Med Surg Exam #1 Exemplars and Medications
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
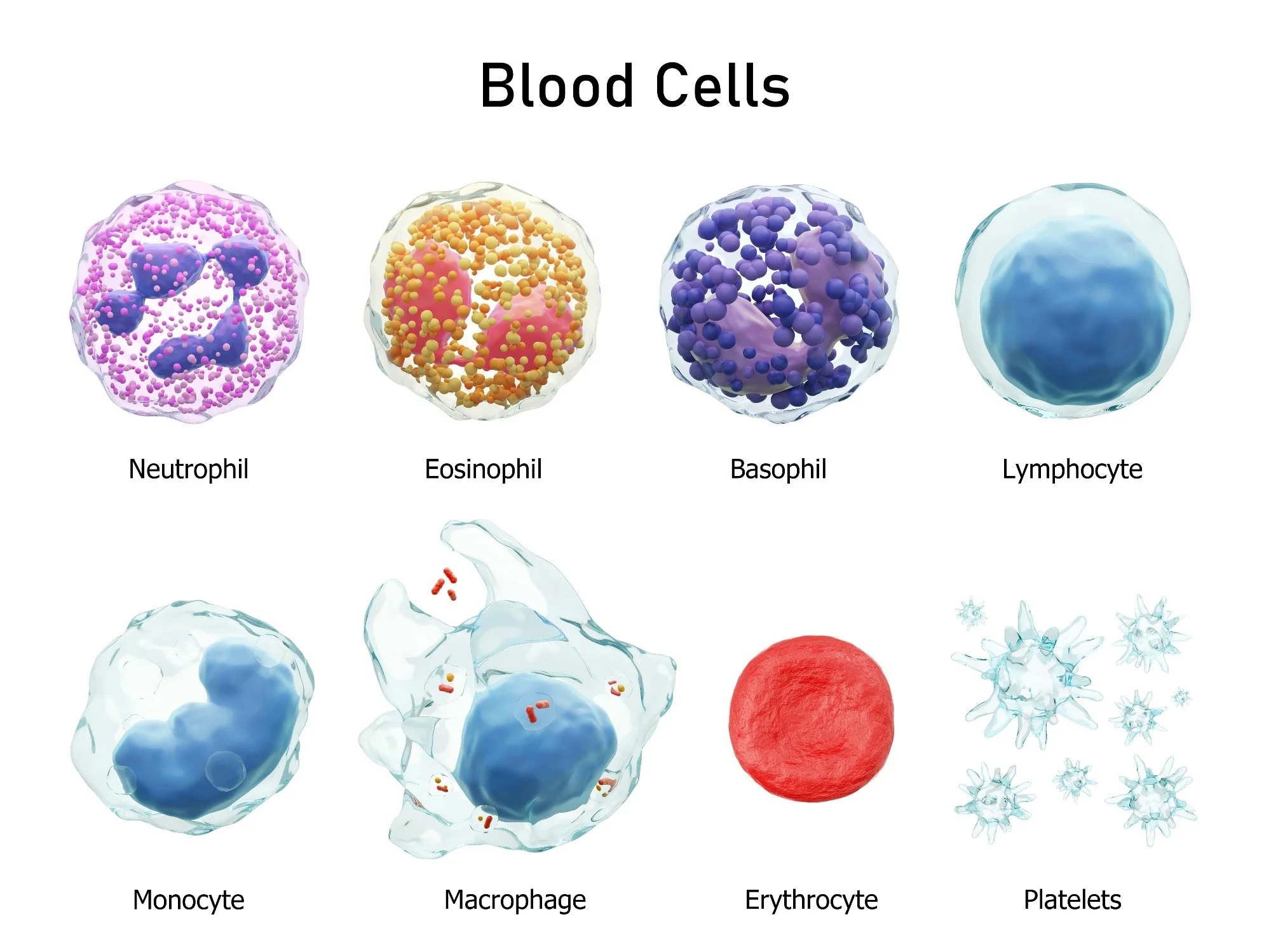
Hematologic System
Encompasses the blood and its components (red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma) along with organs like bone marrow, spleen, and lymph nodes, vital for transporting oxygen/nutrients, defending against infection, and maintaining hemostasis.
Hemostasis
The delicate balance of clotting and bleeding, maintained by the hematologic system.
Anemia
A condition characterized by a deficiency in the number or function of red blood cells or hemoglobin, leading to reduced oxygen delivery to tissues.
Leukemias
Cancers of the blood-forming tissues, marked by the uncontrolled proliferation of abnormal white blood cells that disrupt normal blood cell production and impair the immune system.
Transfusion Therapy
The administration of blood or blood components to a patient, aiming to restore the balance of blood elements lost due to bleeding, disease, or dysfunction, requiring careful matching and monitoring.
Epoetin alfa
A synthetic form of erythropoietin that stimulates the bone marrow to produce red blood cells, used to treat anemia, especially in chronic kidney disease or chemotherapy patients.

