Lec 6 - Hardy-Weinberg to Selections
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
If there IS a fitness advantage to one
genotype then (so would that mean there
is evolution?):
I. p2+2pq+q2≠1
II. The expected values from the HW
equation will match the observed
values
III.The expected values from the HW
equation won’t match the observed
values
IV. p+q=1
A. I, II, IV
B. I, III
C. III, IV
D. I, III, IV
E. II, IV
C. III, IV

You have a population of meerkats who have two
alleles at the locus that codes for nose color (pink
or black) the alleles are k and b. You observe a
population that has the following genotype
frequencies:
kk kb bb
0.36 0.48 0.16
What is the expected frequency of the kb genotype?
A. 0.1152
B. 0.6
C. 0.4
D. 0.48
E. It is impossible to tell from the
given information.
Within a population of cats long hair (l) is recessive and short hair (L) is dominant (so LL
and Ll have short hair). If you know that 20% of the population has long hair which of the
following are true?
I. The allele frequency of the L allele is 0.8
II. 80% of the population has short hair
III.Because q=l=0.2, and p2+2pq+q2=1, then the allele frequency for l is
IV. Because the allele frequency for l is 0.447, then the allele frequency for L is 0.553
II. 80% of the population has short hair
Within a population of cats long hair (l) is recessive and short hair (L) is dominant (so LL
and Ll have short hair). You know that 20% of the population has long hair. If you also
know that L has a frequency of 0.7. Is the population in HW at this locus?
A=yes
B=no
C=you can’t tell from these data
B=no
You have a gene in a
population
A mutation happens
in a germline cell.
Now you have two
alleles. This is a SNP
If there’s no
selection and you
have a large
population what
should happen to
this new allele?
A. It would remain in the population
B. It would disappear from the population
C. It depends on whether it is dominant or
recessive
D. No way to tell
A. It would remain in the population
What if there were
positive selection for
Allele 1 in population 2?
A. The frequency of
allele 1 would go up
in pop 2
B. The frequency of
allele 2 will go up in
pop2
C. The allele frequency
of 2 will stay the
same, but 1 will go
up in pop2.
D. This would suggest
that Allele 1 is
dominant.
A. The frequency of
allele 1 would go up
in pop 2
Positive vs. Negative Selection
36
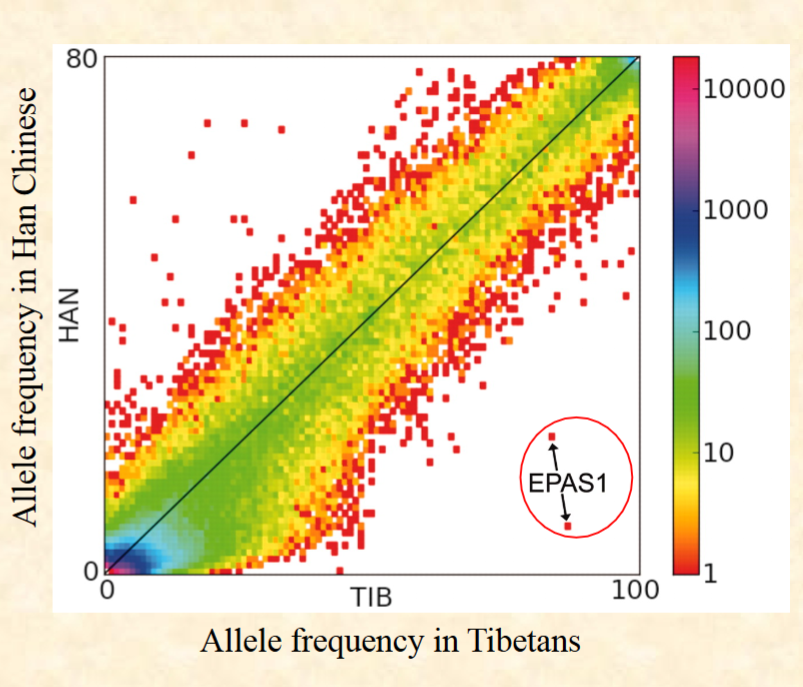
Han Chinese and Tibetans split about 2750 years
ago. This chart shows frequency of single
nucleotide polymorphisms alleles in lots of
different genes between Han and Tibetans. The
color shows the number of SNPs at that locus. If
the gene lies along the diagonal there’s no
difference between number of SNPs in Han and
Tibetan peoples. If it’s far away it means those
mutations are over-represented in the population.
What can be said of the SNPS in EPAS1?
Allele frequency in Tibetans
Allele frequency in Han Chinese
A. They overrepresented in the Tibetans
B. They underrepresented in the Tibetans
C. They overrepresented in the Han
D. All of the above are possible
E. Wait that’s not even a real rainbow
A. They overrepresented in the Tibetans
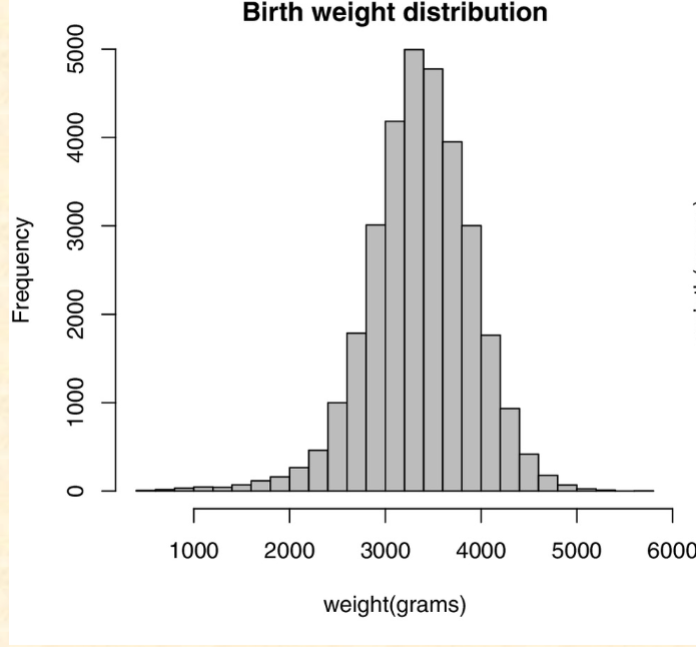
These data show the birthweight of
babies in a recent study. What do you
predict about the genetic basis of this trait?
A. The heterozygous babies for a
birthweight gene probably weigh
about 3 kg
B. Homozygous dominant babies for a
birthweight gene probably weigh
about 3 kg
C. The trait is probably caused by the
interactions of many genes
C. The trait is probably caused by the
interactions of many genes