DNA, DNA!, DNA Terms
4.0(5)Studied by 34 people
Card Sorting
1/30
Last updated 1:12 PM on 11/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
1
New cards
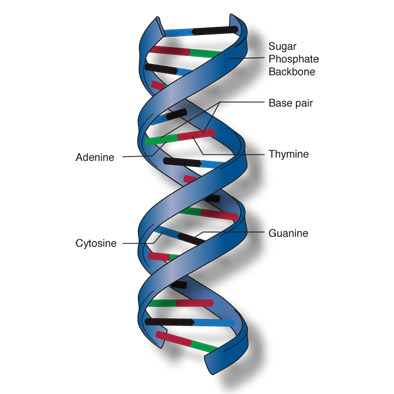
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic Acid; A nucleic acid found in the nucleus of all living cells, which carries the organism's hereditary information.
2
New cards
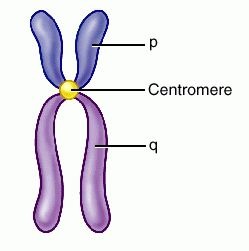
chromosomes
rod-shaped cellular structure made of condensed chromatin; contains DNA, which carries the genetic information that controls inherited characteristics such as eye color and blood type.
3
New cards
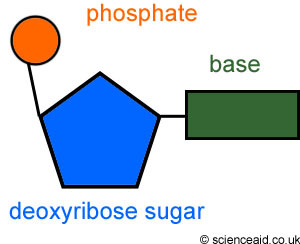
nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
4
New cards
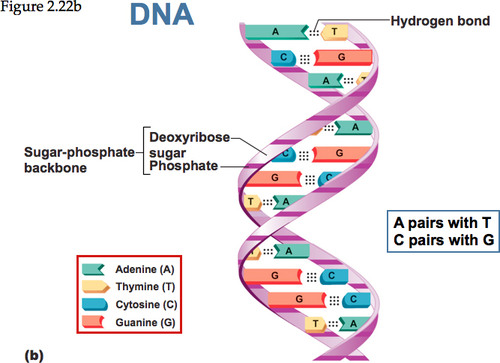
double helix
Shape of a DNA molecule formed when two twisted DNA strands are coiled into a springlike structure and held together by hydrogen bonds between the bases
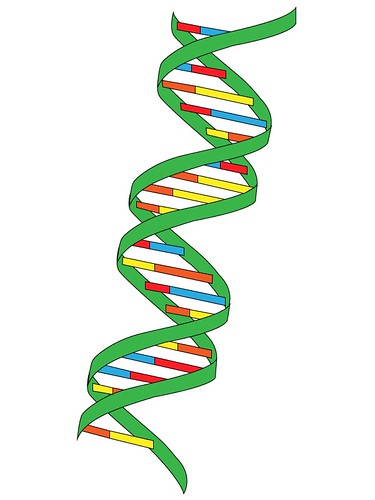
5
New cards
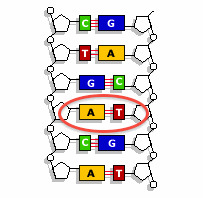
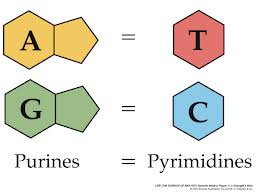
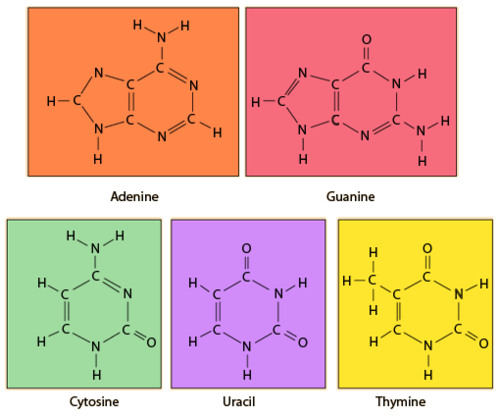
Adenine
nitrogenous base "A"; connects to thymine in DNA and connects to uracil in RNA
6
New cards
Thymine
nitrogenous base "T"; connects to adenine in DNA
7
New cards
sugar
The molecule that is bonded between the phosphate and the base in the DNA double helix
8
New cards
