System Design: URL Shortener
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards based on the lecture notes about designing a URL shortening service, covering key concepts and functionalities.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is the purpose of a URL shortening service?
To convert long URLs into shorter, more manageable URLs that redirect to the original URL.
What is an example of a URL shortening service?
TinyURL.
What is the maximum number of URLs generated per day according to the lecture?
100 million URLs.
What is the maximum URL length assumption in the lecture?
100 characters.
What ratio was assumed for reads to writes in the URL shortening service?
10:1.
What is the estimated storage requirement for 10 years?
36.5 TB.
What are two critical functional requirements for a URL shortening service?
High availability and scalability.
What endpoints are needed for the URL shortening API?
POST api/v1/data/shorten → accepts long url and returns a short one.
GET api/v1/shortURL → return long URL for HTTP redirection.
how does a url shortener work?
A URL shortener works by taking a long URL and converting it into a shorter, unique identifier that redirects users to the original URL when accessed. It typically involves mapping the long URL to a shortened code stored in a database and serving it through a web API. The status code 301 indicates that the requested URL has been permanently moved to a new location, so all future requests should use the new URL.
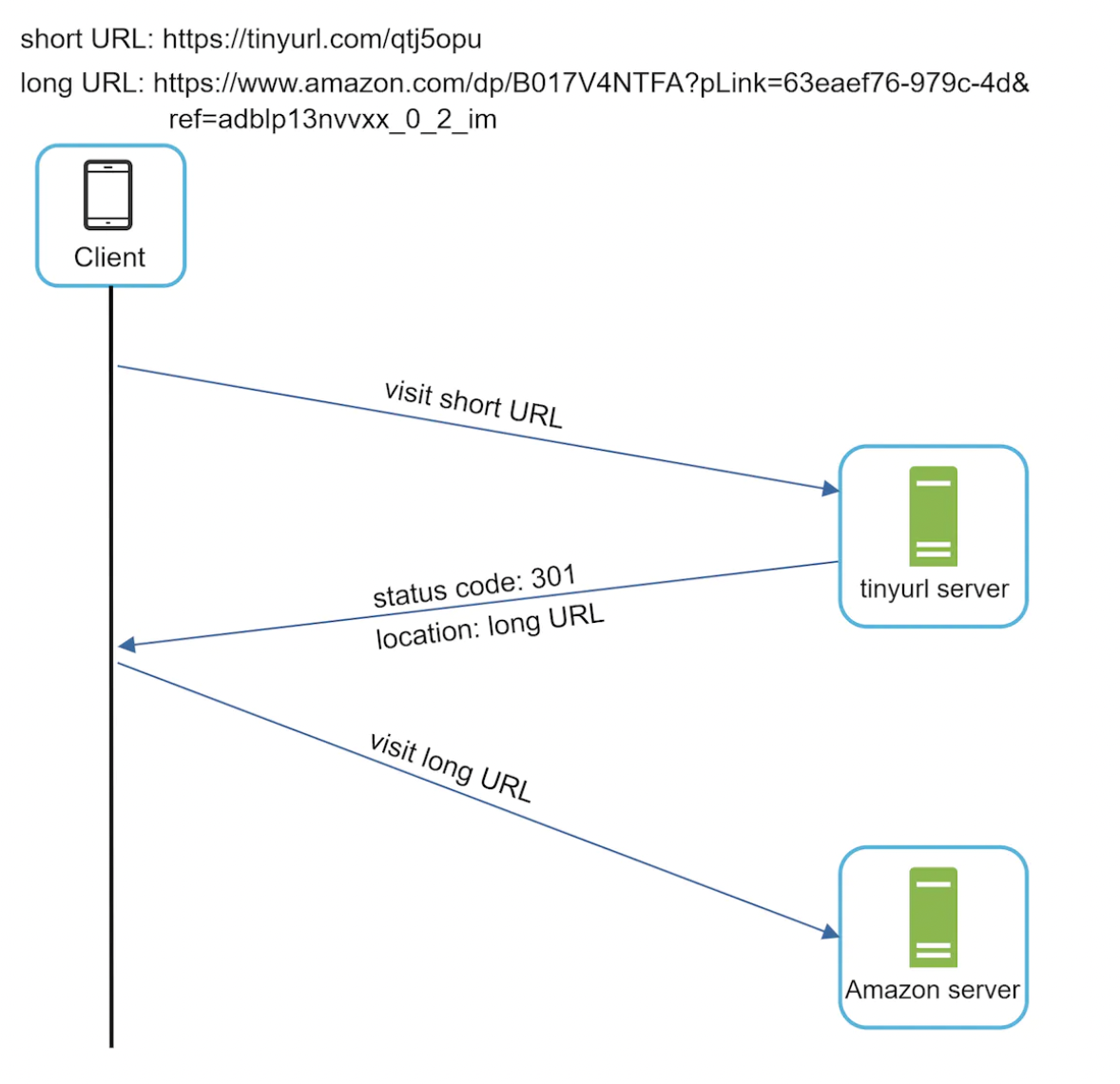
What's the difference between 301 and 302 statuses?
301 is a permanent redirect, while 302 is a temporary redirect for URLs.
How is URL redirection implemented in a URL shortening service?
By storing the
What does the hash function do in URL shortening?
It converts long URLs into short URLs and maps them back.
What character set is used in the hash value for short URLs?
Characters [0-9a-zA-Z].
What is the minimum required length for the hash to support 365 billion URLs?
7 characters.
What is one potential issue using in-memory storage for URLs?
It does not persist across server reboots.
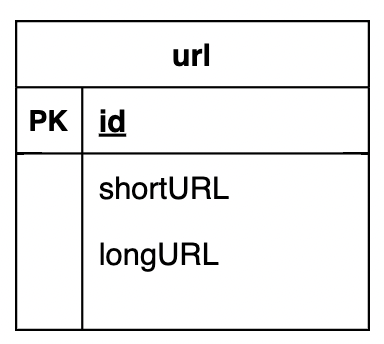
