Unit 1 Psych Notes
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Nervous System
Body’s communication network
Central Nervous System
Brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System
All nerves outside the brain and spinal cord
Autonomic Nervous System
Regulates involuntary functions (autonomic → automatic)
Sympathetic Nervous System
Activates fight or flight preparing body for danger/action (s = stress)
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Promotes relaxation and restores body to calm state (a parachute slows you down)
Somatic Nervous System
Controls voluntary movements and sends sensory info from body to central nervous system
Electroencephalogram “EEG”
Records electrical activity of brain by placing electrodes on scalp
CT (CAT) Scan
X-ray photo
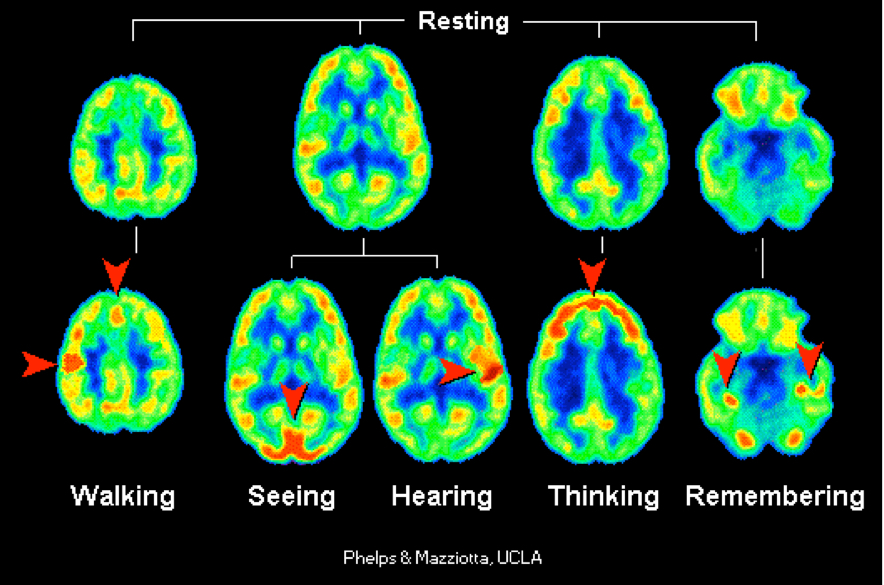
PET Scan
Displays brain activity by detecting radioactive glucose
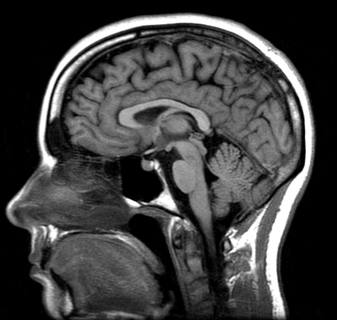
MRI
Magnetic field that gives a detailed picture of the brains soft tissues
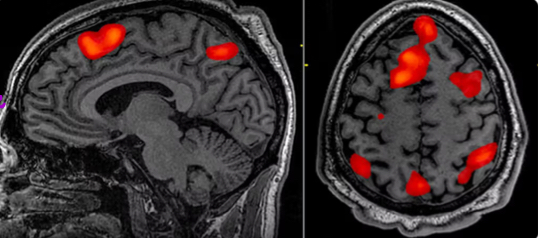
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)
Measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow and oxygen levels
Lesion
Specific tissue destruction
Lesioning
Studying brain function by intentionally damaging or destroying specific areas of the brain in experimental animals
Evolutionary Perspective
Study of how psychological traitors and behaviors have evolved over time to enhance survival and reproductive success
