The X-ray Tube (Ch 5)
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
What makes up the x-ray tube?
Cathode, anode, and glass tube housing
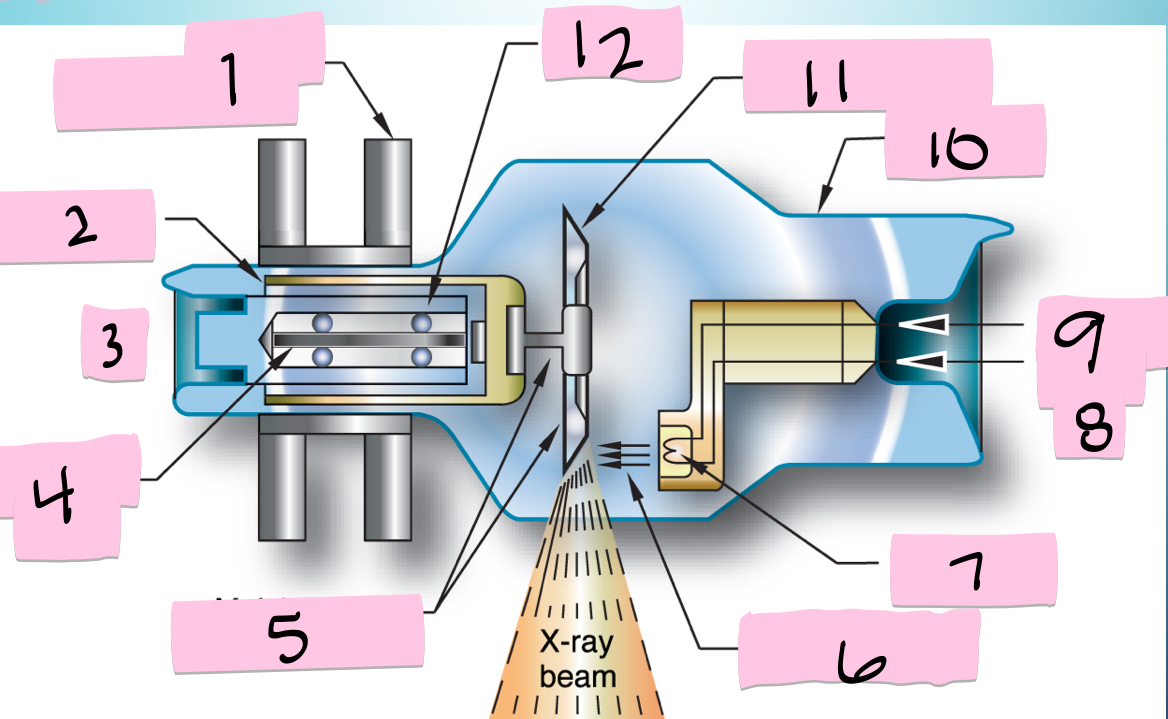
What is 1 pointing to?
Stator electromagnets
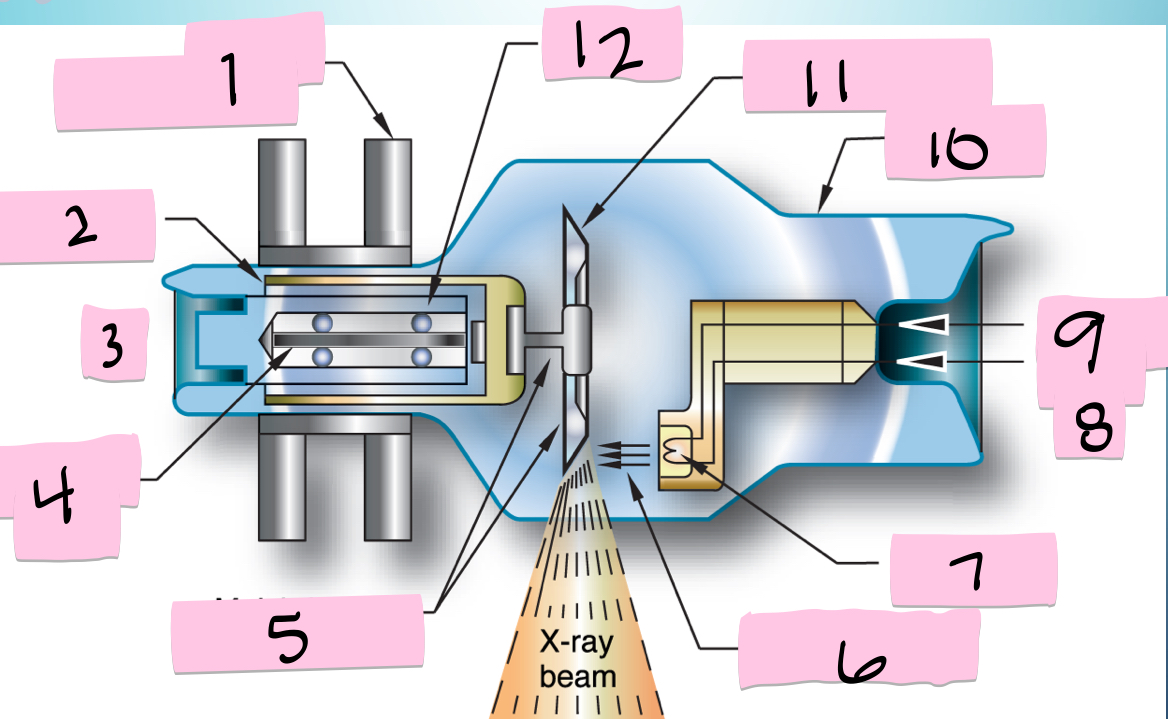
What is 2 pointing to?
