L66: esophagus and pharynx
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
MCQ: which animal may present difficulty in passing a nasogastric tube due to the presence of a pharyngeal diverticulum?
pigs
MCQ: what animals have skeletal muscle throughout their esophageal wall?
canine
bovine
caprine
why do ruminants have skeletal muscle throughout their esophageal wall?
to enable regurgitation for the rumination process
pharynx
a passage and that connects the nasal and oral cavities to the esophagus and larynx respectively.
what structure plays a crucial role in both digestion and respiration?
pharynx
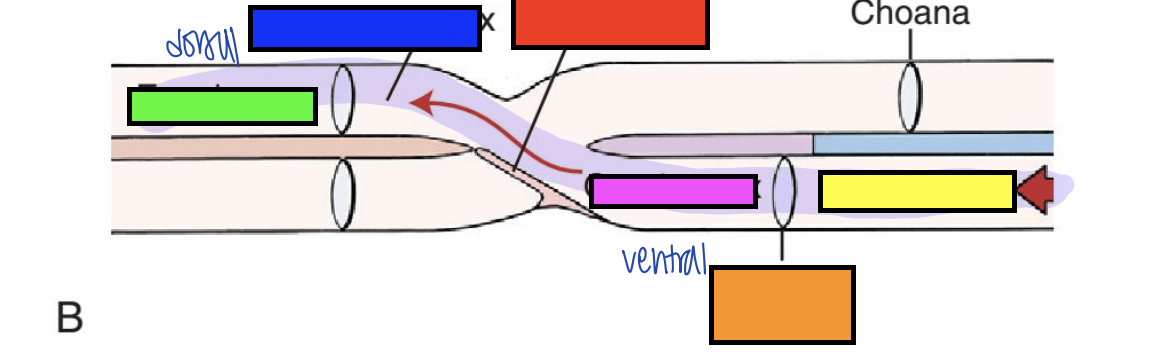
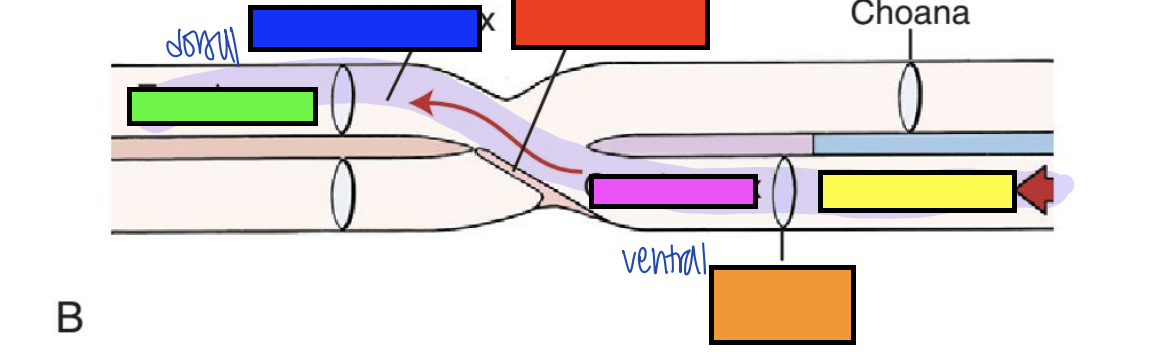
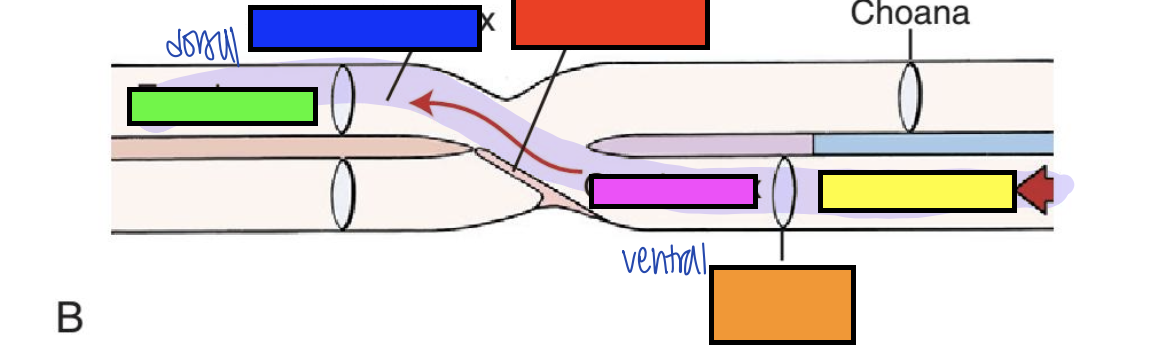
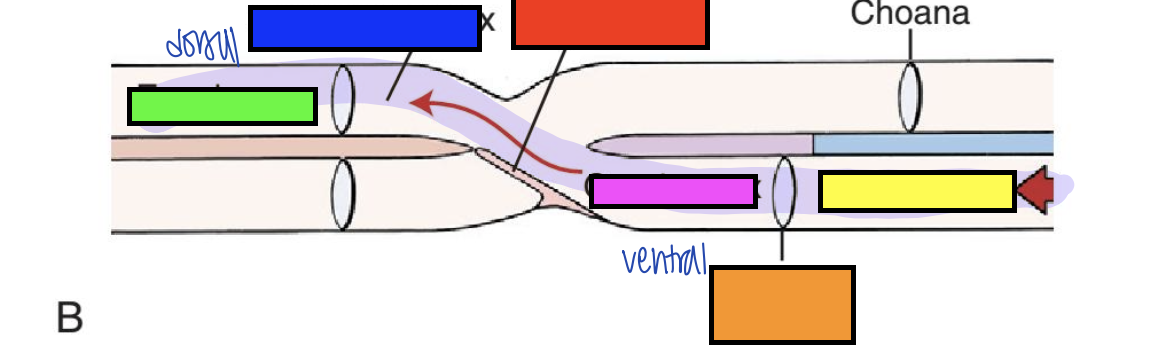
what does crossing from ventral to dorsal of the oropharynx to esophagus allow for in digestion?
smooth swallowing of bolus
what is orange?
isthmus of fauces
what is yellow?
oral cavity
what is pink?
oropharynx
what is green?
esophagus
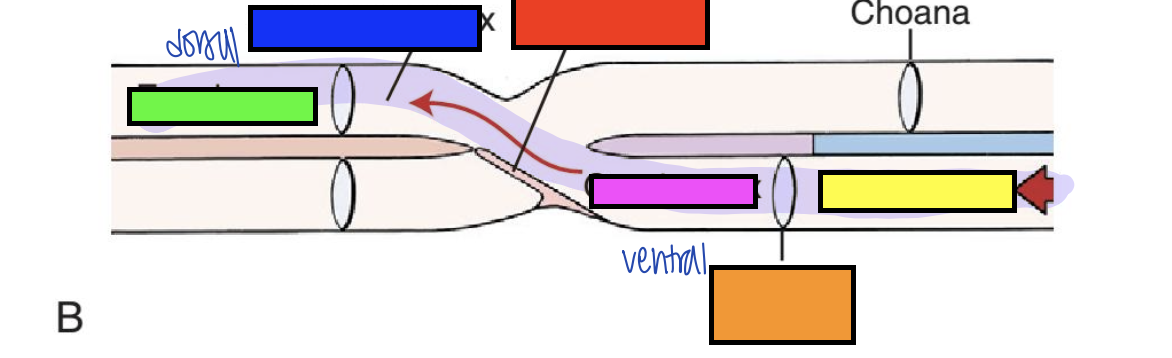
what is blue?
laryngopharynx
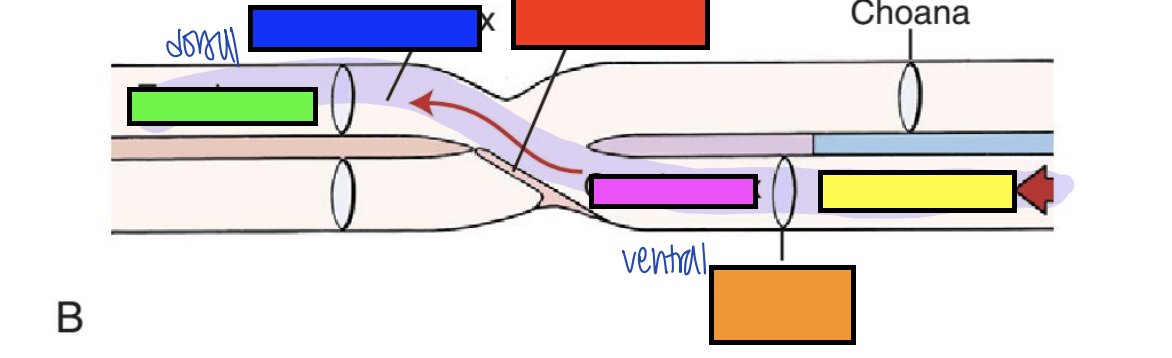
what is red?
epiglottis
what structure is caudal to the oral cavity?
oropharynx
what is the location of the oropharynx?