Natural Selection
Traits that are better suited for the government and more likely to survive and reproduce are passed down generations
Nature “Genes”
Biologically and genetic factors that influence a persons psychological development, traits, behaviors and cognitive abilities
Nurture “Environment”
Environmental influences and experiences that shape a persons psychological development, behaviors and cognitive abilities
Heredity
Genetic info passed down from parents to children
Heritability
Helps us figure out how much of our Graig has come from genes and how much comes from environment
Genetic Predisposition
Inherited likelihood of developing specific traits or conditions due to genetic factors from parents (alcoholism)
Eugenics
BAD - Belief in improving genetic qualities of the population by controlling reproduction to increase desirable traits and decrease undesirable ones (forced sterilization, selective breeding)
Neurons
Basic building block of the nervous system
Sensory Neurons
Sends sensory info (from things like skin, muscles, organs) to the central nervous system
Afferent
Brings info to brain
Efferent
Takes messages from brain
Interneurons
Serve as connectors in the central nervous system sending signals between sensory neurons and motor neurons
Motor Neurons
Sends signals from the central nervous system to muscles, glands and organs controlling voluntary and involuntary movements (tells the muscles to move)
Dentrites
Receive chemical messages and carry them to the cell body (soma)
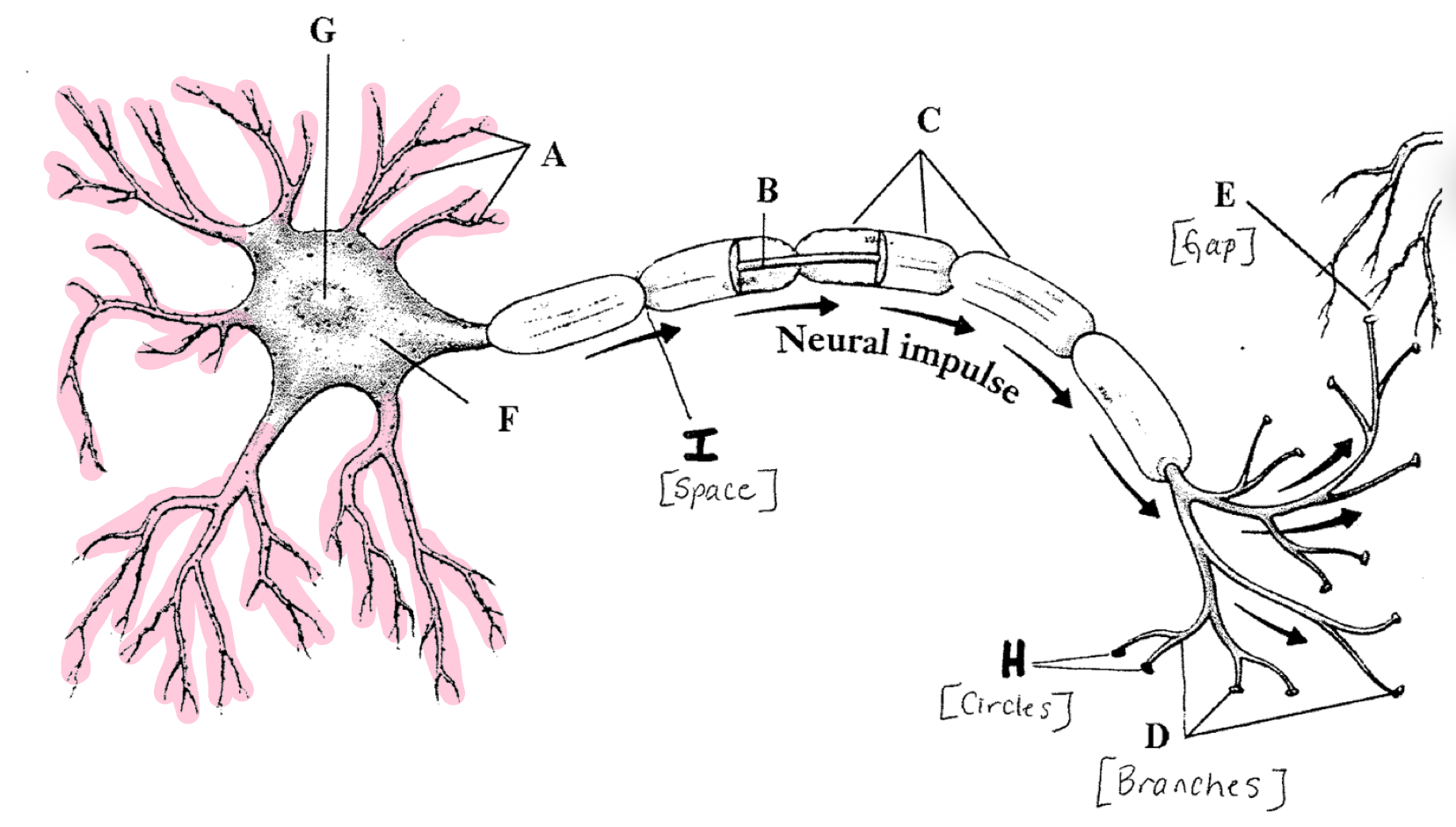
Axon
Carry electrical signals away from the cell
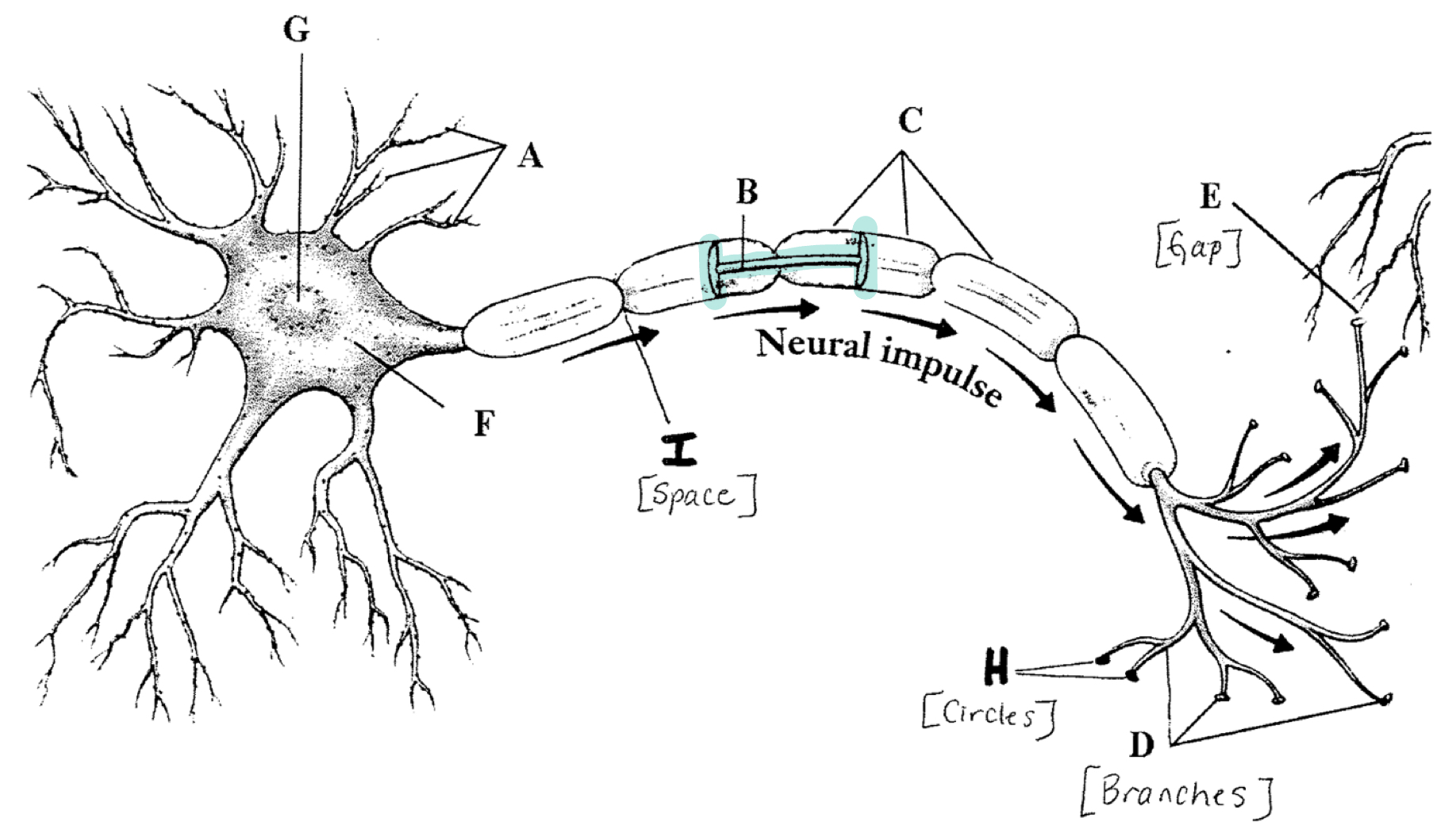
Myelin Sheath
Layer of fatty cells that protect the axon
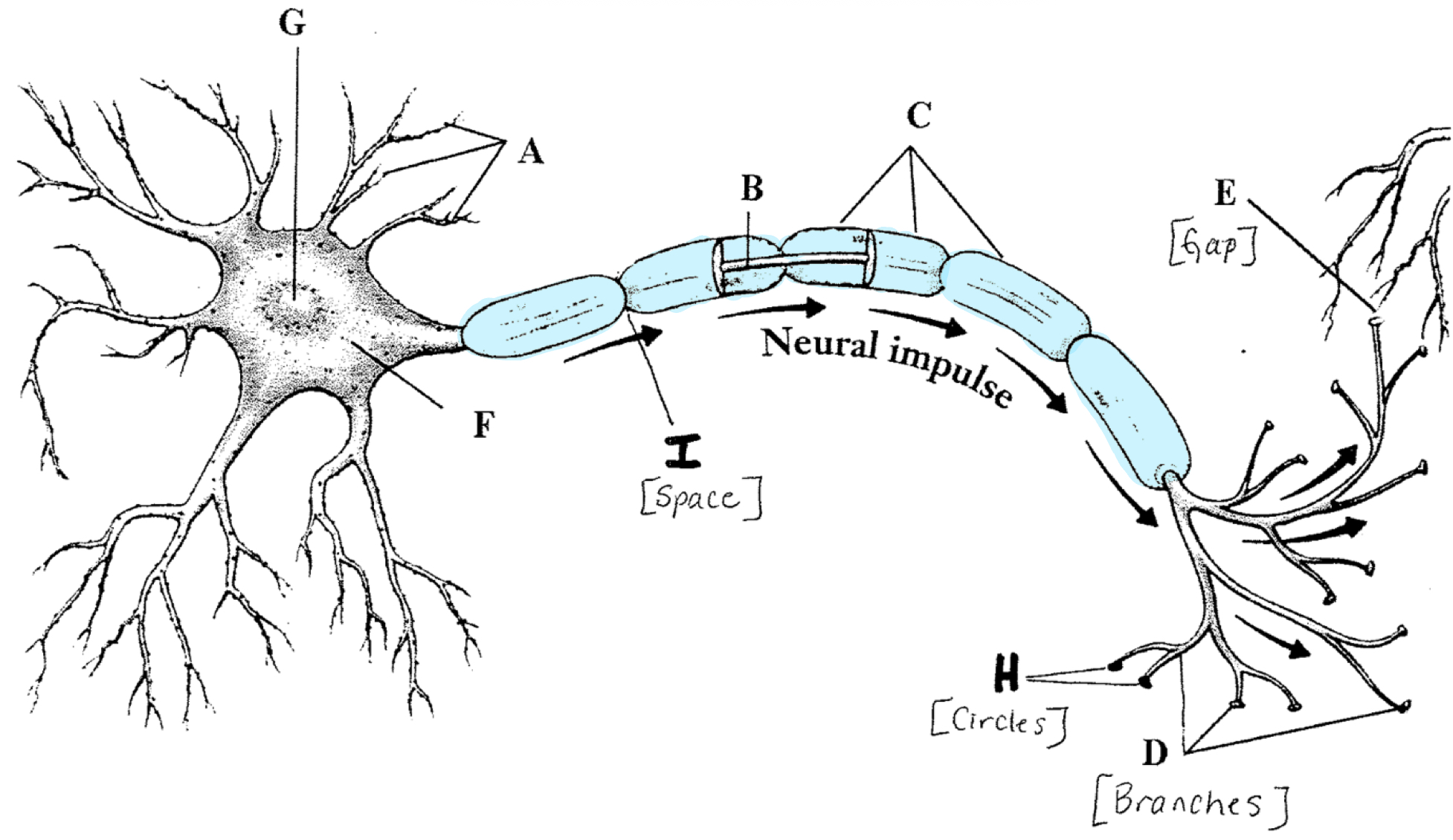
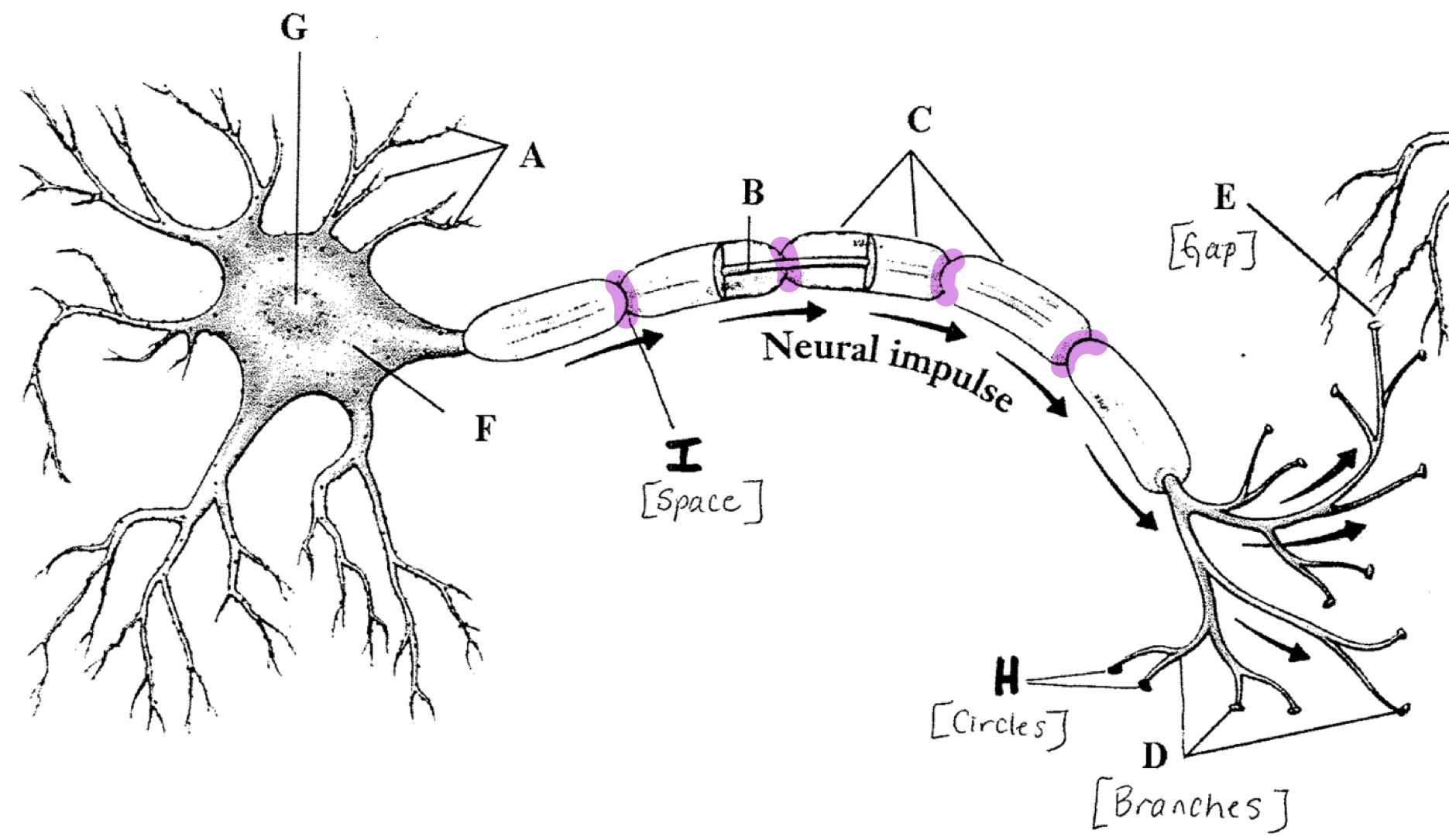
Node of Ranvier
Gaps between myelin sheath
Axon Terminals
Contain neurotransmitters (chemicals)
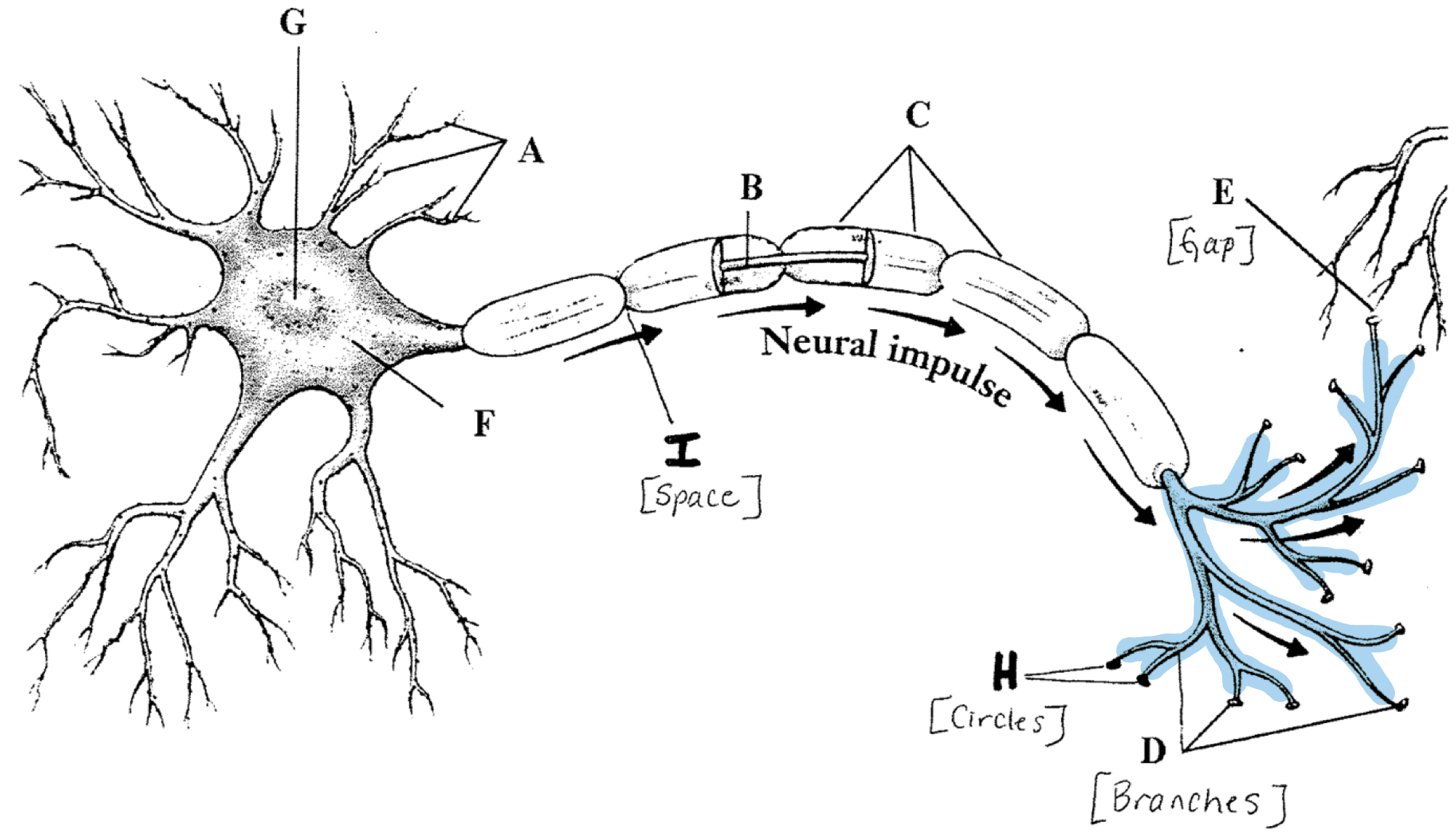
Terminal Buttons
Discharge the neurotransmitters into the synaptic gap
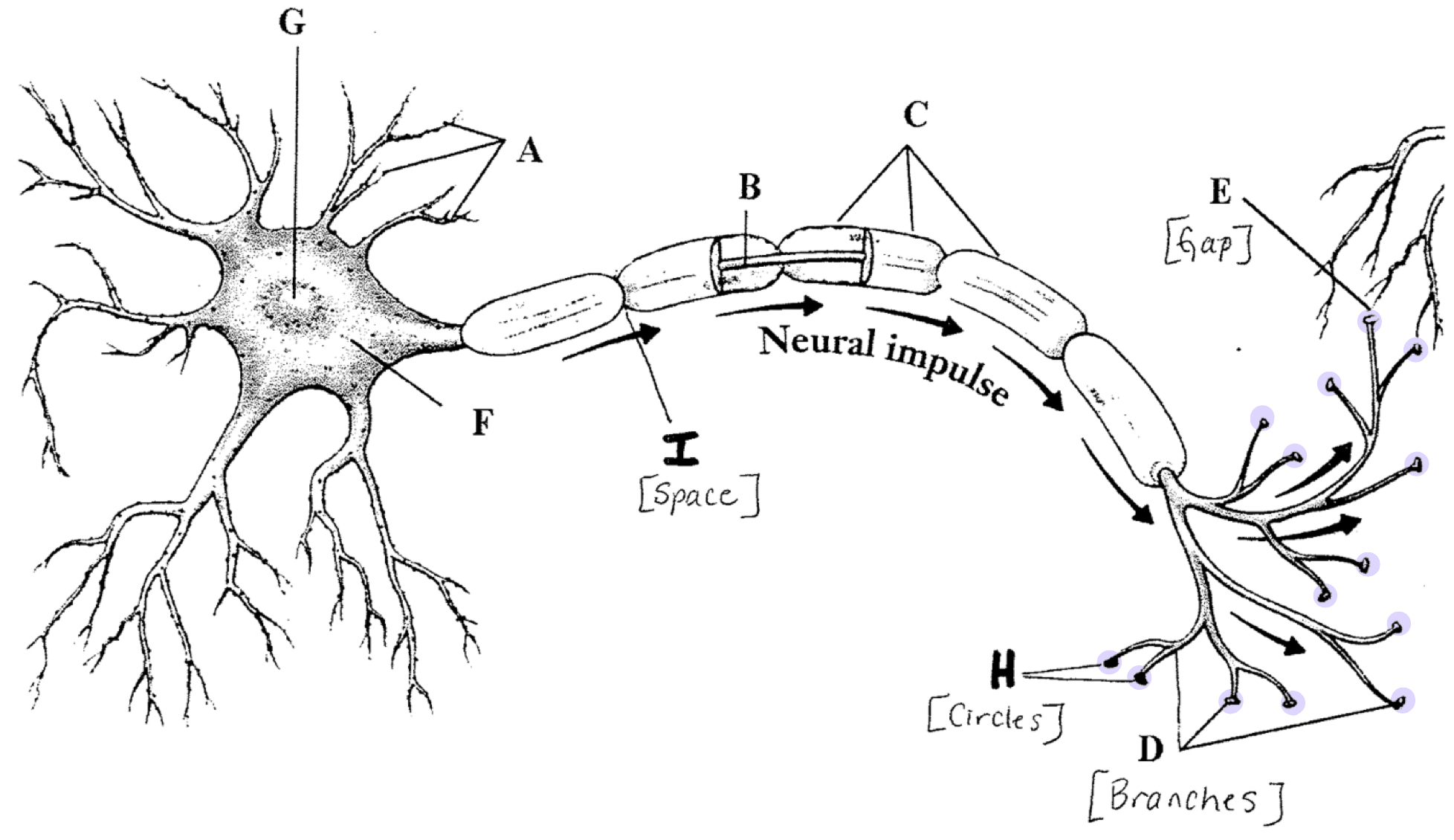
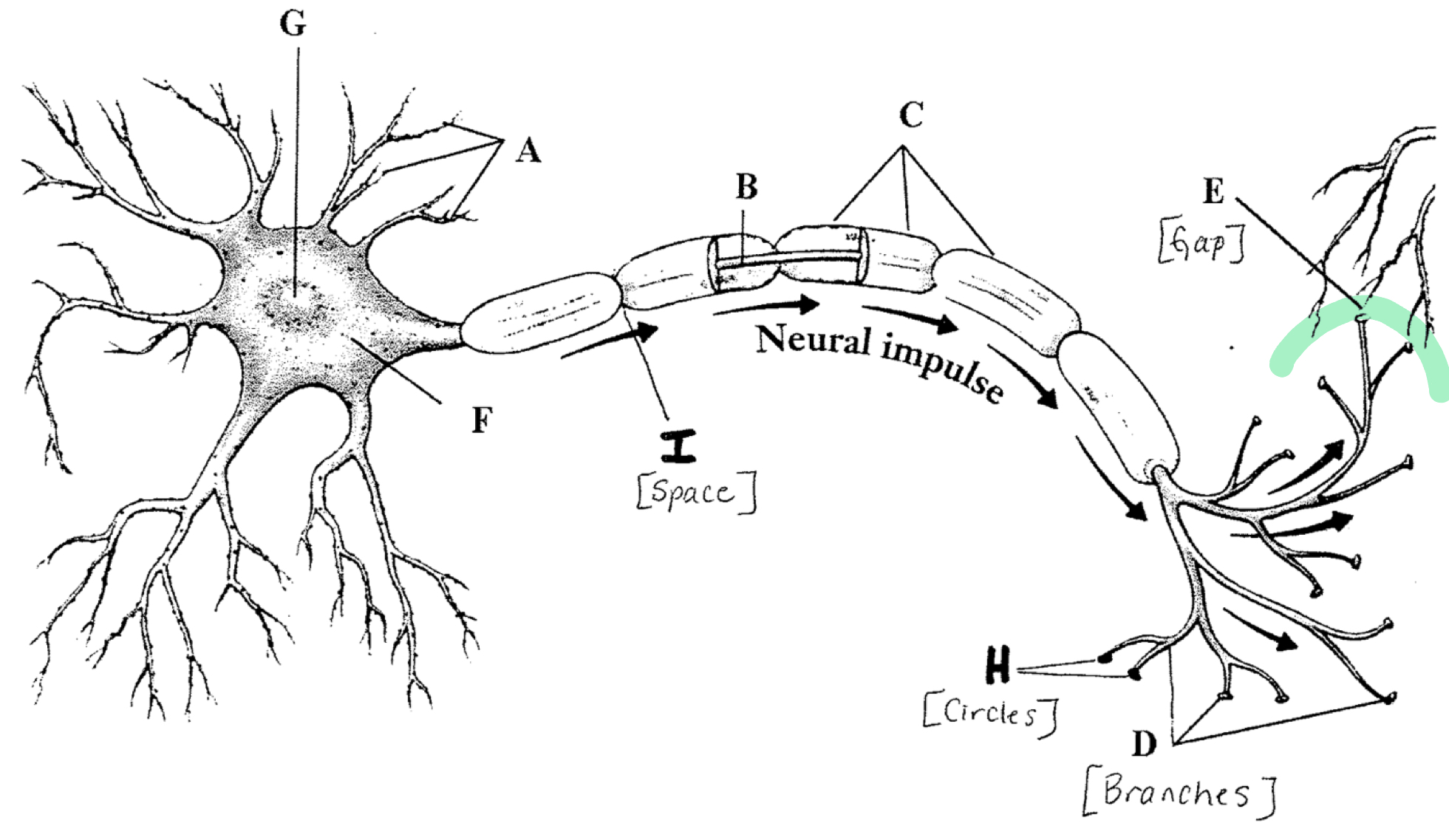
Synapse
The gap between neurons
Mirror Neurons
Brain responds the same when we perform an action and when we see someone doing the same action (it’s why visualization works in sports)