Armature
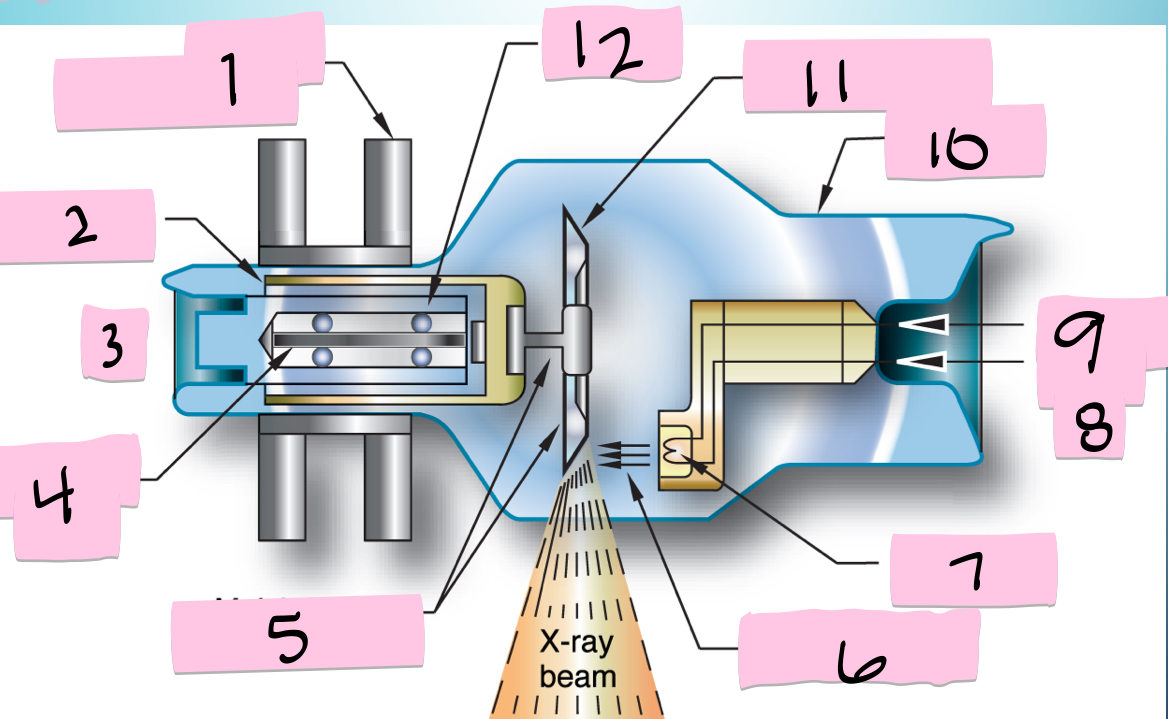
What is 3 pointing to?
+
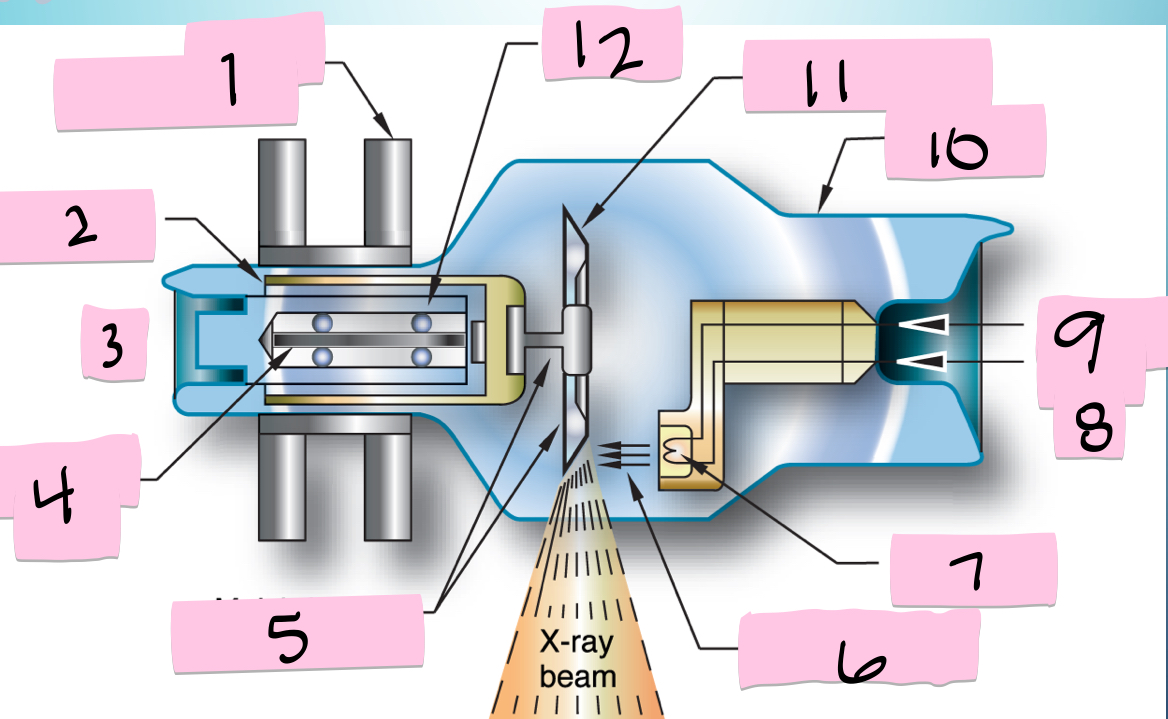
What is 4 pointing to?
Rotating portion
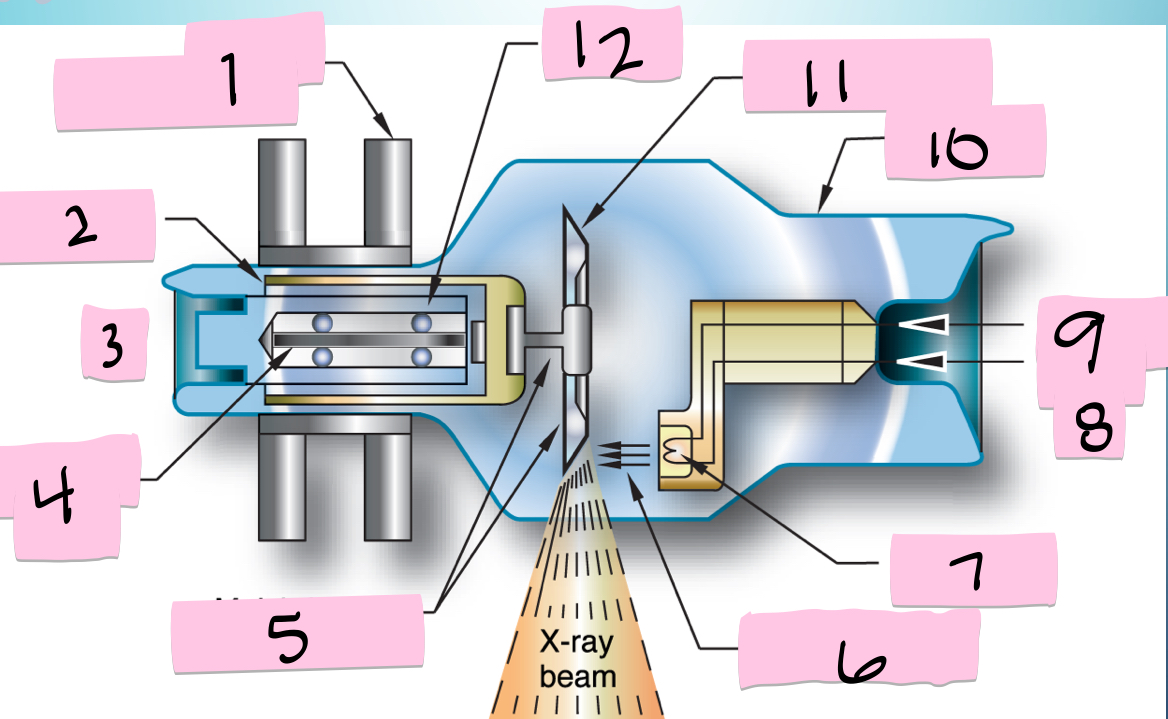
What is 5 pointing to?
