midterm
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
154 Terms
the institute of medicine report in 1999 concluded that roughly 98,000 patients die each year due to what?
medical error
define pressure ulcers
localized areas of tissue damage or necrosis that develop bc of pressure over a bony prominence
traditionally the care and prevention of pressure ulcers has been left to who?
nursing … physicians play a more passive role by signing off nursing initiated orders
what is the current costs of providing care for 1 pressure ulcer?
$3500 - $60,000 depending on stage
define competency
ability or skill; skill needed to perform in a particular role, knowledge in particular domain or value that can be expressed in exaction or combo of all 3
describe competency in terms of a nurse taking care of a cancer patient
skill → placing IVs, listening to patient
knowledge → experience w chemo drugs, knowing what to look for
value → respect for patient’s feelings and preferences
define common competencies
those expected of all health practitioners
define complementary competencies
unique competencies that enhance the delivery of healthcare
define collaborative competencies
those that each profession needs to work together w others
list the 4 competency domains
value/ethics for interprofessional practice
roles/responsibilities
interprofessional communication
teams and teamwork
describe competency domain 1
values and ethics
focus on values of relationships w patients, other professionals etc.
work w individuals of other professions to maintain climate of mutual respect and shared values
describe competency domain 2
roles and responsibility
understanding of how professional roles/responsibilities complement each other
able to clearly describe one’s own professional role and responsibilities to team members and understand others’ roles in relation to one’s own
each profession’s roles vary w/in legal boundaries and will change depending on specific care situation
describe competency domain 3
interprofessional communication
communicating a readiness to work together assist in collaboration
being available, receptive, and willing to discuss - indicate readiness
teamwork and team based competency for better patient centered care requires mastery of new communication technologies
describe competency domain 4
teams and teamwork
cooperating in delivery of care and coordinating one’s care w other professionals so that gaps, redundancies and errors are avoided
shared accountability, problem solving and decision making = characteristics of collaborative/effective teamwork
describe the cell walls of a gram positive bacterium
thick peptidoglycan layer that contains teichoic and lipoteichoic acids
out to in - peptidoglycan → periplasmic space → plasma membrane
describe the cell walls of a gram negative bacterium
thin peptidoglycan layer and outer membrane that contains lipopolysaccharide, phospholipids, and proteins
periplasmic space contain transport, degradative and cell wall synthetic proteins
outer membrane joined to cytoplasmic membrane at adhesion points and is attached to peptidoglycan by lipoprotein links
out to in - outer membrane → periplasmic space → peptidoglycan → peripalsmic space → plasma membrane
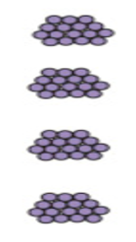
this gram stain is of a gram positive or negative bacteria?
positive
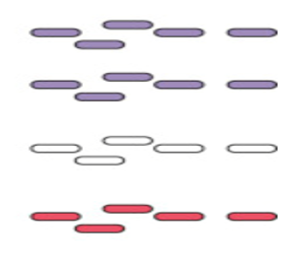
this gram stain is of a gram positive or negative bacteria?
negative
what is a risk factor of antibiotic use to treat C diff?
disrupt barrier function of normal colonic flora, providing niche for C diff to multiply and elaborate toxins
make it more virulent by increasing antibiotic resistance
the risk factor of antibiotic use to treat C diff is associated with what antibiotics?
fluoroquinolone (cipro, levofloaxcin) and clindamycin
why is age a risk factor of C. diff?
comorbidities and suppressed immune system
why is gastric acid suppression a risk factor for C diff?
PPI use *****
is C diff gram positive or gram negative?
gram positive anaerobic spore forming bacillus
C diff produces 2 toxins, describe them
A - enterotoxin that destroys tight cell junctions leading to increased permeability of the intestinal wall and thus diarrhea
B - cytotoxin that targets actin and destroys cellular cytoskeletons
C diff produces surface layer proteins which allows organisms to do what?
bind to intestinal epithelium and cause local damage
which toxin was found to be essential for C diff virulence?
B
what is the treatment of C diff?
stop inciting antibiotic, place in isolation precautions, oral vancomycin or fidaxomicin
recurrent refractory C diff is treated with what?
fecal transplant
how can we prevent/control C diff?
infection control to track and keep surveillance data, enforcing hand hygiene, contact precautions (bathroom in patient room, use of gloves and gowns), cleanliness of C diff patient rooms with sporicidal antiseptic agents, disposable equipment
what are the 4 phases of clinical trials?
assess drug safety and find dosage
efficacy and side effects
compare new treatment w current to see which is better
safety and efficacy
what is bezlotoxumab?
human IgG1 monoclonal antibody which binds to C diff toxin B and neutralizes it to prevent its toxic effects
what is actoxumab?
monoclonal antibody against C diff toxin A
How was the study organized in the “Bezlotoxumab for prevention of recurrent C diff infection” journal?
