Life Science 15
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:40 AM on 6/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
1
New cards
What is scientific thinking?
Scientific thinking acts as a framework for experimentation (a systematic way for us to test out ideas and draw meaningful conclusions).
Rule out explanations that aren’t true to get closer to what is true.
Rule out explanations that aren’t true to get closer to what is true.
2
New cards
How is scientific thinking different from the scientific method?
Scientific thinking and the scientific method are the same things.
The term “scientific method” sounds more rigid and “scientific thinking” sounds like a way of life.
The term “scientific method” sounds more rigid and “scientific thinking” sounds like a way of life.
3
New cards
What are the steps for the scientific method?
Step 1: Make observations
* Before you can come up with a question about something, you have to first observe it through your senses (sight, smell, touch…)
* Look for patterns or cause-and-effect relationships
\
Step 2: Formulate a Hypothesis
* Hypotheses are testable and refutable explanations for something observed in nature
Step 3: Make predictions
* Typically take the form if __*___*__ then ___
* Predictions are differentiated from hypotheses because you’re actually forecasting/predicting the future
\
Step 4: Device and Carry out the Experiment
* Gives the ability to determine whether a hypothesis is correct
* Experiments have to be carefully designed so that you can gain true knowledge and have certainty over what you discover.
Step 5: Draw a conclusion, Make Revisions
* If our hypothesis isn’t true, we go back and modify it and go through the process again.
\
* Before you can come up with a question about something, you have to first observe it through your senses (sight, smell, touch…)
* Look for patterns or cause-and-effect relationships
\
Step 2: Formulate a Hypothesis
* Hypotheses are testable and refutable explanations for something observed in nature
Step 3: Make predictions
* Typically take the form if __*___*__ then ___
* Predictions are differentiated from hypotheses because you’re actually forecasting/predicting the future
\
Step 4: Device and Carry out the Experiment
* Gives the ability to determine whether a hypothesis is correct
* Experiments have to be carefully designed so that you can gain true knowledge and have certainty over what you discover.
Step 5: Draw a conclusion, Make Revisions
* If our hypothesis isn’t true, we go back and modify it and go through the process again.
\
4
New cards
Hypothesis vs. Theory
A hypothesis is a supposition or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation.
Theories are hypotheses about the natural world that are extremely well-supported by empirical data, and also tend to be broader in scope.
Theories are hypotheses about the natural world that are extremely well-supported by empirical data, and also tend to be broader in scope.
5
New cards
What is power?
Power is how confident you are about the results of your experiment
6
New cards
What are the three ways to increase power?
1) Randomize the subjects across control and experimental groups
* Don’t let people sign up for what they want, because if they want it they’ll probably behave with a motive in mind and skew the results.
2) Control
* Control for other variables to make sure there are no underlying differences between groups
* Ex. For the experiment about strength, we want to control for age
3) Use a double-blind design
* Don’t le the subject or the researcher know about which treatment they’re receiving or administering, because when someone knows something should happen this could skew the results
* Removes potential biases/knowledge
* Don’t let people sign up for what they want, because if they want it they’ll probably behave with a motive in mind and skew the results.
2) Control
* Control for other variables to make sure there are no underlying differences between groups
* Ex. For the experiment about strength, we want to control for age
3) Use a double-blind design
* Don’t le the subject or the researcher know about which treatment they’re receiving or administering, because when someone knows something should happen this could skew the results
* Removes potential biases/knowledge
7
New cards
What is pseudoscience? Why is it harmful?
Pseudoscience is when individuals make scientific-sounding claims that are not supported by truth worthy, methodical scientific studies.
They are harmful because they present statements as “facts” that can be misleading.
They are harmful because they present statements as “facts” that can be misleading.
8
New cards
What are anecdotes? Why are they unreliable?
Anecdotes are based on one or a few observations, people conclude that there is or is not a link between two things.
They do not include a large representative population and are not data
They do not include a large representative population and are not data
9
New cards
What is evolution?
Change in allele frequencies of a population over time.
10
New cards
What are genes?
Length of DNA that carries genetic information necessary for producing a functional product. (ex. Protein, trait such as eye color).
11
New cards
What are alleles?
Variation of a gene. We have 2 alleles for each gene because we get one from each parent.
Heterozygous = One domain and one recessive allele (Bb)
Homozygous = Two dominant alleles (BB) or two recessive alleles (bb).
Heterozygous = One domain and one recessive allele (Bb)
Homozygous = Two dominant alleles (BB) or two recessive alleles (bb).
12
New cards
Genes and alleles are both related to DNA. What is the difference between the two?
Genes are the instruction how to build something, and alleles are the different possible variations in those instructions.
13
New cards
What does natural selection consist of?
Necessary and sufficient conditions.
1) Variation: Variation for traits
2) Heritability: Offspring resemble parents more than other individuals in the population.
3) Differential Reproductive Success: Some individuals leave more offsprings than others.
1) Variation: Variation for traits
2) Heritability: Offspring resemble parents more than other individuals in the population.
3) Differential Reproductive Success: Some individuals leave more offsprings than others.
14
New cards
What Is Artificial Selection?
A subset of natural selection where humans cause changes in alleles frequency within a population (Ex. dog breeding).
15
New cards
What are the modes of selection?
1) Directional Selection
2) Stabilizing Selection
3) Disruptive Selection
2) Stabilizing Selection
3) Disruptive Selection
16
New cards
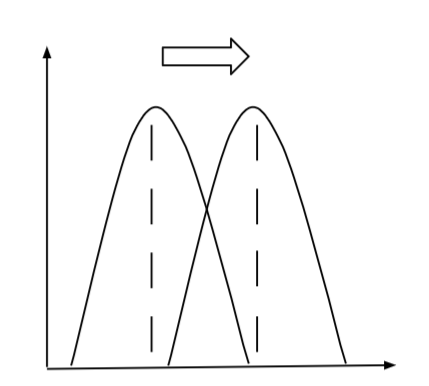
What is Directional Selection?