Molybdenum neck and base
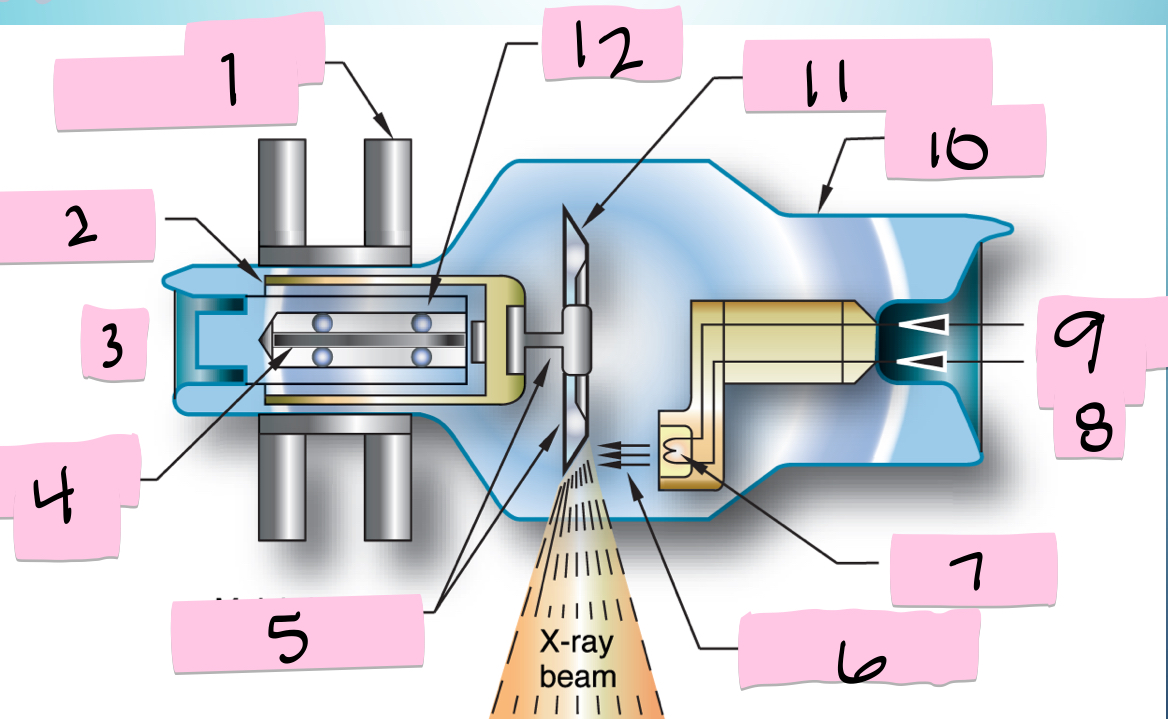
What is 6 pointing to?
Electron beam
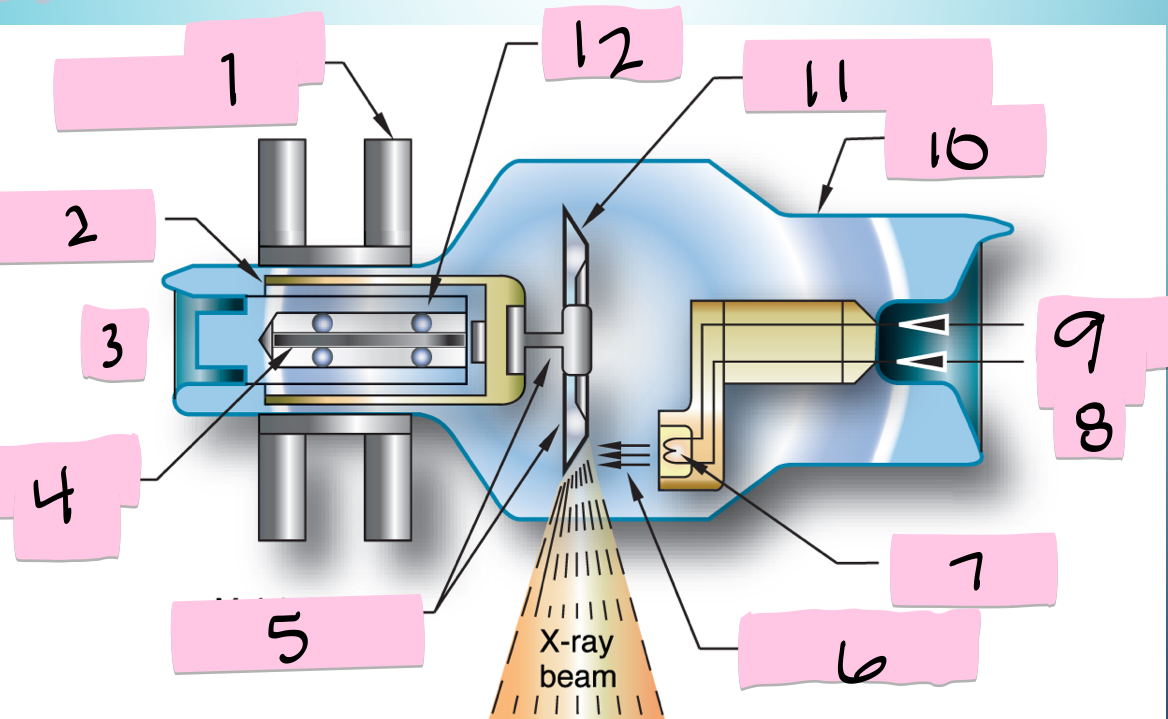
What is 7 pointing to?
Filament
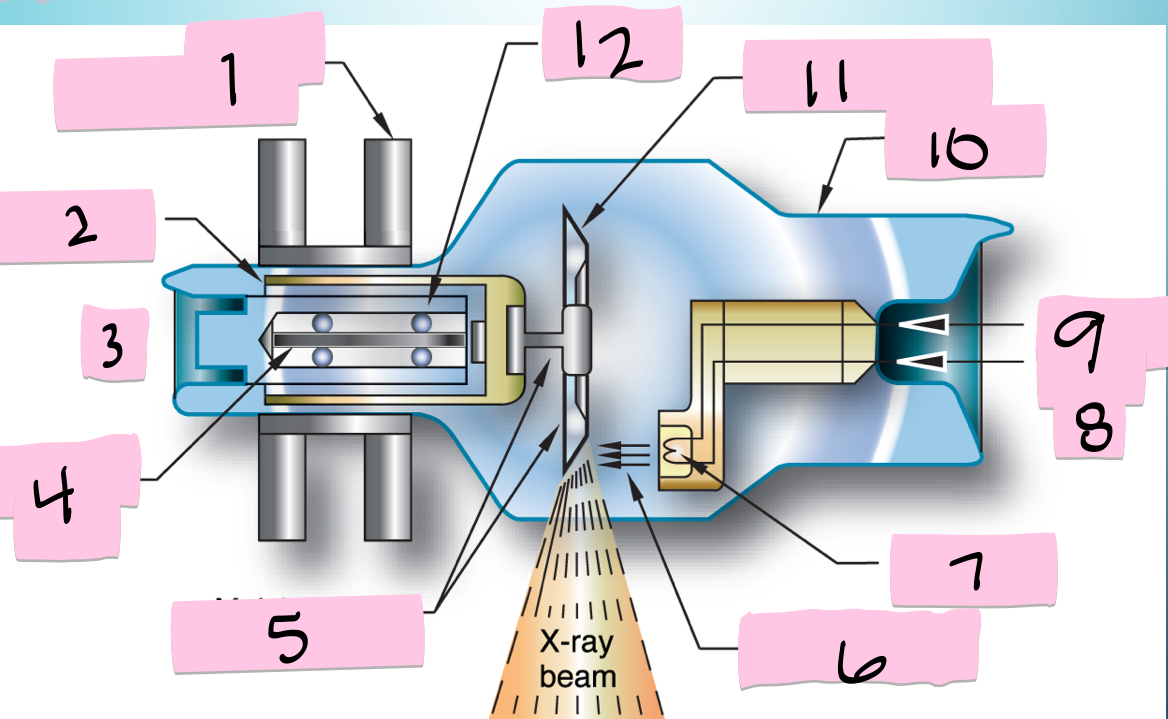
What is 8 pointing to?