phosphate
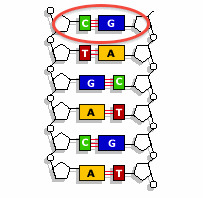
The part of the nucleotide subunit that forms the sides or "rails" of the DNA double helix ladder
9
New cards
Cytosine
nitrogenous base "C" connects with guanine
10
New cards
Guanine
nitrogenous base "G"; connects to cytosine
11
New cards
base
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, and Cytosine are known as these in DNA
12
New cards
Genome
the complete instructions for making an organism, consisting of all the genetic material in that organism's chromosomes
13
New cards
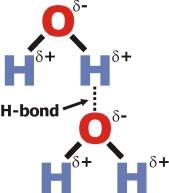
hydrogen bond
bond that connects the base pairs
14
New cards
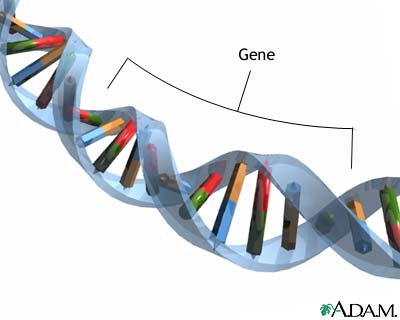
Genes
DNA segments that serve as the key functional units in hereditary transmission.
15
New cards
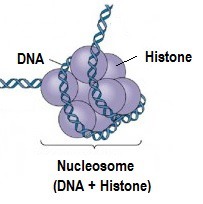
Histones
protein molecules around which DNA is tightly coiled in chromatin
16
New cards
Trait
A characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes.
17
New cards
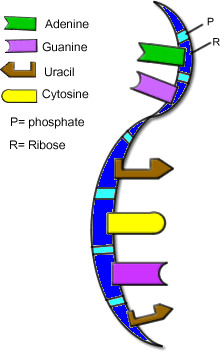
RNA
single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose
18
New cards
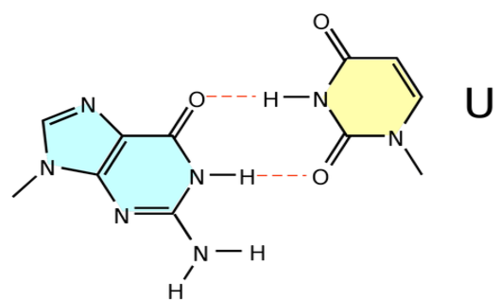
Uracil
a nitrogen-containing base found in RNA (but not in DNA)
19
New cards
framshift mutations are due to?
insertion or deletion of a base pair
20
New cards
substitiution
Mutation in which a nucleotide base is replaced with another.