(Part of Artificial Selection) occurs when individuals with traits on one side of the mean in their population survive better or reproduce more than those on the other.
EX. Miniature ponies - Breeding ponies and then breeding their offsprings with smaller ones and smaller.
EX. Miniature ponies - Breeding ponies and then breeding their offsprings with smaller ones and smaller.
17
New cards
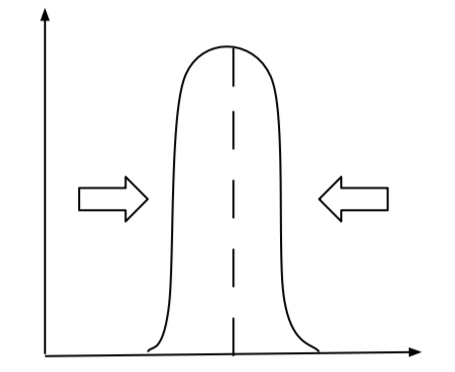
What is Stabilizing Selection?
(Part of Artificial Selection) tends to remove the more severe phenotypes, resulting in the reproductive success of the norm or average phenotypes.
EX. The weight of a baby, we want it to be average size, not too big or not too small.
EX. The weight of a baby, we want it to be average size, not too big or not too small.
18
New cards
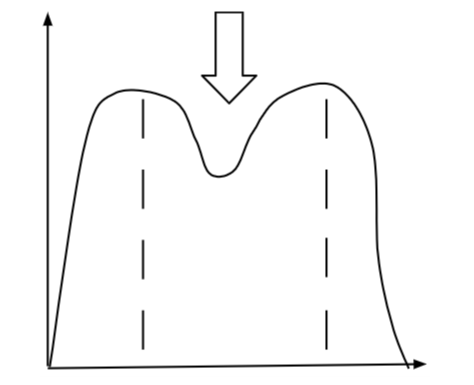
What is Disruptive Selection?
(Part of Artificial Selection) when more extreme phenotypes (or genotypes) within a population have a fitness advantage over intermediate individuals.
EX. Coho Salmon
The ones that are smaller can fit in tighter places and fertilize eggs without others noticing.
The big ones are fighting for territory or eat intruder fishes
The ones in the middle are too slow and big but not big enough.
EX. Coho Salmon
The ones that are smaller can fit in tighter places and fertilize eggs without others noticing.
The big ones are fighting for territory or eat intruder fishes
The ones in the middle are too slow and big but not big enough.
19
New cards
The long-term consequence of stabilizing selection on a population is that the selected trait’s mean value__ and the trait’s variance is ____
stays the same; reduced
20
New cards
What are the agents of Evolution?
1. Gene Flow/Migration
2. Genetic Drift
3. Mutation
4. Natural Selection
21
New cards
What is gene flow/Migration?
Movement of alleles from one population to another due to migration and subsequent reproduction/mating of individuals.
* Changing allele frequencies because some individuals leave and new individuals come.
* Is it enough for individuals to just move to a new era? No, they must reproduce.
* Changing allele frequencies because some individuals leave and new individuals come.
* Is it enough for individuals to just move to a new era? No, they must reproduce.
22
New cards
What is Genetic Drift?
Random change in allele frequencies within a population.
* Happens due to chance (doesn’t matter if good or bad);
* Ex. Population of Bb x Bb offspring (only bb now)
* Happens due to chance (doesn’t matter if good or bad);
* Ex. Population of Bb x Bb offspring (only bb now)
23
New cards
What is Mutation?
Any random change in genetic material (DNA) of an organism.
* Can be caused by radioactivity or UV Radiation.
* Can be caused by radioactivity or UV Radiation.
24
New cards
What is Natural Selection?
Nonrandom elimination of alleles.
* Necessary and Sufficient conditions as followed:
1. Variation of trait
2. Heritability
3. Differential Reproductive Success
* Necessary and Sufficient conditions as followed:
1. Variation of trait
2. Heritability
3. Differential Reproductive Success
25
New cards
Is “survival of the fittest” a good term to describe natural selection? Why or why not?
It is not a good term. Evolutionary success has more to do with __relative reproductive success__ than survival.
Fitness would mean an organism’s reproductive success compared to other organisms in the population in a specific environment.
Fitness would mean an organism’s reproductive success compared to other organisms in the population in a specific environment.
26
New cards
What is Sexual Selection?
Occurs when a trait increases fitness making that individual more attractive to the opposite sex, but decreases survival.
27
New cards
What are the two examples of Sexual Selection?
Example One: Peacocks
* Eyespots are more attractive to peacocks because it indicates access to resources and longevity.
* The underlying features of him serving attracts the female peacock.
* Maybe in more danger but will be more likely to mate and pass on alleles.
Example Two: Frigate Birds/Height In Humans
* Frigate birds are more popular when they have large, red chests.
* Female humans tend to prioritize height in their partners.
* Eyespots are more attractive to peacocks because it indicates access to resources and longevity.
* The underlying features of him serving attracts the female peacock.
* Maybe in more danger but will be more likely to mate and pass on alleles.
Example Two: Frigate Birds/Height In Humans
* Frigate birds are more popular when they have large, red chests.
* Female humans tend to prioritize height in their partners.
28
New cards
What is nature versus Nurture debate about?
Nature: Genes, traits stay the same irrespective of where you were born and raised.
Nurture: Environment, refers to how you were brought up, your environment.
The divide between nature and nurture isn’t always clear. For example, Height (someone has the gene for being tall, but are not getting enough nutrients in their diet)
Nurture: Environment, refers to how you were brought up, your environment.
The divide between nature and nurture isn’t always clear. For example, Height (someone has the gene for being tall, but are not getting enough nutrients in their diet)
29
New cards
What is a Phenotype?
The treats/behavior you observe of an organism (ex. Eye color, height, intelligence)
30
New cards
What is a Genotype?
Genes you carry
31
New cards
What is Norm Of Reaction?
All of the possible phenotypes that can be produced by a single genotype if it were raised in all possible environments.