-
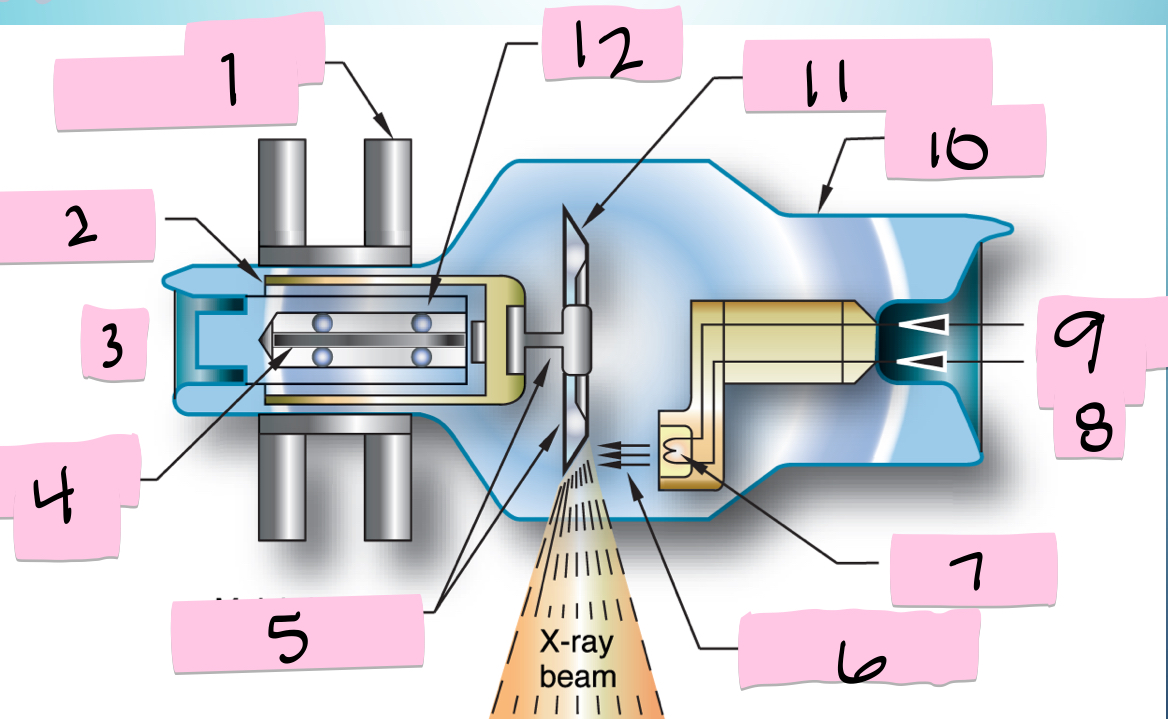
What is 9 pointing to?
Filament circuit
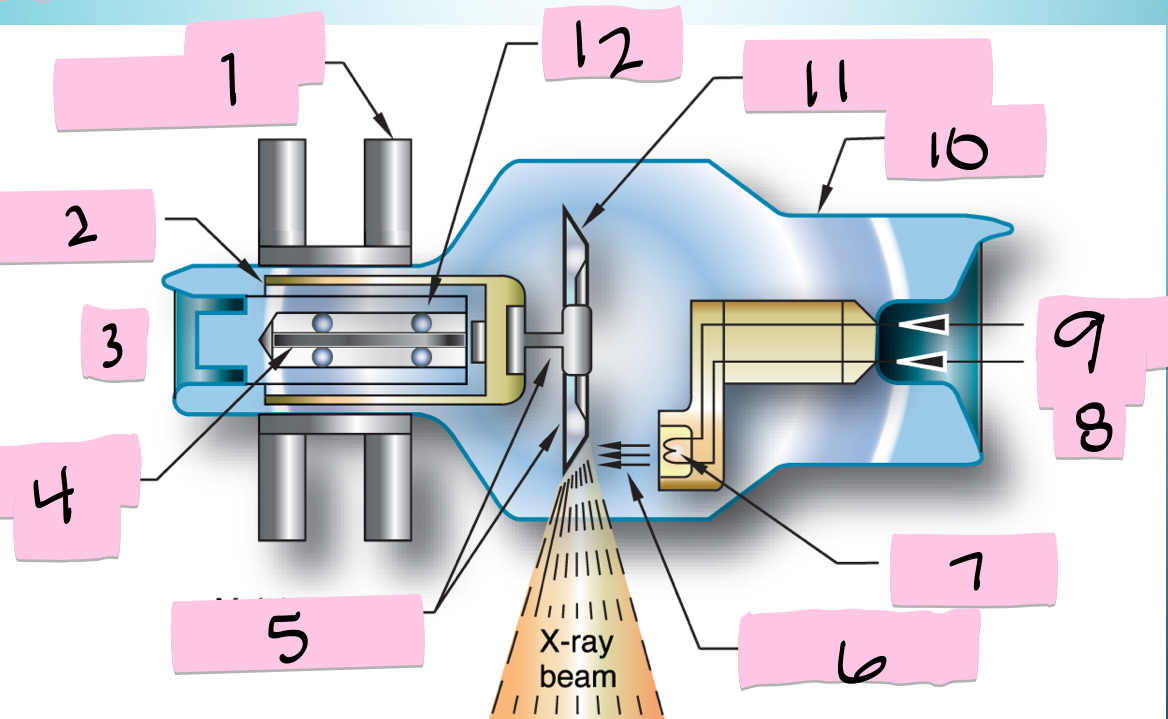
What is 10 pointing to?