Glial Cells
“Support cells” of the nervous that provide structural support, insulation and nourishment to neurons
Relax Arc
Neural pathway that controls reflex reactions (automatic responses to stimuli without conscious thought)
The Homunculus Mapper
There’s a map of your body surface on your brains cortex
Multiple Sclerosis
Chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system by attacking the myelin sheath causing inflammation and damage
Myasthenia Gravis
Chronic autoimmune that affects the neuromuscular junction by producing antibodies that block or distort the receptors for acetylcholine (neurotransmitter that stimulates muscle contraction)
Neural Transmission
Neurons communicate with each other through electrical and chemical signals
Neural Firing
Fluid of the resting axon has negatively charged ions
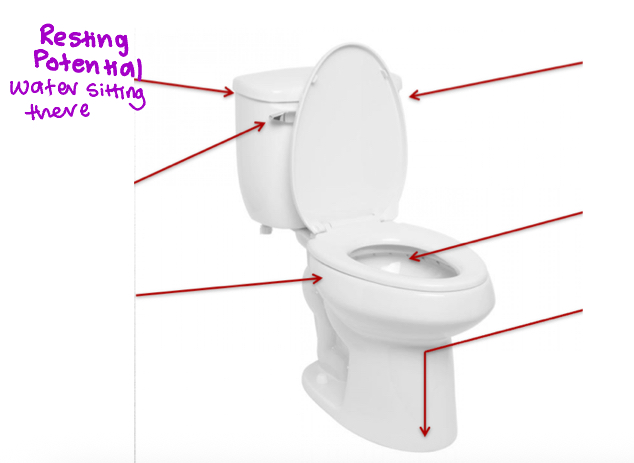
Resting Potential
Stable, negative electrical charge that exists across the cell membrane of a neuron when it is not actively transmitting signals (more sodium ions outside, more potassium ions inside)
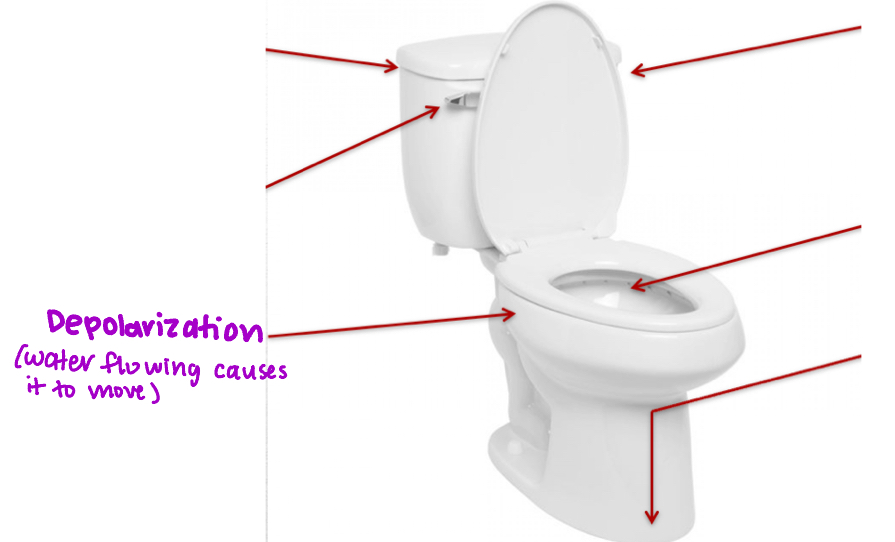
Depolarization
The inside of the neuron becomes less negative compared to outside due to the arrival of positively charged ions through ion channels in the cell membrane
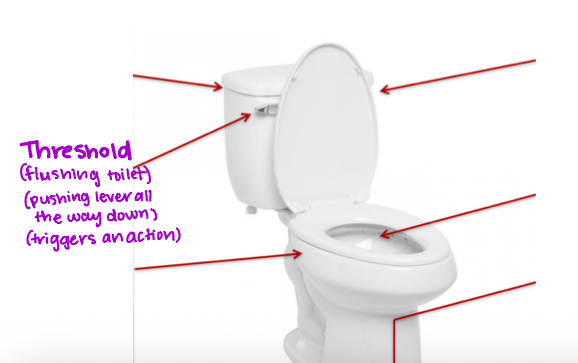
Threshold
Level of stimulation needed to trigger action potential
Action potential
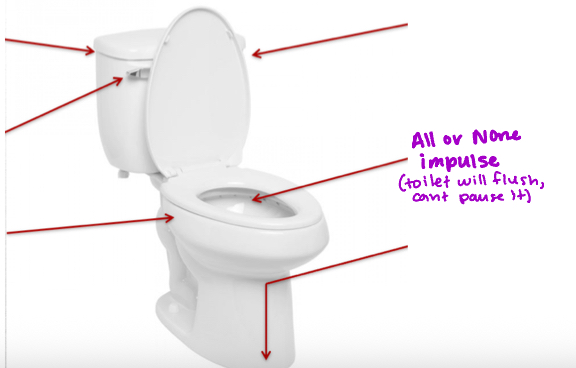