Ferrous Sulfate (Iron)
An iron supplement used to treat or prevent iron-deficiency anemia; iron is essential for the production of hemoglobin, which binds oxygen in red blood cells.

Folic Acid
A synthetic form of folate, a B-vitamin necessary for DNA synthesis and cell division, crucial for the production and maturation of red blood cells; deficiency can lead to megaloblastic anemia.

Hydroxocobalamin (B12)
A form of vitamin B12 used to treat B12 deficiency, which can cause pernicious anemia.
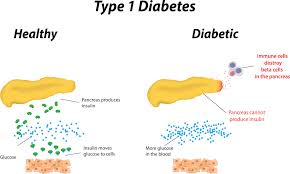
DM Type 1 (Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus)
A chronic condition where the body's immune system mistakenly destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to high blood sugar levels and requiring lifelong insulin therapy.
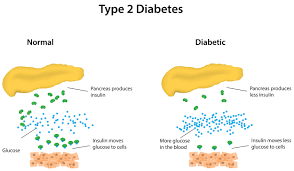
DM Type 2 (Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus)
A metabolic disorder characterized by the body's resistance to insulin or insufficient insulin production, often developing later in life and linked to lifestyle factors.
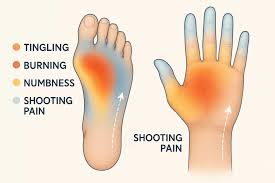
Peripheral Neuropathy
A condition arising from damage to the peripheral nerves, often caused by diabetes, infections, or toxins, manifesting as numbness, tingling, pain, or weakness, primarily in the hands and feet.
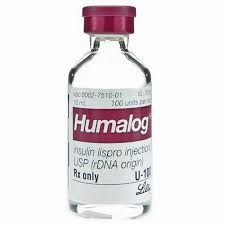
Lispro (Humalog)
A rapid-acting insulin that begins to work within 15 minutes, peaking around 1 hour, and lasting 2 to 4 hours, used to quickly lower blood glucose after eating.
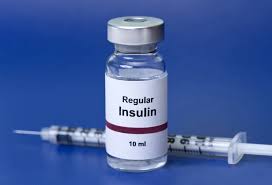
Regular (Humulin R)
A short-acting insulin that starts working within 30 minutes, peaks in 2 to 3 hours, and lasts about 5 to 8 hours, used to control blood sugar during and between meals.
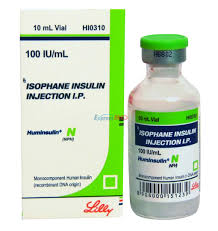
Isophane (NPH)
An intermediate-acting insulin that begins working in 1 to 2 hours, peaks at 4 to 12 hours, and lasts 18 to 24 hours, helping control blood sugar levels throughout the day and night.

Glargine (Lantus)
A long-acting insulin with no pronounced peak, providing a steady level of insulin for about 24 hours, mimicking the body's basal insulin secretion.
Humulin 70/30
A premixed insulin combining 70% intermediate-acting (Isophane NPH) and 30% short-acting (Regular) insulin, designed to provide both basal and mealtime coverage.
D50
A 50% dextrose solution given intravenously to rapidly raise blood glucose levels in severe hypoglycemia.
Glucagon
A hormone injected subcutaneously or intramuscularly that stimulates the liver to release stored glucose, used when a person is unconscious or unable to take oral glucose for hypoglycemia.