* There is flat and steep Norms of Reactions
* There is flat and steep Norms of Reactions
32
New cards
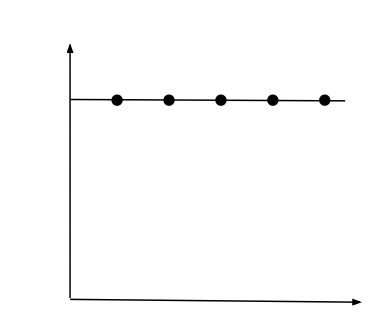
What Is a Flat Norm of Reaction?
Particular genotype always produces the same phenotypes regardless of the environment. The environment doesn’t make a big difference.
Ex. Eye color
* Phenotypes is the y-axis and the environment is the x-axis.
Ex. Eye color
* Phenotypes is the y-axis and the environment is the x-axis.
33
New cards
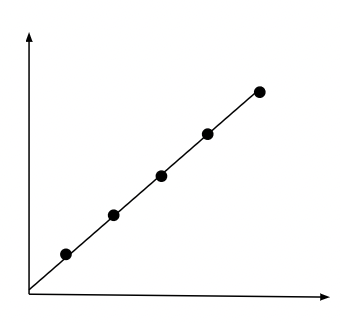
What is a Steep Norm of Reaction?
Particular genotypes can produce many different phenotypes, depending greatly on the environment.
Ex. Height and calcium intake, body weight and the amount of food one eats.
Ex. Height and calcium intake, body weight and the amount of food one eats.
34
New cards
What is a genome?
All of an organism’s genetic material (human genome = every person’s genetic material)
35
New cards
What is a Karyotype?
A picture of all the chromosomes when cells are dividing.
36
New cards
What is Mendel’s First Law?
Segregation.
When an organism makes gametes, each gamete receives one allele.
Fertilization combines the alleles so that the offspring has 2 alleles for each gene.
When an organism makes gametes, each gamete receives one allele.
Fertilization combines the alleles so that the offspring has 2 alleles for each gene.
37
New cards
What is DNA?
Sequence of bases (AGC) that give instructions on how to build chemicals/proteins that form our bodies.
38
New cards
What are chromosomes?
Linear Strands of DNA
39
New cards
What are homologous chromosomes?
A set of one maternal chromosome and one paternal chromosome (we have 23 homologous pair).
40
New cards
What are Autosomal Chromosomes?
Chromosome pairs 1 to 22 non-sex chromosomes (44 single).
41
New cards
What are Sex Chromosomes?
Can be X or Y chromosome
Determines the sex of the baby (XX is female. XY is male.)
Dad chooses the gender of the baby because he has the Y chromosome.
Determines the sex of the baby (XX is female. XY is male.)
Dad chooses the gender of the baby because he has the Y chromosome.
42
New cards
What is a Gamete?
Cells used during sexual reproduction, Sperm and Egg.
43
New cards
What is a Diploid?
Cell that contains a complete set of chromosomes from both parents.
44
New cards
What is a haploid?
Cells with a set of unpaired chromosomes (ex. Gametes)
45
New cards
What is Mitosis?
Reproduction of Somatic cells (Everything besides sex cells)
46
New cards
What is Meiosis?
Process that produces sperm and egg cells.
47
New cards
How many chromosomes do we have before meiosis?
During meiosis?
After fertilization
During meiosis?
After fertilization
Before Meiosis = Diploid
During Meiosis = Haploid
After Fertilization = Diploid
During Meiosis = Haploid
After Fertilization = Diploid
48
New cards
What are Punnett squares used for?
Helps determine what genotype an offspring will have
When drawing the Punnett square females go on the top and males on the side.
Use X/Y superscripts so we know who is Male or female (no superscript for Y chromosome)
When drawing the Punnett square females go on the top and males on the side.
Use X/Y superscripts so we know who is Male or female (no superscript for Y chromosome)
49
New cards
What are Sex-Linked Traits?
Genes that are only found on the X chromosome.
Inheritance of traits may differ between males and females depending on whether the gene is recessive or dominant.
Males are more likely to have traits passed down from mothers because the girls have an extra X which is their second chance.
Inheritance of traits may differ between males and females depending on whether the gene is recessive or dominant.
Males are more likely to have traits passed down from mothers because the girls have an extra X which is their second chance.
50
New cards
What is Altruism? Does it exist?
Altruism: Acts of kindness with no benefits for the individual who performs them but are beneficial to other individuals. It does not exist in nature because kindness has a degree of selfishness. However, we are still kind to others because we want something in return that will increase our fitness. Not real “altruism.”
51
New cards
How is sex determined?
Male Heterogamety: Sex is determined by which sex chromosome is passed down by the father (Ex. Humans)
Female Heterogamety: Sex is determined by which sex chromosome is passed down by the mother (F-XZ/M-XX) Ex, Birds (penguins and Flamingos)
Ploidy: Females are diploid, males are haploid. Females can choose whether to fertilize their eggs with sperm that they collect. Unfertilized eggs remain haploid and develop into male bees.
* This means that male bees do not have fathers, but have a grandfather. (Ex. beens, ants, wasps
Incubation Temperature: Sex is determined by the temperature of eggs (warm = female, cold = male) Ex. Turtles, other reptiles and amphibians
Female Heterogamety: Sex is determined by which sex chromosome is passed down by the mother (F-XZ/M-XX) Ex, Birds (penguins and Flamingos)
Ploidy: Females are diploid, males are haploid. Females can choose whether to fertilize their eggs with sperm that they collect. Unfertilized eggs remain haploid and develop into male bees.
* This means that male bees do not have fathers, but have a grandfather. (Ex. beens, ants, wasps
Incubation Temperature: Sex is determined by the temperature of eggs (warm = female, cold = male) Ex. Turtles, other reptiles and amphibians
52
New cards
Are males or females more likely to have Red-Green Colorblindness/recessive sex-linked traits?
