Systematics
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Systematics
the study of the units of biodiversity, dealing with diversification of lineages through time
inferring phylogeny (relatedness) of extinct and extant (still living) species
using organismal features — morphological, chromosomal, molecular
finding common characters between species
Taxonomy
classificaiton of animals
Phylogeny
evolutionary relationships
Carolus Linnaeus
created the current scheme that we still use today
Taxonomic Categories
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
species
*some groups are incredibly diverse and need to include extra ranks (suborder and subfamily)
Binomial Nomenclature
Genus name, species name
latin names, in italics
Genus is always capitalized, species is lower case
What defines a species
common descent
always need a common ancestor
smallest distinct grouping
molecular and chromosomal characters
reproductive community
interbreeding
mule = male donkey x female horse; cannot reproduce — technically not a true species
Species Concepts
most common: biological species concept
reproductive community of populations
occupy a specific niche
zoologists agree that a species should constitute a lineage with a unique history of evolutionary descent
DNA Barcoding
using a DNA sequence common to all animals
cytochrome C oxidase: protein complex
variation of this gene sequence is smaller within species than between
need blood or tissue sample
Issues with DNA barcoding
sometimes you don’t have blood or tissue to work with so you can’t use this
ex; working with bones or fossils
Homology
character similarity from a common ancestor
ex; endothermy (warm-bloodedness) in humans and bears — feature comes from common ancestor
Convergent Evolution
independent evolution of the same characteristic
ex; endothermy evolved in birds and mammals separately (arose twice in evolutionary history)
Phylogenetic Trees
similar to a cladogram but includes more information, usually genetic
e.g., base substitutions in a specific gene
Cladograms
nested hierarchy of branches with similar derived characters
Phylogeny
evolutionary relationships can take 1 of 3 forms:
monophyly
paraphyly
polyphyly
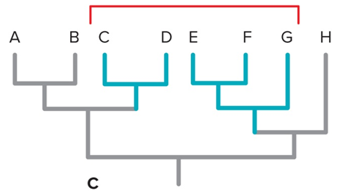
Monophyly
single common ancestor + all descendants
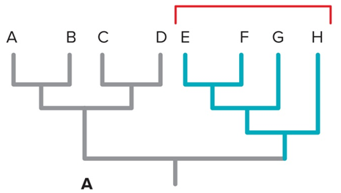
Paraphyly
common ancestor and some of its descents
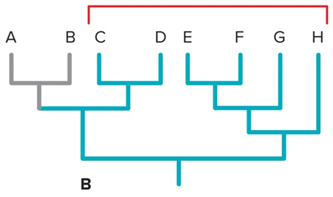
Polyphyly
grouping with no recent common ancestor
LUCA
last universal common ancestor (we don’t actually know what it is)
The Future of Taxonomy?
taxonomy is constantly changing and is not perfect!
we don’t know everything about everything!
e.g., Euspira lewisii is now Neverita lewisii
New taxonomic system in development: Phylocode
based on phylogeny
not hierarchical rankings
could someday replace binomial nomenclature