Bio 210 Exam 1
0.0(0)Studied by 4 people
Card Sorting
1/198
Earn XP
Last updated 6:50 PM on 2/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
199 Terms
1
New cards
What is definition of a cell?
basic structural unit of living organisms that can perform the functions characteristic of life
2
New cards
Who were some of the early figures in cell biology?
Hooke - named cells (dead), Van Leeuwenhook -saw living cells (not animal cells), homunculus, Schleiden and Schwann - animal tissues have cells
3
New cards
What is cell theory?
Schwann - all organisms consist of one or more cells, the cell is the basic unit of structure for all organisms; Virchow added - all cells arise from pre-existing cells
4
New cards
Describe how modern cell biology arose from three different fields.
Cytology - structure of cells; biochemistry - chemical pathways of cells, genetics - information in DNA
5
New cards
Is light a particle or a wave?
both, photon - particle
6
New cards
What is the relationship between energy and wavelength of light?
shorter wavelength = higher energy; longer = lower
7
New cards
What are the wavelengths of visible light?
400-665 nm
8
New cards
What are diffraction and interference?
diffraction - light waves go through slit and disperse; interference is when light waves come together to make a bigger one or cancel out
9
New cards
Describe a lens, including numerical aperture.
angle of usable light, lens gathers this and bends it to focal point, AN = resolution x refractive index (speed of the light)
10
New cards
Describe the following types of microscopy: brightfield, phase contrast, DIC, fluorescent, confocal, TEM, SEM.
bright field - regular light microscopy, phase contrast - changes in phase converted into changes in brightness, DIC - change in interference pattern converted to changes in brightness, fluorescent - tag parts of cell with fluorescent molecules and exciting them and reading emitted wavelengths as it returns to ground state, confocal - same as fluorescent but with precise optical sectioning for looks at different slices, TEM - electrons shot through specimen to make image (smaller wavelength = higher resolution), SEM - electrons shot onto surface and bounce off
11
New cards
What tools are used to aid in microscopy?
microtomes- slicer; freeze fracture - splits open plasma membrane to see inside
12
New cards
What elements are common in organisms?
HCON
13
New cards
What is the difference between a covalent bond and ionic bond?
covalent - electrons shared equally, ionic - full charges, electrons taken
14
New cards
Why are bond energies important?
energy required to make 1 mole of bond, C-C are high bond energy
15
New cards
Be able to draw the common side groups of carbon-containing molecules (such as carboxyl)
\
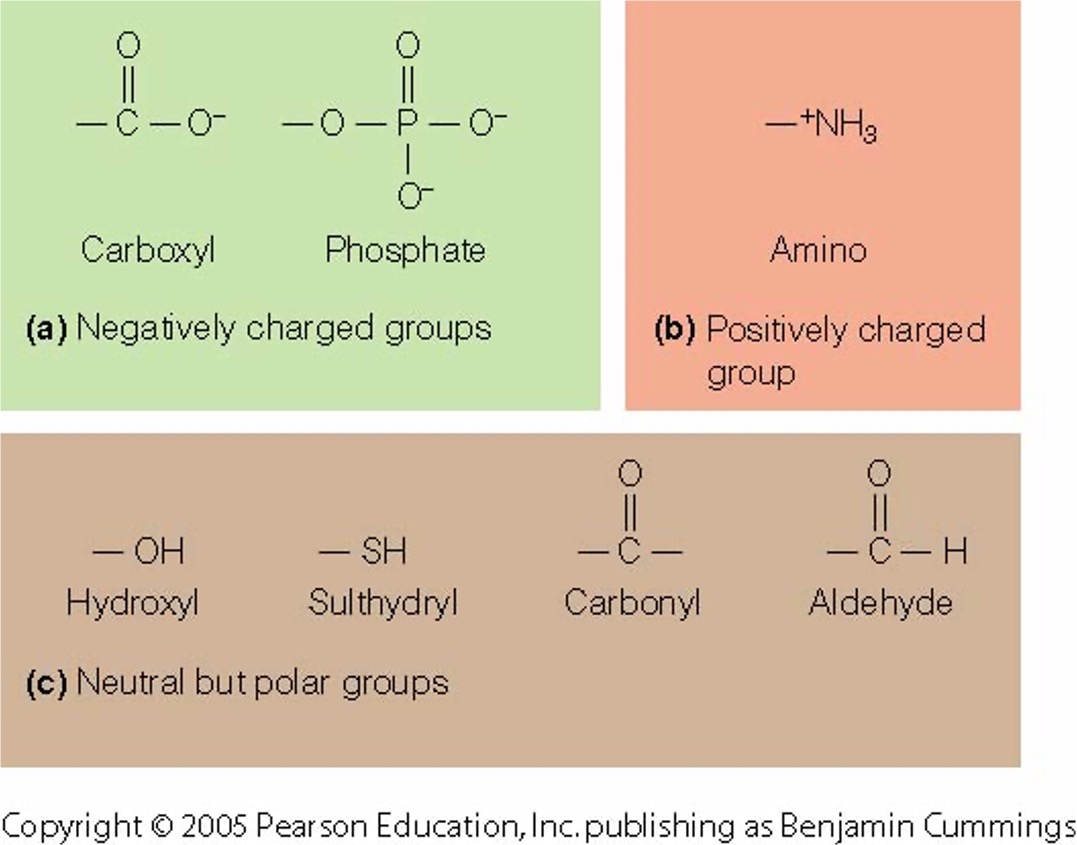
16
New cards
Describe the biologically important properties of water.
