Petroleum geology exam
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Define thermal maturity.
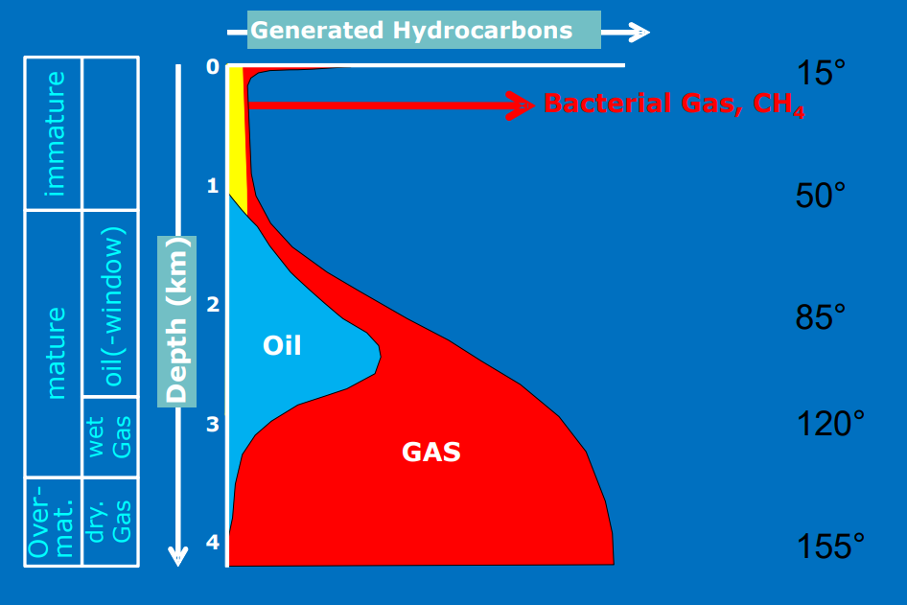
Draw a depth diagram with the different maturity levels (immature oil, oil, gas).
Which maturity level produces which hydrocarbons?
The degree to which OM in sedimentary rocks has been exposed to elevated temperatures over geological time.
immature: organic matter, waxes, bacterial gas.
mature: mostly oil and some wet gas
overmature. Mostly dry gas
Define API gravity (name API of different HCs)
API = American Petroleum Institute: It is a value to specify the density of oil in comparison to density of water.
API = 141.5/SG -131.5
Extra-Heavy: < 10° API
Heavy: 10° - 22° API
Medium: 22° - 30° API
Light Oil: 30° – 45° API
Paralffinic Oils > 35° API
Gas Condensate > 45° API
Aromatic intermediate Oils < 35° API
How does biodegradation influence API gravity?
Microbes preferentially consume light hydrocarbons, removing high API components = lower API = higher viscosity, sulphur & asphalting content = higher acidity
How can you distinguish bacterial and thermogenic gas?
Bacterial Gas: produced by bacteria from organic matter in sediments or liquids at low temperatures ( <80° C)
Primary Bacterial Gas: Produced by bacteria from organic matter in sediments.
Isotipically light
Extremely dry
Secondary Bacterial Gas: Produced by anaerobic bacteria from liquid petroleum.
Isotropic and molecular composition depending on degree of (methanogenic) biodegradation.
Thermogenic Gas: produced by thermal processes from organic matter in sediments or liquid petroleum. Isotipically heavier, wet (isotopy and wetness maturity dependent)
Associated gas: petroleum gas, associated with oil
Non-Associated gas: formed at temperature, where liquid petroleum is no longer stable.
=> wetness decreases w/ thermal maturity, increasing C1/(C2+C3) ratio while isotropic ratio increases
Up to what temperature is biodegradation effective?
Biodegradation is effective up to 80°C. It is the bacterial alteration of crude oil.
What is paleo-pasteurization?
the natural "sterilization" of a reservoir due to elevated temperatures (>80°C) that prevent microbial biodegradation, thus preserving the integrity and quality of hydrocarbons in the subsurface over millions of years.