21
New cards
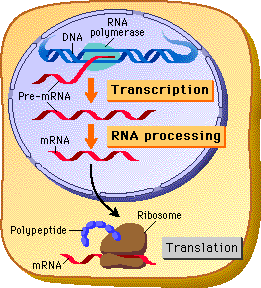
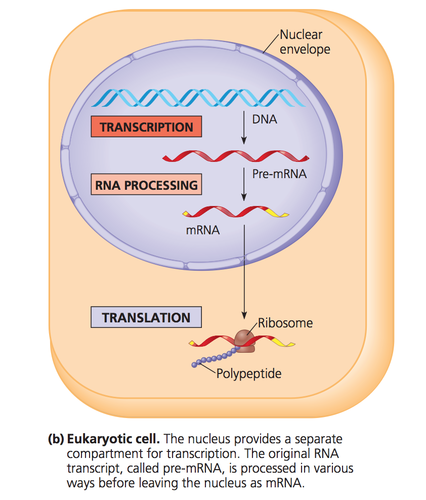
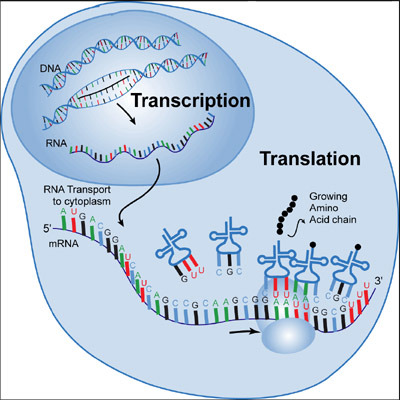
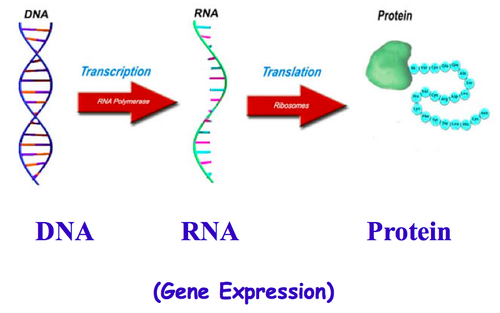
Transcription
synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template
22
New cards
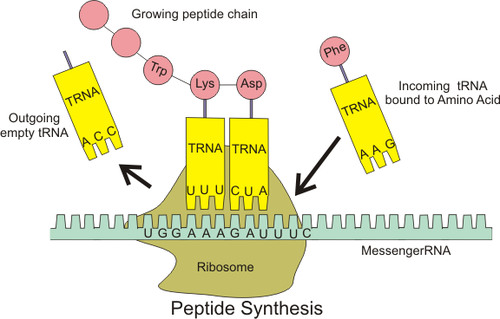
Translation
Process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced
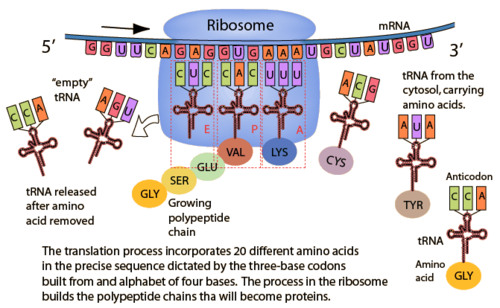
23
New cards
Where does transcription occur?
nucleus
24
New cards
Where does translation occur?
ribosome
25
New cards
tRNA
transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome
26
New cards
mRNA
messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome
27
New cards
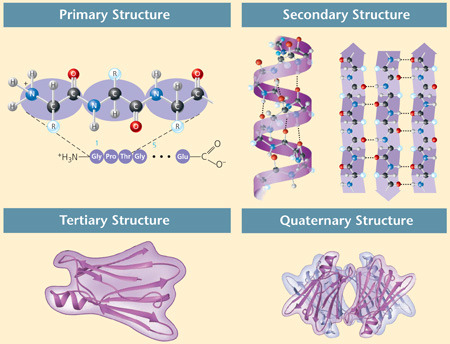
Protein
made of one or more chains of amino acids and that is a principal component of all cells
28
New cards
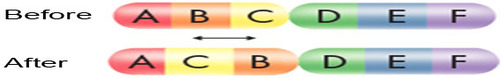
inversion mutation
A mutation involving a piece of a chromosome that breaks off and reattaches in reverse orientation.
29
New cards
Why does transcription occur?
Organelles for protein synthesis (ribosomes) are found in the cytoplasm. DNA is too large to move out of the nucleus, so a section is copied into RNA.
30
New cards
Why does translation occur?
It is putting together the amino acids to make the proteins
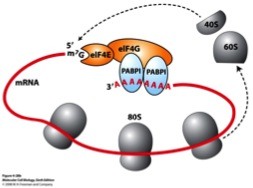
31
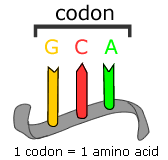
New cards
Codon
a sequence of three nucleotides that together form a unit of genetic code in a DNA or RNA molecule.