cohesion - H bond with itself, surface tension; adhesion - H bond with other things; polar - partial charges; universal solvent
17
New cards
Why and how are cell membranes permeable?
permeable to small non-polar molecules; some proteins act as gates/channels
18
New cards
What is an amphipathic molecule?
has both non-polar and polar ends
19
New cards
What is a condensation reaction (dehydration synthesis)?
when molecules are slammed together and a water pops out
20
New cards
What is hydrolysis?
when water is slammed into a bond to break molecules apart
21
New cards
Describe self-assembly.
proteins fold on their own by non-covalent interactions (partial or full charges, H bonds); some proteins need chaperones
22
New cards
What are the four basepairs of DNA?
A-T, C-G
23
New cards
How is the double helix held together?
nucleotides held by covalent phosphodiester bonds, helices stabilized by H bonds
24
New cards
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
DNA → RNA → Proteins
25
New cards
What is a gene?
piece of DNA transcribed into a RNA
26
New cards
What are the various types of RNA?
mRNA - carries DNA info out of nucleus; rRNA - ribosomal RNA; tRNA - transfer RNA; miRNA - micro RNA
27
New cards
How are enhancers and promoters used in the genome?
enhancers - attract transcription protein factors; promoters - TATA box, gets RNA polymerase to bind to DNA there
28
New cards
Describe post-transcriptional modifications.
5’ cap, 3’ poly A tail, splice out introns keep exons
29
New cards
What is a codon?
3 letter code (3 nucleotides) coding for 1 amino acid
30
New cards
Describe the steps of translation.
Initiation 1 - tRNA binds small subunit along with start codon; large subunit binds over tRNA complex
Elongation1 - tRNA brings in all following amino acids, making peptide bonds, empty tRNA ejected
Termination 1 - stop codon, 3/64 are stop codons, everything falls off and apart, peptide chain released
Elongation1 - tRNA brings in all following amino acids, making peptide bonds, empty tRNA ejected
Termination 1 - stop codon, 3/64 are stop codons, everything falls off and apart, peptide chain released
31
New cards
How is gene (protein) activity controlled?
transcription, post-transcription, translation, post-translation
32
New cards
Be able to draw an amino acid and a dipeptide.