Males… if they get just one recessive allele they will have the trait
Females won’t get it unless both mom and dad pass down the recessive alleles.
If the mother has one recessive allele, males have a 50% chance of inheriting that trait (females have 0 or 50% depending on the father)
If the mother has two recessive alleles, males have a 100% chance of inheriting that trait (females have a 0 0r 100% depending on the father)
If the mother is homozygous dominant, both male and female offspring have a 0% of getting colorblindness.
Females won’t get it unless both mom and dad pass down the recessive alleles.
If the mother has one recessive allele, males have a 50% chance of inheriting that trait (females have 0 or 50% depending on the father)
If the mother has two recessive alleles, males have a 100% chance of inheriting that trait (females have a 0 0r 100% depending on the father)
If the mother is homozygous dominant, both male and female offspring have a 0% of getting colorblindness.
53
New cards
When does the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium occur?
1. When there is no evolution occurring
2. When there is random mating
54
New cards
What is the difference between incomplete dominance and codominance?
Incomplete Dominance: Dominant allele does not mask the effects of recessive allele.
Codominance: Both alleles are expressed.
Codominance: Both alleles are expressed.
55
New cards
What is produced through Meiosis 1?
1. Chromosomes become visible (uncoiled)
2. Chromosomes duplicate themselves (remember they are actually linear!)
3. Crossing over (Recombination) - 4 Unique strands
4. Tetrads line up in the center of the cell
5. Pulling tetrads apart, become centromeres do not split (still X and X)
* Still have copies for every gene
56
New cards
What is produced through Meiosis 2?
1. Sister chromatids become visible
2. Centromeres begin to split
* Eggs: Uneven division of cytoplasm.
3. Result: 4 Gametes are produced for sexual reproduction from each parent.
57
New cards
What problem can happen during cell division? When can it occur?
Unequal distribution of chromosomes
Occurs during Meiosis 1, meiosis 2, or Mitosis
Meiosis 1: Nondisjunction
* Homologous do not separate 3 V.S 1 chromosomes
* E..g 3 #21 Chromosomes -→ Down Syndrome
* E.g Too many/toofew sex chromosomes
Occurs during Meiosis 1, meiosis 2, or Mitosis
Meiosis 1: Nondisjunction
* Homologous do not separate 3 V.S 1 chromosomes
* E..g 3 #21 Chromosomes -→ Down Syndrome
* E.g Too many/toofew sex chromosomes
58
New cards
What is Shared Genes/ Kin Selection?
When alleles that you have causes you to try to improve the reproductive selection for another individual carrying those same alleles (family/relatives). Being kind to them increases the likelihood that the alleles you shared will be passed on.
59
New cards
What is Indirect Fitness? Direct Fitness? Inclusive Fitness?
Indirect Fitness + Direct Fitness = Inclusive Fitness
Indirect Fitness + Direct Fitness = Inclusive Fitness
Indirect Fitness: Fitness from the shared allele that are passed down from your relatives.
Direct Fitness: Fitness from personal reproduction more offspring yourself relative to other individuals and passing down those alleles.
Inclusive Fitness: Fitness - Reproductive Success of yourself and relatives/# of genes that are passed down to future generations. To improve inclusive fitness best to do both.
Direct Fitness: Fitness from personal reproduction more offspring yourself relative to other individuals and passing down those alleles.
Inclusive Fitness: Fitness - Reproductive Success of yourself and relatives/# of genes that are passed down to future generations. To improve inclusive fitness best to do both.
60
New cards
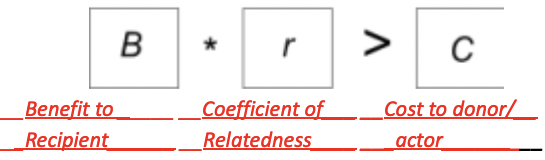
What is Hamilton’s Rule?
Hamilton’s Rule helps us to determine the likelihood an individual is going to do an altruistic act
Kindness will occur when
B \* r > C
B= Benefit to the Relative
r= Coefficient of Relatedness 0.0-1.0
C= Cost to donor/Actor
Kindness will occur when
B \* r > C
B= Benefit to the Relative
r= Coefficient of Relatedness 0.0-1.0
C= Cost to donor/Actor
61
New cards
How do you calculate r?
Up up Up. Down Down Down. One path Is when you go up family tree to nearest common ancestor and back down the tree to person in question. There may be multiple paths between two people.
All paths are created equal: each connection is worth 0.5 (we get 1/2 autosomal DNA from each parent so r=0.5 between parent and child)
Multiply within the path and add between different paths.
All paths are created equal: each connection is worth 0.5 (we get 1/2 autosomal DNA from each parent so r=0.5 between parent and child)
Multiply within the path and add between different paths.
62
New cards
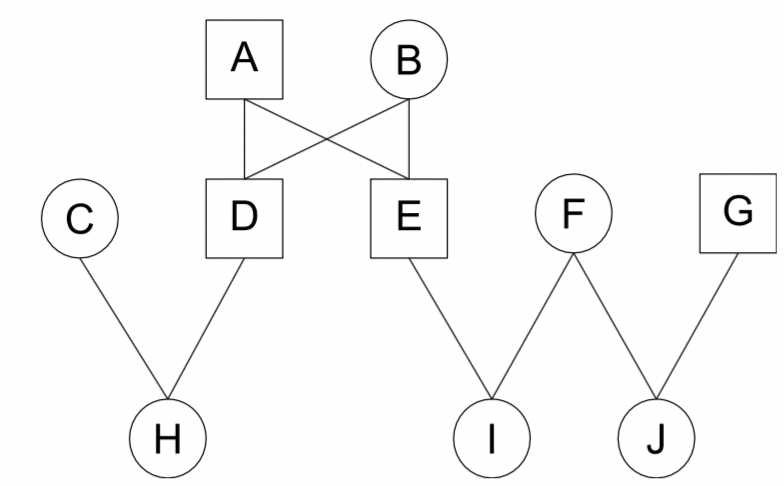
Calculate the R of this image
A-→D - Relationship? R?