2 double blind randomized placebo controlled phase 3 trials
2000+ adults receiving standard of care oral antibiotics were randomized into 4 groups (bezlotoxumab, actoxumab, combo, and normal saline placebo)
rank the treatment groups from smallest infection recurrence to largest
actoxumab-bezlotoxumab → bezlotoxumab → actoxumab → placebo
the use of bezlotoxumab together with standard oral antibiotic therapy was associated with what result?
significantly lower rate of recurrent infection than oral antibiotic therapy alone
did the addition of actoxumab produce any significant results in the bezlotoxumab study?
no, it didn’t improve efficacy
who are hospitalists?
specialists in inpatient medicine who will be responsible for managing care of hospitalized patients in the same way that primary care physicians are responsible for managing care of outpatients
define patient centered care
providing care that is respectful of and responsive to individual patient preferences, needs, values and ensuring that patient values guide all clinical decisions
define patient experience
sum of all interactions, shaped by an organization’s culture, that influence patient perceptions across continuum of care
how is patient experience measured and what does it measure?
measured by patient satisfaction survey and measures patients perception about communication w nurses and Drs, communication ab medicines, pain management, cleanliness and quietness, responsiveness of staff, discharge information and overall ranking
define patient engagement
actions taken by individuals to obtain greatest benefit from health care services available to them
greater patient involvement in care
what are the hospitalist values?
concern for value of care, delivering patient centered care, ensuring safe and timely discharges, making accurate diagnosis, communicating clearly
what are the requirements to becoming a hospitalist?
MD or DO, 3 years in internal medicine or sometimes family medicine
skills → those of internist
knowledge → extensive medical knowledge to make diagnoses
what is the correlation between quality and cost?
improved quality is usually less expensive
hospitalists will be expected to embrace what?
concept of value and drive its use into everyday practice
define quality
safe, effective, efficient, equitable, patient centered
define cost
unit cost of care delivery by hospitalists
what is the equation for value?
value = quality/cost
define value for clinicians
decreasing overuse and inefficiency, while improving compliance w evidence based care
define value for patients
enriching the patient experience and concentrating on patient centered outcomes
give an example of something that is of high cost but produces high net benefit and high value
MRI for epidural abscess
give an example of something that is of high cost but produces low net benefit and low value
routine MRI for low back pain
give an example of something that is of low cost but produces high net benefit and high value
universal HIV screening
give an example of something that is of low cost but produces low net benefit and low value
preoperative testing prior to low risk surgery
endocarditis is an infection caused by what?
bacteria that enter the bloodstream and settle in heart lining, heart valve or blood vessel
how does endocarditis manifests itself?
mass of platelets, fibrin, microorganisms, and scant inflammatory cells
endocarditis most commonly involves what in the body?
heart valve
describe the mortality of endocarditis
high → 15-22% in hospital and 40% w/in 5 years
describe the endocarditis team
team led by cardiac surgeons that brings together cardiac surgeons, cardiologist, endocardiographers, and infectious disease specialists to discuss diagnosis and management of cases
describe the following of the endocarditis team
intervention, primary endpoint, and secondary endpoint
intervention = formation of team
primary end pt. = impact of the team on the rate of all-cause in-hospital mortality
secondary end pt. = evaluate effect of team on 6 month and 1 yr mortality, rate of surgery, time to surgery, duration of antibiotic treatment, length of hospital stay, occurrence of cardiac or neurological sequelae
what were the outcomes of the endocarditis team?
significant reductions in time to surgical procedure, duration of antibiotic treatment and length of hospital stay
found nonsignificant reductions in in-hopsital 6 month and 1 yr mortality rates
team and surgery were independent factors linked to survival
what are the responsibilities and roles of a medical and health services manager?
lead and manage healthcare organizations
set and monitor organizational strategy
monitor performance
implement business functions of finance, HR management, information management, marketing, and environmental management
concern over the fiscal health of organization
what are the education requirements for medical and health services managers?
MPH, MHA, or MBA (maybe a hospital fellowship too)
in smaller settings, bachelor’s degree is sufficient
no licensing (except for nursing home administrators)
what is a consequence of no standard licensing for medical and health services managers?
substantial variability in the educational backgrounds and experiences
what are the values of medical and health services managers?
appreciate systems aspect of their work (understand how micro-decisions affect everything/one), loyal to their organization and its success, comfortable working in chain of command, value interpersonal skill and organizational political skill, and evidence based management (use of research evidence on management decision making)
occupational interests is defined as what?