Envelope
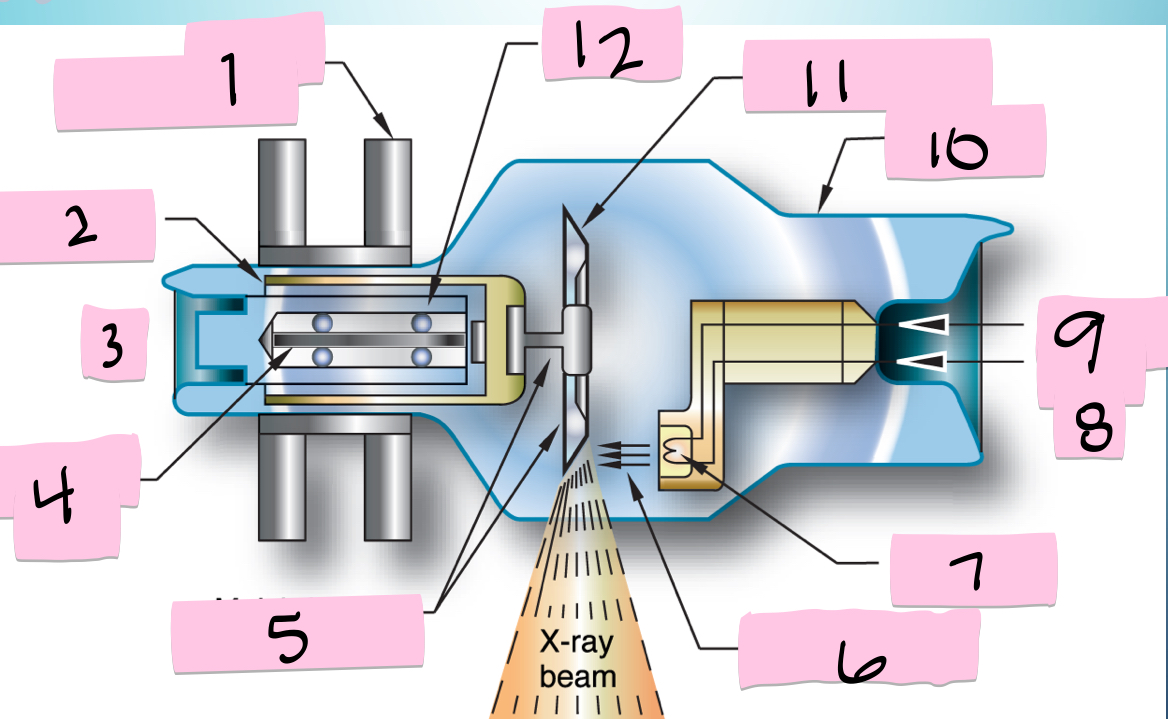
What is 11 pointing to?
Tungsten anode
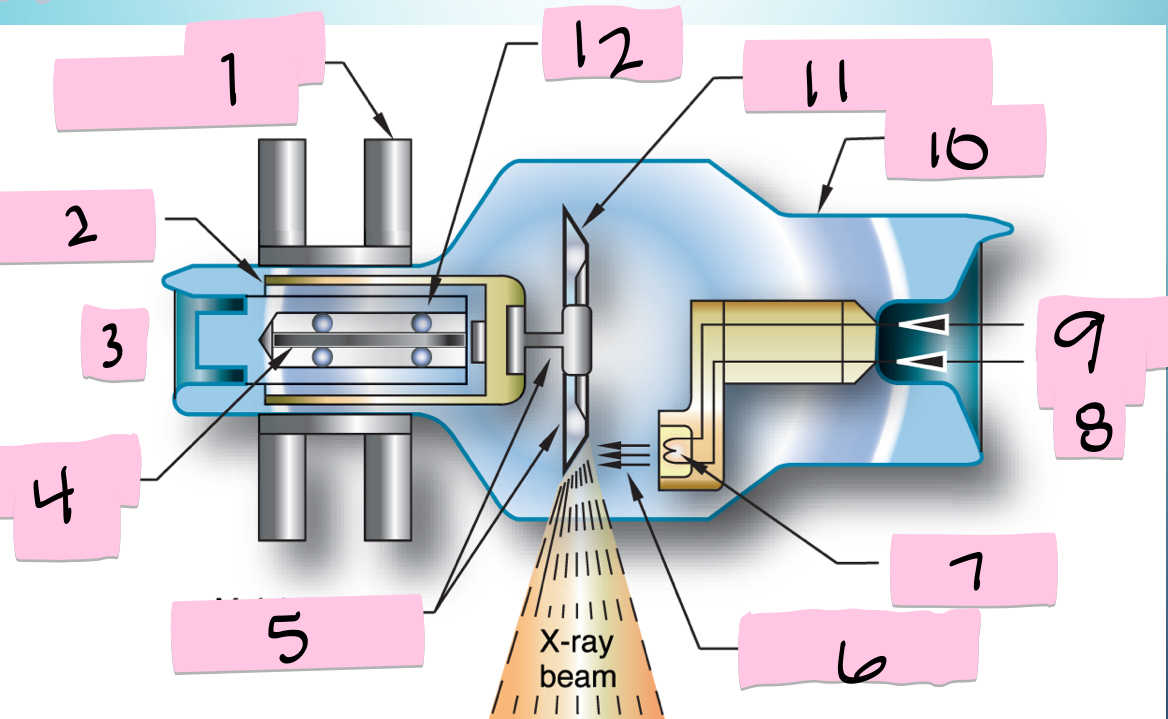
What is 12 pointing to?
Bearing
What side is the negative side of the tube?
Cathode
What are the functions of the cathode assembly?
to produce a thermionic cloud
conduct the high voltage between the cathode and anode
focus the electron stream
What are the parts of the cathode assembly?
Filament, focusing cup, associated wiring
What is the filament?
A small, thin coil of thoriated tungsten
How thick in the filament?
0.1-0.2 mm
What is the atomic number of thorium?
90
Why is tungsten used for the filament?
high melting point (3370 degrees C)
hard to vaporize
What is the melting point of thoriated tungsten?
3420 degrees C
What do some tubes also use other than tungsten?
Molybdenum or rhenium
What is the atomic number of rhenium?
75
What is the melting point of molybdenum?
2620 degrees C
What is the melting point of rhenium?
3170 degrees C
What is the atomic number of molybdenum?
42
The length and width of the filament have a great affect on what?
Recorded detail (focal spot size)
How many filaments do most modern tubes have and what are they called?
2, dual focus tube
For dual focus tubes with a small focal spot, how big is it?
0.3 - 1 mm
For dual focus tubes with a large focal spot, how big is it?
1 - 3 mm
Why would you use a small focal spot on a dual focus tube?
For better detail
Why would you use a large focal spot on a dual focus tube?