D-→E - Relationship? R?
I-→J- Relationship? R?
E-→H - Relationship? R?
D-→J - Relationship? R?
A-→H - Relationship? R?
H-→I - Relationship? R?
\
A-→D - Relationship? R?
D-→E - Relationship? R?
I-→J- Relationship? R?
E-→H - Relationship? R?
D-→J - Relationship? R?
A-→H - Relationship? R?
H-→I - Relationship? R?
\
A-→ D = Parent/Child R= 0.5
D-→ E = Siblings R= 0.5
I-→J- Half-Sibling R= 0.25
E-→H - Uncle/Aunt R= 0.25
D-→J - Not related R= 0
A-→H - Grandparent R= 0.25
H-→I - Cousins R= 0.125
\
D-→ E = Siblings R= 0.5
I-→J- Half-Sibling R= 0.25
E-→H - Uncle/Aunt R= 0.25
D-→J - Not related R= 0
A-→H - Grandparent R= 0.25
H-→I - Cousins R= 0.125
\
63
New cards
What Is Reciprocal Altruism?
When alleles you have causes you to be kind to another individual with the expectation that the recipient will return the favor at some later time (thereby helping your own reproductive success)
Is this common with non-related individuals in non-humans species? - No
Is this common with non-related individuals in non-humans species? - No
64
New cards
What are the conditions for Reciprocal Altruism?
1. Repeated Interactions
2. Higher benefit to recipient relative to the cost of the actor
* Like Hamilton’s rule, but without the r
3. Ability to keep tabs on people and punish cheaters
* Freeloaders may crash the system because this system depends on reciprocity. Establishes trust.
65
New cards
What are design features of the Human Brain?
1. Good at recognizing faces
* Helps us keep track of cheaters
2. Keep track of cheaters
* So we don’t get duped
3. Consumers of social information
* Know who is generally a cheater or a generous person
66
New cards
How can you enhance cooperation?
1. Play around with the perceived costs and benefits
* To convince someone to help…make cost seem lower and benefits higher (need to print or get fired)
2. Distinguish cheaters and kind people
* Facilitate building of reputation, honest signals. (Ex. Blood donor sticker. Yale donor list)
3. Reduce the perceived vulnerability of partners
* Make the first step: gifts. They are more likely to reciprocate
67
New cards
What animal is a crucial example of Shared Genes/Kin Selection?
Belding Ground Squirrels
* Older female Belding Ground Squirrels make alarm calls that place them in danger, but increase the likelihood that their relatives will survive.
* Older females = have more relatives as males go to other territories to look for mates, but females stay
* Older female Belding Ground Squirrels make alarm calls that place them in danger, but increase the likelihood that their relatives will survive.
* Older females = have more relatives as males go to other territories to look for mates, but females stay
68
New cards
What animal is a crucial example of Reciprocal Altruism?
Vampire Bats
* Vampire bats regurgitate blood for other vampire bats that are starving. In the future, the bats that helped out other bats are more likely to be helped out themselves compared to the bats that refused to help before.
* Vampire bats regurgitate blood for other vampire bats that are starving. In the future, the bats that helped out other bats are more likely to be helped out themselves compared to the bats that refused to help before.
69
New cards
What is Loci?
The location of a gene in a chromosome.
70
New cards
What is the Complete Theory of Kindness?
1. Shared Genes (Related)
2. Reciprocity (Get and Give)
3. Unexpected Kindness
71
New cards
What is Unexpected Kindness?
When individuals behave so as to benefit other individuals while incurring a cost themselves.
The behavior is actually evolutionary maladaptive (usually is a result of mismatch).
* Relates to Belding Ground Squirrels because when they get displaced to a new territory they still do the alarm calls due to their maladaptive behaviors.
* Continue to do something that places them in danger at no direct benefit to them.
The behavior is actually evolutionary maladaptive (usually is a result of mismatch).
* Relates to Belding Ground Squirrels because when they get displaced to a new territory they still do the alarm calls due to their maladaptive behaviors.
* Continue to do something that places them in danger at no direct benefit to them.
72
New cards
What is Maladaptive Behavior? And Mismatch?
Mismatch: When in an environment that isn’t the one we evolved for or became behaviorally adapted to.
Ex. 24/7 food leaves to overeating, unlike hunter-gatherers, The same behavior doesn’t fit in a new environment.
Ex. Being kind to people far away by donating. In H-G days see the same people all the time.
Rule of Thumb/ Kin Recognition:
When instincts lead you to behave accordingly to the way that used to be adaptive but results in maladaptive behavior because you’re in a novel environment. Expect them to be true because they usually are.
1. Spacial Association: Those that are around us are more likely to be relatives
2. Social Association: Those that you have known for a long time
3. Phenotype matching: appear/behave similarly
Ex. 24/7 food leaves to overeating, unlike hunter-gatherers, The same behavior doesn’t fit in a new environment.
Ex. Being kind to people far away by donating. In H-G days see the same people all the time.
Rule of Thumb/ Kin Recognition:
When instincts lead you to behave accordingly to the way that used to be adaptive but results in maladaptive behavior because you’re in a novel environment. Expect them to be true because they usually are.
1. Spacial Association: Those that are around us are more likely to be relatives
2. Social Association: Those that you have known for a long time
3. Phenotype matching: appear/behave similarly
73
New cards
What is “Unexpected” Cooperation?
Cooperation in **Honey Bees**
Sisters have the same genes from the father and half of the mother’s genes because…
All sisters share all the sperm from the father but only receive a random half of their mother’s genes as the mother may pass on genes from both their mother and father.
\
Coefficient of relatedness between honey bees
* Mother and daughter: 0.5
* Female and sister: 0.75 (1.0 = exactly same genes. Half are the same. But they share half of their mother therefore, we help mothers make more sisters because their coefficient relatedness is higher.
Female honey bees can often increase fitness by..
Helping mothers reproduce more offspring/sisters, more relatedness than their own children.