From Palatoglossal folds and arches, to the hyoid apparatus
what structure is caudal to the nasal cavity?
nasopharynx
where does the laryngopharynx have more obvious tubular construction?
at the beginning of the esophagus
Common Pharynx/intralaryngeal opening
the region where the oropharynx, nasopharynx, and laryngopharynx meet, facilitating the passage of air and food
what structures does the soft palate separate?
separates nasophaynx from oropharynx
what structure has to be lifted during swallowing and vomiting?
soft palate
what structure protects the airways during the act of swalliowing?
epiglottic cartilage
what does the epiglottic cartilage cover?
Oropharyngeal surface/lingual surface
Laryngeal surface
when is the only time the laryngopharynx will be open?
when bolus opens it for swallowing otherwise collapsed to prevent air from entering esophagus
what are the categories of the muscles of the pharynx?
pharyngeal constrictors
pharyngeal dilators
pharyngeal shorteners
what are the pharygeal constrictor muscles?
hyopharyngeus
thyropharyngeus
cricopharyngeus
what is the pharyngeal dilator muscle?
stylopharyngeus
what are the pharyngeal shortener muscles?
pterygopharyngeus
palatopharyngeus
the muscles of the pharynx are mainly associated with which structure?
laryngopharynx
function of pharyngeal dilators
enlarges the pharynx during swallowing, bolus will assist
function of pharyngeal constrictors
muscles contract to close passage of laryngopharynx and push food into esophagus
hyopharyngeus muscle location
hyoid appratatus to the pharynx
thyropharyngeus muscle location
thyroid cartilage of the larynx to the pharynx
cricopharyngeus muscle location
cricoid cartilage of larynx to pharynx
function of palatopharyngeus muscle
pulls pharynx forward and lifts soft palate slightly upward
function of pterygopharyngeus
pulls pharynx slowly forward when swallowing has been intiated
location of pterygopharyngeus muscle
pterygoid bone of the skull towards the pharynx
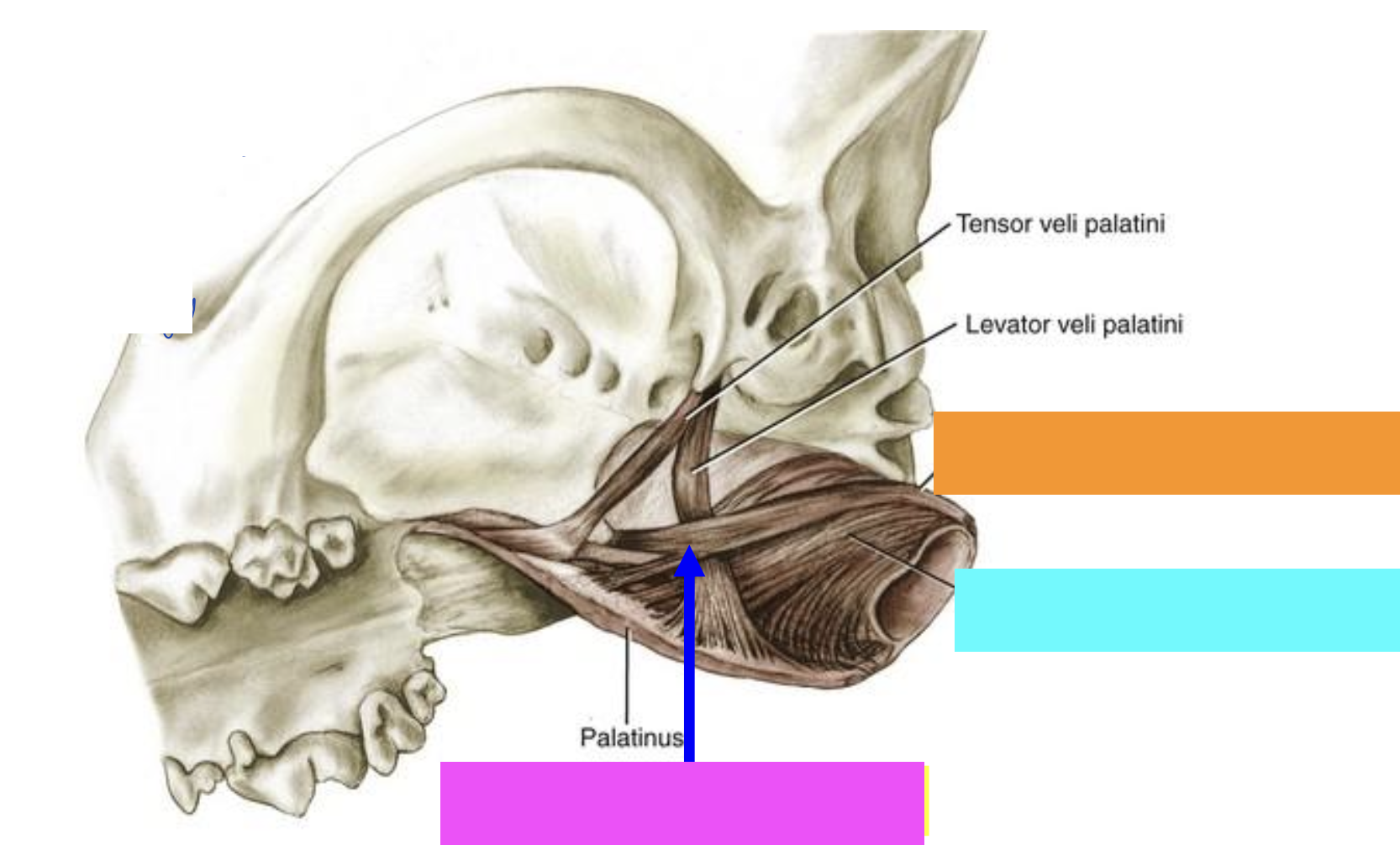
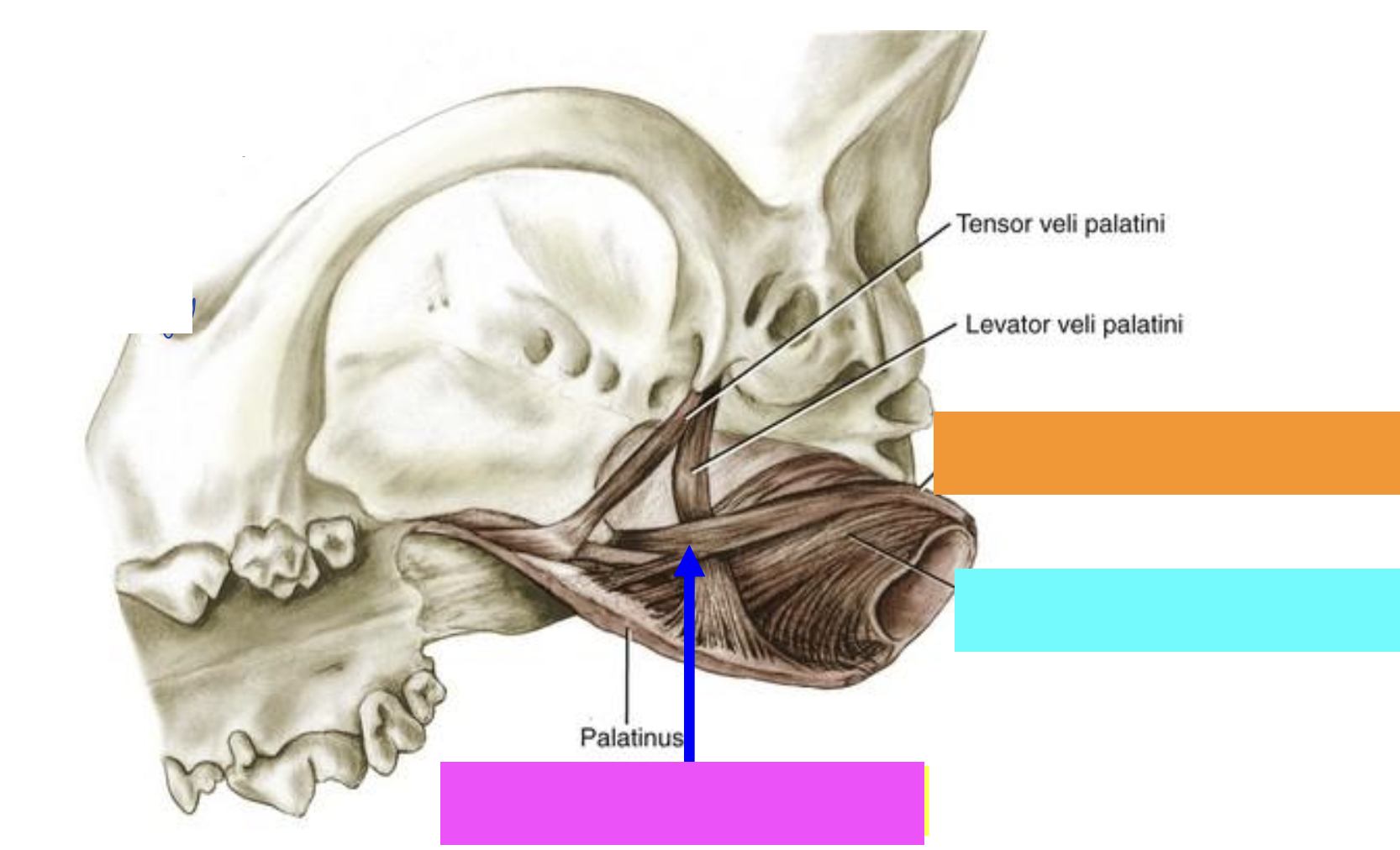
what is orange?