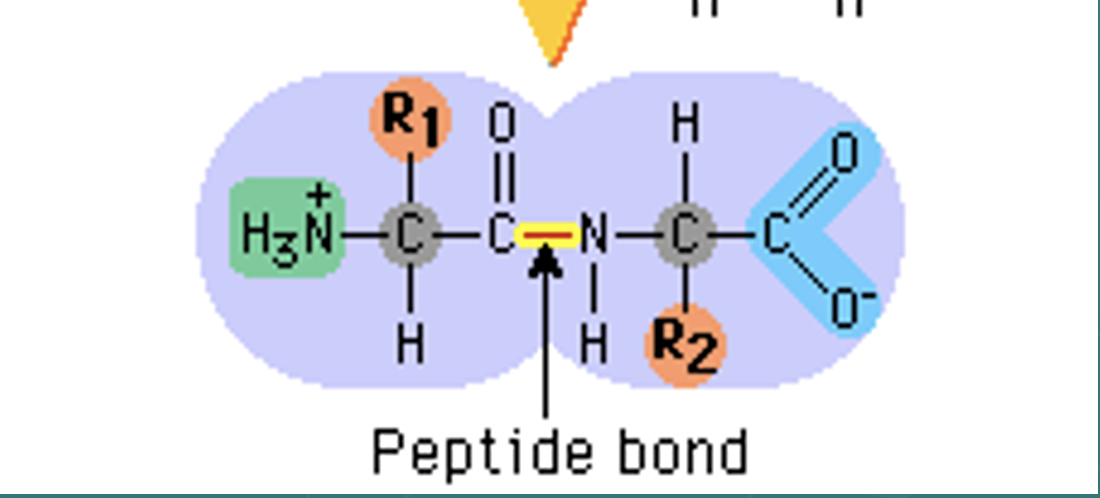
33
New cards
Be able to tell if an amino acid is hydrophilic or hydrophobic from its R group
polar - have NH2 or OH, basic have +, acidic have -; nonpolar = have CH3
34
New cards
What is a protein?
full folded functioning peptide
35
New cards
Define multimer proteins.
protein with multiple polypeptide chains
36
New cards
Describe the primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure of proteins.
primary - string of amino acids, secondary - alpha helices and beta sheets, tertiary - one subunits 3D conformation, quaternary - multimeric, multiple subunits conformation
37
New cards
Why are small molecules found in proteins?
add function to protein, like heme in hemoglobin
38
New cards
What is a catalyst and how do enzymes work?
catalysts speed up rxns, decrease activation energy, changes rate not eq.
39
New cards
Describe the active site, allosteric sites, and feedback inhibition.
active site - cluster where catalytic event occurs, allosteric site - away from the active site, feedback inhibition - enough product is made so a product binds to an allosteric site earlier in the pathway to shut it off
40
New cards
What are the two common covalent modifications to control protein activity?
phosphorylation - kinase, dephosphorylation - phosphatase
41
New cards
How does size limit a cell?
surface area to volume ratio, need adequate diffusion
42
New cards
What are the three domains of life?
eukaryota, bacteria, archaea
43
New cards
Describe the structure of Archaea and Bacteria.
don’t have organelles
archaea - use L-glycerol in membrane, isoprene in phospholipid bilayer, hydrocarbon chains can connect across, ribosomes like eukaryotes; halophiles - salty; thermophiles - hot
bacteria - peptidoglycan in cell walls, DNA circular, DNA has few proteins associated, distinct ribosomes
archaea - use L-glycerol in membrane, isoprene in phospholipid bilayer, hydrocarbon chains can connect across, ribosomes like eukaryotes; halophiles - salty; thermophiles - hot
bacteria - peptidoglycan in cell walls, DNA circular, DNA has few proteins associated, distinct ribosomes
44
New cards
Describe the properties of Eukarya
larger, membrane bound organelles to organize function, linear DNA, nucleus with chromosomes, exocytosis and endocytosis, mitosis/meiosis, complex RNA processing
45
New cards
What is Endosymbiotic Theory?
mitochondria came from aerobic bacteria engulfed by other prokaryote and made it a eukaryote; chloroplasts came from cyanobacteria in the same way
46
New cards
What does each of the organelles do?
plasma membrane - boundary, structure
vacuole - storage
ribosomes - make proteins
rough ER - site for ribosomes
smooth ER - makes lipids
nucleus - chromatin, DNA, double membraned
mitochondria - ATP
chloroplasts - triple bilayered, photosynthesis
golgi - protein sorting and modification
lysosomes - trash can
peroxisomes- carry things mitochondria to chloroplast
vesicles - secretory in and out of cell and through organelles
cytoskeleton - structural, microtubules - motility/chromosome movement, microfilaments - muscle movement, amoeboid movement, cleavage furrows
extracellular matrix - collagen and proteoglycan in animals; cellulose in plants
\
vacuole - storage
ribosomes - make proteins
rough ER - site for ribosomes
smooth ER - makes lipids
nucleus - chromatin, DNA, double membraned
mitochondria - ATP
chloroplasts - triple bilayered, photosynthesis
golgi - protein sorting and modification
lysosomes - trash can
peroxisomes- carry things mitochondria to chloroplast
vesicles - secretory in and out of cell and through organelles
cytoskeleton - structural, microtubules - motility/chromosome movement, microfilaments - muscle movement, amoeboid movement, cleavage furrows
extracellular matrix - collagen and proteoglycan in animals; cellulose in plants
\
47
New cards
Are viruses and prions alive?