What type of database structure can be used instead of a hash table for storing URLs?
A simple relational table is preferrable.
In the simplified version, we're storing the URLs in a hash table. That is problematic as we'll run out of memory and also, in-memory doesn't persist across server reboot.
What algorithm is suggested for generating unique IDs in a distributed environment?
Twitter's snowflake algorithm.
What is a Bloom filter used for in the context of URL shortening?
To help detect collisions in the hash function without querying the database.
How does base62 conversion work in generating short URLs?
It converts a unique ID into a string of characters consisting of 62 potential characters.
What is a key advantage of using an ID-based approach for short URLs?
Collisions are not possible because IDs are unique.
What does introducing a cache in the service improve?
It improves read performance.
What happens if a short URL is not found in the cache?
The long URL is fetched from the database and stored in cache.
What is a rate limiter used for in the URL shortening service?
To protect against malicious actors trying to make excessive shortening requests.
How can the web server tier be scaled?
By introducing more stateless service instances.
What are two common approaches for scaling the database layer?
Replication and sharding.
What additional feature can provide insights about URL usage?
Integrating analytics tracking.
What fundamental concepts are emphasized in distributed systems as discussed?
Availability, consistency, reliability.
What is recommended for handling potential server load when choosing between status codes?
Choose 301 if you want to avoid extra server load.
Is it possible to delete or update shortened URLs in the proposed design?
No, for simplicity, it is assumed they cannot be updated or deleted.
What approach is suggested to keep the URL shortening service simple? In terms of the hash function
Using base62 encoding for the URL shortening.
What is meant by 'fault tolerance' in the context of the URL shortener?
The ability of the system to continue operation despite failures.
How can we track the number of clicks on a shortened URL?
By integrating analytics features in the service.