Pterygopharyngeus muscle
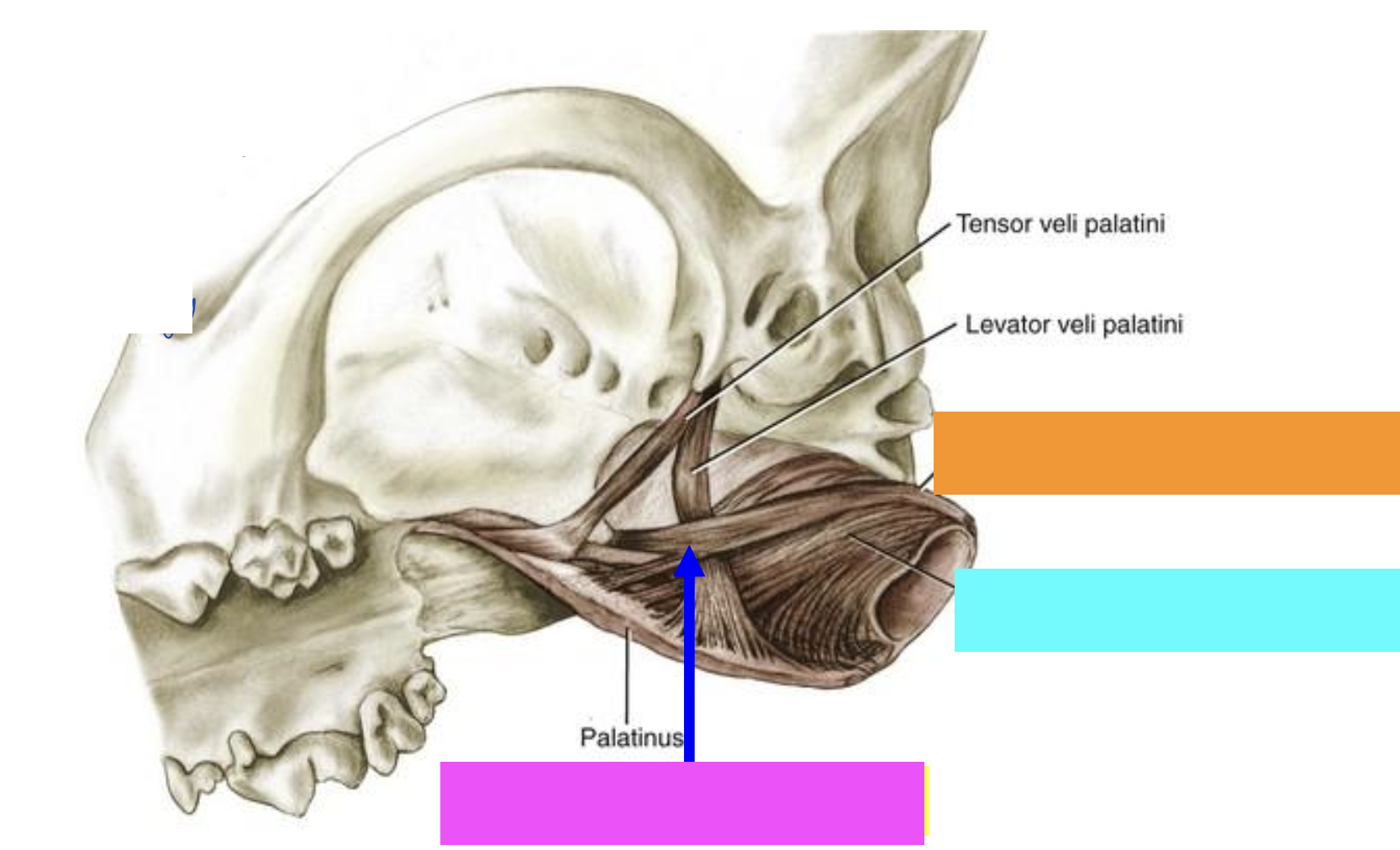
what is blue?
Palatopharyngeus muscle
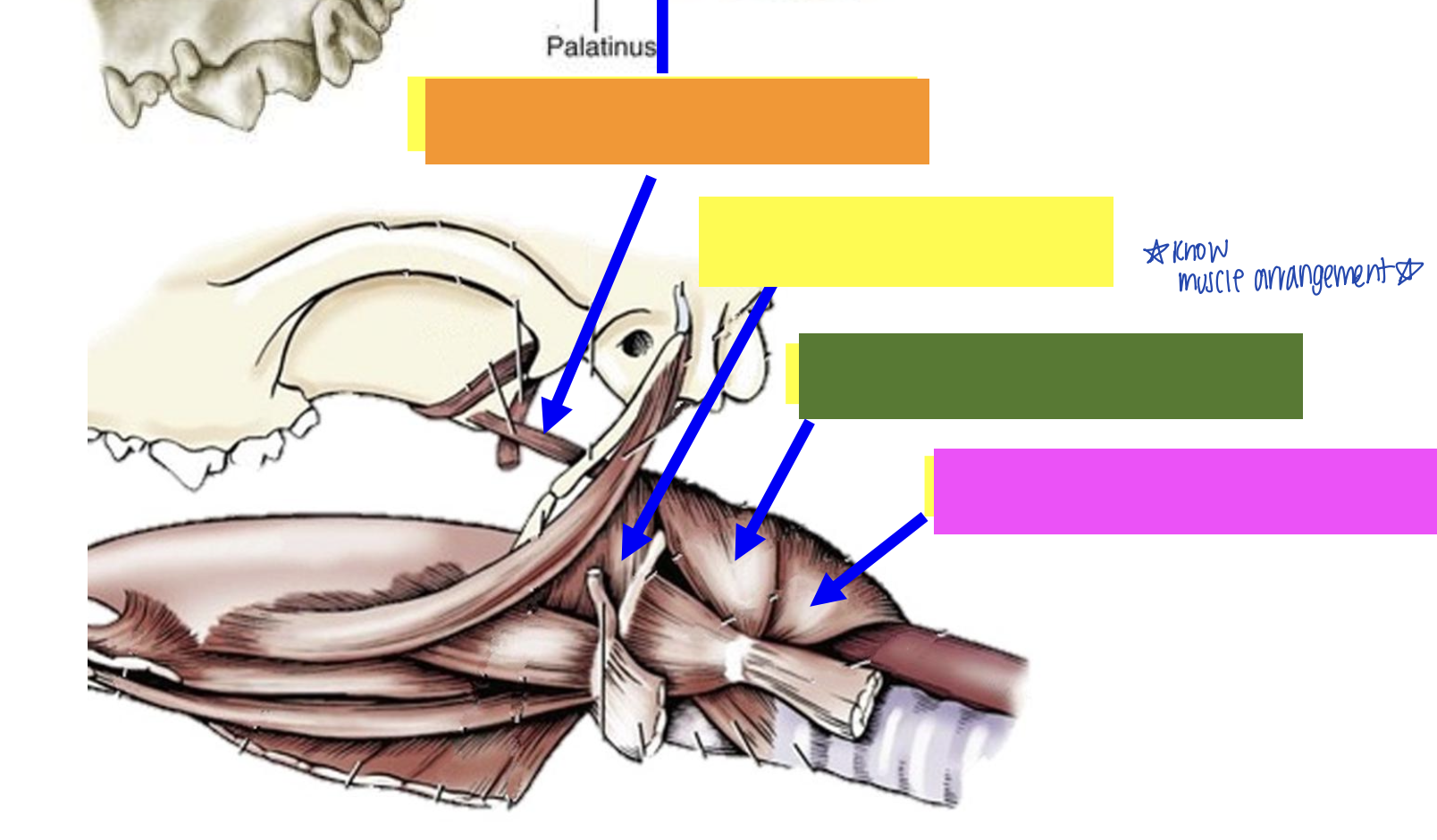
what is pink?