For large techniques- so the filament does not become damaged
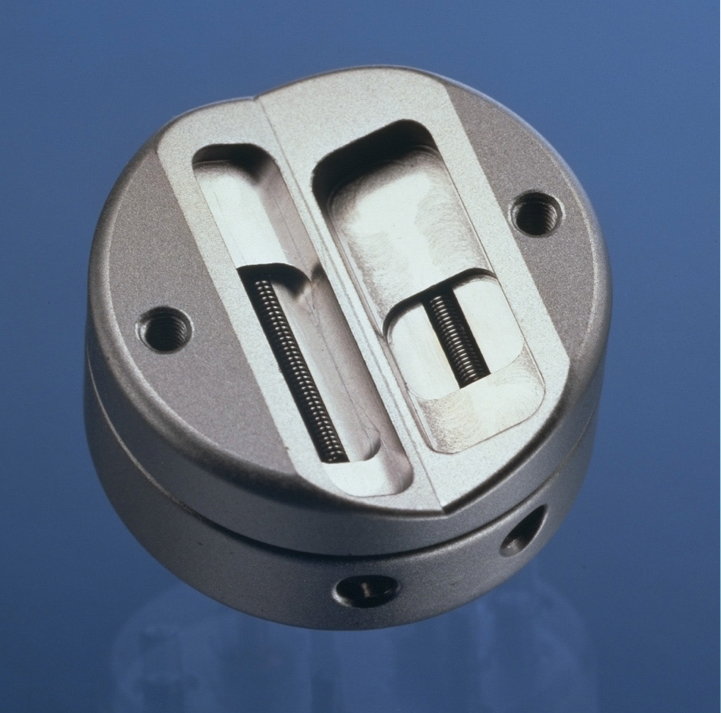

What is this?
Dual filaments in focusing cup
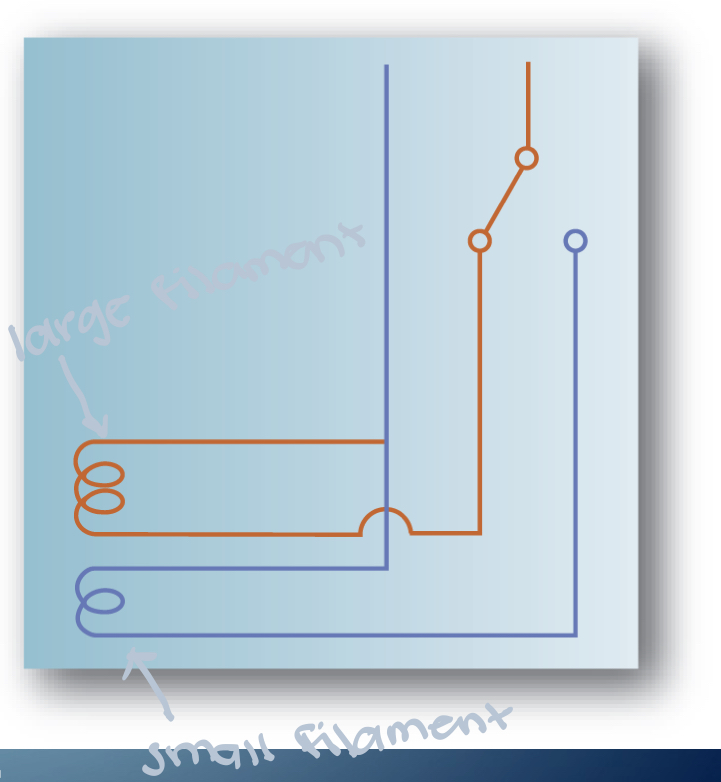
What is this?
Dual filament wire
What is the purpose of the filament?
It provides enough resistance to the flow of electrons that the heat produced will cause thermionic emission
When electrons leave the surface of the wire of the filament what forms?
An electron cloud
When high voltage is applied to the cloud it will be drawn towards the ______
Anode target
How many hours of tube life does the average filament have?
6-9 hours
How many exposures does the average filament life have?
10,000 to 20,000
What is the focusing cup?
A shallow depression in which the filament sits
How is the focusing cup charged?
Negatively to focus the electrons
What is the purpose of the focusing cup?
To narrow thermionic cloud as it is driven towards the anode
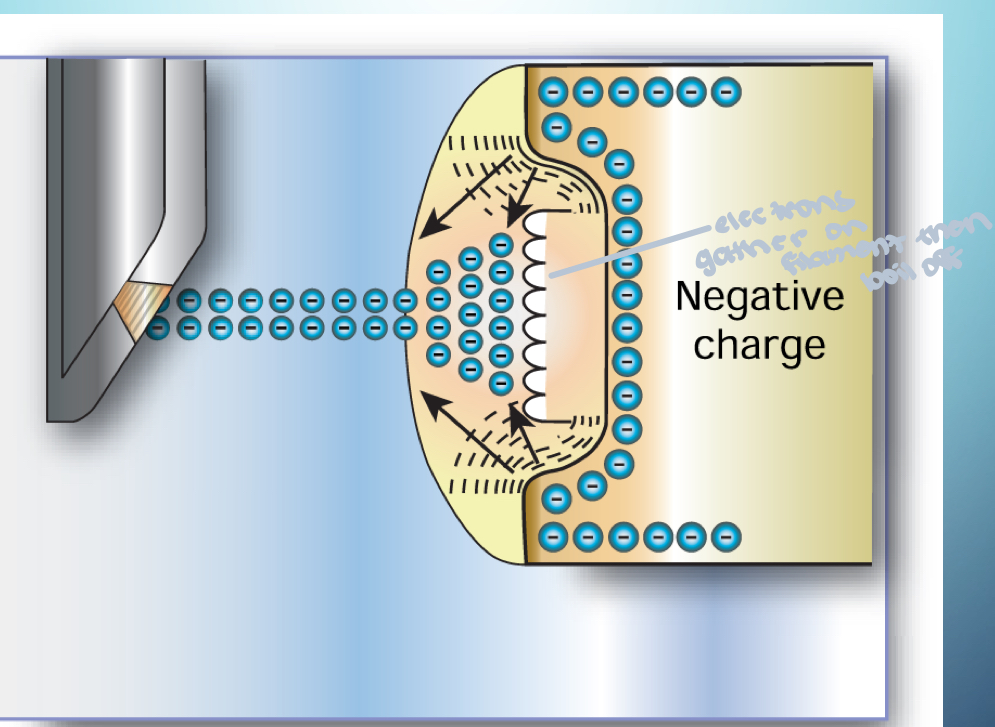
What is this?
Focusing cup
What happens when the focusing cup is not working properly?
The efficiency of the tube decreases— focal bloom
What causes the space charge effect?
When there are too many electrons around the filament
What makes up the anode assembly?
Anode, stator, rotor
What are the functions of the anode assembly?
serves as the target surface for the high-speed electrons from the cathode
the source of the x-ray photons
conducts the high voltage from the cathode
serves as the primary thermal conductor
What side of the x-ray tube do electrons travel from?
Cathode (filament)
Where are the x-rays actually produced?
Anode
What are the two types of anodes?