\
What are the consequences of the queen bee mating with more than 1 male bee?
Females would be less likely to help because new sisters would only be 0.25.
Females might leave and reproduce on their own.
Loyal: 0.75
Own kinds: 0.5
Cheats: 0.25
\
Inbreeding in **Naked Mole Rats**
*Why are naked mole rats so inbred? What is their coefficient of relatedness?*
They live in isolated underground systems and are inbred for up to thousands of generations/r=.99
Because of their living situation, they start mating with one another.
\
*What is a consequence of this mating pattern?*
There are non-reproductive workers that help the queen mate and reproduce because that’s a lot more helpful for their fitness. Cooperation is extreme.
\
**Truces during WWI**
How do spontaneous truces start between units on different sides of a war?
One side makes a gesture (take long after lunch, aim elsewhere)
\
How are these truces ended by generals?
People are punished and relocated to another location
\
Sisters have the same genes from the father and half of the mother’s genes because…
All sisters share all the sperm from the father but only receive a random half of their mother’s genes as the mother may pass on genes from both their mother and father.
\
Coefficient of relatedness between honey bees
* Mother and daughter: 0.5
* Female and sister: 0.75 (1.0 = exactly same genes. Half are the same. But they share half of their mother therefore, we help mothers make more sisters because their coefficient relatedness is higher.
Female honey bees can often increase fitness by..
Helping mothers reproduce more offspring/sisters, more relatedness than their own children.
\
What are the consequences of the queen bee mating with more than 1 male bee?
Females would be less likely to help because new sisters would only be 0.25.
Females might leave and reproduce on their own.
Loyal: 0.75
Own kinds: 0.5
Cheats: 0.25
\
Inbreeding in **Naked Mole Rats**
*Why are naked mole rats so inbred? What is their coefficient of relatedness?*
They live in isolated underground systems and are inbred for up to thousands of generations/r=.99
Because of their living situation, they start mating with one another.
\
*What is a consequence of this mating pattern?*
There are non-reproductive workers that help the queen mate and reproduce because that’s a lot more helpful for their fitness. Cooperation is extreme.
\
**Truces during WWI**
How do spontaneous truces start between units on different sides of a war?
One side makes a gesture (take long after lunch, aim elsewhere)
\
How are these truces ended by generals?
People are punished and relocated to another location
\
74
New cards
What is “Unexpected Conflict?”
**Gestational diabetes** happens when...there is a tug of war over nutrients in mother’s body during gestation.
Fetus:
* Gets nutrients from mother’s blood
* Produces hormones (hPLL Human Placental Lactogen) that dilate mother’s blood vessels/ make them wider so it can get more nutrients.
Mothers:
* Can’t give fetus all the resources if she wants to have more offspring
* Increases the amount of insulin (a hormone that
* decreases blood glucose levels, encourages
* glucose to enter cells) so that there are less
* nutrients in blood vessels so she can have more
* offspring. More nutrients for herself.
* Removes food from bloodstream
Why does conflict occur?
Fetuses are related to themselves by 1.0 so they expect the mothers to take care of them but mothers may want
to have more children in the future as it is related to the fetus by .5.
Fetus:
* Gets nutrients from mother’s blood
* Produces hormones (hPLL Human Placental Lactogen) that dilate mother’s blood vessels/ make them wider so it can get more nutrients.
Mothers:
* Can’t give fetus all the resources if she wants to have more offspring
* Increases the amount of insulin (a hormone that
* decreases blood glucose levels, encourages
* glucose to enter cells) so that there are less
* nutrients in blood vessels so she can have more
* offspring. More nutrients for herself.
* Removes food from bloodstream
Why does conflict occur?
Fetuses are related to themselves by 1.0 so they expect the mothers to take care of them but mothers may want
to have more children in the future as it is related to the fetus by .5.
75
New cards
What is the Ultimatum Game?
Game where a proposer chooses to give $5 and keep $35 (stingy offer) or give $15 and keep $25 (generous offer).
The responder gets to choose which proposals they want to accept.
\
What are the results? Why are they surprising?
● Some people make generous offers (1/4)
○ Don’t want to hurt reputation or risk not getting any money
● Some people reject free money (10%+)
○ Willing to pay price to enforce belief in fairness
○ We want to punish people for being stingy
● According to economists people should always say yes and give the smallest amount and accept any money but
this turns out not to be true because humans are designed to have a sense of justice/gratitude, react with
emotions.
● Reflect reciprocal reactions
● When proposals are chosen by computers, all responders accept
● When there are risks to one’s reputation, proposals tend to be fairer (posting pictures of them and offer)
The responder gets to choose which proposals they want to accept.
\
What are the results? Why are they surprising?
● Some people make generous offers (1/4)
○ Don’t want to hurt reputation or risk not getting any money
● Some people reject free money (10%+)
○ Willing to pay price to enforce belief in fairness
○ We want to punish people for being stingy
● According to economists people should always say yes and give the smallest amount and accept any money but
this turns out not to be true because humans are designed to have a sense of justice/gratitude, react with
emotions.
● Reflect reciprocal reactions
● When proposals are chosen by computers, all responders accept
● When there are risks to one’s reputation, proposals tend to be fairer (posting pictures of them and offer)
76
New cards
What are nucleotides
Basic structural unit of DNA aka bases.
* A is paired with T
* T is paired with A
* G is paired with C
* A is paired with T
* T is paired with A
* G is paired with C
77
New cards
Is DNA complementary?
Yes, DNA is complementary because DNA is double-stranded, one side has a sequence, and the other side has the paired base.
* Individuals differ in their DNA sequence by 0.1% meaning 99.9% of everyone’s DNA is identical. This means about 3 million differences out of 3 billion base pairs are different.
* Individuals differ in their DNA sequence by 0.1% meaning 99.9% of everyone’s DNA is identical. This means about 3 million differences out of 3 billion base pairs are different.
78
New cards
Why is our DNA so alike? What part of our DNA has the most variation?