Pterygopharyngeus muscle
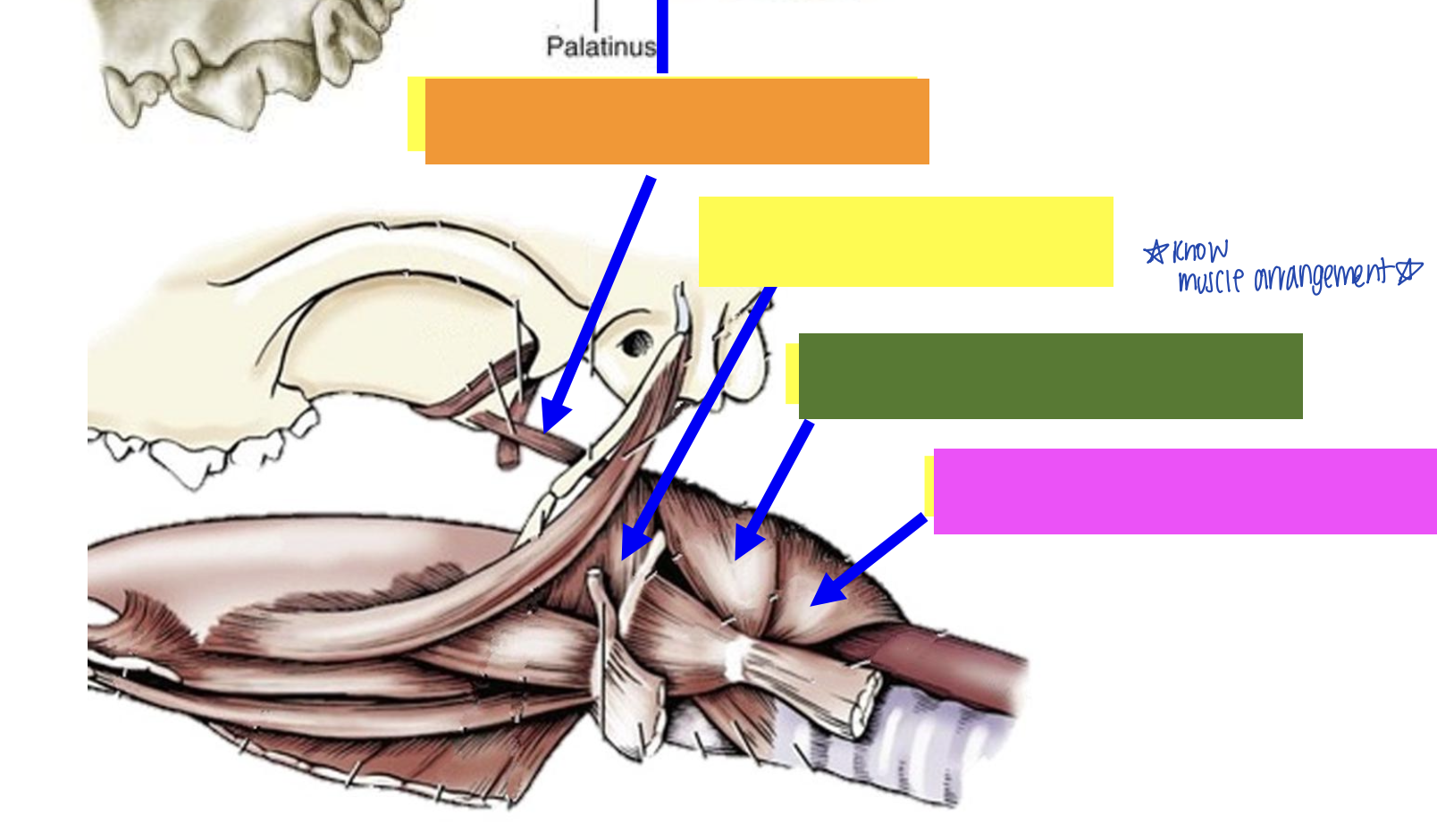
what is orange?
Pterygopharyngeus muscle
what is yellow?
Hyopharyngeus muscle
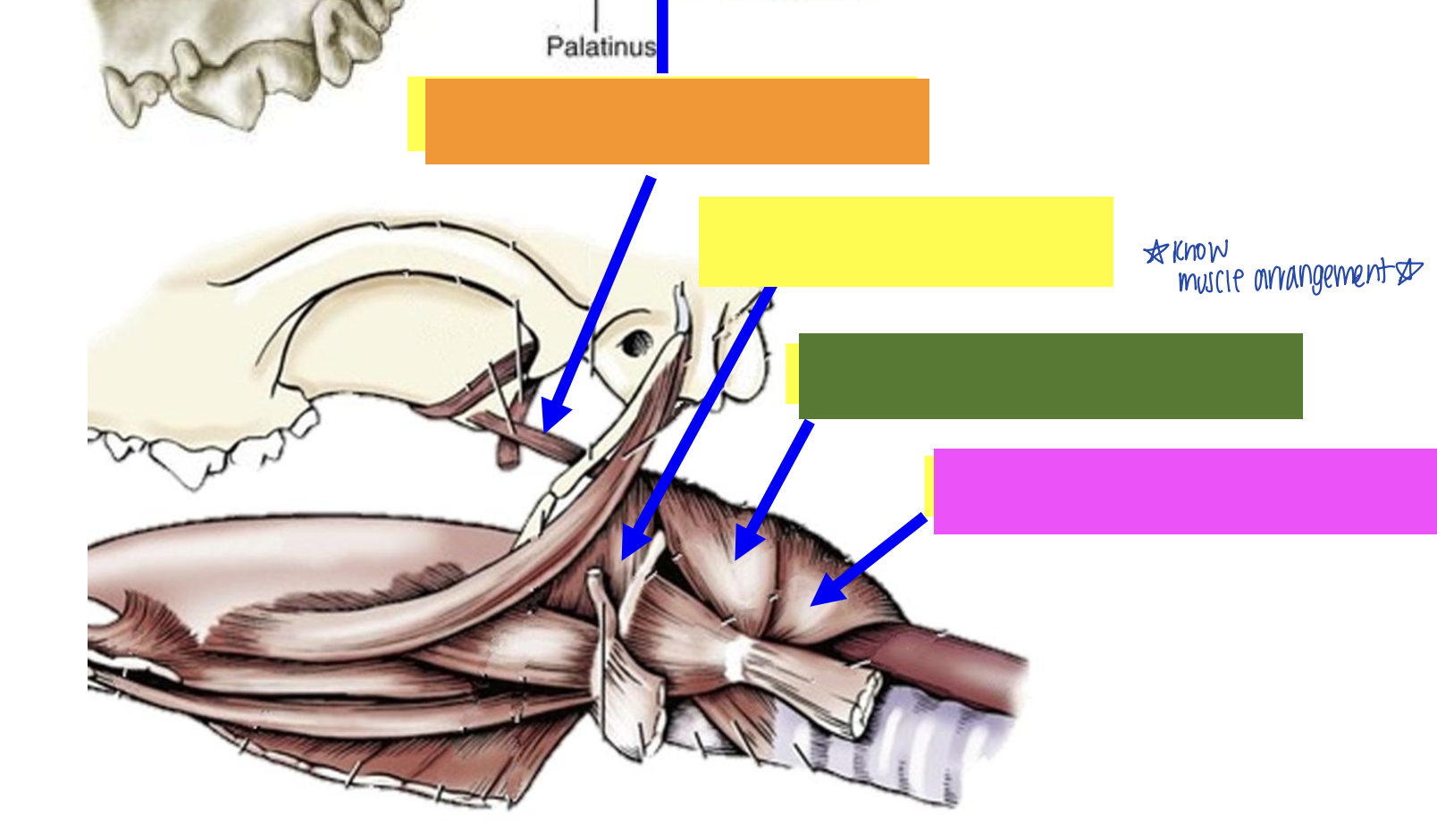
what is green?