no, no metabolism, needs hosts to live
48
New cards
What does a membrane do?
define limits of cell, creates internal organelles, pt. of contact between cell and environment
49
New cards
What are the major categories of lipids?
phospholipids and glycolipids, can have glycerol or sphingosine backbones
50
New cards
Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model.
membrane is big network of phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins, everyhting is vibrating/rotating in the plane of the membrane
51
New cards
What affects membrane fluidity?
anchored proteins, unsaturated tails move easier, less packing more fluid, cholesterol binds to phospholipids at high temp = less fluid / cholesterol prevents packing at low temps = more fluid
52
New cards
What do proteins do in the membrane?
let things in and out, anchor things, integral proteins - pass through membranes all the way, peripheral proteins - associated by binding on either face of bilayer, lipid anchored proteins - inserted into membrane, receptors, transport, enzymes
53
New cards
Microscopy that turns variations in refractive index (phase) into variations in contrast
phase contrast
54
New cards
Focuses light on the specimen
condenser lens
55
New cards
Microscopy that uses optical sectioning and a narrow depth of focus
confocal
56
New cards
The ability to distinguish two objects as separate entities
resolution
57
New cards
Studies the chemicals found within cells
biochemistry
58
New cards
Studies the information found in DNA
genetics
59
New cards
Product of textile industry that allowed visualization of cells
dye
60
New cards
The basic structural unit of living organisms that can perform the functions characteristic of life
cell
61
New cards
Wavelength shone onto fluorescent specimen
excitation
62
New cards
Wrote basic cell theory
Schwann
63
New cards
The angle of usable light that a lens can gather
angular aperture
64
New cards
Expanded cell theory to include that all cells arise from pre-existing cells
Virchow
65
New cards
Lens that gathers light from the specimen
obective
66
New cards
Wavelength gathered from fluorescent specimen
emission
67
New cards
Tool used to slice sections of a specimen for microscopy
microtome
68
New cards
Distance from center of a lens to the focal point
focal length
69
New cards
Named cells; saw dead ones
Hooke
70
New cards
A particle of light
photon
71
New cards
The study of cells
cytology
72
New cards
Microscopy that uses polarized light and coverts difference in refractive index (phase) into differences in brightness
DIC differential interference contrast
73
New cards
Microscopy that uses regular light on a specimen
bright field
74
New cards
Microscopy that uses molecules that are excited and emit a particular wavelength
fluorescence
75
New cards
idea that sperm contain preformed humans
homunculus
76
New cards
A method to visualize the inner surfaces of the plasma membrane
freeze fracture
77
New cards
Measure of the slowing down of light in anything other than a vacuum
refractive index
78
New cards
The phenomenon of waves bending after passing through a slit
diffraction
79
New cards
First to see living cells
Van Leeuwenhoek
80
New cards
Electron microscopy of the surface of a specimen
Scanning EM
81
New cards
The phenomenon that waves combine to reinforce or cancel each other out
interference
82
New cards
Commonly used fluorescent protein from a jellyfish
GFP
83
New cards
Lens that focuses light on the eye
ocular
84
New cards
Electron microscopy through a thinly sliced specimen
Transmission EM
85
New cards
The beginning of the polypeptide strand
N-terminus
86
New cards
DNA sequences that attracts transcription factors
Enhancer
87
New cards
Small RNA used to degrade mRNA
miRNA
88
New cards
Polymer of amino acids
protein
89
New cards
The process of transferring information from DNA to RNA
transcription
90
New cards
To refold a protein into its normal "native" state
renature
91
New cards
"water loving", polar molecules
hydrophilic
92
New cards
Occurs when a molecule breaks into two, consuming a water molecule in the process
hydrolysis
93
New cards
Polymer of sugars
polysaccharide
94
New cards
Property of water to hydrogen bond with other molecules
adhesion
95
New cards
The start codon
AUG
96
New cards
RNA used to bring amino acids to the ribosome
tRNA
97
New cards
Added to the 3' end of mRNA
poly A tail
98
New cards
Added to the 5' end of mRNA
cap
99
New cards
Energy required to break 1 mole of a bond (kcal/mole)
bond energy
100
New cards
Strand of DNA that is copied into RNA
gene