preferences in work environment
O*NET interests → realistic, investigative, artistic, social, enterprising, and conventional
define the realistic occupational interest from the O*NET program
involve work activities that include practical, hands on problems and solutions
deal w plants, animals and real-world materials
many of the occupations require working outside and don’t involve a lot of paperwork or working w others
define the investigative occupational interest from the O*NET program
working w ideas, and requires an extensive amt of thinking
involve searching for facts and solving problems mentally
define the artistic occupational interest from the O*NET program
working w forms, designs and patterns
require self-expression and work can be done w/o following clear set of rules
define the social occupational interest from the O*NET program
working with, communicating with and teaching people
helping or providing service to others
define the enterprising occupational interest from the O*NET program
starting up and carrying out projects
leading people and making many decisions
require risk taking and often deal w business
define the conventional occupational interest from the O*NET program
following set procedures and routines
working w data and details more than w ideas
clear line of authority to follow
define accountable care organization
groups of Dr, hospitalists and other healthcare providers who come together voluntarily to give coordinated high quality care
define beneficiary
person that receives any of the benefits of insurance coverage
define capitation
payment of a fee to a healthcare provider providing services to a number of people, such that the amt paid is determined by the number of total patients
define coinsurance
amt a beneficiary must pay for medical care after they have met their deductible
insurance company may pay for 80% of an approved amt and the patient will pay 20%
define copayment
flat fee that a beneficiary must pay each time they receive medical care
patient may pay $10 for every dr visit, while insurance plan covers rest
define coverage limits
max amt that a health insurance plan may pay for certain healthcare services
some polices may also have a max annual or lifetime coverage amt
after any of these limits are reached, then the policyholder may have to pay for the remaining costs
define deductible
amt of the beneficiary must pay each year before their health insurance coverage plan begins paying
define exclusions/limitations
services that are not covered by a plan, must be clearly define in plan literature
define fee for service
payment system where healthcare services are unbundled and paid for separately
define formulary
insurance providers list of covered drugs
define health maintenance organization (HMO)
form of managed care in which all care is received from participating providers w/in the network
referral from primary care provider needs to be obtained prior to seeing specialists
define health reimbursement account (HRA)
account established by employer to pay an employee’s medical expenses
only the employer can contribute to HRA
define health savings account (HSA)
account established by an employer or individual to save $ toward medical expenses on a tax free basis
why do many small businesses don’t offer employer based insurance?
increased costs of premiums
describe private insurance
a growing market in which an employee will buy their own insurance bc their employer doesn’t offer it
more expensive
define medicare
federal insurance for people over 65 years old regardless of medical history or income
describe the following of medicare part A
description, coverage, premium payments, portion of benefit spending
hospital insurance plan largely financed through social security taxes from employers and employees
coverage - hospital stays, skilled nursing facility stays, home health visits, and hospice care
premium - most don’t pay as long as they or their spouse paid medicare taxes while working, if don’t qualify then they pay $441/month
benefit spending - 31% of total
describe the following of medicare part B
description, coverage, premium payments, portion of benefit spending
outpatient services insurance financed by federal taxes and monthly premium from beneficiaries
coverage - ppl eligible for A and elect to pay B premium, Dr visits, outpatient services, home health visits, required equipment (wheelchair + walkers)
premium - pay standard amt but can be adjusted based on income
benefit spending - 20% of total
describe the following of medicare part C
description, coverage, premium payments, portion of benefit spending
medicare advantage program, through which beneficiaries can enroll in private health plan and receive medicare covered benefits
coverage - Part A,B and/or D services
premium - determined by private health plan
benefit spending - 22% of total
describe the following of medicare part D
description, coverage, premium payments, portion of benefit spending
voluntary, subsidized outpatient prescription drug benefit
coverage - outpatient prescription drugs
premium - monthly premium that varies, include copayments/coinsurance
benefit spending - 11% of total
define medicaid
largest health insurance program in US covering 1/5 people and 1/3 children
administered by individual states w federal govt. support
must be low income and a child, pregnant, adult w dependent children, have a severe disability or over 65 years old
describe the affordable care act
legislation aimed at decreasing number of uninsured
intended to streamline healthcare delivery and improve healthcare outcomes
expand medicaid coverage to those in poverty and establish state level health insurance exchanges
define medical ethics
rigorous academic discipline that combines philosophy, history, sociology and theology which helps clinicians navigate complex moral choices
what are the 4 widely accepted facets of medical ethics that constitute values of the field?
autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence and justice
define autonomy
patient has the right to refuse or choose their treatment
necessary to empower patients to make informed decisions about their health
informed consent, medical confidentiality, listening to patients/answering questions
describe beneficence
clinician should act in the best interest of the patient at all times
provide net medical benefit to patients w minimal harm
must be ablate provide best treatments possible and need rigorous effective education and training both before and during working
describe nonmaleficence
to do no harm
all decisions must be made w respect to risks/harms that patient can face (physical, $$, psychological)
describe justice
fair and equitable distribution of limited healthcare resources
moral obligation to act on basis of fair adjudication b/w competing claims