Thyropharyngeus muscle
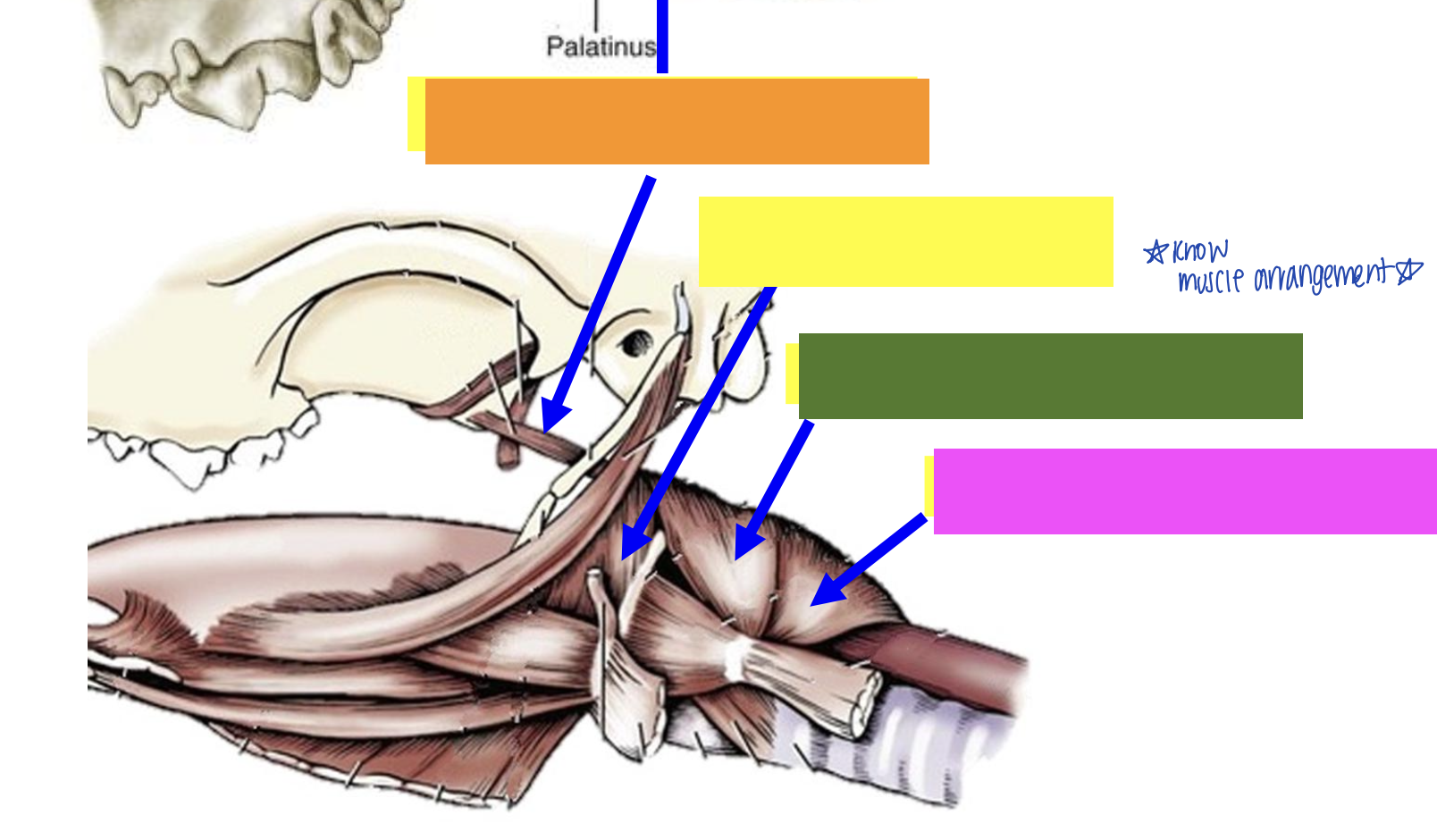
what is pink?
Cricopharyngeus muscle
what provides motor innervation to the muscles of the pharynx (in order of the amount they play a role in i.e. 1= plays a major role)?
vagus nerve (CN X)
glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
cranial root of the accessory nerve (CN XI) -very little role!
what provides sensory innervation to the muscles of the pharynx (in order of the amount they play a role in i.e. 1= plays a major role)?
glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
vagus nerve (CN X)
trigeminal nerve (CN V)
what initates the swallowing reflex?
bolus reaching oropharynx region
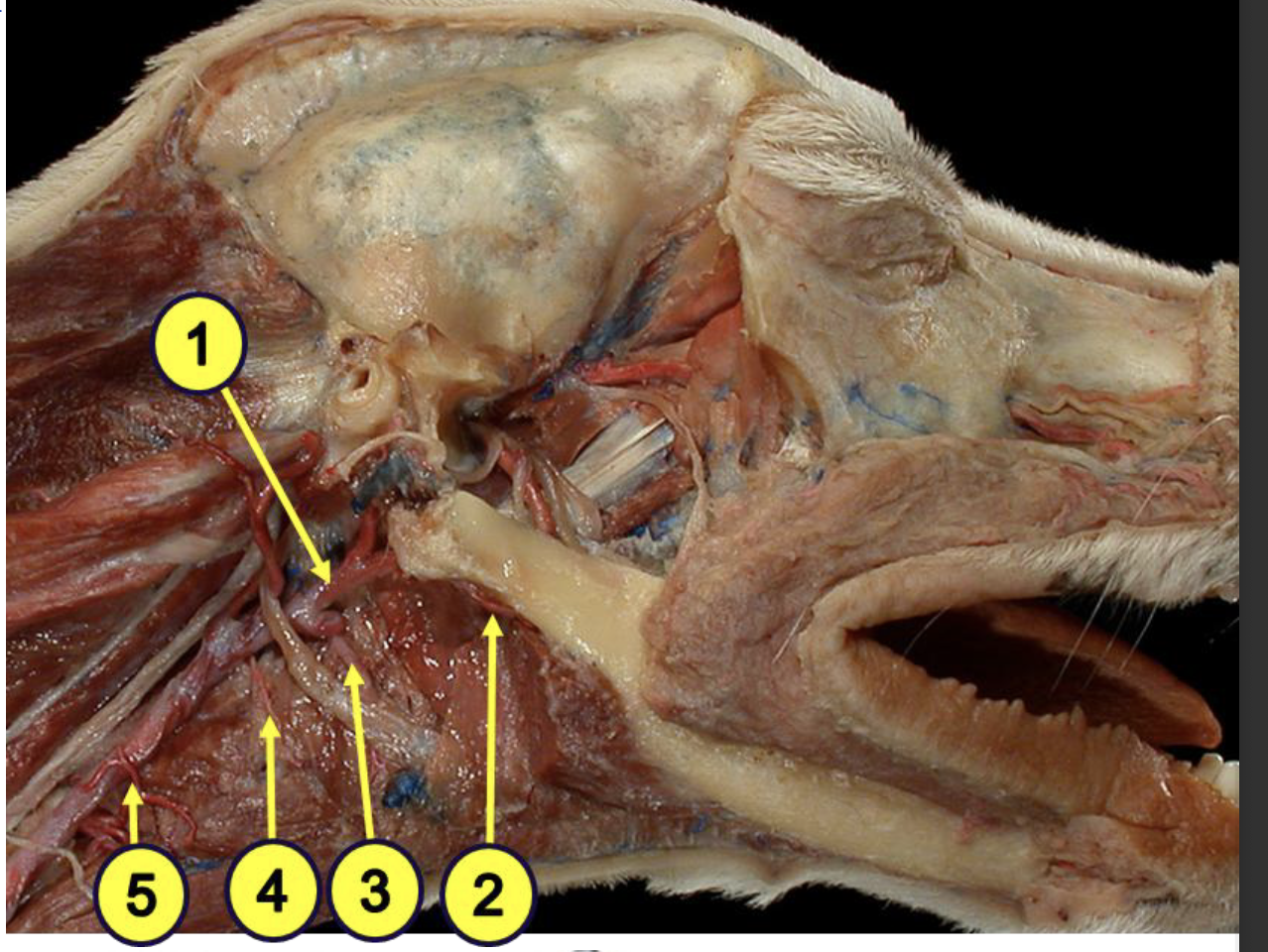
what is 1?