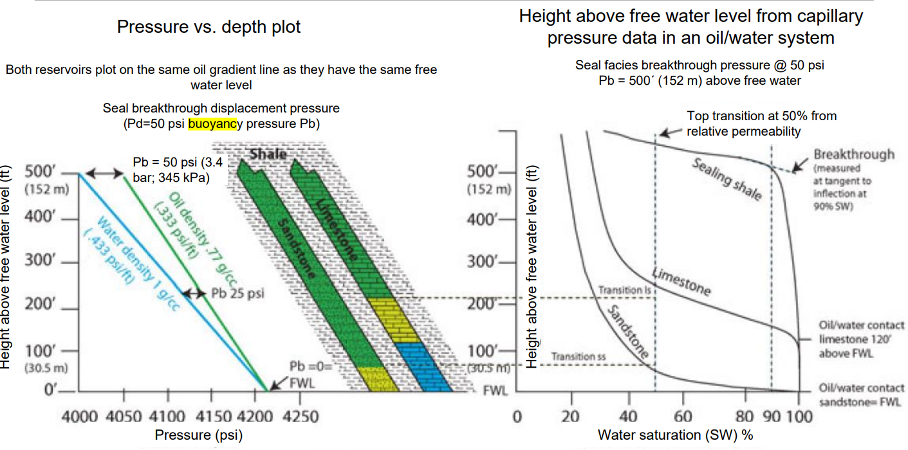
What is buoyancy?
Draw a Saturation vs. Height over free water level diagrams for a sandtone reservoir and a shale sealing rock.
The upward force exerted on a fluid or object submerged in a fluid due to a density difference between two phases (petroleum & pore water) used to describe the secondary migration process
Define “net to gross” in a reservoir geological context.
Describes the proportion of a reservoir rock that is porous and permeable, capable of storing and allowing fluid flow, in relation to the total thickness of the sedimentary strata.
Net thickness: Thickness of a rock within the sedimentary layer, with effective fluid storage and transmission.
Gross thickness: total thickness of sedimentary layer, include all rock types, regardless of porosity or permeability. Reservoir rocks and non-reservoir rocks.
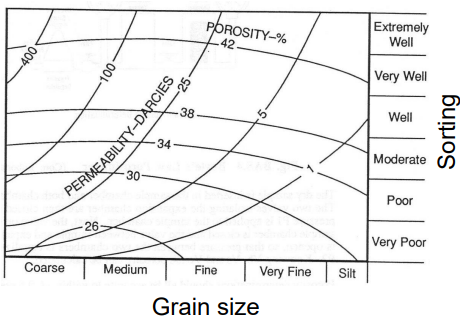
How do grain size and sorting affect permeability and porosity in sandstones?
Draw a Sorting vs. Grain Size diagram, and show the effects by drawing lines at equal permeability/porosity.
larger, well-sorted grains generally result in higher porosity and permeability, better for fluid storage and transport.
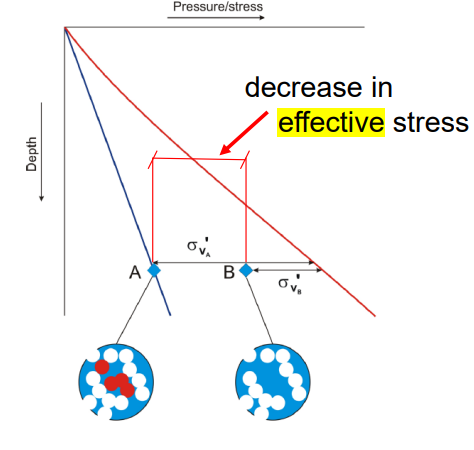
Draw the hydrostatic and lithological pressure over depth and do the same for disequilibrium compaction.
How does that influence effective stress?