Stationary and rotating
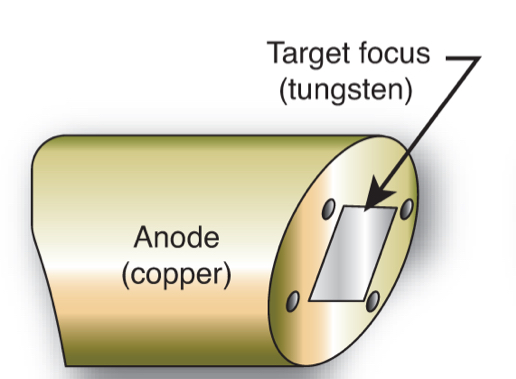
What type of anode is this?
Stationary
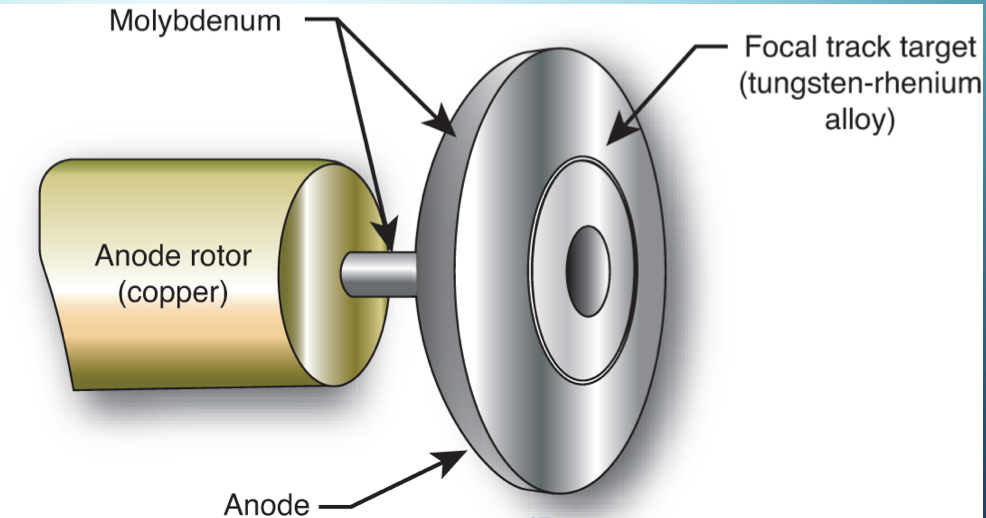
What type of anode is this?
Rotating
Describe the stationary anode:
a block of tungsten imbedded in the 45 degree angled end of a copper rod
about 1.5 cm x 1 cm surface area
only found in dental equipment and old x-ray units
Describe the rotating anode:
provides a greater surface area
dissipates heat better
used in most modern x-ray units
How large is the focal spot for the stationary anode?
4 mm squared
How large is the focal spot for the rotating anode?
1835 mm squared
How large is the rotating anode disk?
5 to 13 cm in diameter
What is the rotating anode disk made of?
Molybdenum
What is the target focal track made of?
Tungsten-rhenium alloy
What makes with the rotating anode?
rotating anode disk
target focal track
anode disk backing
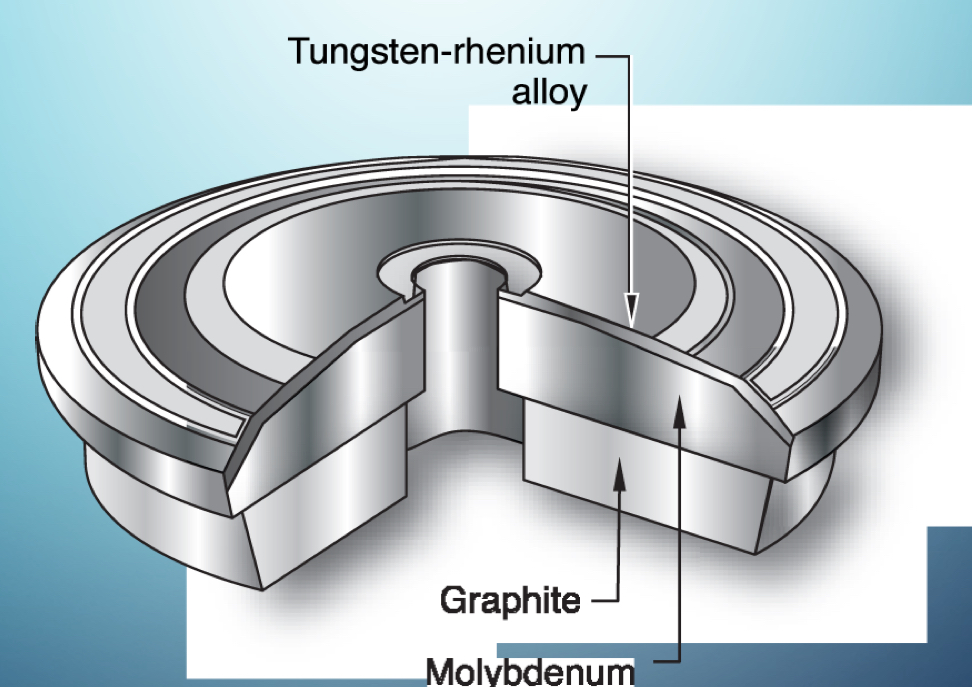
What is this?
Rotating anode
What are the advantages of using tungsten as the target material?
high melting point (3370 degrees C)
high atomic number (74)
heat conducting ability
Why would you want to use rhenium?
Its used due to elasticity when focal track expands due to rapid heat
Why would you use graphite molybdenum backing?
Allows double heat loading capabilities
What is the stress relieved anode?
majority of anodes
dissipates heat more efficiently
still needs warm up of tube
What is the target area also called?
Target, focus, focal point, focal spot or focal track
Where is the area of electron interaction?
The target area (where x-rays are created)
What is the actual focal spot?
The physical area of the focal track that is impacted by the electrons
What is the effective focal spot?
The area of the focal spot that is projected out of the tube toward the patient
What controls the effective focal spot?