external carotid artery
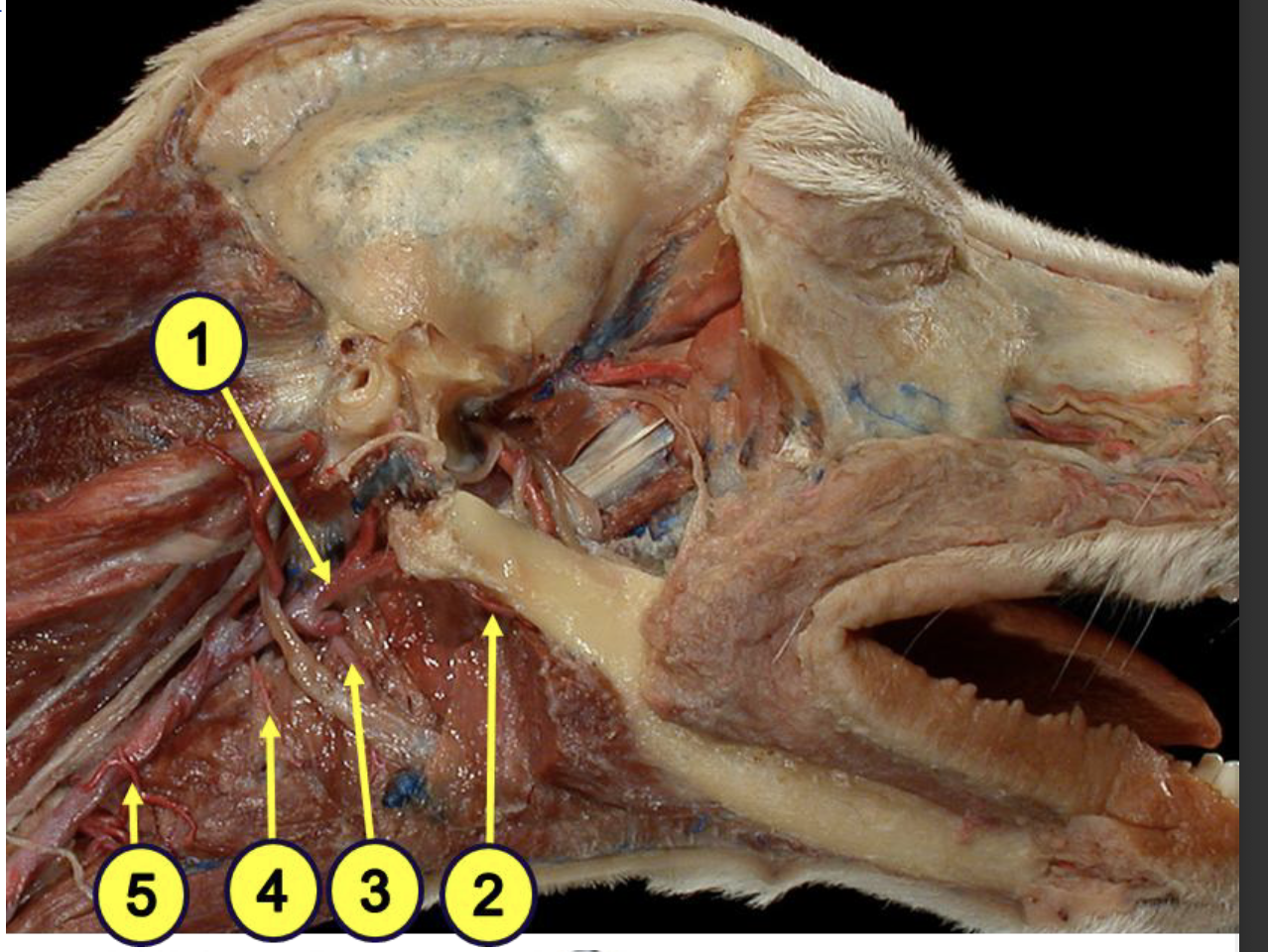
what is 2?
facial artery
what provides the major blood supply of the pharynx?
ascending pharyngeal artery
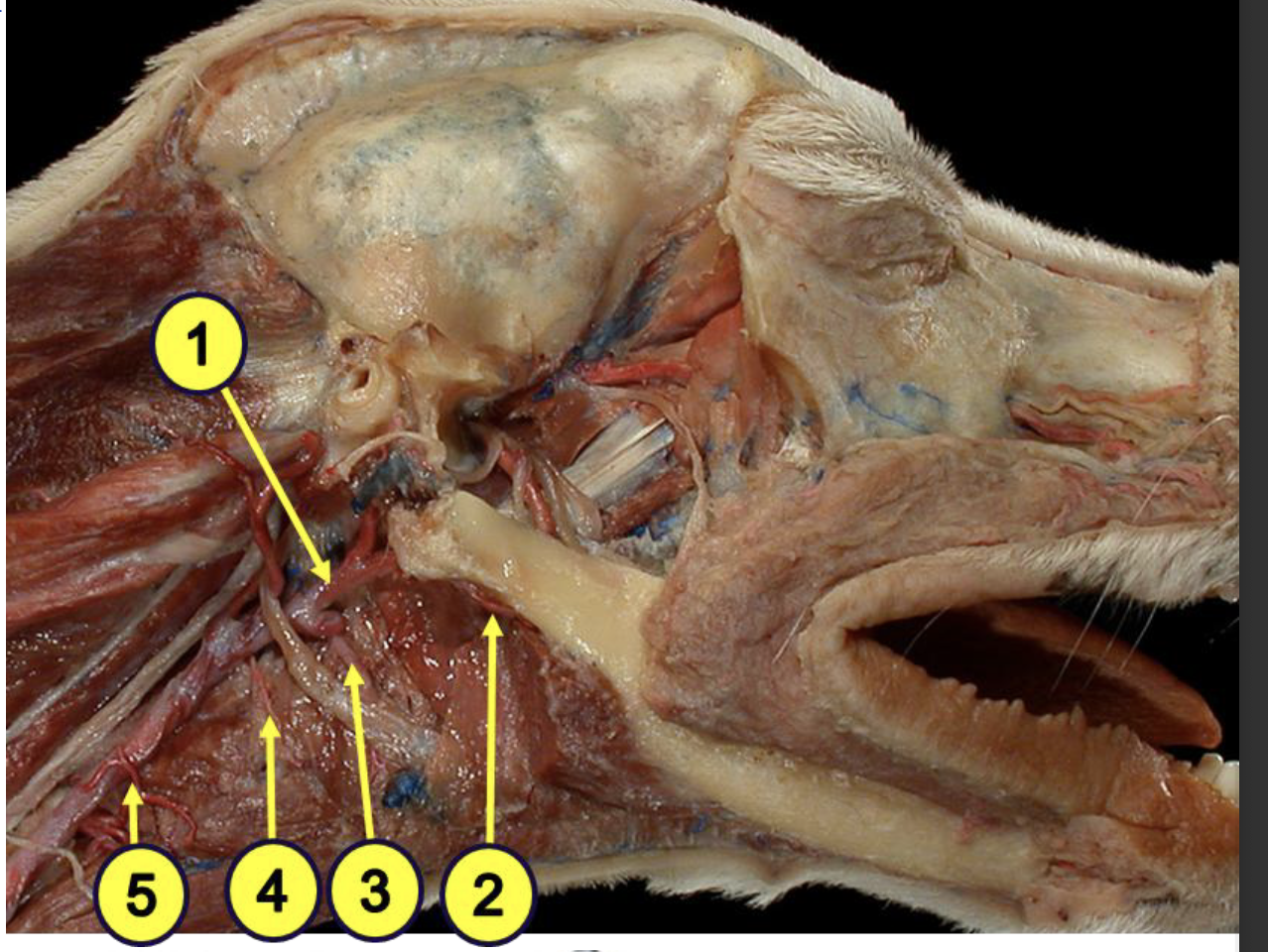
what is 3?
lingual artery
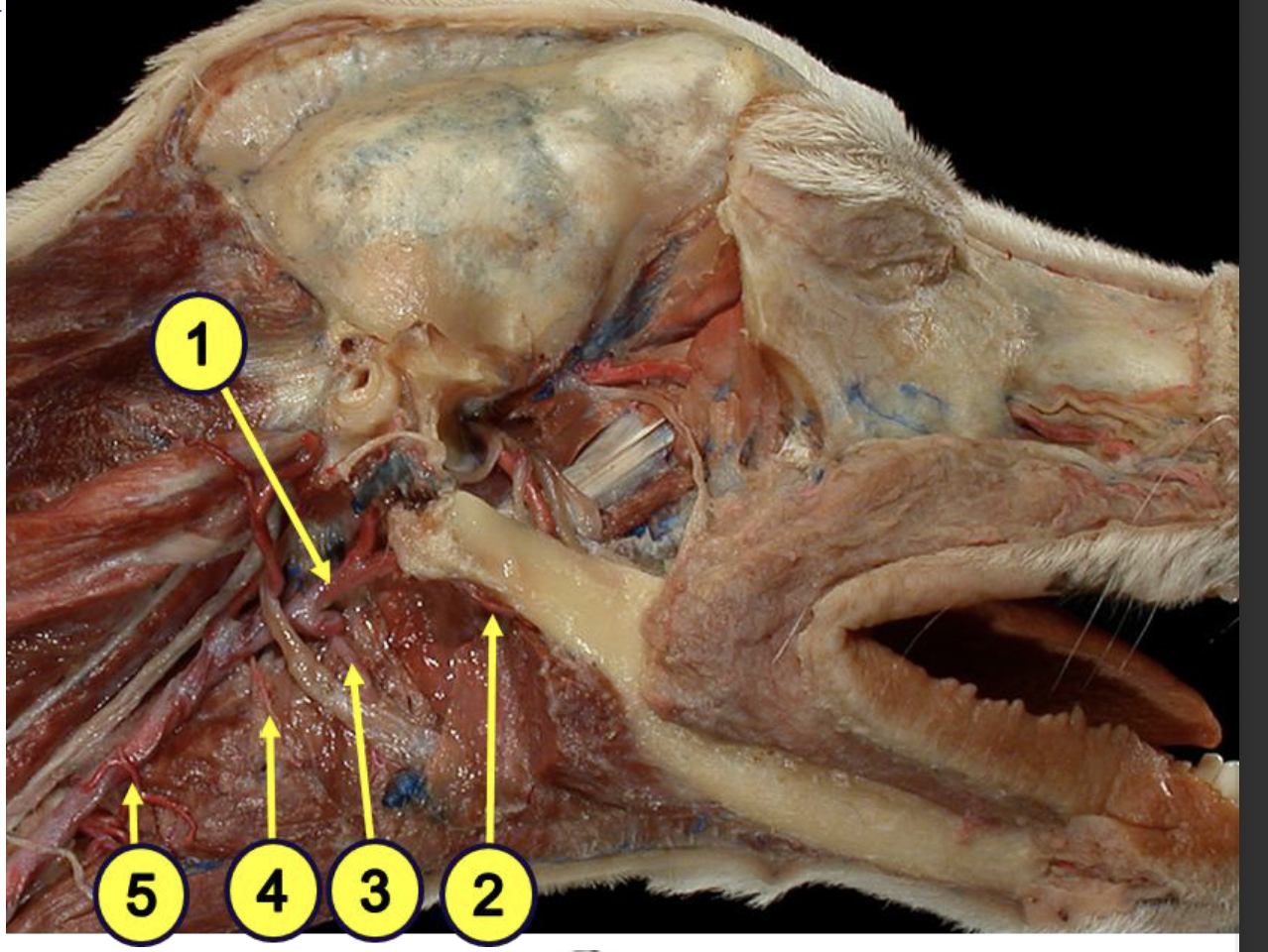
what is 4?