Effective stress is the difference between lithostatic and hydrostatics pressures.
high pore pressure = low effective stress
Desiquilibrium compaction is when a mudrock can’t dewater fast enough for the pore fluid to remain in hydrostatic equilibrium as it compacts under increasing vertical/lateral stress. = overpressure by loading
increases pore pressure = decreases effective stress
What is the difference between shale oil production and oil shale production?
Shale Oil Production: Gas and Oil produced directly from extremely low permeable source rock. Requires fracking (hydraulic fracturing) and horizontal drilling.
Oil Shale Production: Organic matter-rich (but thermally immature) rock which yields significant amount of shale oil and gas during low-temperature pyrolysis. Produced during artificial heating.
Which 2 technical advancements have really pushed oil shale production?
Horizontal Drilling
Allows access to large reservoir volumes along shale beds.
Greatly increases contact with the productive zone.
Hydraulic Fracturing (Fracking)
Creates artificial permeability by fracturing the rock.
Allows oil to flow to the wellbore in otherwise impermeable shale.
Name the important elements and processes for/in a petroleum system.
Elements
Source rocks: Where the HCs are formed
Reservoir rocks (porous, permeable rocks): Where the HCs migrate.
Seal rocks (impermeable clay): Rock formation that is impermeable and laterally continuous. Holds HCs back from further migration.
Overburden: exerts pressure and also temperature. as well as reservoir compaction.
Processes:
Generation
Migration
Accumulation
Trapping
Preservation
How does the naming work for a petroleum system?
The PS has a stratigraphic, geographic, and temporal extent
Its name combines the names of the source rock and the major reservoir rocks and also expresses a level of certainty (known, hypothetical, speculative) (!) (.) (?)
Describe two wireline logs to correlate the lithology and calculate the sand to shale ratios.
Sonic Logs: Measures the interval transit time of acoustic waves over discrete distances.
The speed of sound is affected by density and elastic properties of the rock. Different lithologies have different velocities, helping to differentiate the rock types and correlate lithological boundaries.
It is a function of lithology. If lithology is known, porosity is easily deduced.Gamma Ray: measures the natural radioactivity of the isotopes of Uranium, Thorium and Potassium40. It identifies if there are shale intervals
Used to identify and correlate lithological changes.Neutron Logs: helps to distinguish sand from shale based on hydrogen content.H is concentrated in the fluid-filled pores.
Briefly describe the neutron and the density log.
What are they used for?
How do these logs react in the presence of hydrocarbons? (eg. Water vs. Gas).
Density Logs: Emits medium-energy gamma rays and measures returning gamma ray energies.
Gamma rays are scattered (Compton scattering) as a result of collisions with electrons in the formation → measures electron density/ bulk density
HCs have lower density than water. =>
gas filled pores = low density = high density porosity
water filled pores = high density = low density porosity
Neutron Logs: Emits high-energy neutrons and measures slowed-down neutrons or emitted gamma rays
sensitive to hydrogen content in pores → Because hydrogen is concentrated in the fluid-filled pores, radiation is a function of porosity
gas filled pores = less H-conc = low neutron porosity
water filled pores = high H-cons = high neutron porosity
They both estimate porosity
Explain the tectonics of the Vienna basin
pull-apart basin formed in a strike-slip tectonic regime: formed when blocks of the Earth's crust move sideways past each other along strike-slip faults
Dominated by normal faults and strike-slip fault zones.
Explain the darcy’s law and solve it to show the permeability
Darcy’s Law describes the flow of a fluid through a porous medium. It is fundamental in hydrogeology and petroleum engineering for calculating permeability of reservoir rocks.
Q = kA∆p/ µL
What is relative permeability?
Relative permeability is the ability of a rock to transmit one fluid when multiple fluids (like oil, water, and gas) are present.
kr = k_eff/k_abs
Explain the use of drilling cuttings
small rock fragments created during drilling, and transported to the surface by the drilling mud
Evaluation of HC shows
Reservoir and lithological descriptions
Geological correlation and formation identification
Verification of wireline log response
Design of strip logs (lithology vs. depth).