Why? Humans have a lot of familiar traits: limbs, faces, organs, etc.
Variation? Most differences can be found in the non-coding DNA (90%). Allows more room for mutation and variations. (DNA fingerprinting looks at the differences in these parts to identify people).
Variation? Most differences can be found in the non-coding DNA (90%). Allows more room for mutation and variations. (DNA fingerprinting looks at the differences in these parts to identify people).
79
New cards
What is DNA Fingerprinting?
Method to identify an individual by observing unique patterns in their DNA. Commonly used to solve crimes and paternity testing.
(Repition of nucleotides is unique for everyone).
(Repition of nucleotides is unique for everyone).
80
New cards
What is a Short Tandem Repeat (STR) locus?
*short tandem repeat. Key word: Tandem (bikes). One behind another. Locus = particular place (Loci = plural)*
* *Repeating units in DNA that are 4-5 nucleotides long (ex. AATCG)*
* *The units/sequence is the same, but can be repeated different # of times (depending on the allele you have)*
* *Just like any other gene, there are 2 alleles for each STR (one mom, one dad. Ex. Mom can pass down allele 6 and dad can pass down allele 4).*
* *Repeating units in DNA that are 4-5 nucleotides long (ex. AATCG)*
* *The units/sequence is the same, but can be repeated different # of times (depending on the allele you have)*
* *Just like any other gene, there are 2 alleles for each STR (one mom, one dad. Ex. Mom can pass down allele 6 and dad can pass down allele 4).*
81
New cards
Where do we find STR loci?
Part of 90% of DNA that doesn’t code for anything/specific protein/structural traits (maybe important for gene expression/noncodig RNA?)
Individuals have many different STR loci.
Ex. STR 1 STR 2 1/10 \* 1/10 = 1/100
Individuals have many different STR loci.
Ex. STR 1 STR 2 1/10 \* 1/10 = 1/100
82
New cards
What are the steps to create a DNA fingerprint?
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
* Take DNA from anything containing cells (white blood cells, semem, saliva, hair, dead skin cells)
* Heat up DNA to separate the strands
* Add in bases and new strands will develop - repeat process
* *Great way to have lots of DNA fragments to work with*
Gel Electrophoresis
* \
* *Put DNA into electrophoresis gel that has a positive charge on one end*
* *DNA is negatively charged and will move through gel towards positive charge (generate electric current - opposites attract)*
* *Smaller DNA fragments (fewer repeats) are able to move further/faster but larger strands move slower because they get tangled/struggle*
* *DNA “bands” can be seen using fluorescent dyes/radioactivity.*
* Take DNA from anything containing cells (white blood cells, semem, saliva, hair, dead skin cells)
* Heat up DNA to separate the strands
* Add in bases and new strands will develop - repeat process
* *Great way to have lots of DNA fragments to work with*
Gel Electrophoresis
* \
* *Put DNA into electrophoresis gel that has a positive charge on one end*
* *DNA is negatively charged and will move through gel towards positive charge (generate electric current - opposites attract)*
* *Smaller DNA fragments (fewer repeats) are able to move further/faster but larger strands move slower because they get tangled/struggle*
* *DNA “bands” can be seen using fluorescent dyes/radioactivity.*
83
New cards
Is it (better/worse) to look at a fewer or greater number of STR loci/bands when creating DNA fingerprints. Why?
There are usually 10 different alleles in a population.
If you only have 1 for example and there were 10 possible types of alleles (# of repeats), you would have 1/10 chance for one allele and 1/100 for both.
Better to look for more loci (FBI says 13) because if you have 13 loci (26 alleles/bands) then your chances would be 1/10^26 and you can be a lot more certain about the results and be sure that you did not mistaken people.
* The US Combined DNA index System database includes 20 STR loci.
\
If you only have 1 for example and there were 10 possible types of alleles (# of repeats), you would have 1/10 chance for one allele and 1/100 for both.
Better to look for more loci (FBI says 13) because if you have 13 loci (26 alleles/bands) then your chances would be 1/10^26 and you can be a lot more certain about the results and be sure that you did not mistaken people.
* The US Combined DNA index System database includes 20 STR loci.
\
84
New cards
What are the similarities and differences between STR loci and genes for structural traits?
Similarities:
* 2 alleles - one from mom and one from dad
* Both contain DNA
* Both have some degree of variation
STR Loci:
* Does not code (noncoding)
* Contains more genetic variation
* Does not impact phenotype
* Does not code for protein
Genes for structural traits
* Coding is present
* Contains less genetic variation
* Does impact phenotype - Ex. Hair/Fur, eye color
* Usually codes for proteins
* \
\
* 2 alleles - one from mom and one from dad
* Both contain DNA
* Both have some degree of variation
STR Loci:
* Does not code (noncoding)
* Contains more genetic variation
* Does not impact phenotype
* Does not code for protein
Genes for structural traits
* Coding is present
* Contains less genetic variation
* Does impact phenotype - Ex. Hair/Fur, eye color
* Usually codes for proteins
* \
\
85
New cards
What type of blood cells carry DNA?
Red blood cells do not carry DNA.
White Blood Cells carry DNA.
White Blood Cells carry DNA.
86
New cards
What are the uses of DNA Fingerprinting?
It can help solve unsolvable crimes, resolve paternity issues, can prove innocence of peoplee unjustly convicted, and immigration.
87
New cards
When it comes to food, humans have taste preference. What are they and why do they exist?
Prefer food that is high in fat
● Stores the most energy of all macromolecules (9 kcal vs. 4 kcal)
● In EEA (environment of evolutionary adaptiveness)/hunter-gatherer society - we had to make sure that we had enough energy to survive even when food sources were unpredictable so we were motivated to eat foods that had more fat
\-Have taste preference for lipids because it stores energy and heat insulation which was important for our ancestors who struggled to find food.