cranial laryngeal artery
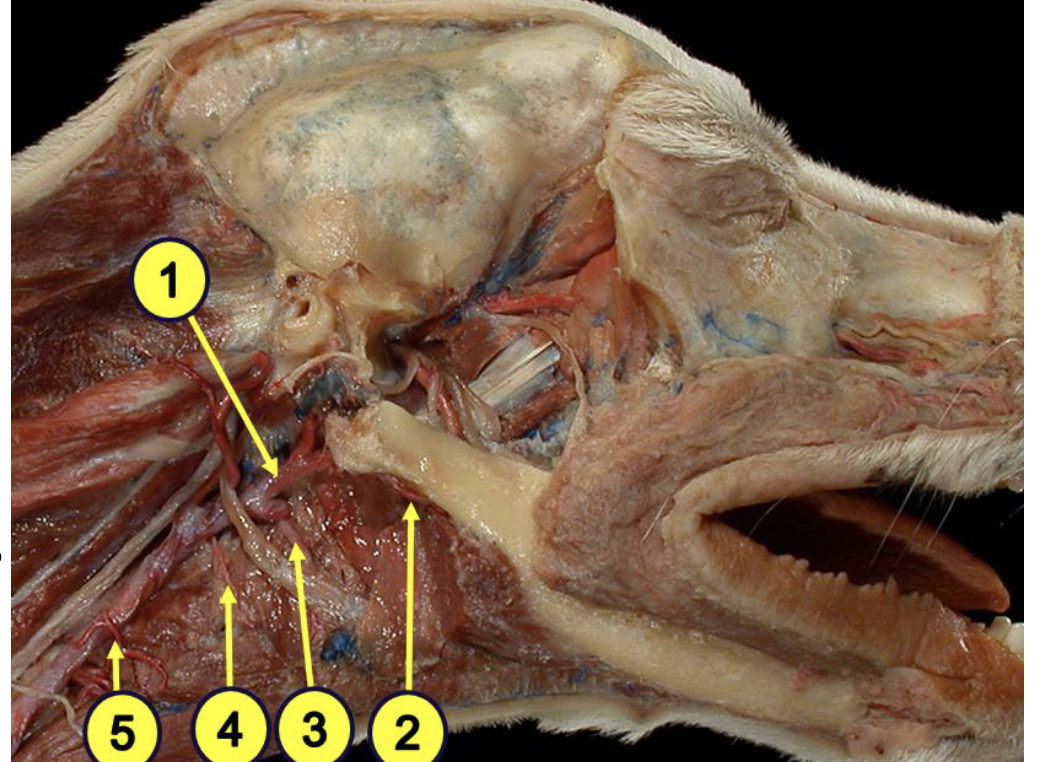
what is 5?
cranial thyroid artery
what does the pharyngeal plexus and satellite veins drain into?
internal and external jugular veins
describe the pharynx in the horse
long and narrow for obligate nasal breathing
describe the soft palate in the horse
longer soft palate that lies beneath epiglottic cartilage which prevents oral breathing
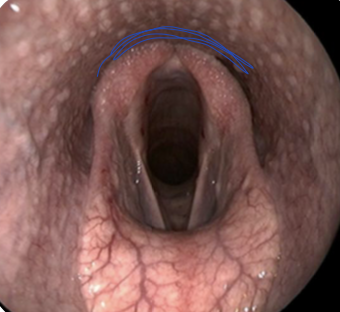
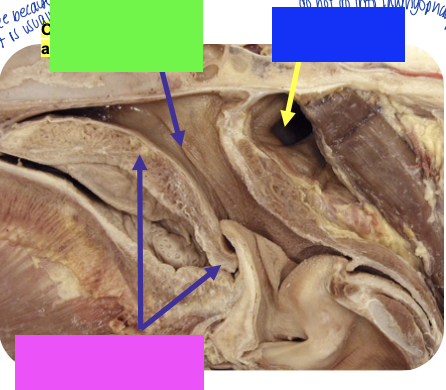
what is the blue line showing?
opening of laryngopharynx should be somewhere along this line but cannot see because usually it is collapsed
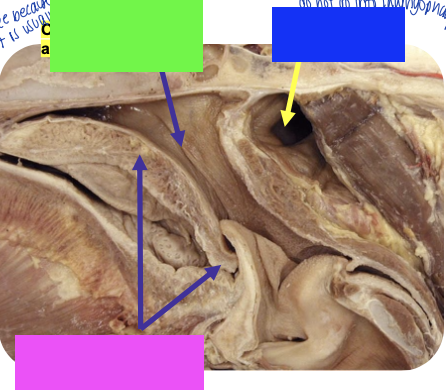
what is pink?
soft palate
what is blue?
guttural pouch
what is green?
opening of auditory tube
what is the function of the auditory tube in horses?
connects middle ear to nasopharynx to help cool down blood going to the brain
what is the pharynx adapted for in ruminants?
rumination and prevention of aspiration during regurgitation
what is the process of rumination?
regurgitation, remastication, and reswallowing food
describe the pharynx of ruminants
have wider pharynx to allow swallowing of larger boluses
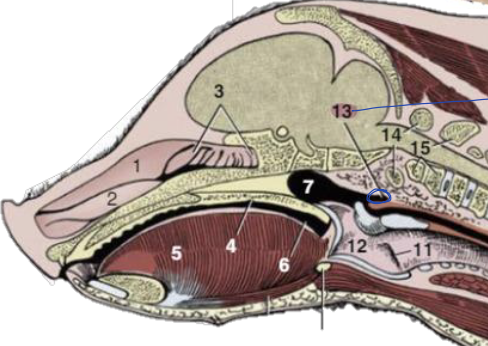
what is 13?
pharyngeal diverticulum
what does the soft palate of ruminants allow for?
limited oral breathing
what makes up the pharyngeal plexus?
