inert support medium (ceramic) to increase surface/mass ratio
(use ceramic honeycomd maesh/sponge)
- spead onto an inert support medium (ceramic) to increase surface/mass ratio
(use ceramic honeycomd maesh/sponge)
88
New cards
What is catalyst poisoning?
unwanted impurities adsorb to the catalyst's active sites and don't desorb
this blocks the active sites on the catalyst's surface
this blocks the active sites on the catalyst's surface
89
New cards
What effect does catalyst poisoning have on catalytic activity?
decreases the effectiveness of the catalyst over time
90
New cards
How else can a catalyst be degraded?
finely divided catalysts can be gradually lost from their support medium
91
New cards
What is the Haber process?
a method that produces ammonia
N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
92
New cards
What heterogeneous catalyst does the Haber process use?
an iron (Fe) catalyst
93
New cards
Define homogeneous catalyst
a catalyst that is in the same phase as the reactants
94
New cards
How do homogeneous catalysts work?
they form intermediates to give a different reaction pathway with lower Ea (activation energy)
95
New cards
Why does the reaction between S2O8^2- and I- ions have a high Ea in normal conditions?
they are two negative ions repeling each other so Ea will be high
96
New cards
Which transition metal ions catalyse the reaction between S2O8^2- and I- ions?
Fe^2+
97
New cards
Define the term autocatalysis
when the product of a reaction is also a catalyst for that reaction
98
New cards
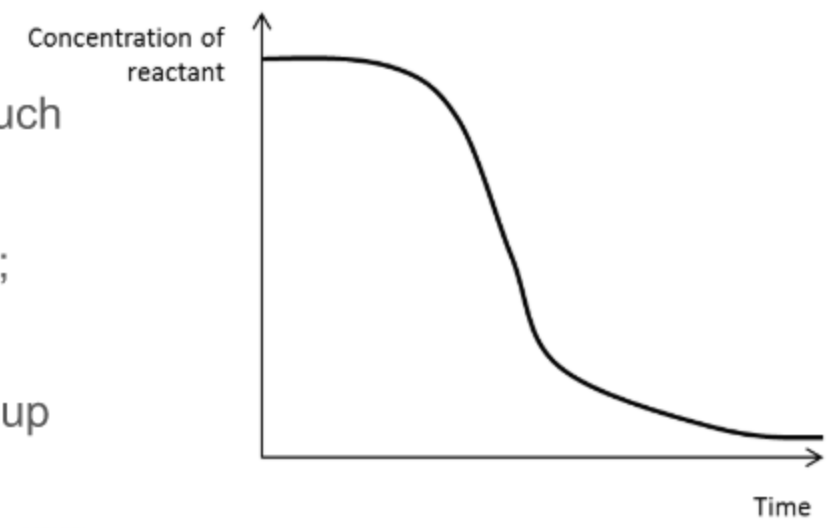
What does a concentration of reactant against time graph for an autocatalysed reaction look like?
\
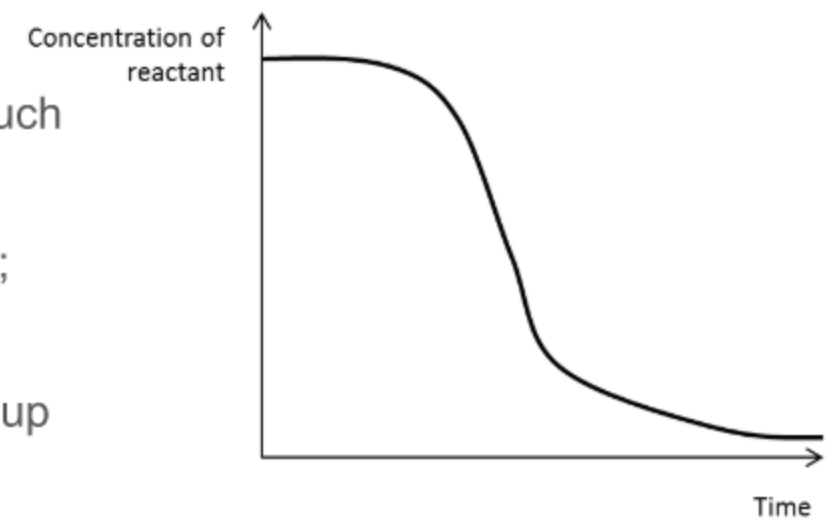
99
New cards
Explain each stage of a concentration-time graph for an autocatalysed reaction
it is initially slow and uncatalysed as not much of the catalyst has been formed
the rate increases as catalyst is made
it slows down again as reactants are used up
the rate increases as catalyst is made
it slows down again as reactants are used up
100
New cards
What transition metal ion autocatalyses the reaction between C2O4^2- and MnO4- ions?
Mn^2+