Glipizide
A sulfonylurea that stimulates the pancreas to release more insulin, used in Type 2 diabetes.

Glyburide
A sulfonylurea with a similar mechanism to glipizide, promoting insulin secretion, used in Type 2 diabetes.

Metformin
A biguanide that decreases glucose production by the liver and improves insulin sensitivity, often the first-line treatment for Type 2 diabetes.

Neurontin (Gabapentin)
A medication used to treat neuropathic pain, such as from peripheral neuropathy, by modulating nerve activity, though not an antidiabetic itself.
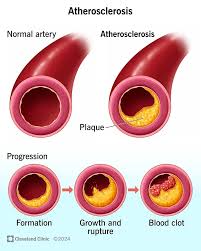
Atherosclerosis
A specific type of arteriosclerosis where plaque builds up inside the arteries. This plaque, made of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances, hardens and narrows the arteries, limiting the flow of oxygen-rich blood.
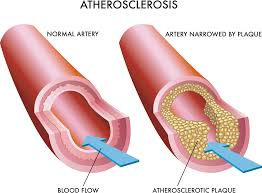
Arteriosclerosis
A general term for the thickening and hardening of the arteries. This condition occurs when blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrients from the heart become stiff and less elastic.
Heart Failure-chronic
A long-term condition in which the heart can't pump enough blood to meet the body's needs, meaning it isn't working as efficiently as it should, and can worsen over time.
Hypertension
High blood pressure, occurring when the force of blood against the walls of your arteries is consistently too high, usually defined as blood pressure above 130/80 mmHg.

Antihypertensives
Medications used to lower blood pressure by working through various mechanisms to reduce the pressure exerted by the blood against the artery walls.

Beta-Blockers
Drugs that block the effects of adrenaline (epinephrine) on the body’s beta receptors, slowing down the heart rate and reducing blood pressure.

Beta-1 Selective Beta-Blockers
A type of beta-blocker (e.g., Metoprolol) that primarily blocks beta-1 receptors in the heart, reducing heart rate and blood pressure with fewer effects on the lungs.

Non-Selective Beta-Blockers
A type of beta-blocker (e.g., Propranolol) that blocks both beta-1 and beta-2 receptors, affecting the heart, lungs, blood vessels, and other tissues.

ACE Inhibitors
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (e.g., Lisinopril) block the enzyme ACE, which is needed to produce angiotensin II, thereby helping relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure.

ARBs (Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers)
Medications (e.g., Losartan Potassium (Cozaar)) that block angiotensin II from binding to its receptors in blood vessels, preventing vessel narrowing and lowering blood pressure.

Alpha-Blocker
Medications (e.g., Prazosin (Minipress)) that block alpha-1 receptors in blood vessels, causing them to relax and widen, which lowers blood pressure.

Calcium Channel Blocker
Drugs (e.g., Amlodipine (Norvasc)) that prevent calcium from entering heart and blood vessel cells, leading to relaxation and widening of blood vessels, which lowers blood pressure.

Nitrates
Vasodilator medications (e.g., Nitroglycerine) that widen blood vessels, often used to treat angina (chest pain) by increasing blood flow to the heart.

Antihyperlipidemic
Medications used to lower lipid (fat) levels in the blood, primarily cholesterol and triglycerides.

Statins
Drugs (e.g., Atorvastatin calcium (Lipitor)) that block an enzyme in the liver needed to make cholesterol, thereby reducing cholesterol levels in the blood.

Diuretics
Medications that help the kidneys remove excess water and salt from the body, which lowers blood pressure.

Loop Diuretics
A type of diuretic (e.g., Furosemide (Lasix)) that works in the loop of Henle in the kidney, causing a powerful diuretic effect.

Potassium Sparing Diuretics
A type of diuretic (e.g., Spironolactone (Aldactone)) that helps remove excess water and salt from the body while retaining potassium.

Thiazide Diuretics
A type of diuretic (e.g., Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ)) that works in the distal tubule of the kidney, promoting sodium and water excretion.

Cardiac Glycosides
Medications (e.g., Digoxin) that increase the force of heart contractions and slow down the heart rate, used to treat heart failure and irregular heartbeats.