vagus nerve
glossopharyngeal nerve
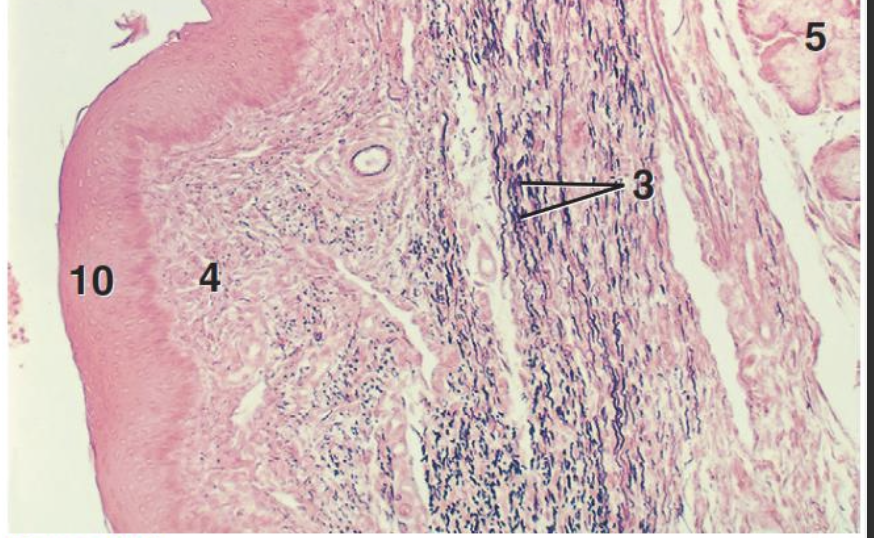
describe the microscopic anatomy of the nasopharynx
ciliated epithelium to trap and clear debris
describe the microscopic anatomy of the oropharynx and laryngopharynx
protective stratified squamous epithelium to withstand mechanical stress
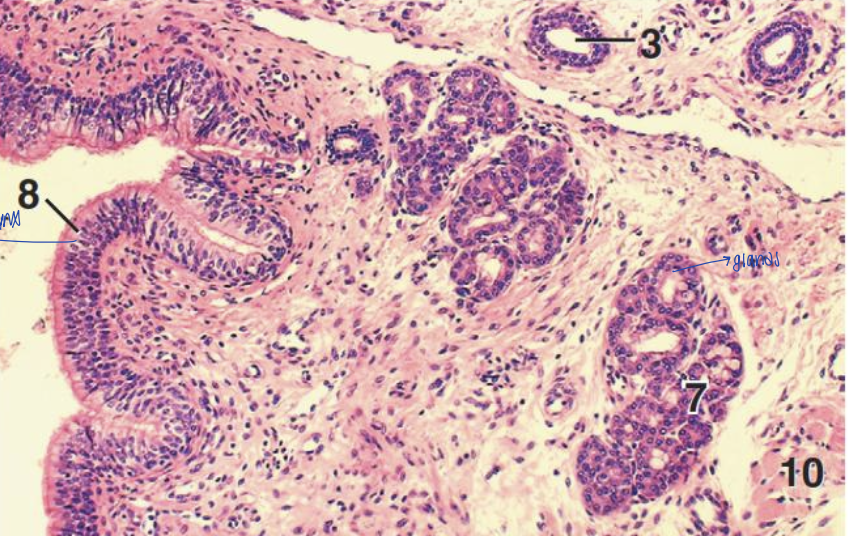
what structure is this?
nasopharynx of the dog
what structure is shown?
oropharynx of dog
what can tonsils initate?
immune response, it is the first line of defense of the digestive system
what are the types of tonsil tissues?
pharyngeal
palatine
lingual
paraepiglottic
which species have paraepiglottic tonsils?
pig and horse
location of lingual tonsils
embedded in the mucosa of the tongue (root)
which species have well developed lingual tonsils?
bovine and small ruminants
what are palatine tonsils associated with?
oropharyngeal surface
which species have palatine tonsils visible in the tonsilir fossa?
dogs and cats
which species have palatine tonsols?
dog, cat, horse, ruminants, pigs
where are palatine tonsils located in ruminants?
deep within the muosa (tonsillar sinus)
where are palatine tonsils visible in the pig?
soft palate
where are the pharyngeal tonsils?
associated with nasopharynx
what does it mean if the pharyngeal tonsil is tubal?
it is around the opening of the auditory tube
MALT
mucosa associated lymphoid tissue
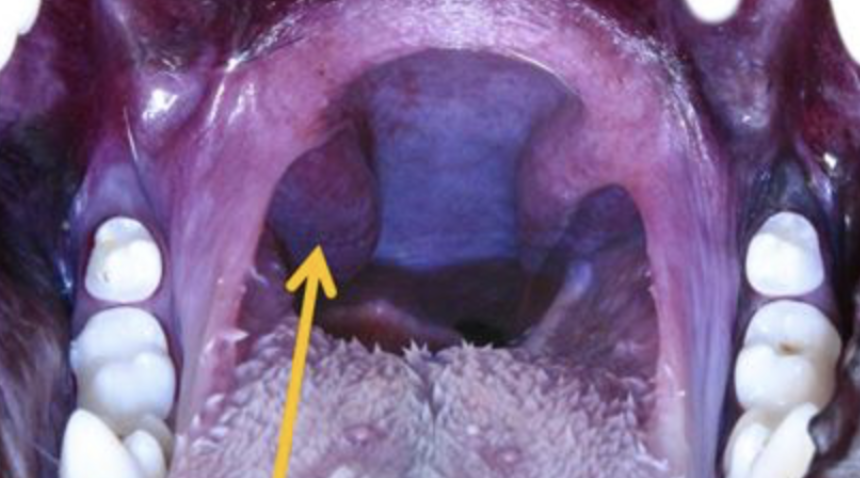
what is the arrow pointing at?
palatine tonsils
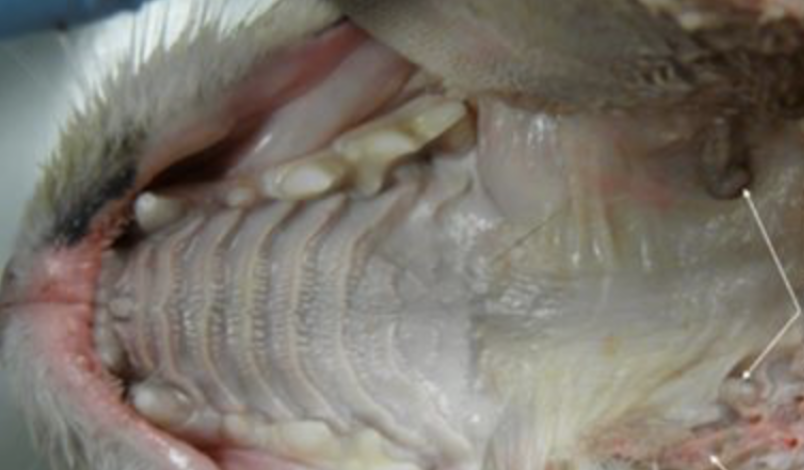
what is the arrow pointing at?
palatine tonsils
which species have large palatine tonsils with deep crypts for antigen trapping?
ruminants and pigs
which species have scattered lymphoid tissue rather than a well-defined tonsillar structure?
horses
which species have deep crypts in the palatine tonsils making them more prone to tonsillitis?
dogs
MCQ: Which animal does not have clearly visible palatine tonsils?
horse
where does the esophagus extend from and to?
extends from cricoid cartilage to the cardia of the stomach
what parts is the esophagus broken down into?
cervical part
thoracic part
abdominal part
where does the esophagus move when you go down along the neck in the cervical region?
left lateral position
what is the esophagus?
tubular and muscular hollow organ that connects the pharynx to the stomach, allowing the passage of food and liquid
describe the location of the cervical part of the esophagus>
from the pharynx (Cricoid cartilage of the larynx) to the cardia of the stomach
what muscles make up the cranial/upper esophageal sphincter in the cervical part of the esophagus?
cricopharyngeus muscle
thyropharyngeus muscle
what is the location of the lower esophageal sphincter/ cardiac sphincter in the cervical part of the esophagus?
at the opening into the stomach at the cardia of the stomach
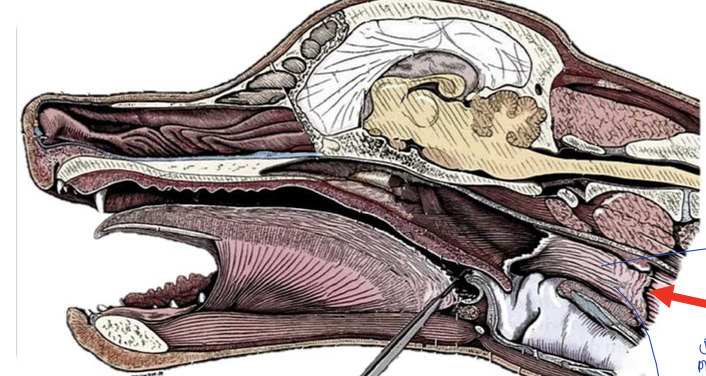
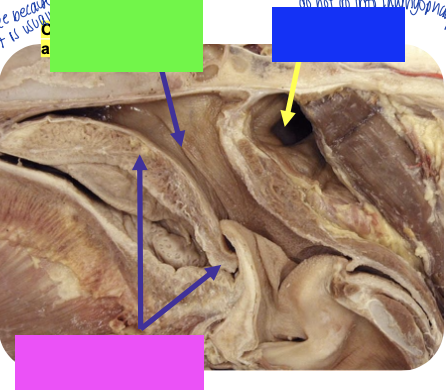
what is the red arrow pointing to?
pharyngoesophageal limen
what muscles if constricted will close the passage of the laryngopharynx to allow food to go through the esophagus?
thyropharyngeus muscle
cricopharyngeus muscle
what is the location of the thoracic part of the esophagus?
from thoracic inlet to the esophageal hiatus of the diaphragm; within the mediastinum
what is the location of the abdominal part of the esophagus?
liver to left side of esophageal notch