All or none electrical charge that travels down am axon
All or Nothing Principle
Once a neuron reaches the threshold it will fire an action potential and can’t stop
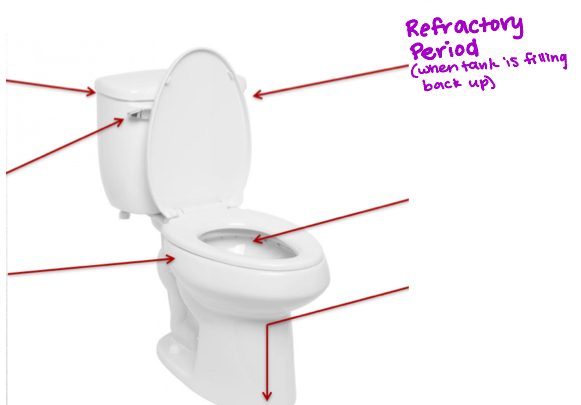
Refractory Period
Period after an action potential when the neuron is unable to make another action potential
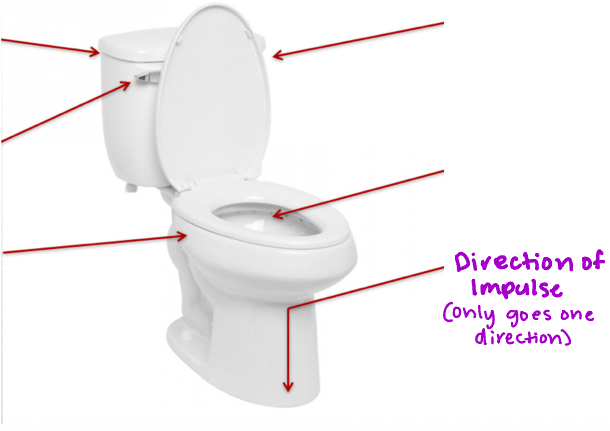
Direction of Impulse
Neuron firing only goes in one direction
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messages that transmit signals between neurons allowing for communication within nervous system
Excitatory Neurotransmitters
Increase the likelihood of an action potential
Presynaptic Neuron
Neuron 1 releases neurotransmitters
Postsynaptic Neuron
Neuron 2 catches neurotransmitters