The size of the actual focal spot (length of the filament) and the anode target angle
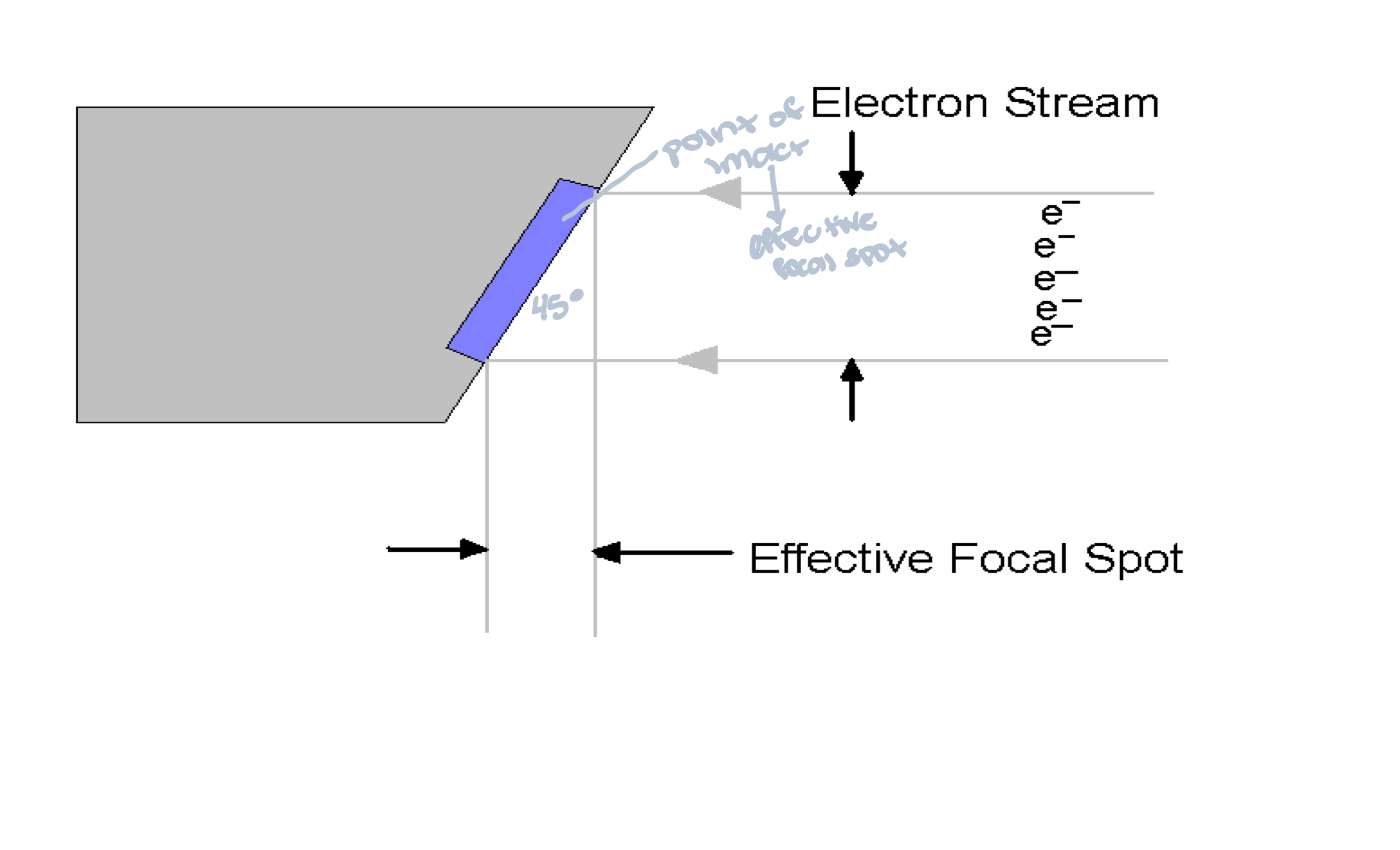
What is this?
Actual focal spot
What is the line focus principal?
When the target is angled (less than 45 degrees) the effective focal spot is smaller than the actual focal spot
The _____ the angle, the _____ the effective focal spot
Smaller
What doee anode angles range from?
7 to 17 degrees
What is the most common anode angle?
12 degrees
Due to the geometry of the angled anode target, the radiation intensity is greater on the _____ side
Cathode
The intensity of the x-ray beam can vary as much as ____ from anode to cathode
45%
What makes up the induction motor?
Stator and rotor
Describe the stator:
outside the glass envelope
series of electromagnets that rotate the rotor
switch is pressed halfway sends current to stator
What turns the anode?
Rotator
If stator fails to rotor I twill not turn _____
Anode
Describe the rotor:
located inside the stator
electromagnetic field causes stator to turn causing rotor to turn
What speed does the rotor turn at?
3200-3600 RPM
High speed rotor revolve at ____ RPM
10000
What lines the shaft of the rotor?
Ball bearings
How long does ball bearings coast for?
60 seconds and slow down when exposure is taken
What is the glass envelope made of?
Heat-resistant Pyrex glass
What does the glass envelope do?
Encloses all of the cathode assembly and all of the anode assembly except the stator
What is the window of the glass envelope?
Thinner section where the primary beam exits the tube
The glass envelope maintains the ______
Vacuum
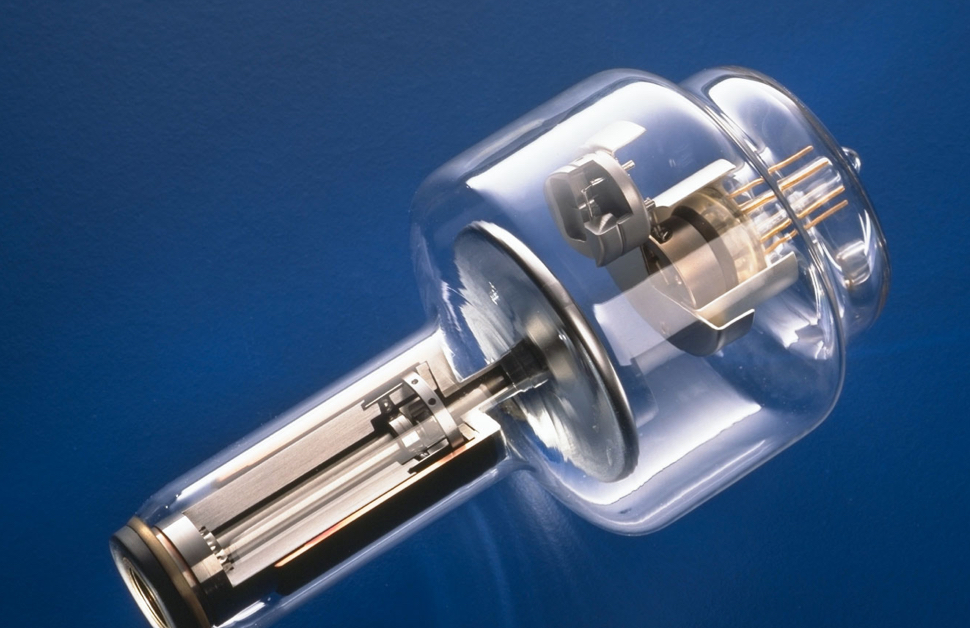

What is this?
Glass envelope
What are the two types of envelopes?
Glass and metal
Where are metal envelopes more common?
In CT
What do metal envelopes do?
prolong tube life
still have window segment
After envelope is constructed, _____ is removed from tube
Air
What does the vacuum do?
Allows electrons to flow without interference from gas atoms of air (increases efficiency of tube)
What are the functions of protective housing?
controls leakage and scatter radiation
insulates the high voltage
provides a means to cool the tube
How are x-rays produced?
Isotropically
The tube housing is designed to absorb most of the x-rays except those in the ______
Primary beam
What is the housing made of and lined with?
made with cast steel and lined with lead