● Stores the most energy of all macromolecules (9 kcal vs. 4 kcal)
● In EEA (environment of evolutionary adaptiveness)/hunter-gatherer society - we had to make sure that we had enough energy to survive even when food sources were unpredictable so we were motivated to eat foods that had more fat
\-Have taste preference for lipids because it stores energy and heat insulation which was important for our ancestors who struggled to find food.
88
New cards
Where does fuel come from?
Fuel comes from energy stored in chemical bonds.
* *Bonds in molecules are broken down and new molecules are created. These new bonds store less energy. The energy released is used as fuel.*
* *Bonds in molecules are broken down and new molecules are created. These new bonds store less energy. The energy released is used as fuel.*
89
New cards
What are macromolecules?
*Large organic (contain carbon/found in living systems) molecules made up of smaller building blocks.*
*Molecules that are necessary for life/provide energy/structure.*
*4 types: Lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids*
* Monomers: *subunits; molecules that can be bonded with other molecules; Relatively simple sets of building blocks linked together by covalent bonds.*
* Polymers: *structure with repetitions of similar units; possible to form an almost infinite variety of complex molecules, called polymers*
*Molecules that are necessary for life/provide energy/structure.*
*4 types: Lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids*
* Monomers: *subunits; molecules that can be bonded with other molecules; Relatively simple sets of building blocks linked together by covalent bonds.*
* Polymers: *structure with repetitions of similar units; possible to form an almost infinite variety of complex molecules, called polymers*
90
New cards
What are lipids?
They are also referred to as fats.
Function: *Storehouse for energy/dense source of energy that can be efficiently stored in the body ● Also good insulator/keeps body warm*
Types of fats: refers to the hydrocarbon chain of the fatty acids
There are two types: saturated and unsaturated fats.
Function: *Storehouse for energy/dense source of energy that can be efficiently stored in the body ● Also good insulator/keeps body warm*
Types of fats: refers to the hydrocarbon chain of the fatty acids
There are two types: saturated and unsaturated fats.
91
New cards
What are saturated fats?
Less healthy for individuals.
* *Straight tails/can be packed tightly together*
* *More likely to be stored as fat rather than used for energy*
* *Solid at room temperature*
* *Single bonds (Carbons connected with 2 Hydrogens)*
Examples: *Butter, cheese, meat (animal fats)*
* *Straight tails/can be packed tightly together*
* *More likely to be stored as fat rather than used for energy*
* *Solid at room temperature*
* *Single bonds (Carbons connected with 2 Hydrogens)*
Examples: *Butter, cheese, meat (animal fats)*
92
New cards
What are unsaturated fats?
More healthy for individuals.
* *Cannot be packed together tightly*
* *Less likely to be stored as fat/easier to break down (enzymes have better access)*
* *Tend to be liquid at room temperature*
* *Kinked tails (double bonds that connect carbon - fewer hydrogen molecules)*
* Examples: *Vegetable oil, fish, walnuts (plant/fish fats)*
* *Cannot be packed together tightly*
* *Less likely to be stored as fat/easier to break down (enzymes have better access)*
* *Tend to be liquid at room temperature*
* *Kinked tails (double bonds that connect carbon - fewer hydrogen molecules)*
* Examples: *Vegetable oil, fish, walnuts (plant/fish fats)*
93
New cards
Which type of fat is better for your health? Why?
*Unsaturated fats are better because they are more reactive and can get more nutrients.*
94
New cards
Why do humans love food with more lipids?
*Contains more than twice as much stored energy as other macromolecules (9kcal vs 4)*
*● Humans have evolved to want to store energy (ancestors are hunter-gatherers. Haven’t adapted to current environment).*
*● Humans have evolved to want to store energy (ancestors are hunter-gatherers. Haven’t adapted to current environment).*
95
New cards
What Is partially-hydrogenated vegetable oil and why do we use it?
*Take oil and bubble up hydrogen (hydrogen atoms will attach to fat structure at some places)*
*● Double bonds will become single bonds*
*● Why: Longer shelf life & control desired texture/melting point (ex. chocolate)*
*● Double bonds will become single bonds*
*● Why: Longer shelf life & control desired texture/melting point (ex. chocolate)*
96
New cards
What are carbohydrates?
Function: *Primary fuel source (Provide energy for the body)/Form structure of cells.*
97
New cards
What are the types of carbohydrates?
Simplest sugars monosaccharides
* *Linear/ring structure with 3-7 carbon atoms*
* *Fast/immediate energy*
* Examples: *Glucose (plants), fructose (fruit, veggies)*
Complex carbohydrates/polysaccharides
* *Simple sugars linked together (with glycosidic linkages)*
* *Energy breaks down more slowly (or not at all)*
* Examples: *Glycogen, starch (energy storage in plants), cellulose/lignins/pectins/gums (fiber in our diet)*
* *Linear/ring structure with 3-7 carbon atoms*
* *Fast/immediate energy*
* Examples: *Glucose (plants), fructose (fruit, veggies)*
Complex carbohydrates/polysaccharides
* *Simple sugars linked together (with glycosidic linkages)*
* *Energy breaks down more slowly (or not at all)*
* Examples: *Glycogen, starch (energy storage in plants), cellulose/lignins/pectins/gums (fiber in our diet)*
98
New cards
What is cellulose?
*Used for structural support in plants (is fiber: adds bulk -> helps move food through digestive system)*
* *A complex carbohydrate, indigestible by humans, that serves as the structural material for a huge variety of plant structures. It is the single most prevalent organic compound on earth.*
* *A complex carbohydrate, indigestible by humans, that serves as the structural material for a huge variety of plant structures. It is the single most prevalent organic compound on earth.*
99
New cards
How is cellulose different from other carohydrates (starch)?
*Humans and mammals can’t digest because we can’t break down bonds (beta amylase only found in plants, bacteria, and fungi).*
* *Plant carb (fiber) helps move food through the digestive system -> shows why it is important for humans*
* *Plant carb (fiber) helps move food through the digestive system -> shows why it is important for humans*
100
New cards
What are Fibers?
Fibers are plant carbohydrates (aka cellulose, lignins, pectins, gums) that humans can’t digest